Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Feb 16, 2025; 17(2): 100793
Published online Feb 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i2.100793
Published online Feb 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i2.100793
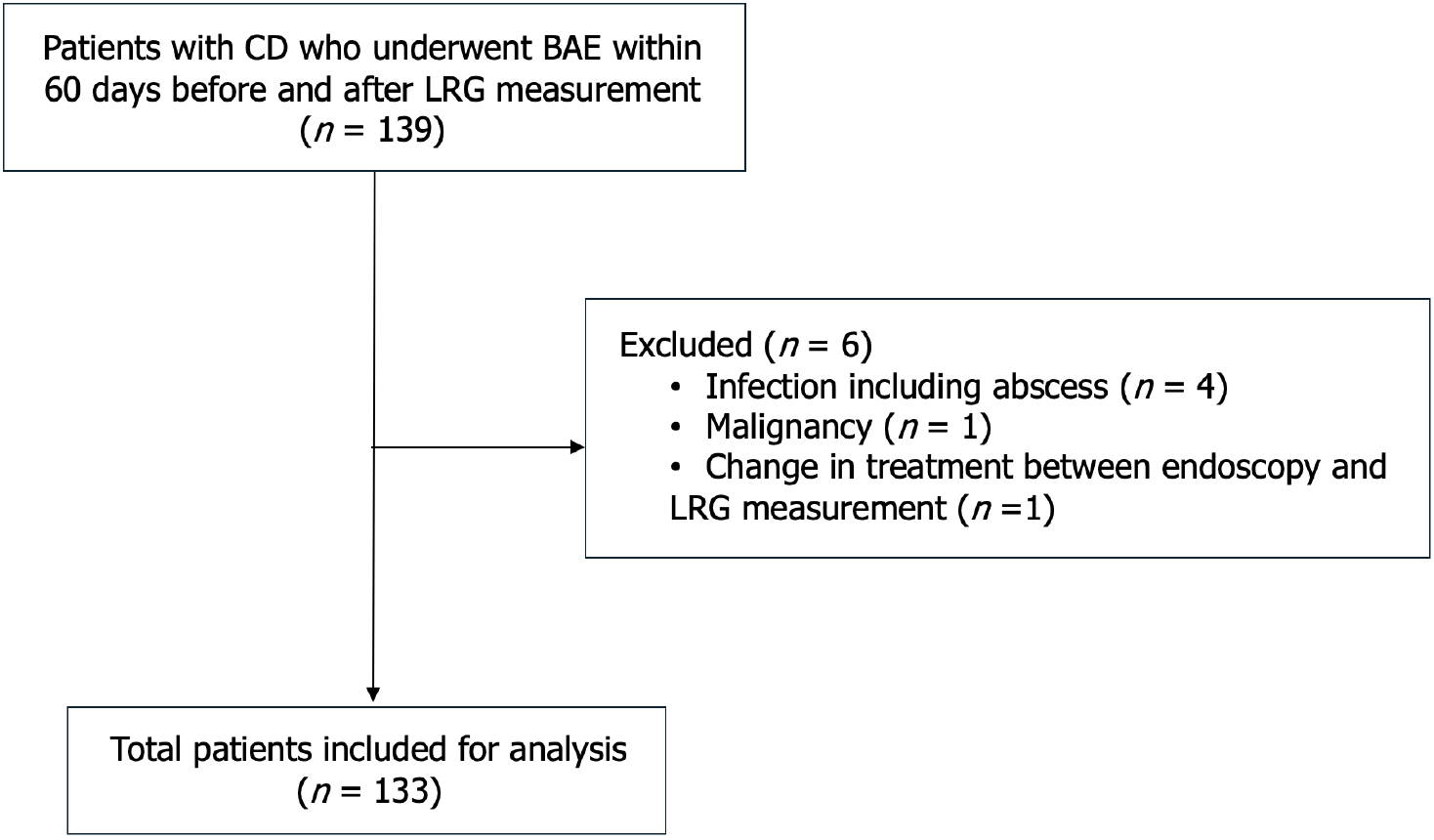
Figure 1 Flow chart of the study inclusion and exclusion process.
CD: Crohn’s disease; BAE: Balloon-assisted enteroscopy; LRG: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein.
