Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2021; 13(10): 473-490
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.473
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.473
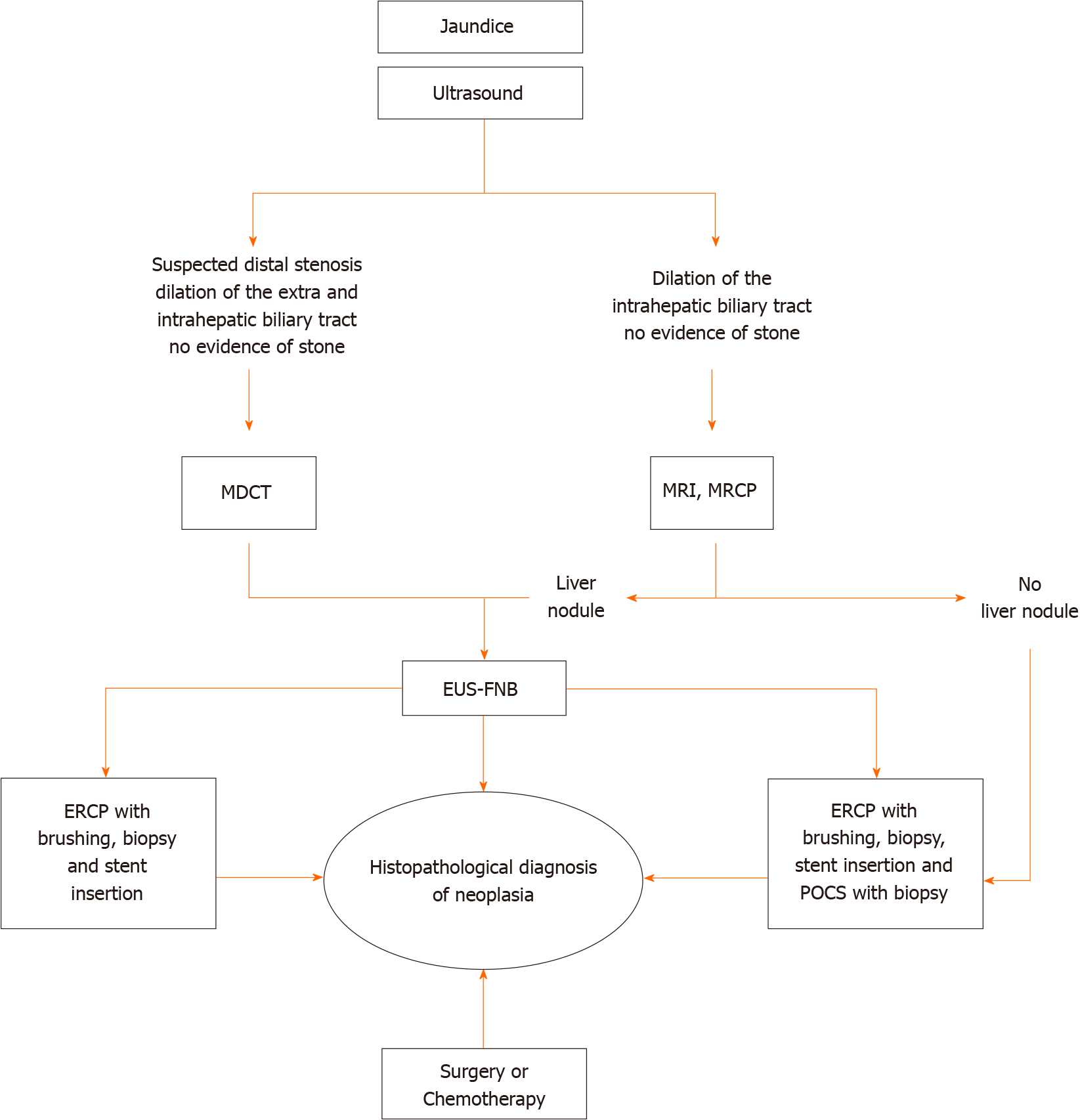
Figure 1 Algorithm of imaging investigations in biliary stenosis.
