Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2021; 13(10): 529-542
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.529
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.529
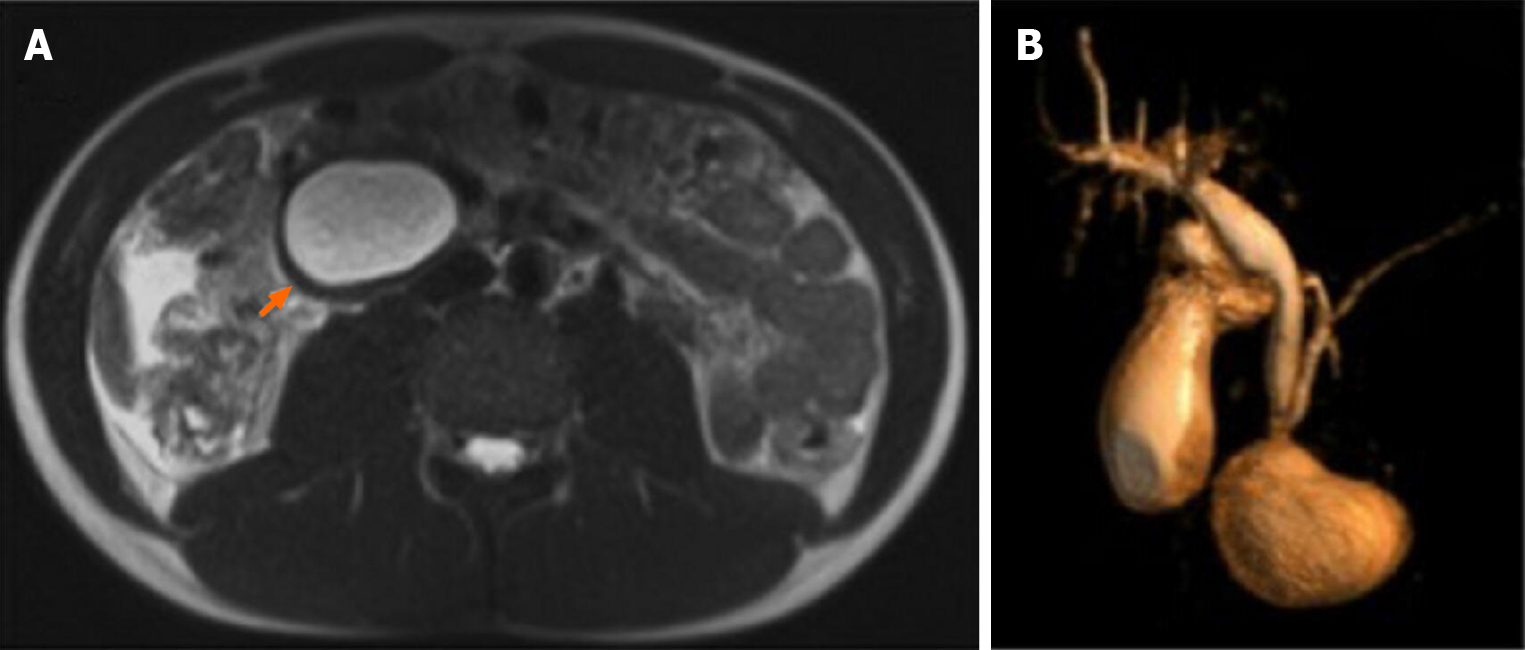
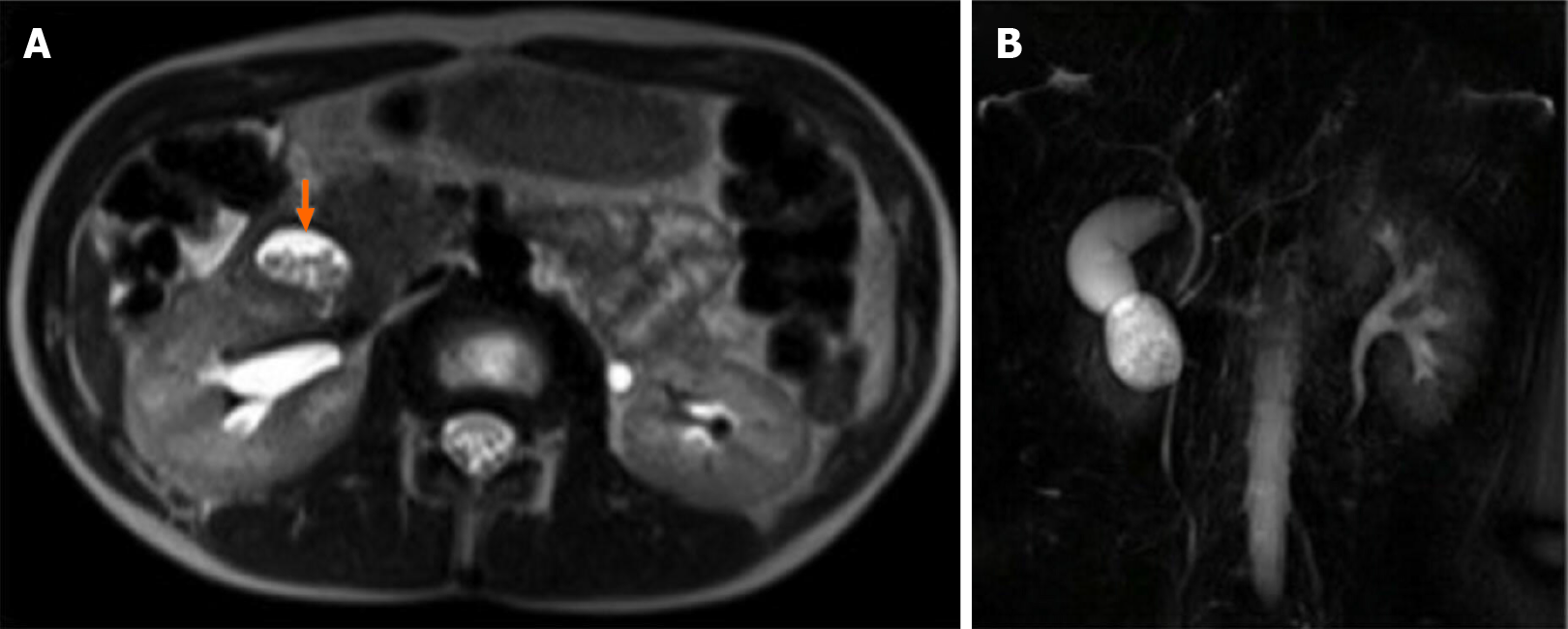
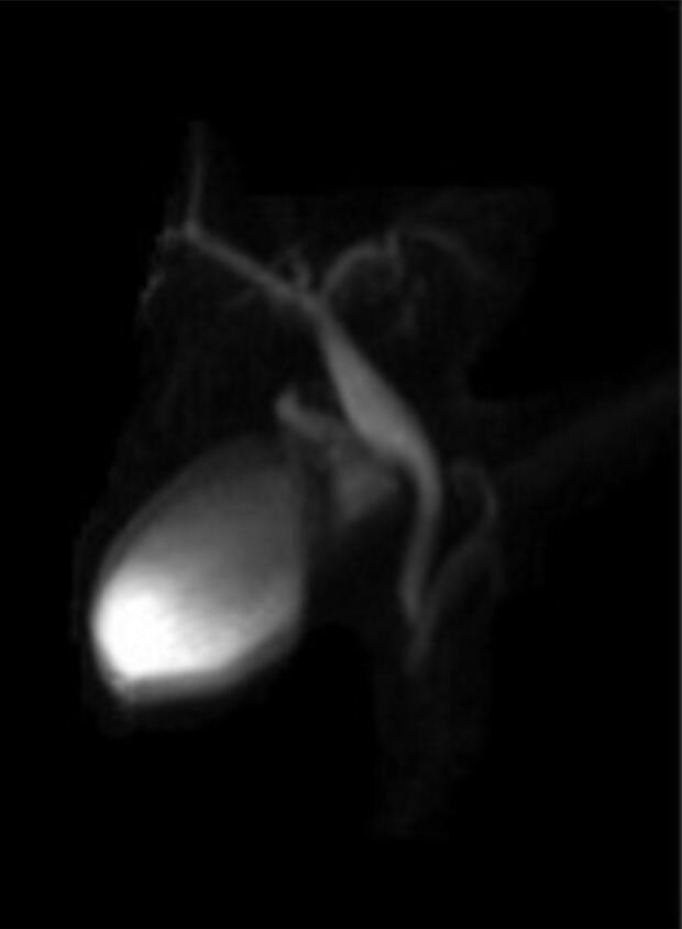
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging on HASTE T2 w sequence.
