Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Feb 16, 2020; 12(2): 53-59
Published online Feb 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i2.53
Published online Feb 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i2.53
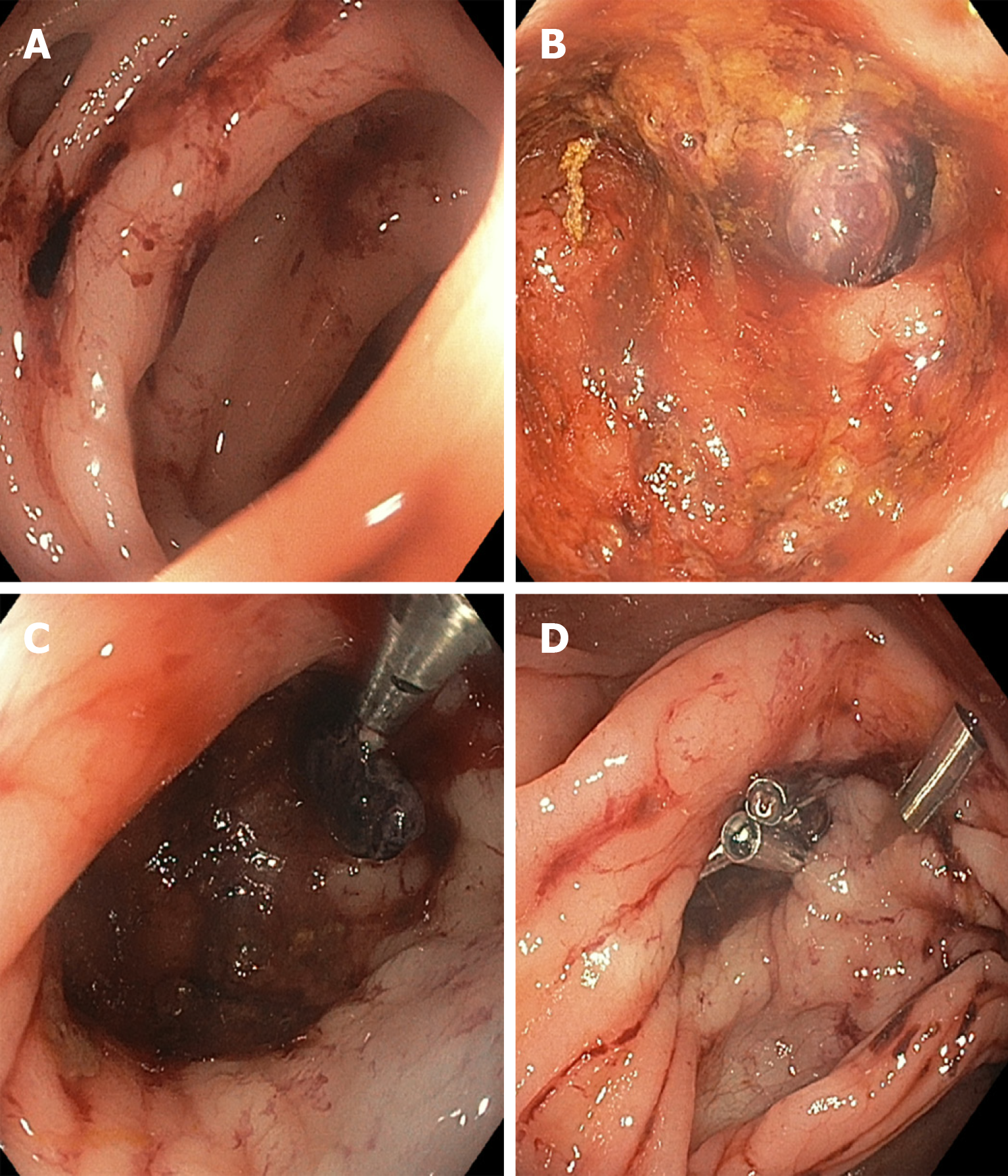
Figure 1 Endoscopic treatment of diverticular bleeding.
A: Diverticula with fresh blood nearby; B: Interrogation of the diverticula reveals a visible vessel within a diverticulum; C: Through-the-scope clipping of the visible vessel following submucosal 1:10000 epinephrine injection; D: Additional clipping performed to secure more durable hemostasis.