MDCT: Multidetector computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; MRCP: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography; EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasound-fine needle aspiration; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; POCS: Peroral cholangioscopy.
Figure 2
Three cases of patients with distal stenosis in which the diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma was made by forceps biopsy during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
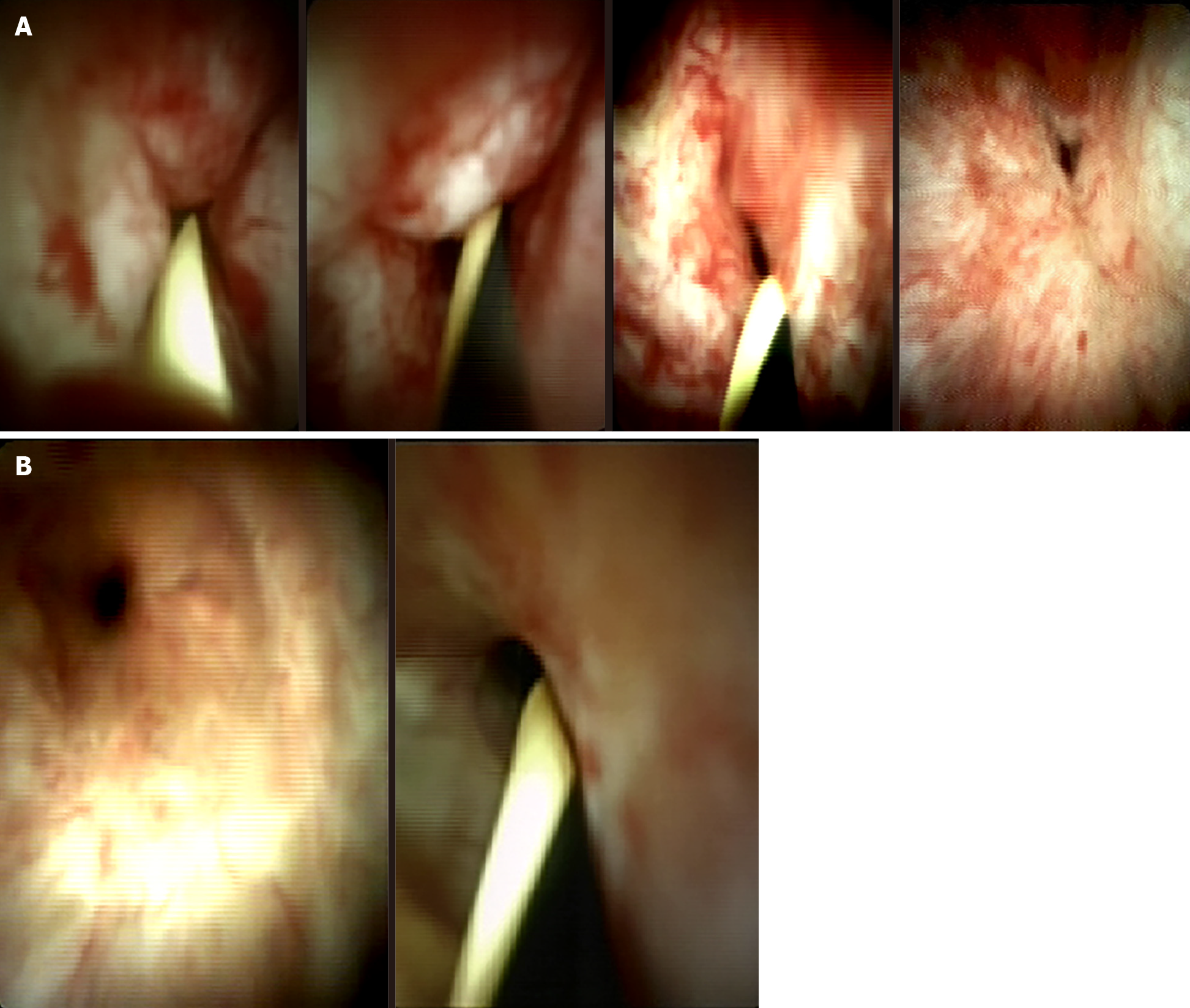
Figure 3 Digital (SpyGlass) cholangioscopy images.