A: Homogeneously hyperintense cyst located within the duodenum, which was partially occluded (arrow); B: On 3D cholangiographic reconstruction, intrahepatic bile ducts were normal, cystic duct was dilated with tortuous course and common hepatic duct presented saccular dilation. Common bile duct had a caliber at the upper limits of the normal range with a regular course and was in communication with periampullary duodenal duplication cysts.
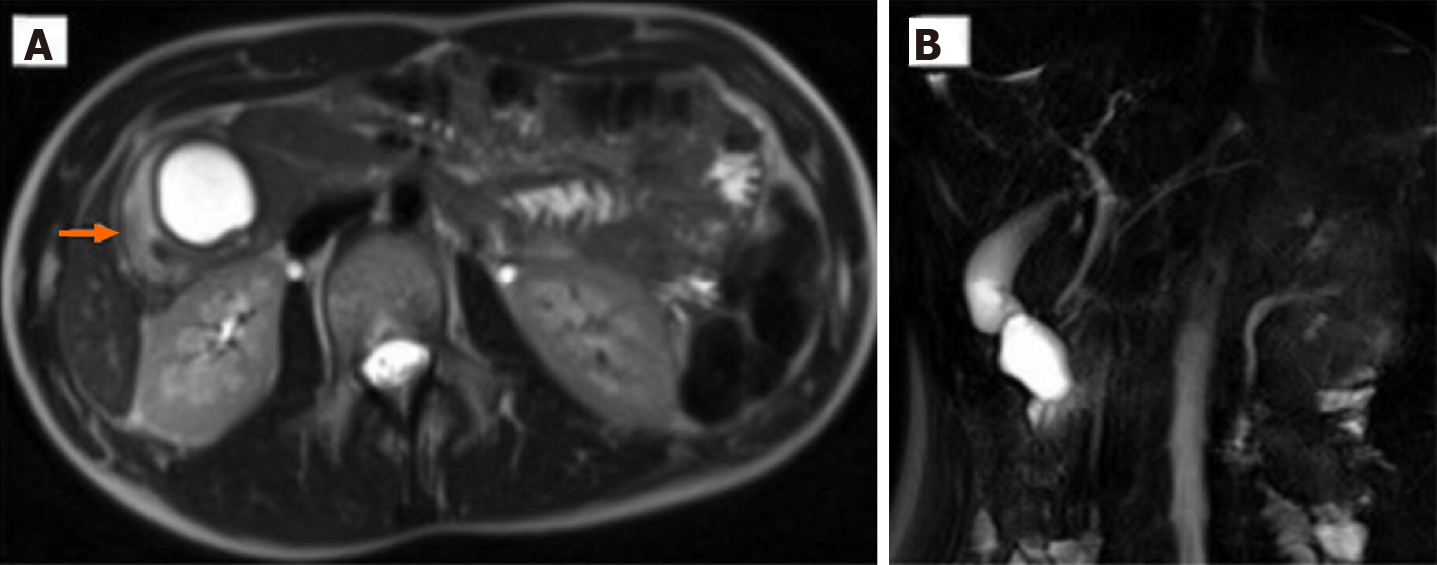
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging of case 2.