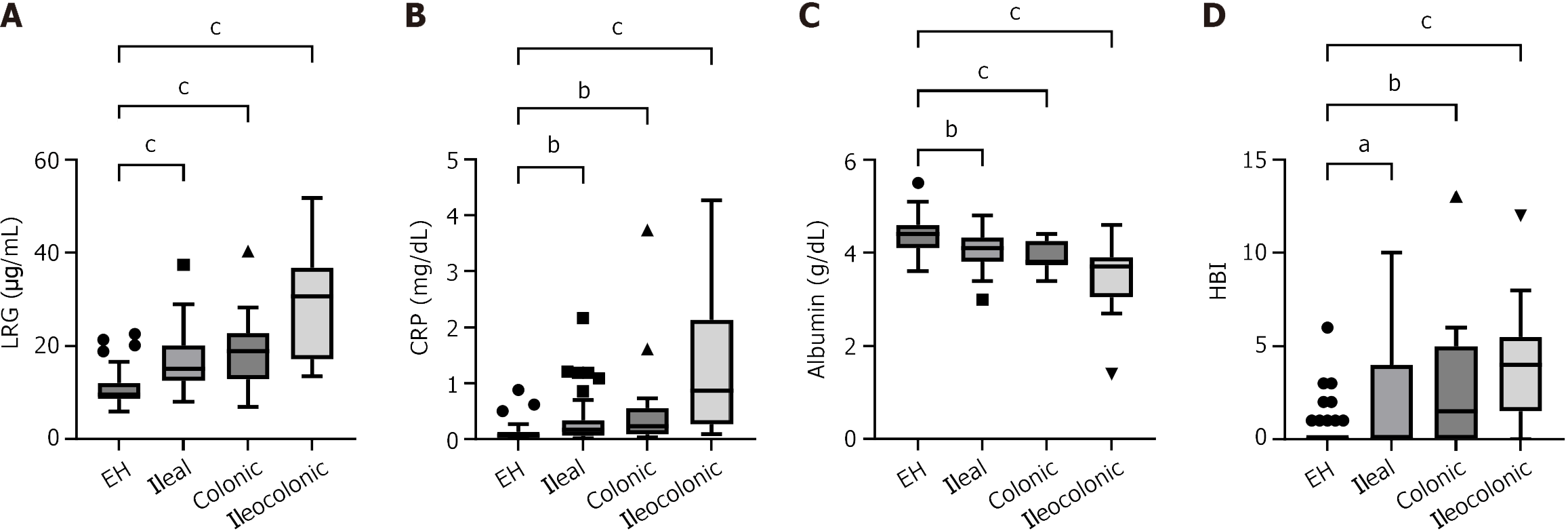
Figure 2 Comparison of each parameter among the endoscopic healing (n = 61), ileal (n = 43), colonic (n = 16), and ileocolonic groups (n = 13).
aP < 0.05; bP < 0.01; cP < 0.001. The endoscopic healing group exhibited significantly different leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein, C-reactive protein, albumin, and Harvey-Bradshaw index compared with the ileal, colonic, and ileocolonic groups. A: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; B: C-reactive protein; C: Albumin; D: Harvey-Bradshaw index. LRG: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; EH: Endoscopic healing; CRP: C-reactive protein; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw index.