A: Cholangiocarcinoma; B: Benign stenosis.
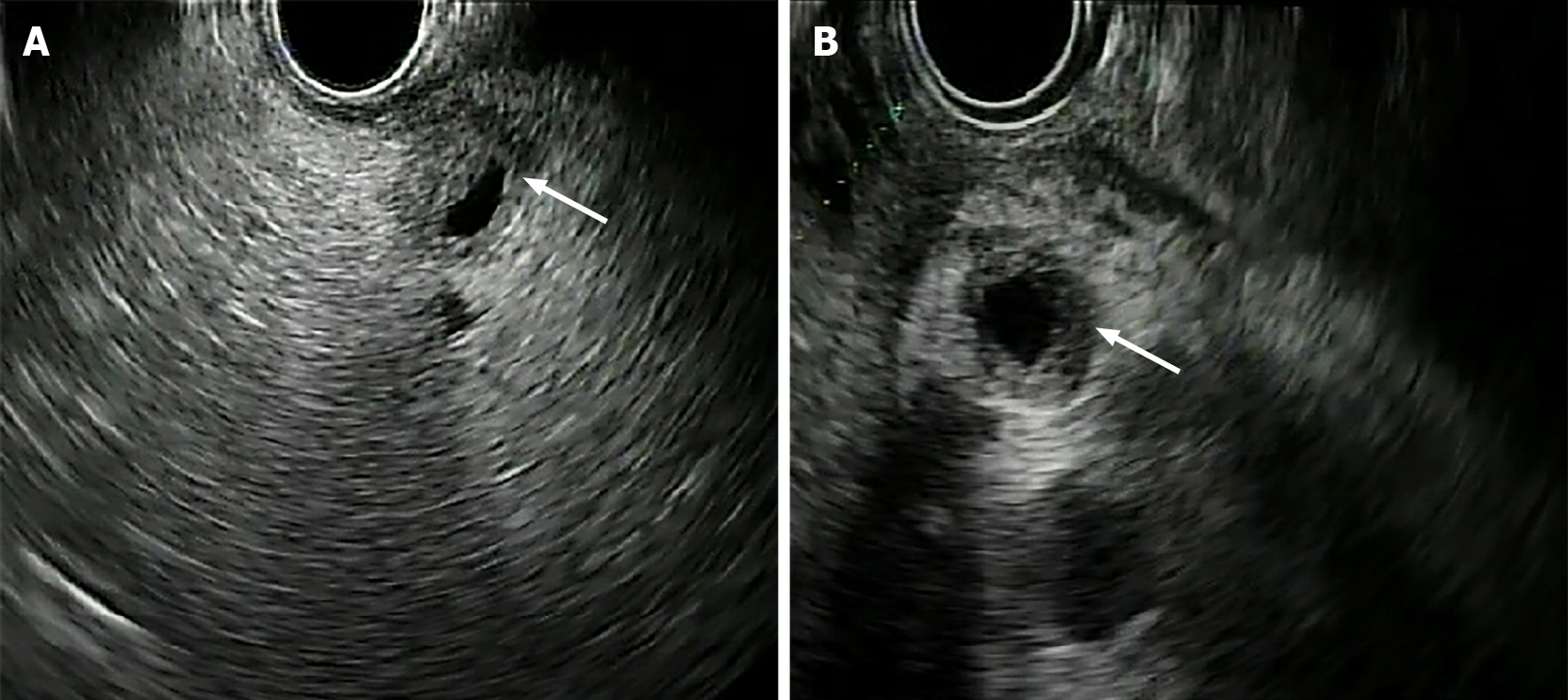
Figure 4 Two cases of cholangiocarcinoma evaluated with endoscopic ultrasound.
