Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Oct 16, 2021; 13(10): 451-459
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.451
Published online Oct 16, 2021. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.451
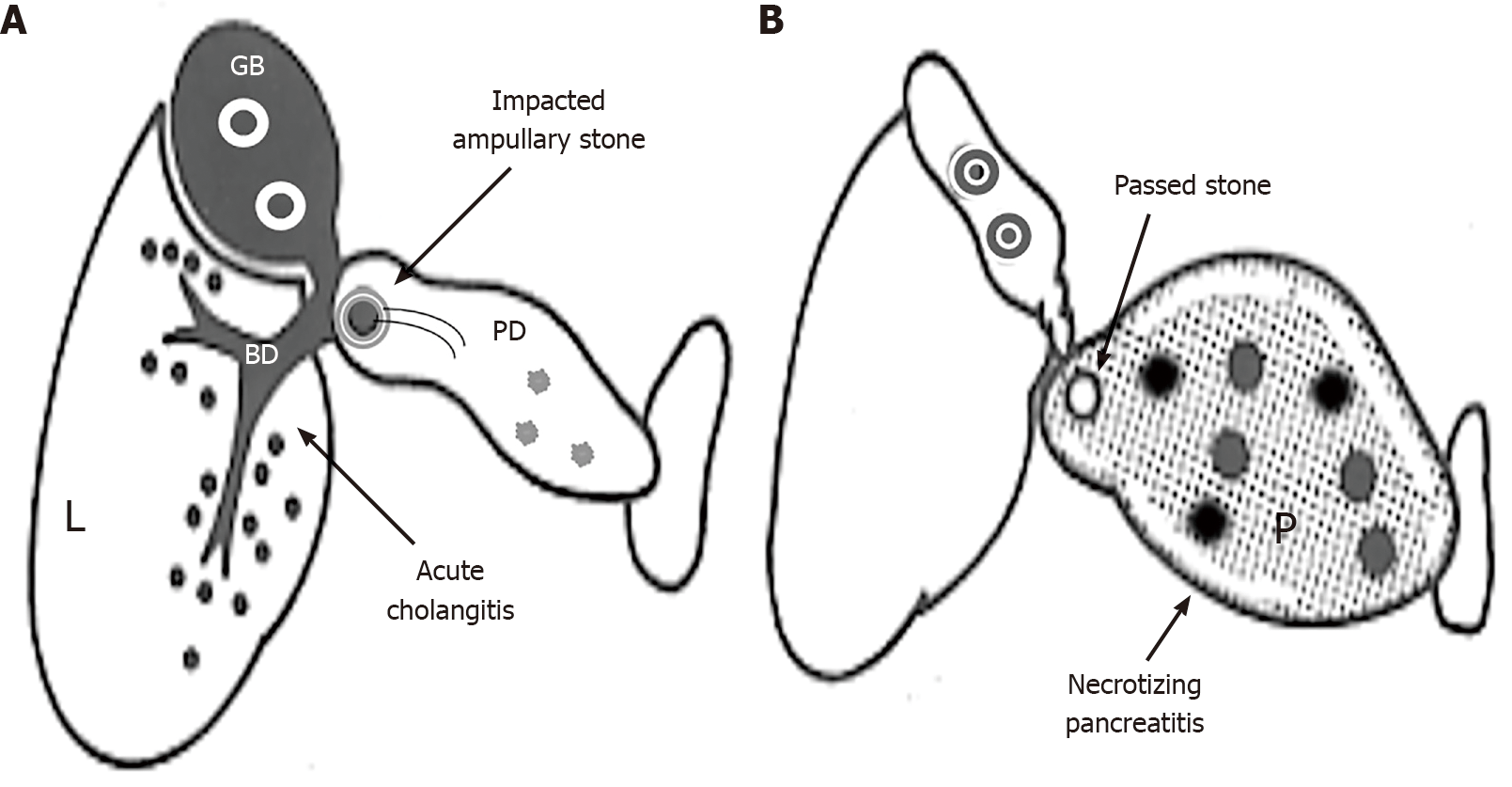
Figure 1 Subdivisions of gallstone pancreatitis with severe disease into gallstone cholangiopancreatitis and gallstone necrotizing pancreatitis.
A: Gallstone cholangiopancreatitis with persistent ampullary stone impaction and ascending acute cholangitis complicated with minimal or mild pancreatic inflammation due to biliopancreatic obstruction; B: Gallstone necrotizing pancreatitis caused by the reflux of bile or duodenal contents into the pancreas (P), not complicated by acute biliary tract disease due to the passage of stones. L: Liver; BD: Bile duct; GB: Gallbladder; PD: Main pancreatic duct.