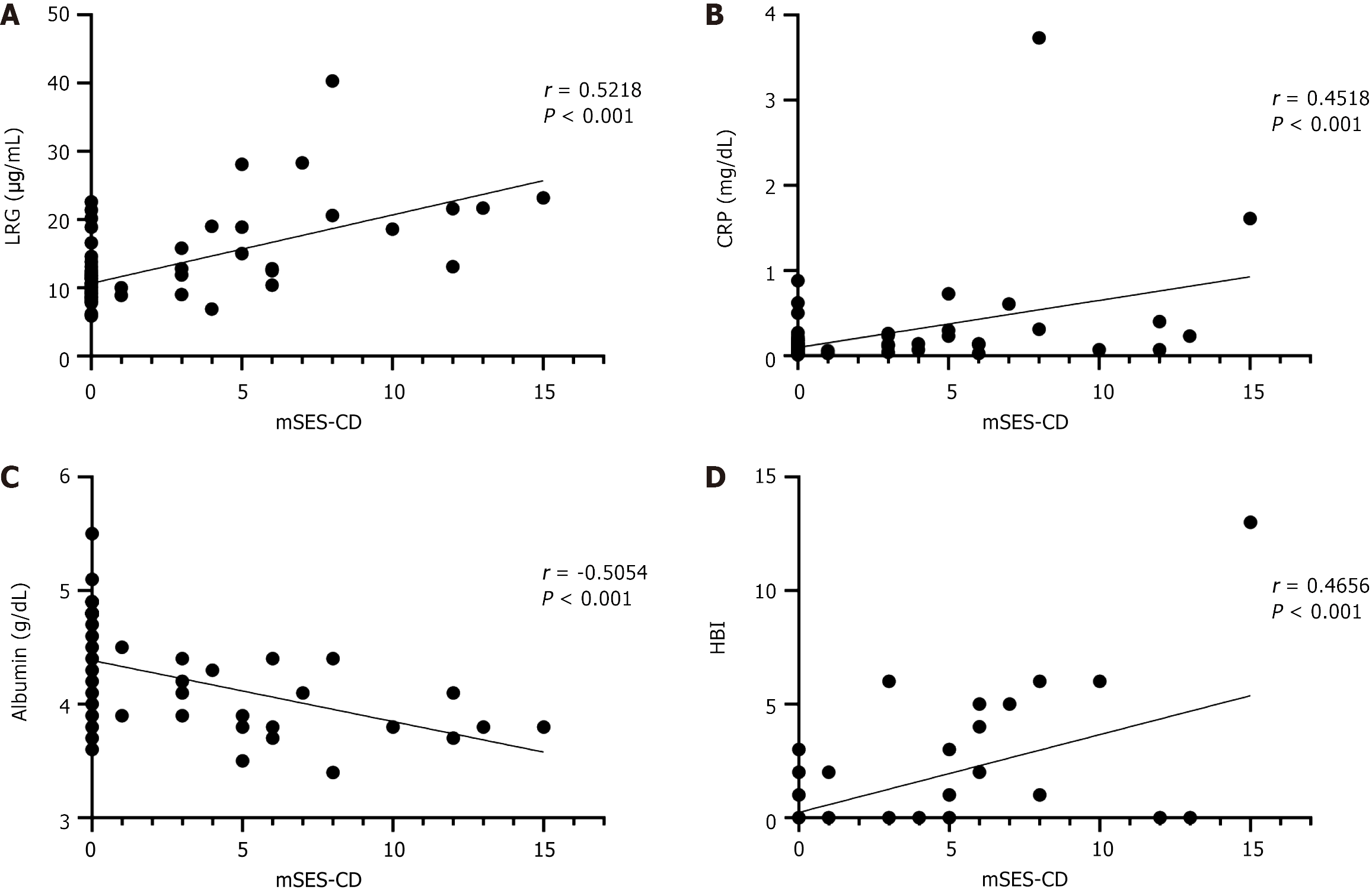
Figure 3 Correlation of each parameter with the endoscopic activity in the colon (n = 77).
Endoscopic activity was assessed using modified simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease. All parameters showed relatively good correlations with endoscopic activity in the colon. A: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; B: C-reactive protein; C: Albumin; D: Harvey-Bradshaw index. mSES-CD: Modified simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease; LRG: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; CRP: C-reactive protein; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw index.