A: Distal stenosis of the main biliary tract; B: Stenosis of the proximal-middle tract of the main biliary duct. Arrows indicate the stenotic tract.
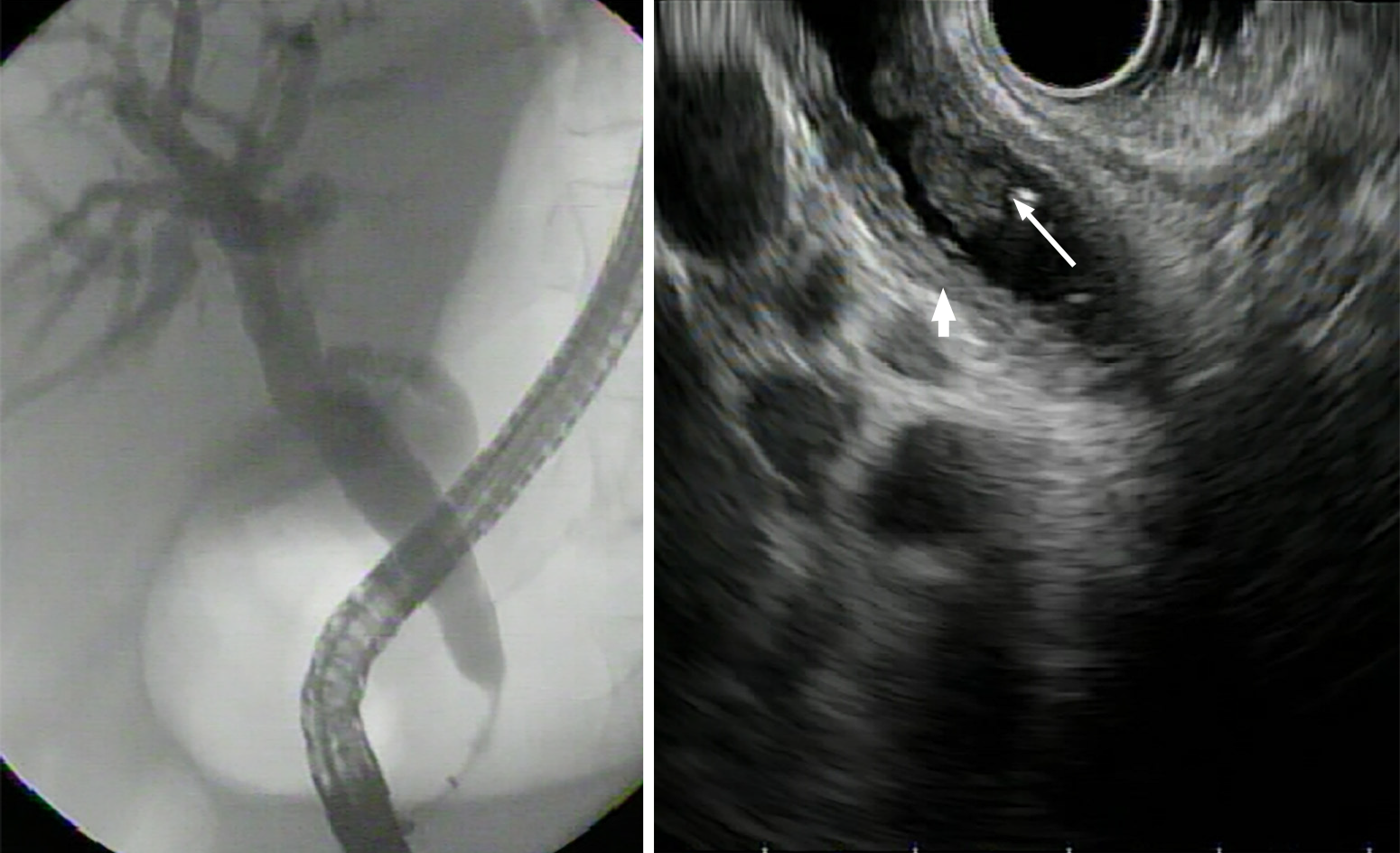
Figure 5 Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound image of a stenotic tract of the distal biliary duct.