A: Round homogeneously hyperintense lesion at the level of uncinate process of the pancreas determined a major compression on the second portion of duodenum (arrow); B: At cholangiographic reconstruction, the intra- and extrahepatic biliary tree and pancreatic ductal system were normal.
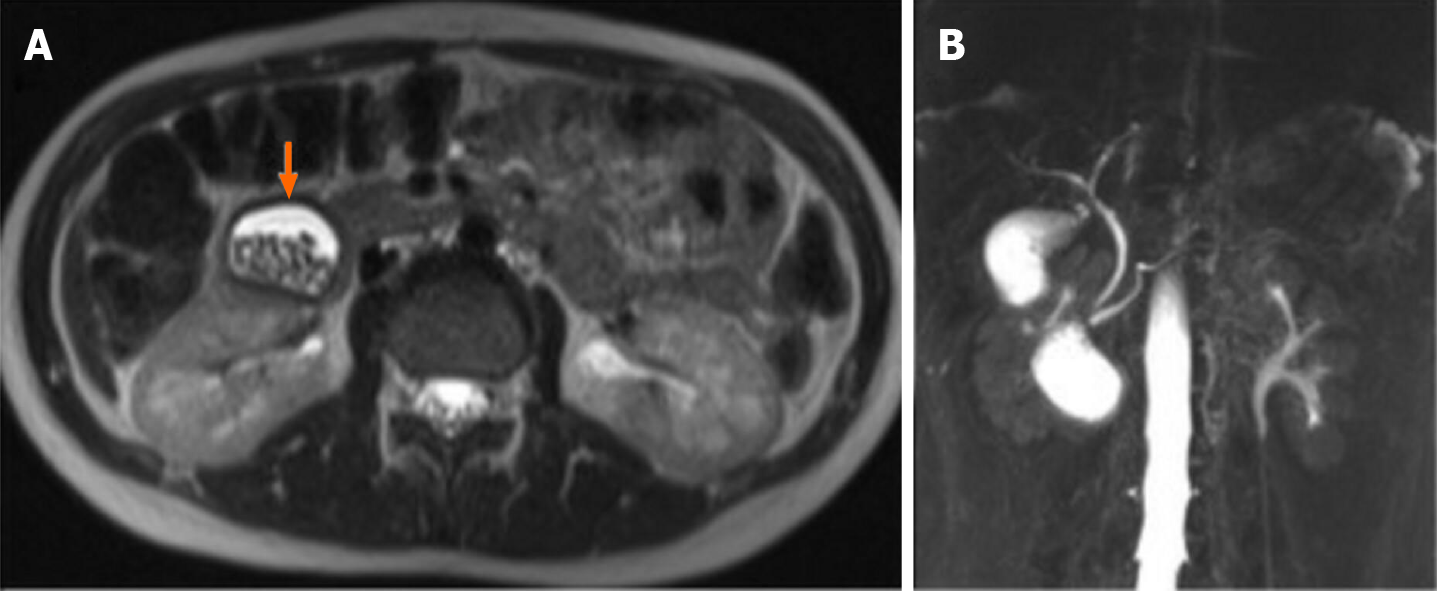
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance imaging of case 3.
A: An oval heterogeneously hyperintense lesion containing multiple stones and located in the second part of the duodenum; B: Cholangiographic reconstruction showed normal gallbladder and intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts.
Figure 4
Magnetic resonance imaging showed periampullary duodenal duplication cysts filled with stones.
