Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Dec 16, 2021; 13(12): 638-648
Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.638
Published online Dec 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.638
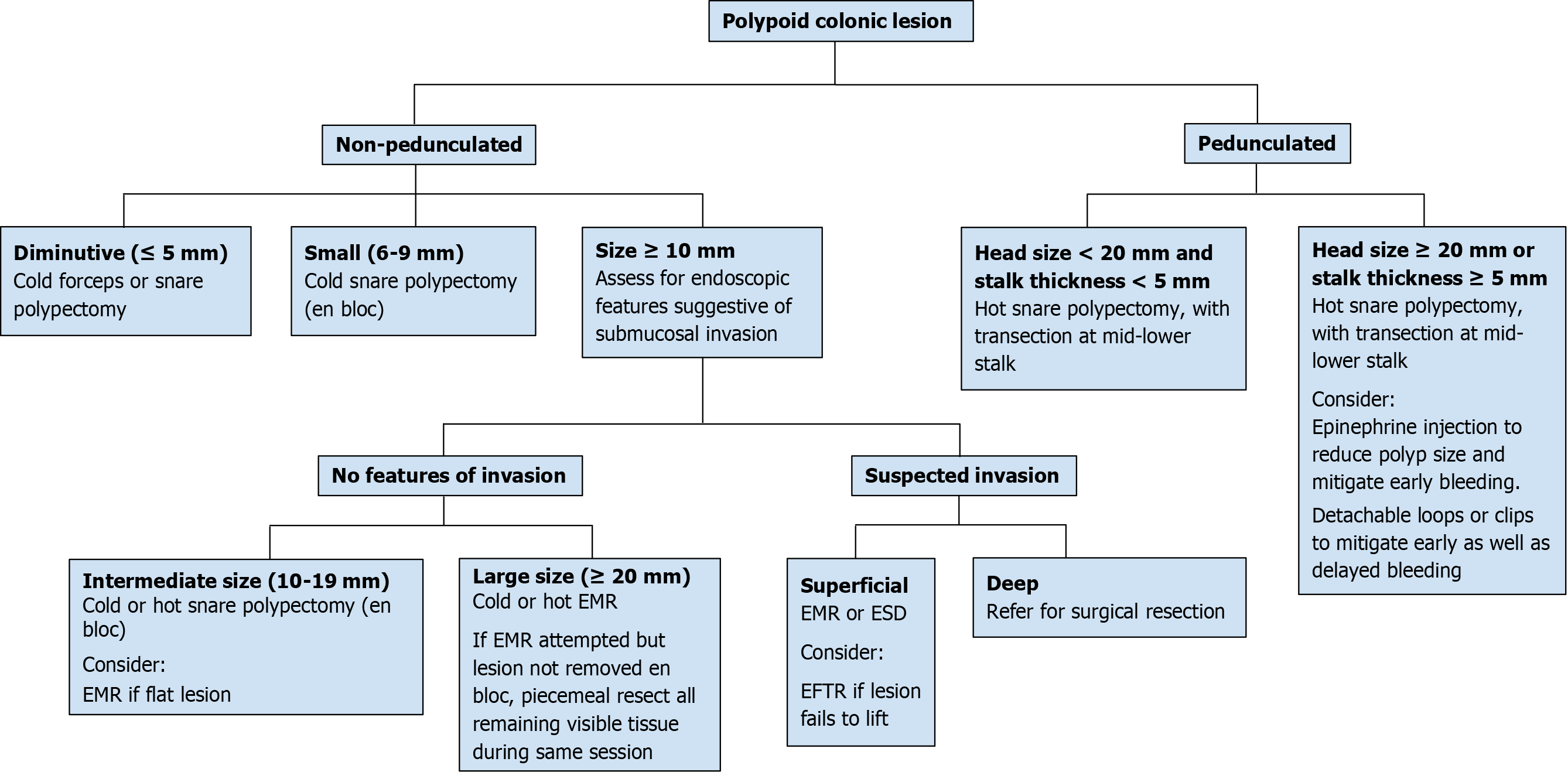
Figure 1 Polyp management algorithm based on morphology, size, and suspicion of submucosal invasion.