In the endoscopic ultrasound image, the nodule inside the main biliary tract (large arrow) and thickening of the bile duct wall (small arrow) are visible.
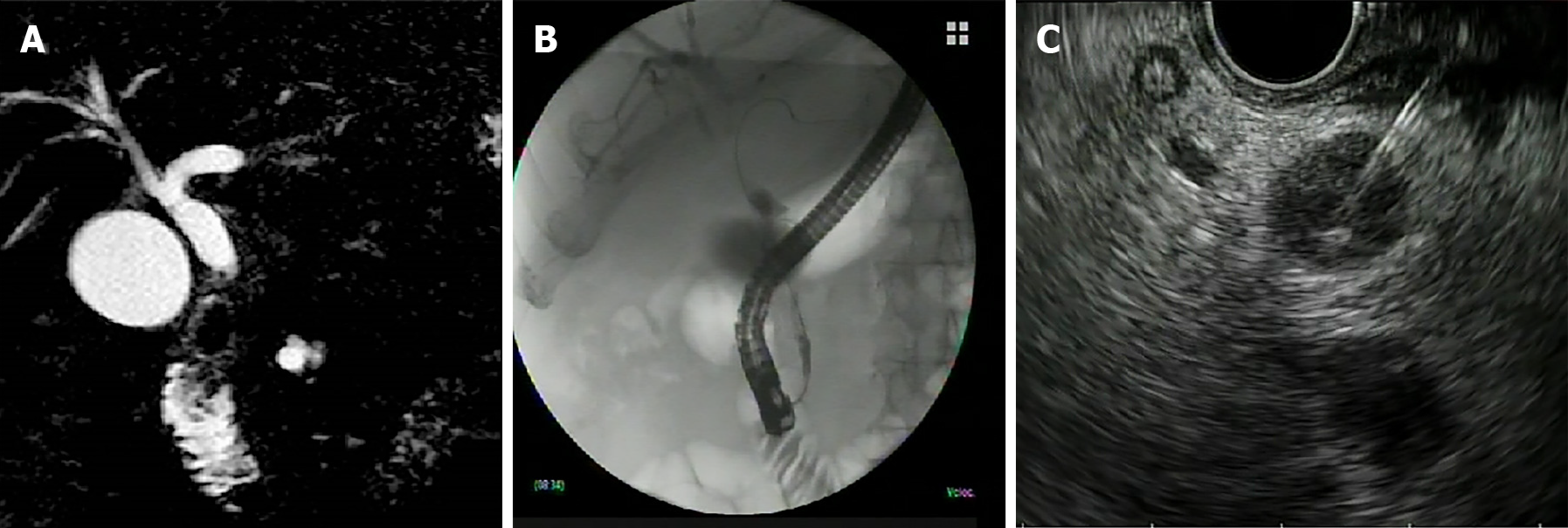
Figure 6 Adenocarcinoma of the main biliary tract.
A: Magnetic resonance image of suspected neoplastic stenosis; B: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography image confirming the stenosis; C: Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration of the stenotic tract for tissue diagnosis.