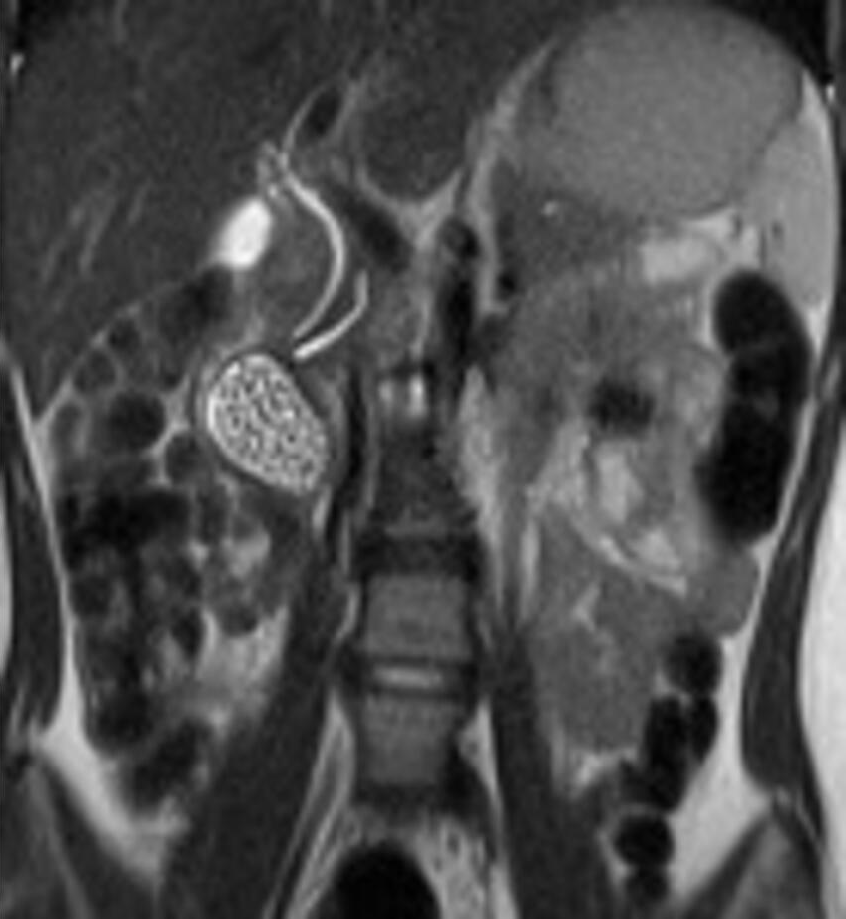
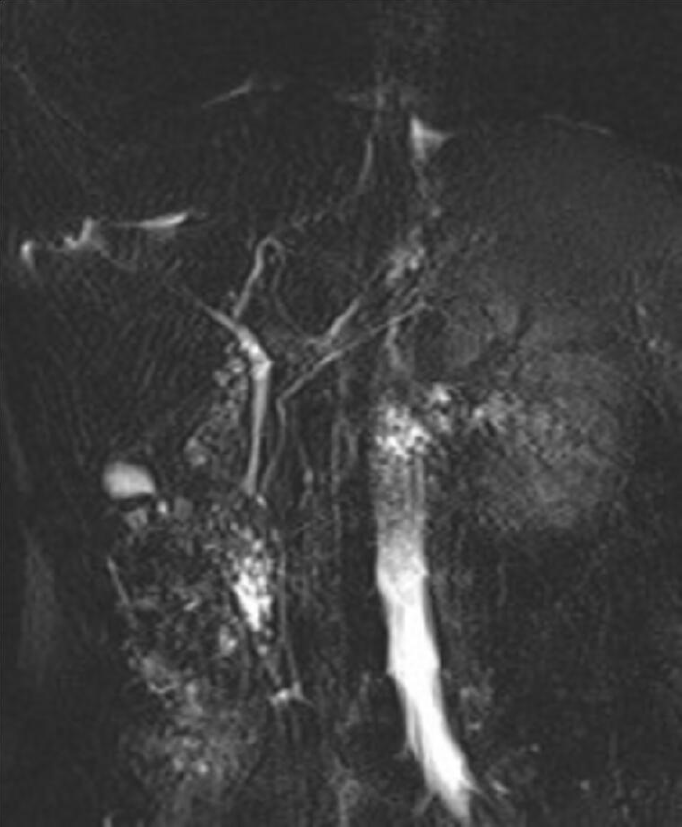
Figure 5 Magnetic resonance imaging.
