Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 16, 2025; 17(1): 103404
Published online Jan 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.103404
Published online Jan 16, 2025. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.103404
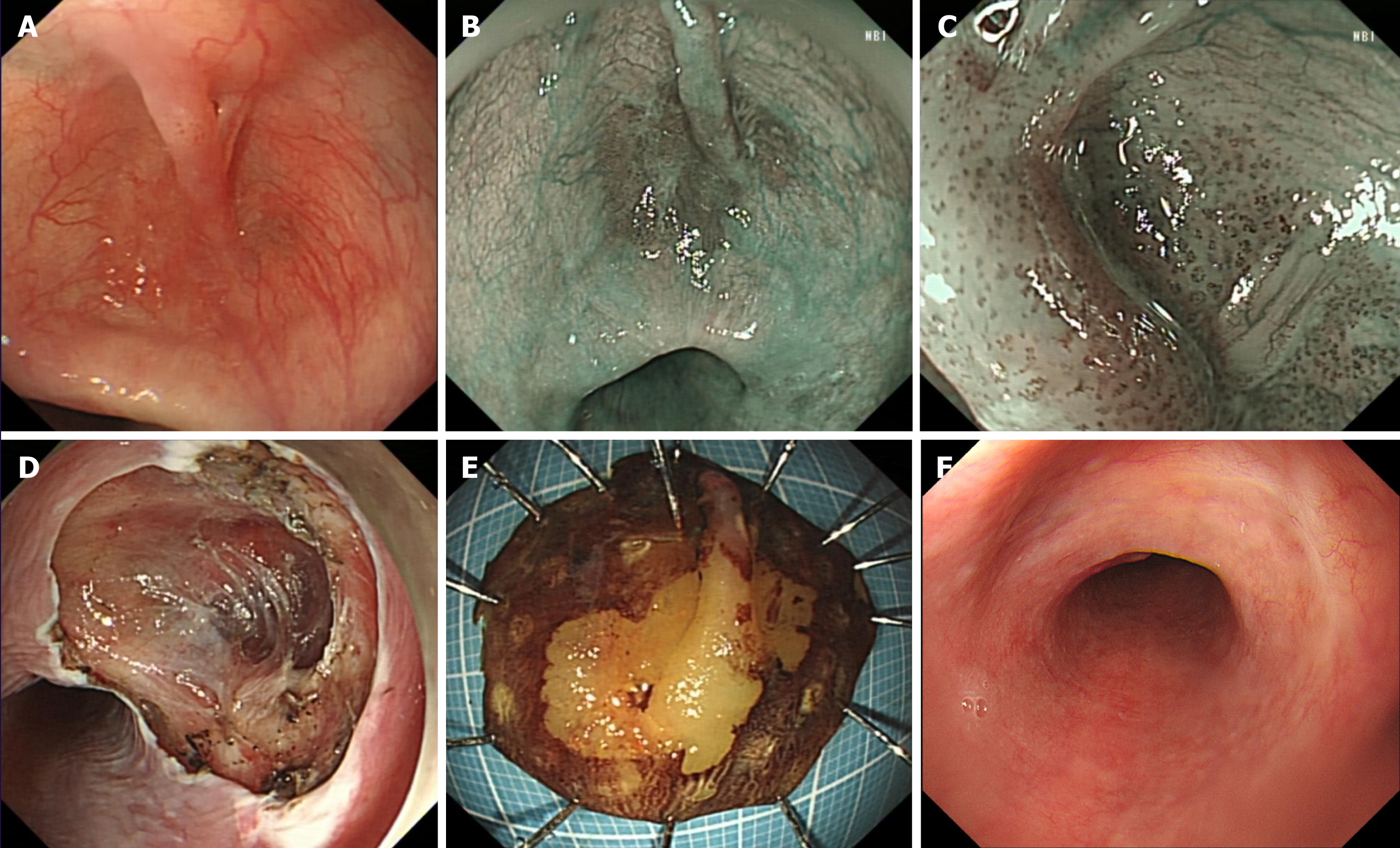
Figure 1 Gastroscopy appearance of lesion.
A: Patchy erythema with bridge like protrusions in the esophageal diverticulum under white light; B: The lesion under narrow band imaging appears tea brown in color; C: Intrapapillary capillary loops under magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging shows B1 type; D: Endoscopic submucosal dissection postoperative wound; E: Lodine staining after lesion dissection; F: Scar like changes observed during 3-month postoperative follow-up.