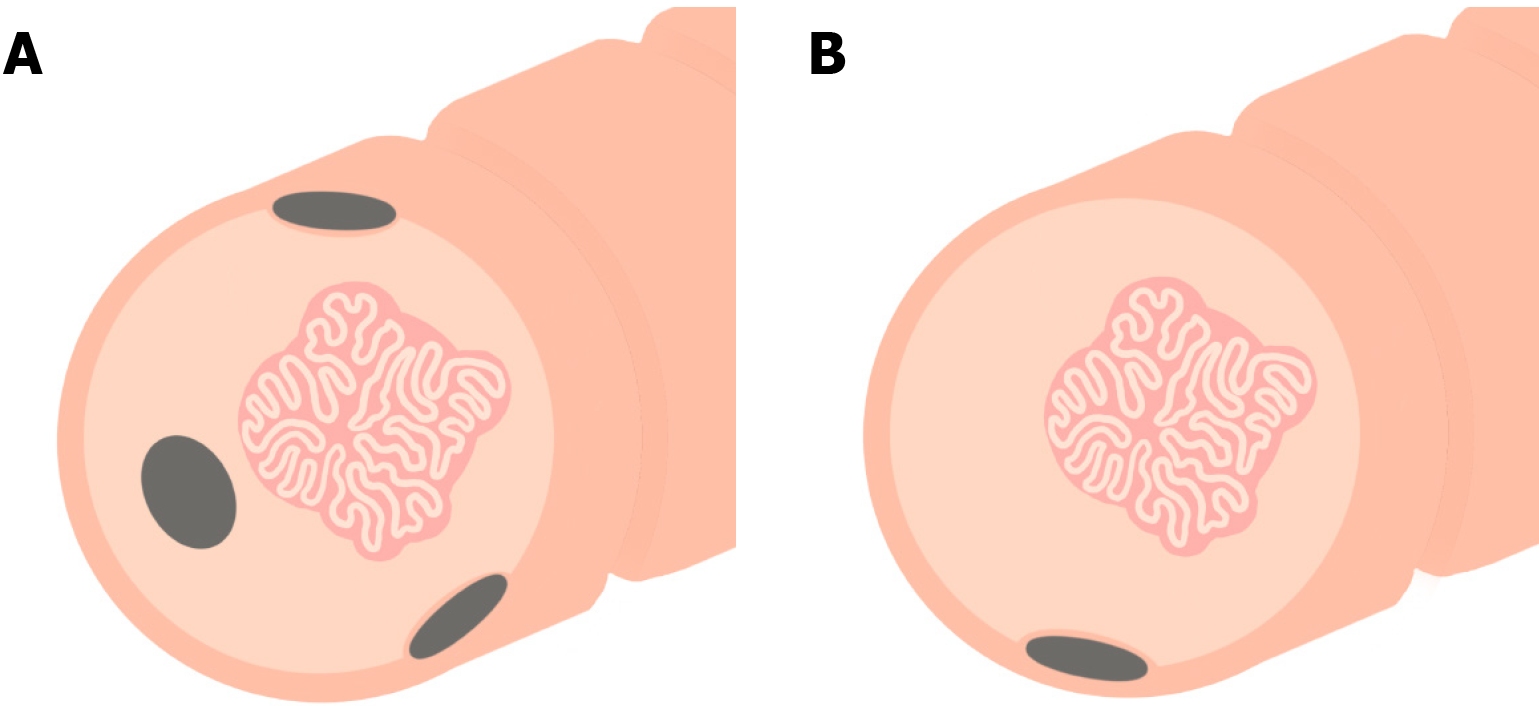
Figure 2 Guidelines for placing an endoscopic tattoo prior to resection.
As an overarching principle, the location of the tattoo relative to a polyp should be guided by anatomical factors and institutional practices in addition to being well-described and photodocumented in the procedure report. A: When tattooing with the intent of referral for surgical resection, the tattoo should generally be placed immediately distal to the polyp and circumferentially in multiple quadrants to facilitate intraoperative visualization; B: When tattooing with the intent of referral for advanced endoscopic resection, tattoo should not be injected into or under the polyp, and care should be taken to not inject an excess volume of ink, as this may spread submucosally toward the polyp and subsequently complicate resection; a single tattoo, 3-5 cm distal to the polyp (or one haustral fold distal), is generally appropriate.
