Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jun 16, 2020; 12(6): 193-197
Published online Jun 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i6.193
Published online Jun 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i6.193
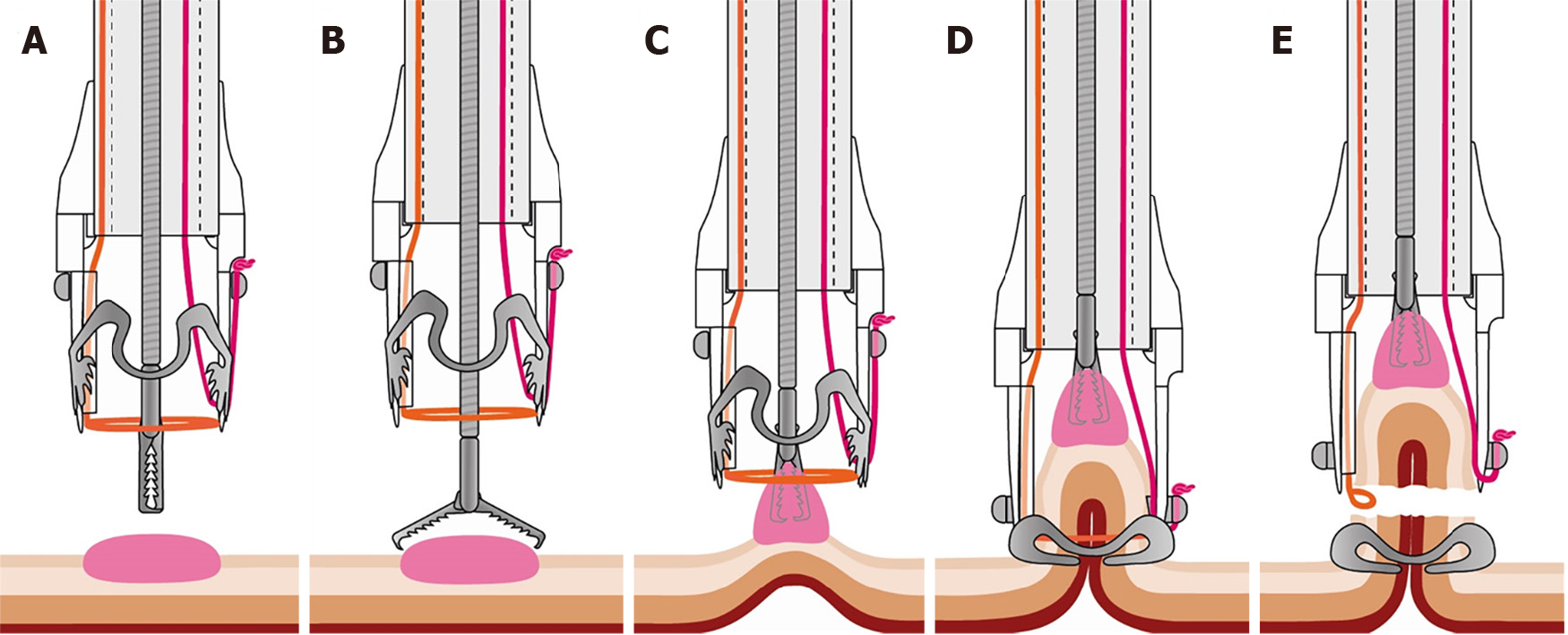
Figure 1 Illustration of the full-thickness resection device procedure.
A and B: Grasping forceps are advanced through the working channel of the endoscope; C: The target lesion is grasped and pulled into the cap; D: The over-the-scope clip is deployed and creates a full-thickness plication of the gastrointestinal wall; E: The pseudopolyp is resected above the over-the-scope clip with the preloaded snare (Courtesy of Ovesco Endoscopy AG, Tuebingen, Germany, with permission).