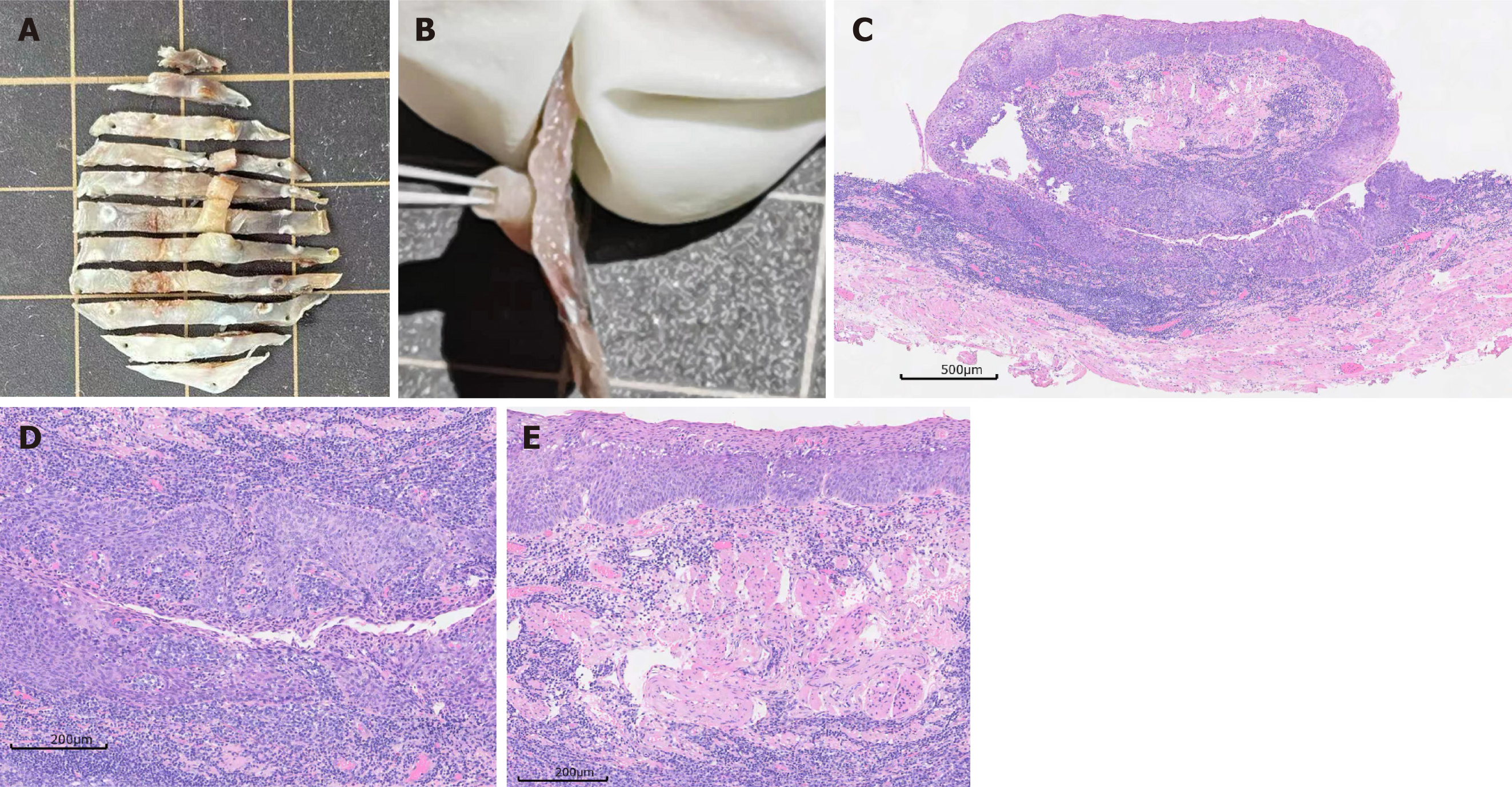
Figure 2 Pathological biopsy after specimen fixation.
A: Sample after tissue incision, the red dashed line represents the front of the 2B tissue strip; B: On the side of the tissue strip, the raised mucosal bridge is a solid tubular structure; C: Pathological hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining presented the mucosal bridge spanning the intrinsic mucosa of the esophagus, × 40; D: Pathological HE staining presented the tubular structure and esophageal mucosa, showing high-grade intraepithelial neoplasia and in situ cancer of squamous epithelium, × 100; E: Pathological HE staining presented the tubular structure. The axis of the tubular structure is composed of proliferating arteriovenous vessels and fibrous smooth muscle tissue, × 100.
- Citation: Liu YL, Liu J, Wang YT. Early esophageal cancer with mucosal bridging in the resting room: A case report. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2025; 17(1): 103404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v17/i1/103404.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v17.i1.103404