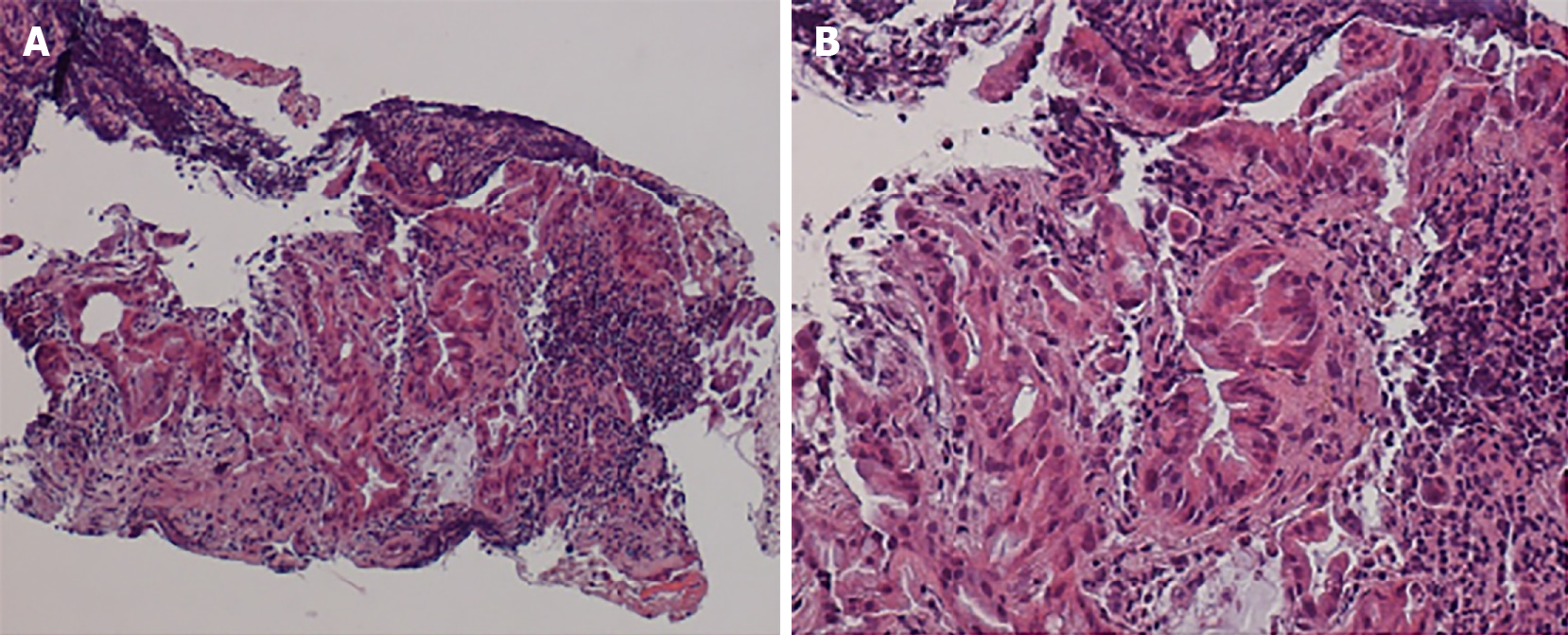
Figure 7 Histology of specimen collected by endoscopic ultrasound-fine needle aspiration from cholangiocarcinoma in a hepatic nodule.
A: Hematoxylin and eosin staining, magnification × 40; B: Hematoxylin and eosin staining, magnification × 100.
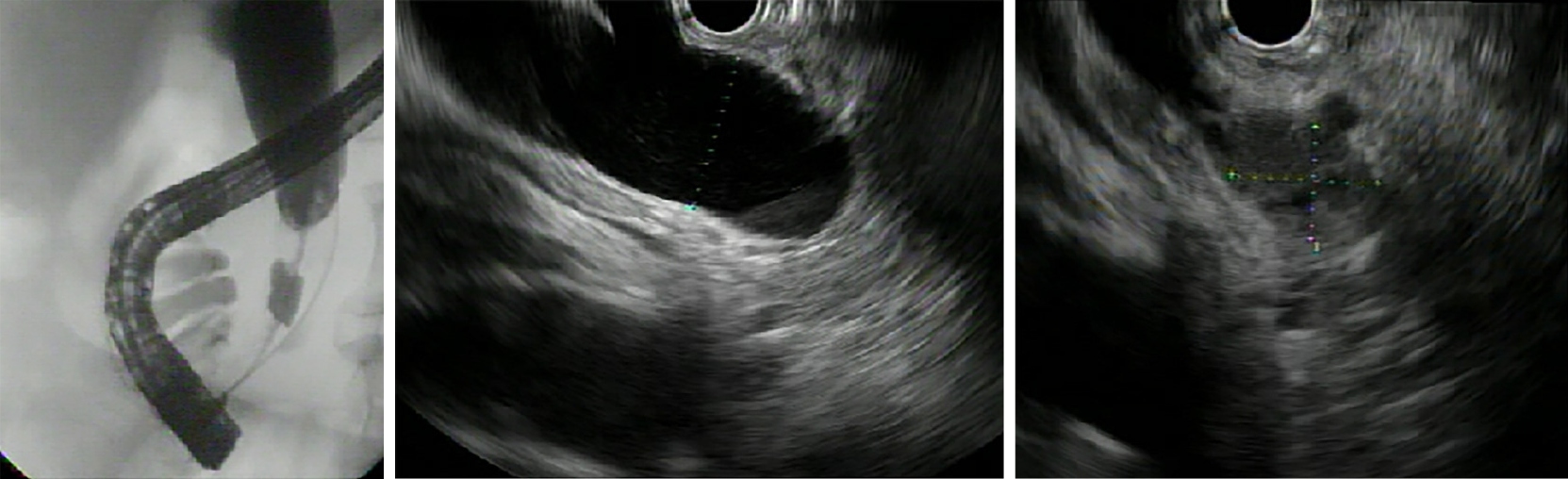
Figure 8 Diagnosis of cholangiocarcinoma of the distal tract of the main biliary duct, obtained in a single session by