A: Oval mass is located below the gallbladder and lateral to the common bile duct and pancreatic duct, adjacent to the pancreatic head. The cyst was filled with fluid and multiple stones; B: Cholangiographic reconstruction showed normal gallbladder and intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts.
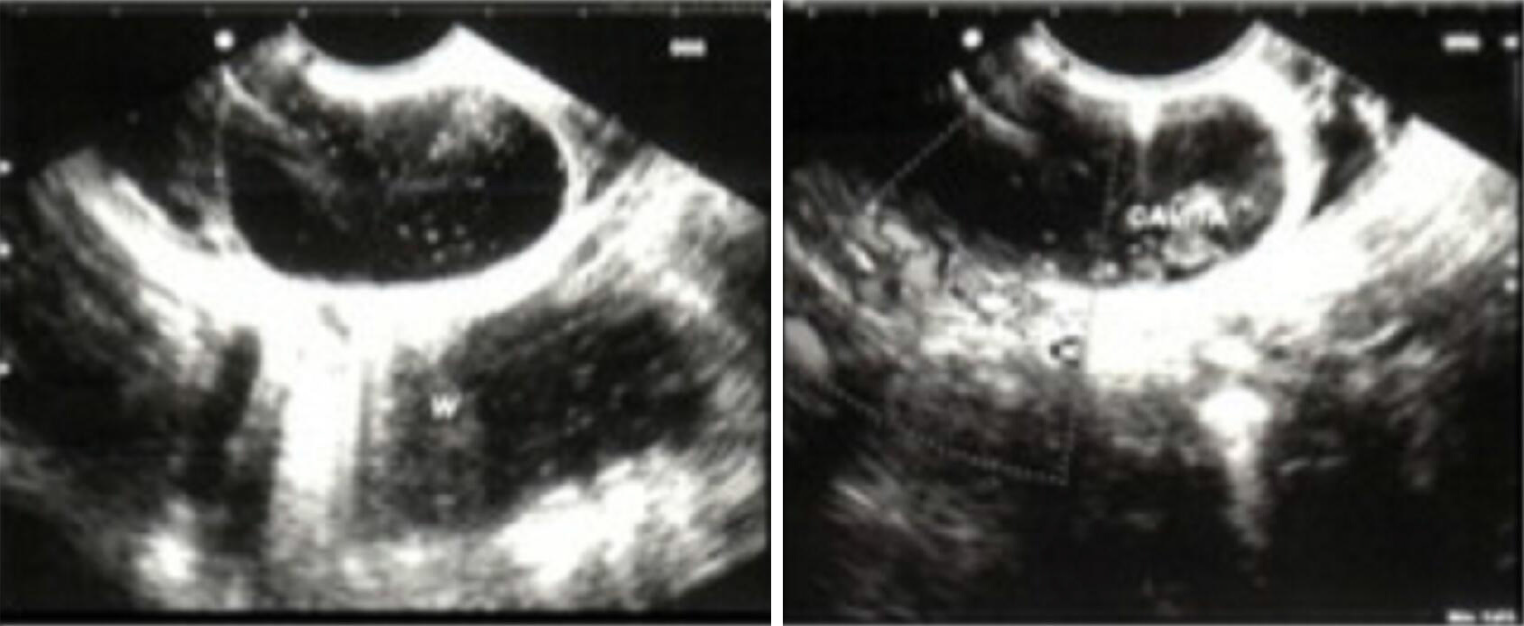
Figure 6 Endoscopic ultrasound.
The probe is inside the duodenum, and the common wall separates the duodenum and the duodenal duplication.