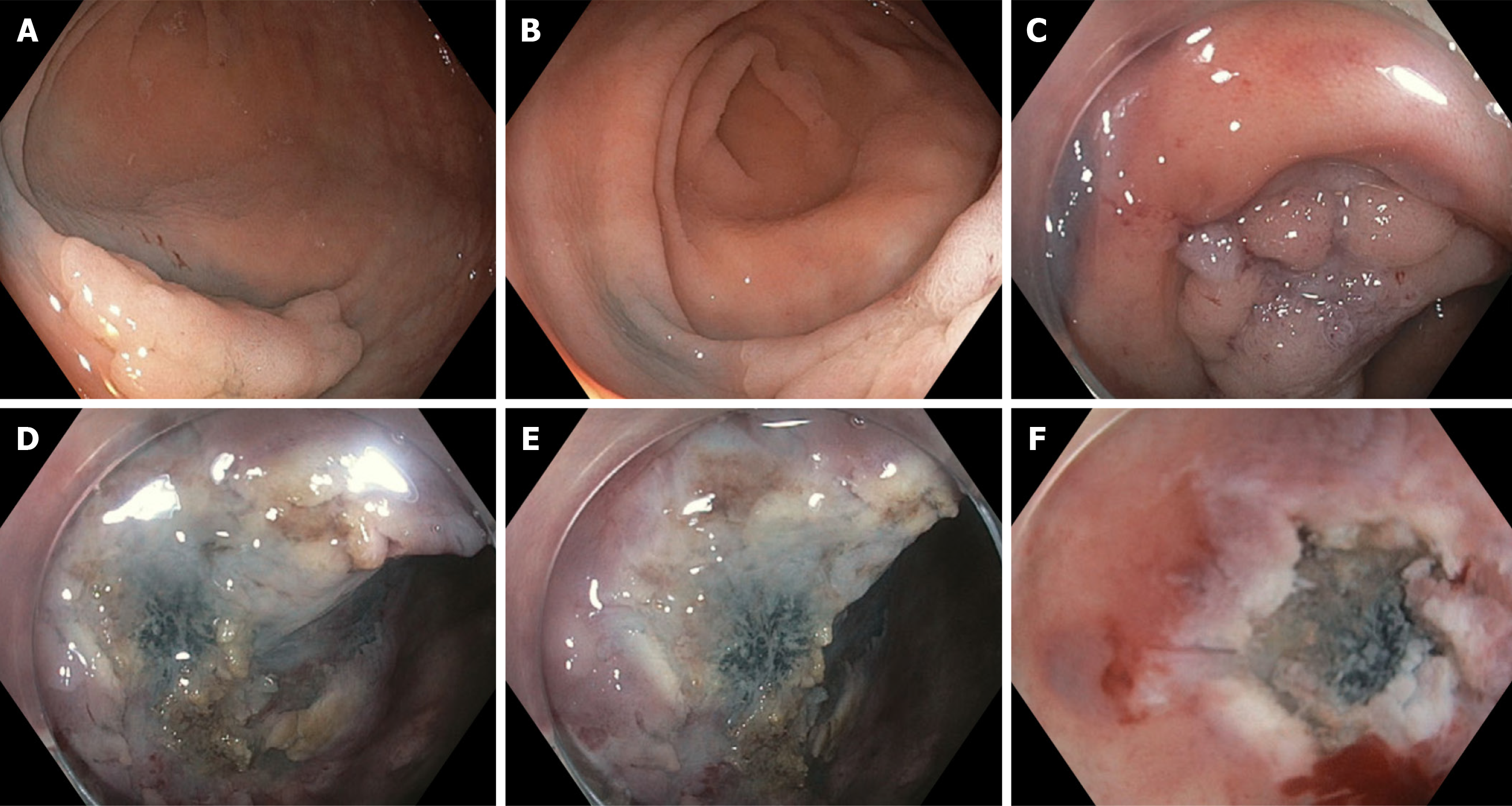
Figure 3 Endoscopic mucosal resection complicated by prior endoscopic tattooing.
A and B: Presence of previously placed tattoo ink proximal and lateral to a large (25 mm) sessile polyp, suggestive of injection being made too close to (or under) the polyp and/or an excess volume of ink injected; C: Suboptimal lifting after 10 cc of saline and 13 cc of submucosal injectable composition as a result of submucosal fibrosis from the prior tattoo, complicating en bloc endoscopic mucosal resection; D, E and F: Tattoo ink and associated tissue fibrosis can be seen infiltrating the submucosa directly under the polyp.