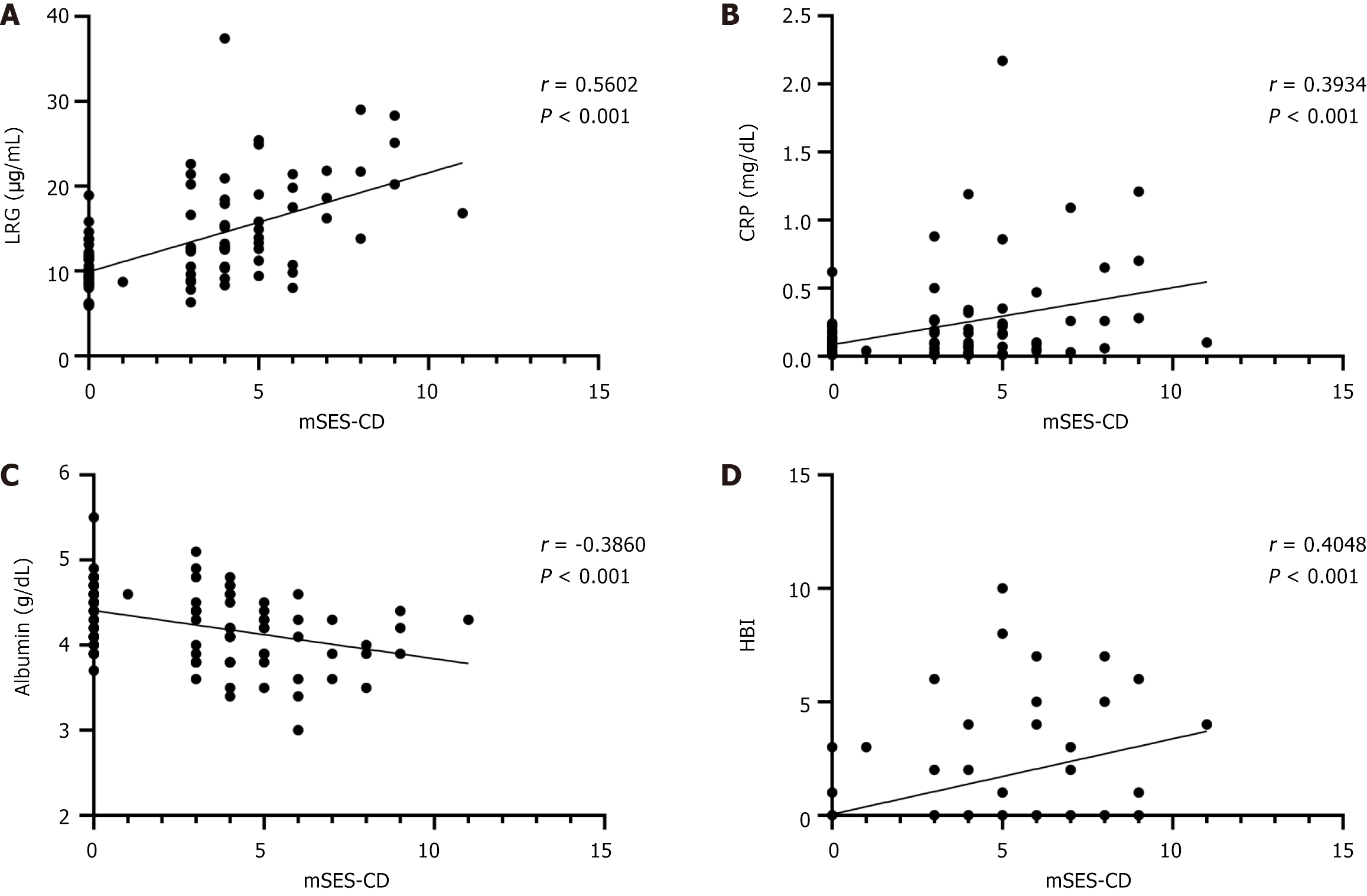
Figure 4 Correlation of each parameter with the endoscopic activity in the ileum (n = 104).
Endoscopic activity was assessed using mSES-CD. C-reactive protein, albumin, and Harvey-Bradshaw index did not show strong correlations with endoscopic activity in the ileum, whereas leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein was markedly correlated with endoscopic activity. A: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; B: C-reactive protein; C: Albumin; D: Harvey-Bradshaw index. mSES-CD: Modified simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease; LRG: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; CRP: C-reactive protein; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw index.