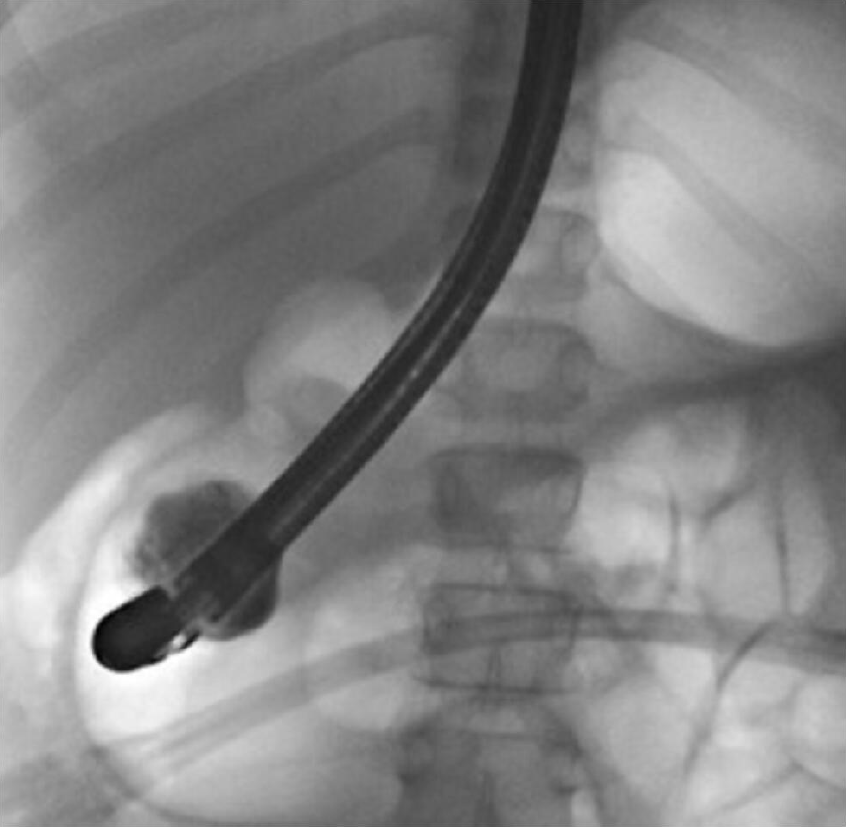
Figure 7 Endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography.
After distal papillotomy, contrast filled the periampullary duodenal duplication cysts.
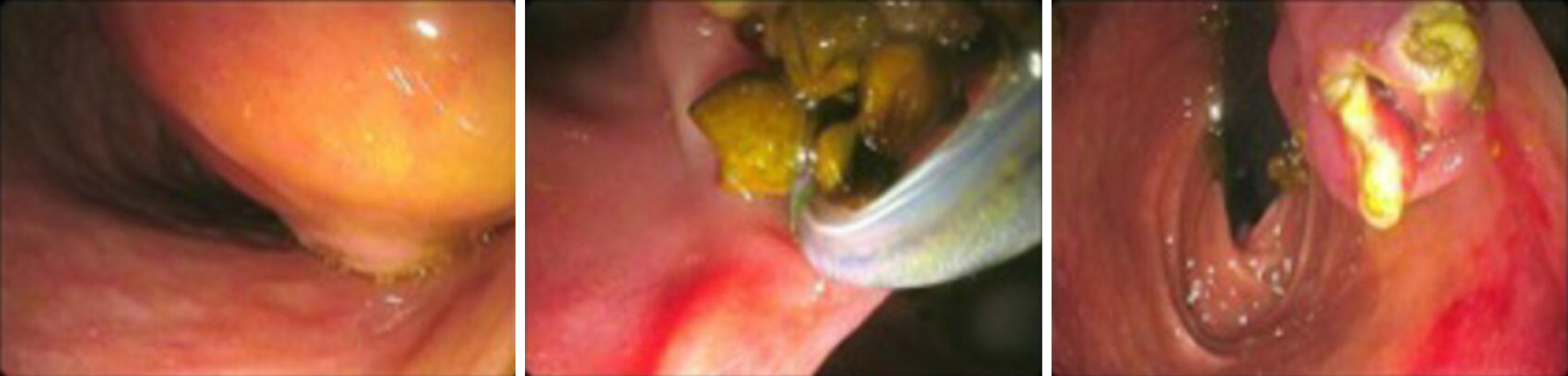
Figure 8
Cyst marsupialization was performed with subsequent extraction of biliary microstones.