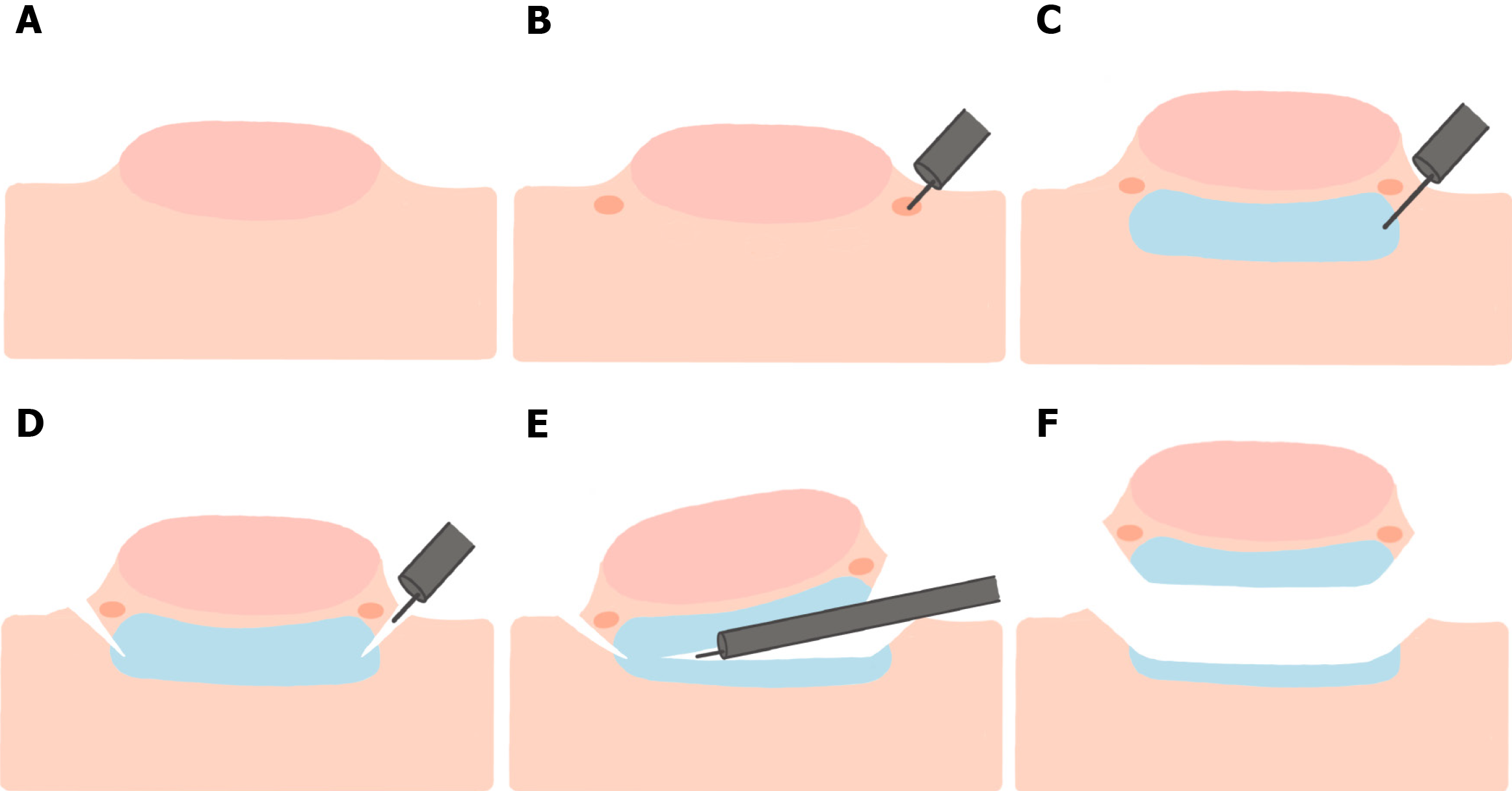
Figure 4 Key steps in performing endoscopic submucosal dissection.
A: A large polyp is encountered and deemed to be endoscopically resectable; B: Markings are made around the polyp to delineate the borders; C: The polyp is raised with a submucosal injection solution; D: Incision is made into the submucosa using an endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) knife; E: The ESD knife is subsequently used to dissect the polyp in conjunction with serial additional injections; F: The polyp is removed en bloc.
- Citation: Markarian E, Fung BM, Girotra M, Tabibian JH. Large polyps: Pearls for the referring and receiving endoscopist. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(12): 638-648
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i12/638.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i12.638