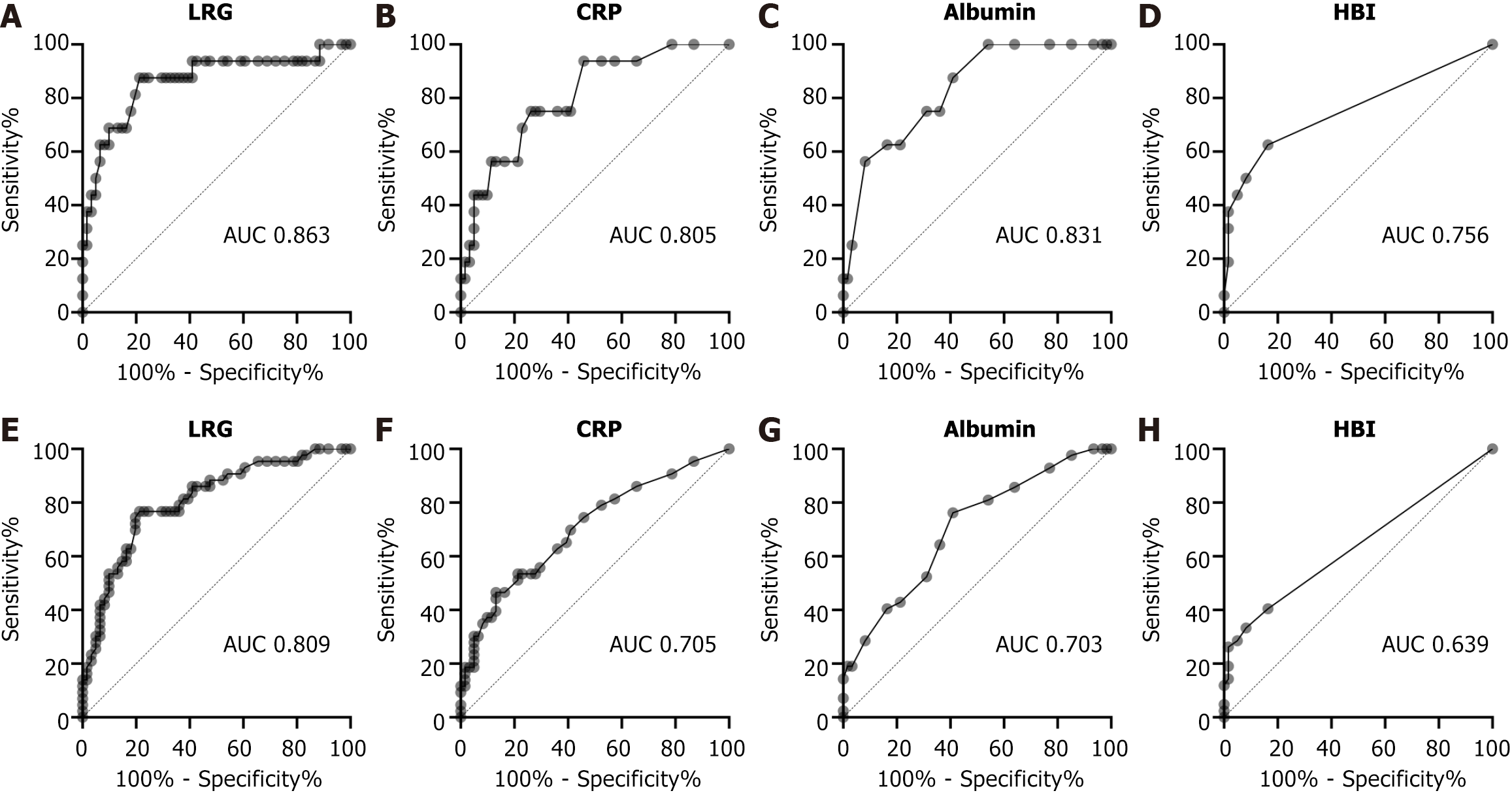
Figure 5 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of each parameter in predicting the endoscopic activity in the colon and ileum.
The area under curves of leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein, C-reactive protein, albumin, and Harvey-Bradshaw index in the colon were relatively high. Conversely, in the ileum, all of these values were lower than those in the colon; however, only leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein remained relatively high. A-D: Receiver operating characteristic analysis of each parameter in predicting the endoscopic activity in the colon; E-H: Receiver operating characteristic analysis of each parameter in predicting the endoscopic activity in the ileum. LRG: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; CRP: C-reactive protein; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw index; AUC: Area under curves.