Figure 9
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography performed 3 months after the endoscopic treatment did not show periampullary duodenal duplication cysts.
Figure 10
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography performed after 9 mo endoscopic treatment did not show periampullary duodenal duplication cysts.
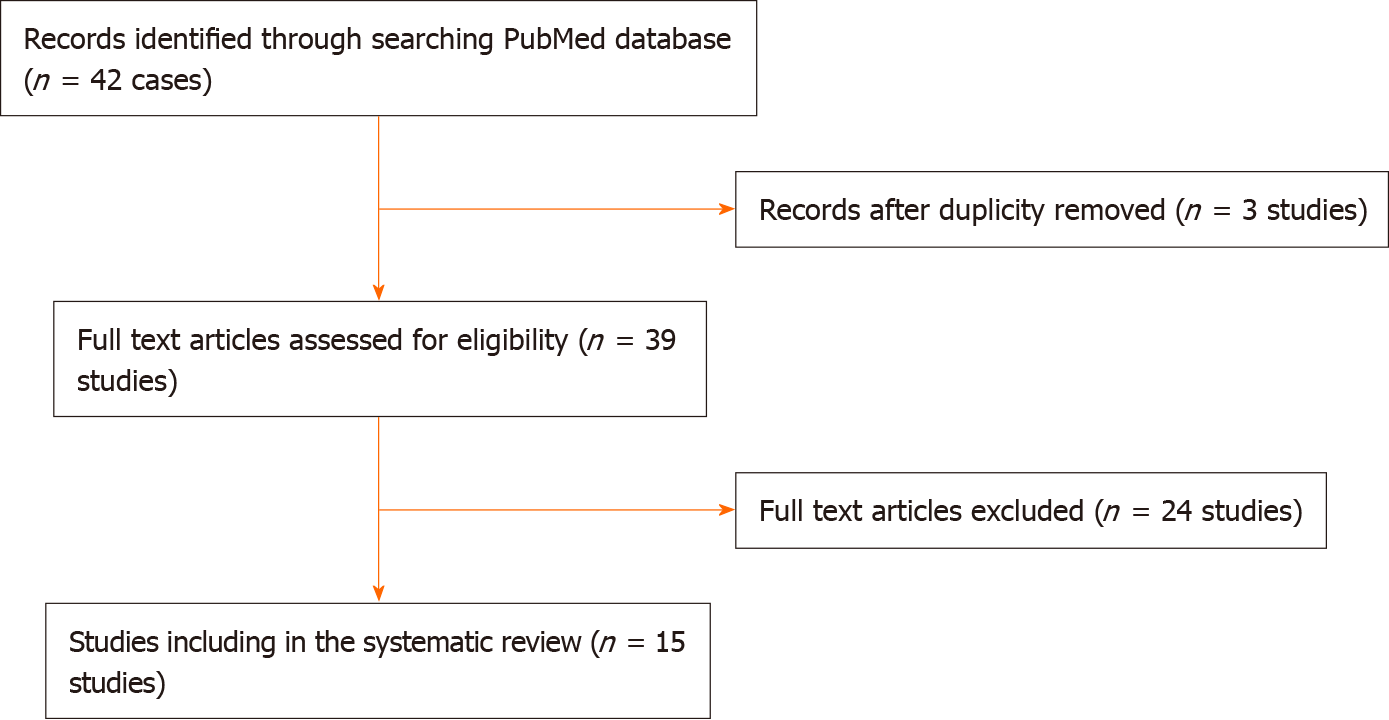
Figure 11
PRISMA 2009 flow diagram.
- Citation: Bulotta AL, Stern MV, Moneghini D, Parolini F, Bondioni MP, Missale G, Boroni G, Alberti D. Endoscopic treatment of periampullary duodenal duplication cysts in children: Four case reports and review of the literature. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(10): 529-542
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i10/529.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.529