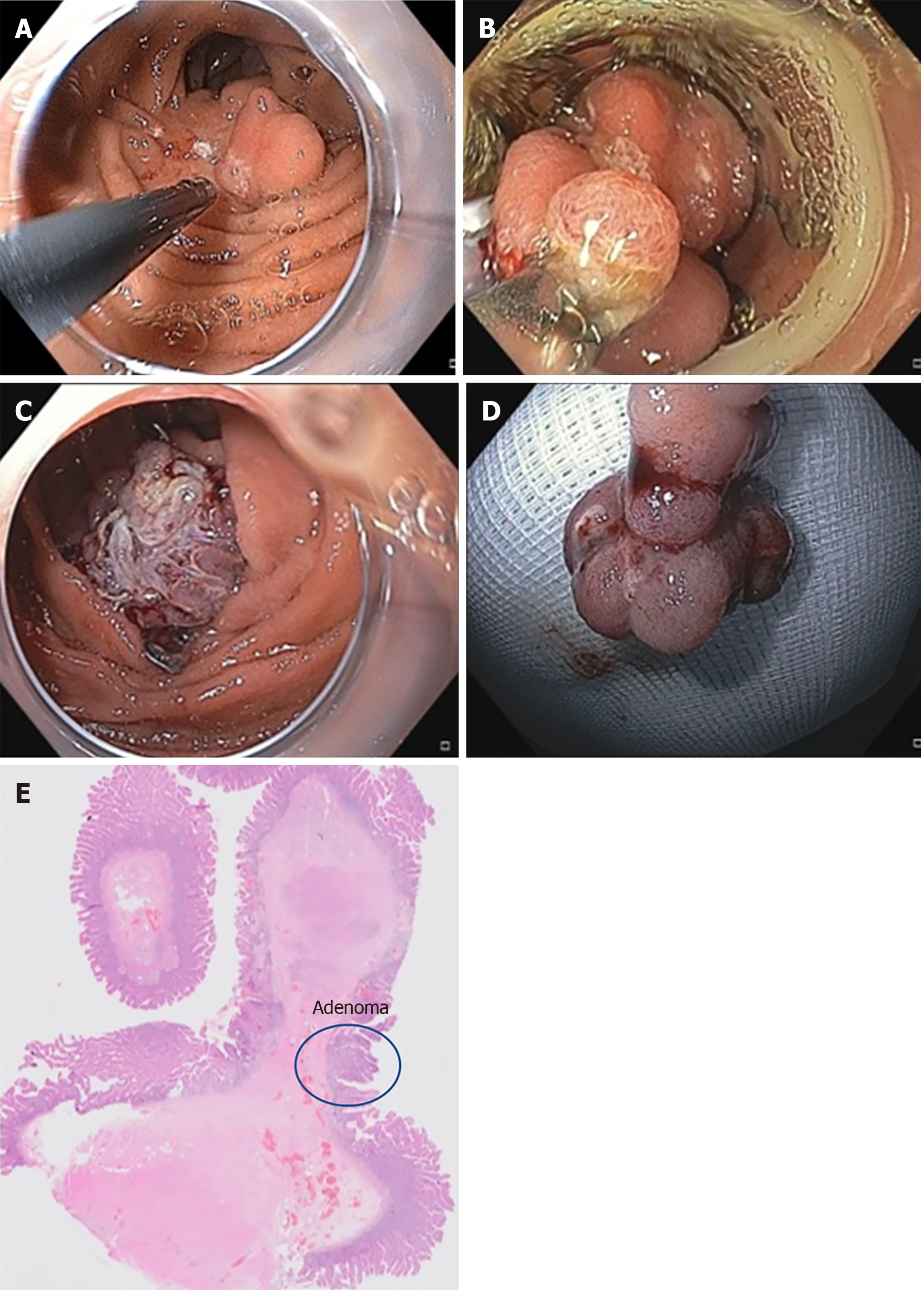
Figure 2 Full-thickness resection of the duodenal adenoma.
A: Endoscopic image of the recurrent adenoma. Marks were made by argon plasma coagulation; B: Endoscopic view with the mounted full-thickness resection device; C: View after resection with a correctly placed over-the-scope clip; D: Resection specimen; E: Histology of the specimen showing a small low-grade adenoma with R0 resection.
- Citation: Gericke M, Mende M, Schlichting U, Niedobitek G, Faiss S. Repeat full-thickness resection device use for recurrent duodenal adenoma: A case report. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2020; 12(6): 193-197
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v12/i6/193.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v12.i6.193