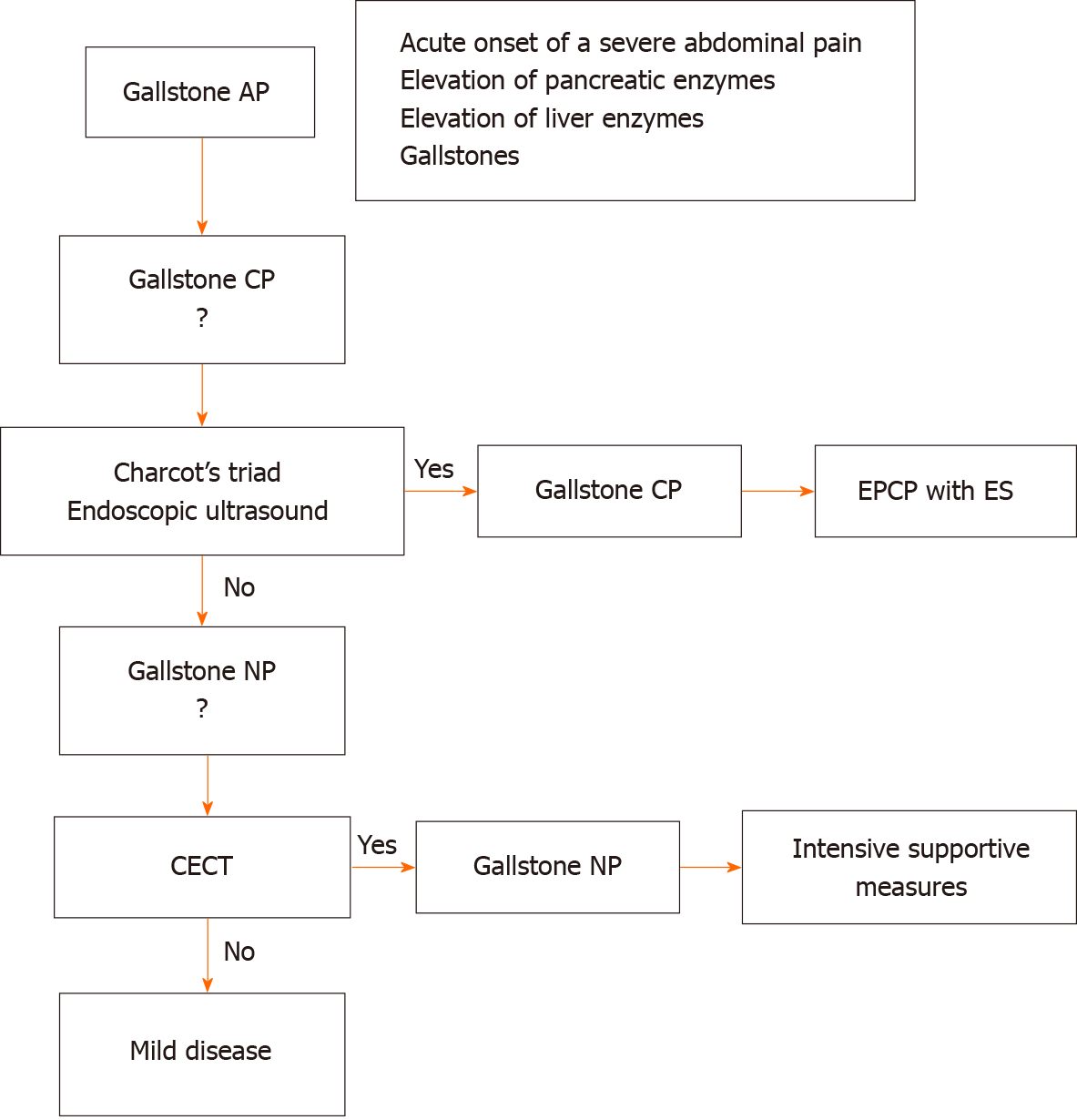
Figure 2 The algorithm for the diagnosis and initial treatment of gallstone pancreatitis.
AP: Acute pancreatitis; CECT: Contrast-enhanced computed tomography; CP: Cholangiopancreatitis; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography; ES: Endoscopic sphincterotomy; NP: Necrotizing pancreatitis.
- Citation: Isogai M. Proposal of the term “gallstone cholangiopancreatitis” to specify gallstone pancreatitis that needs urgent endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2021; 13(10): 451-459
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v13/i10/451.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v13.i10.451