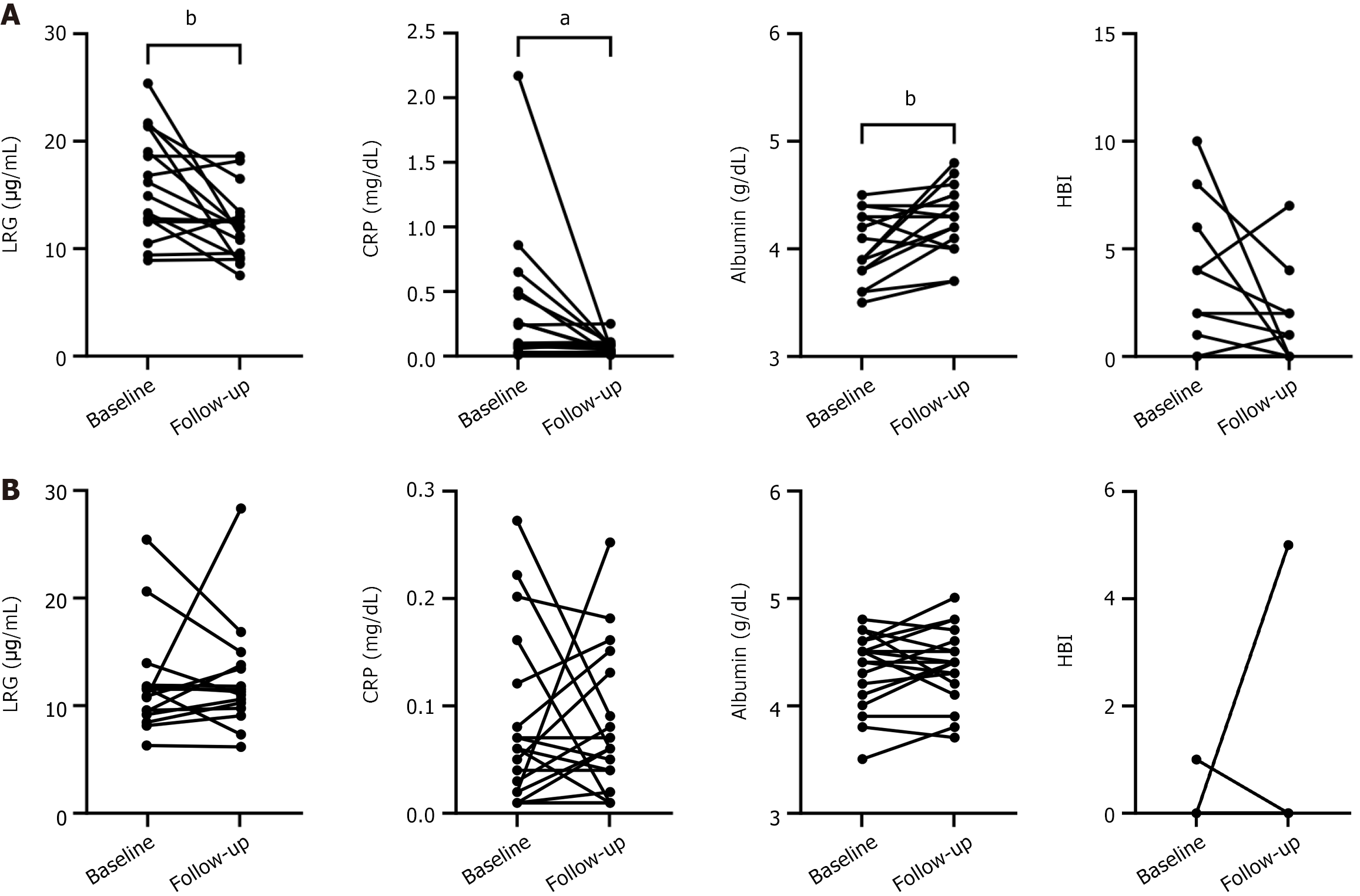
Figure 6 Changes in each parameter in patients who underwent follow-up balloon-assisted enteroscopy.
aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01. Patients who improved the Modified simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease (mSES-CD) in the ileum had significantly lower leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein, C-reactive protein, and albumin levels, whereas these parameters did not show significant differences in patients whose simple endoscopic score for Crohn’s disease remained unchanged. The Harvey-Bradshaw index consistently showed no significant differences. A: Patients with at least one point of improvement in the mSES-CD in the ileum (n = 16); B: Patients with unchanged mSES-CD in the ileum (n = 19). LRG: Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein; CRP: C-reactive protein; HBI: Harvey-Bradshaw index.
- Citation: Ohno M, Nishida A, Otsuki A, Yokota Y, Imai T, Bamba S, Inatomi O. Leucine-rich alpha-2 glycoprotein as a superior biomarker to C-reactive protein for detecting small bowel lesions in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(2): 100793
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i2/100793.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i2.100793