biopsy during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography and endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration.
Endoscopic ultrasound images show dilation of the common bile duct and stenosis of the distal tract due to a neoplastic nodule.
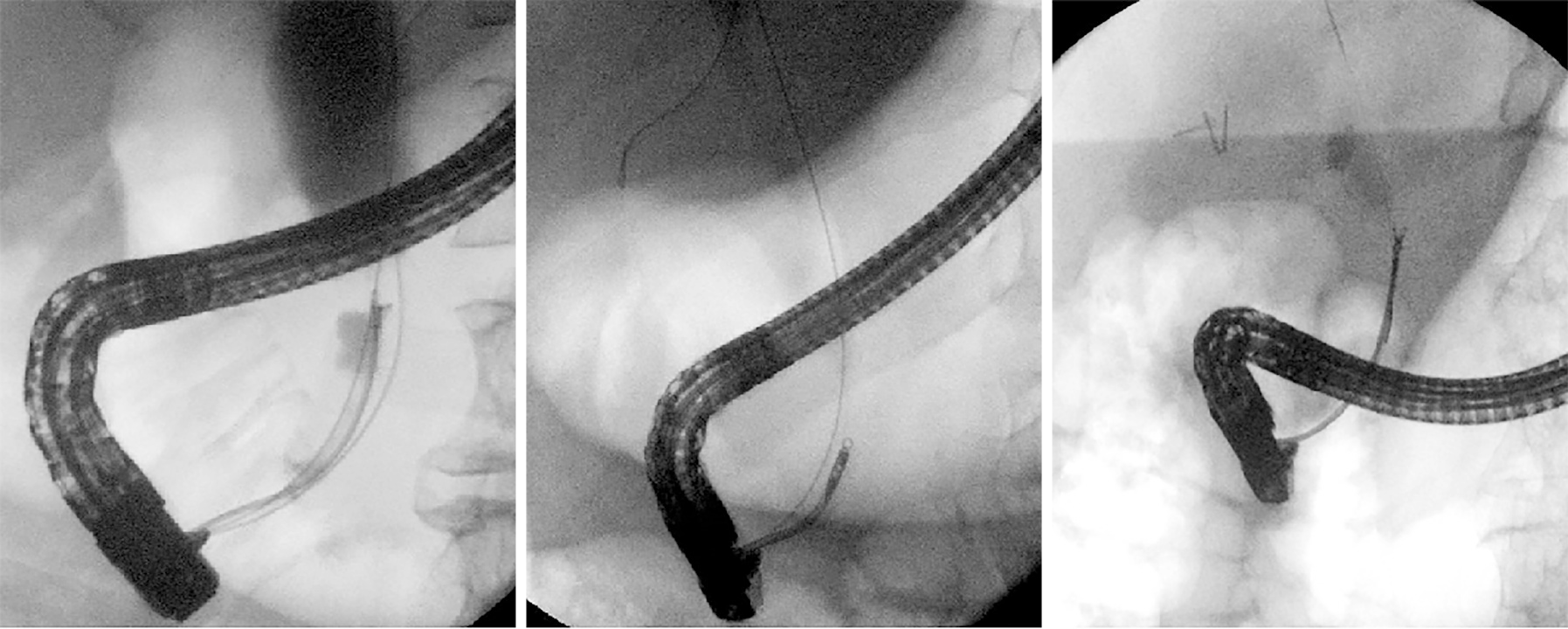
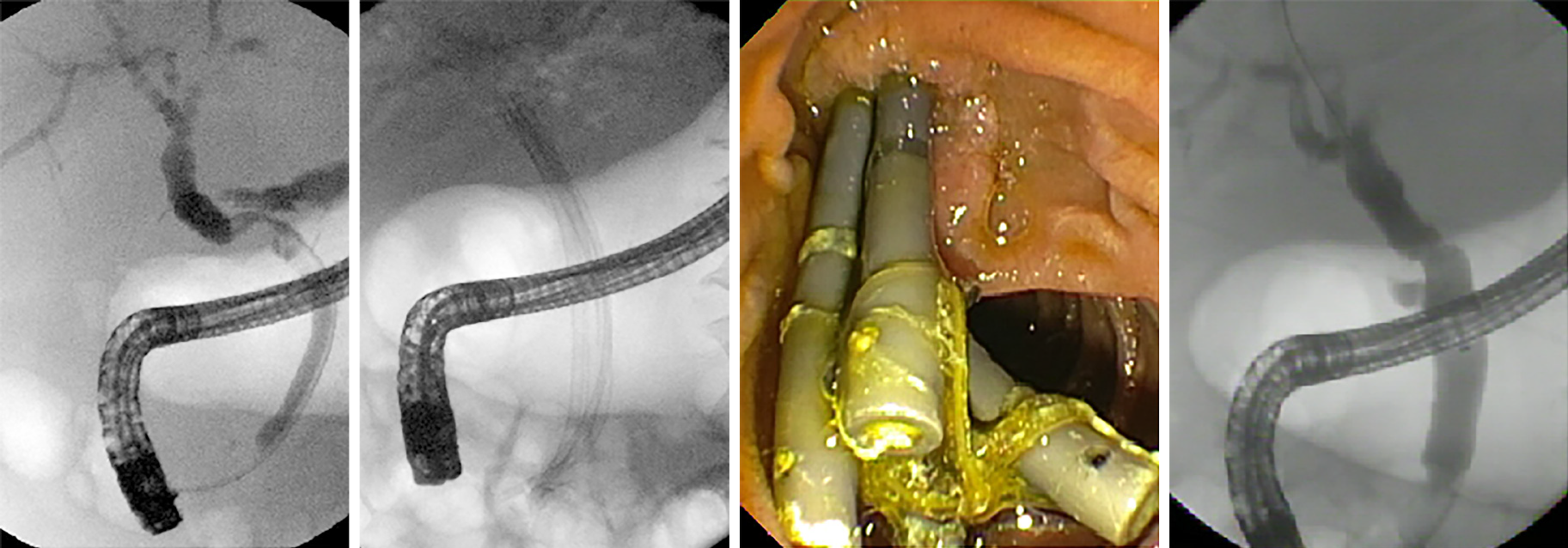
Figure 9 Multi-stenting treatment of anastomotic stenosis after liver transplantation.
The image on the far right shows complete resolution of the stenosis.
- Citation: Del Vecchio Blanco G, Mossa M, Troncone E, Argirò R, Anderloni A, Repici A, Paoluzi OA, Monteleone G. Tips and tricks for the diagnosis and management of biliary stenosis-state of the art review. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(10): 473-490
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i10/473.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.473