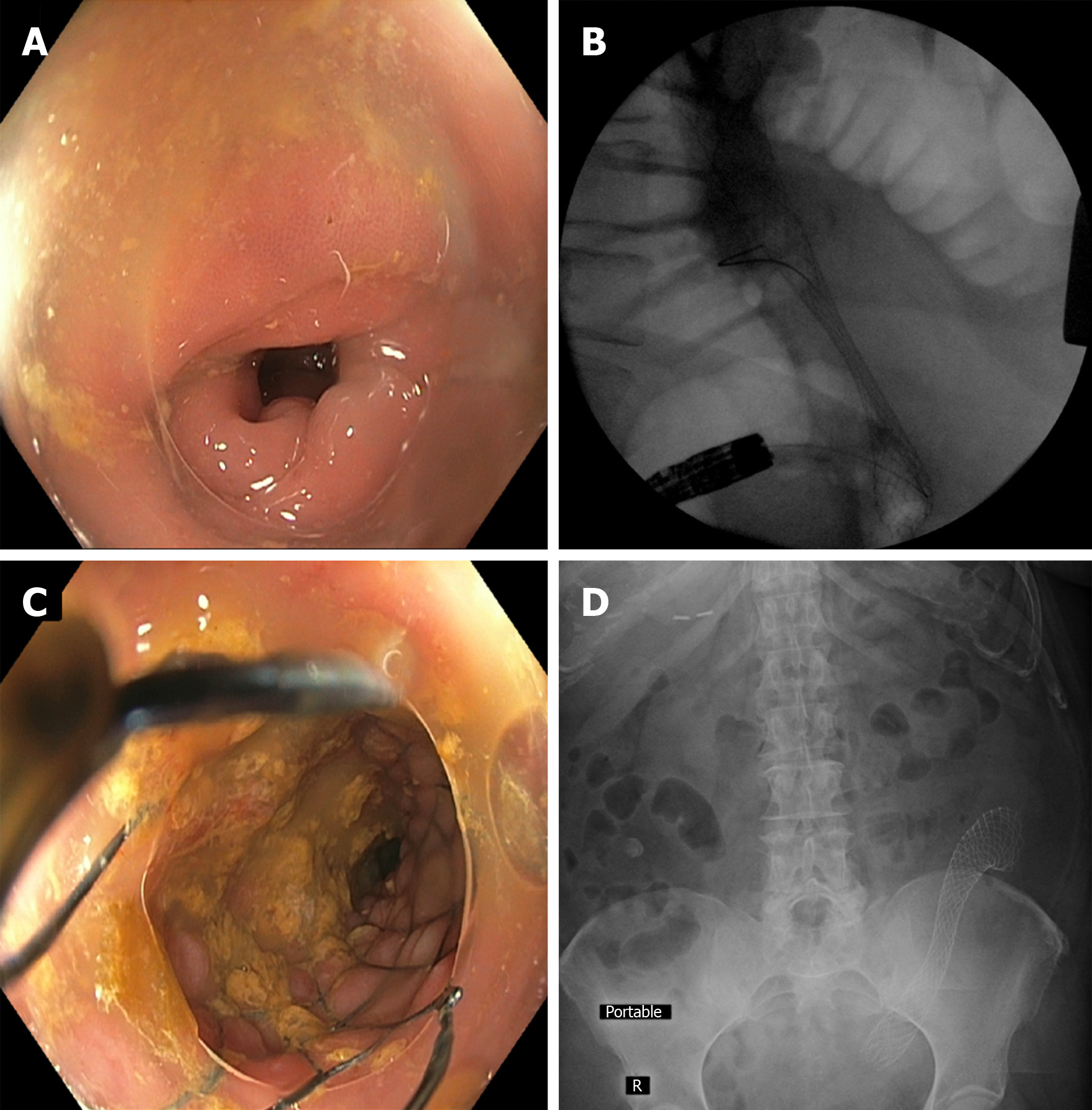
Figure 2 Colonic stent placement within a diverticulitis-associated strictures.
A: Sigmoid colon luminal narrowing due to diverticulitis-associated fibroinflammatory stricture; B: Fluoroscopic view of colonic self-expanding metal stent deployment with appreciable waist; C: Luminal view immediately after stent deployment within the stricture; D: Post-procedure abdominal x-ray showing stent in good position and with notable expansion. This management approach can allow for successful bowel preparation and 1-stage segmental resection instead of emergent partial colectomy with temporary colostomy.
- Citation: Fejleh MP, Tabibian JH. Colonoscopic management of diverticular disease. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2020; 12(2): 53-59
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v12/i2/53.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v12.i2.53