Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2020; 12(11): 469-487
Published online Nov 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i11.469
Published online Nov 16, 2020. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v12.i11.469
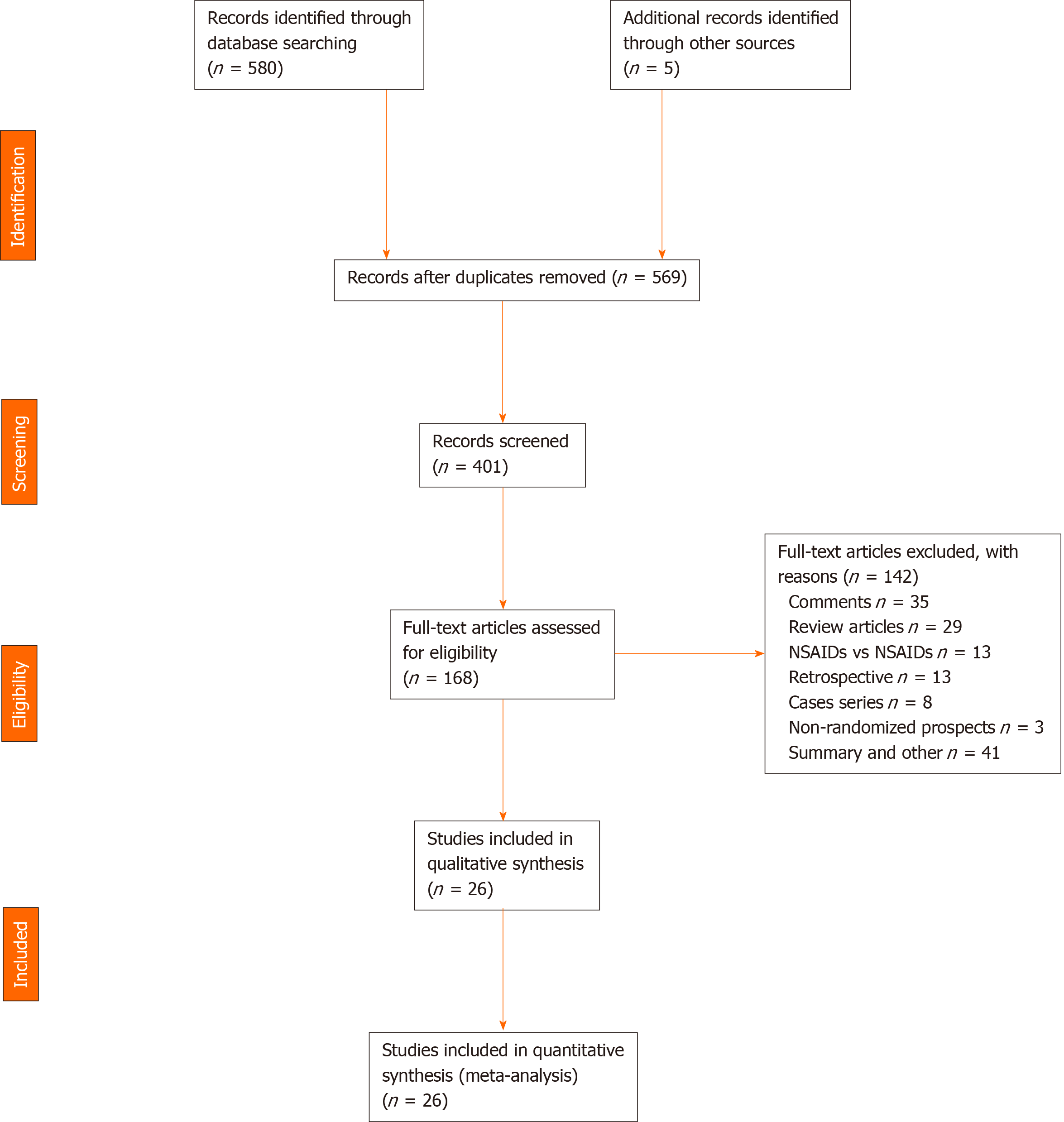
Figure 1 Inclusion of 26 randomized controlled trials in the PRISMA flowchart.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
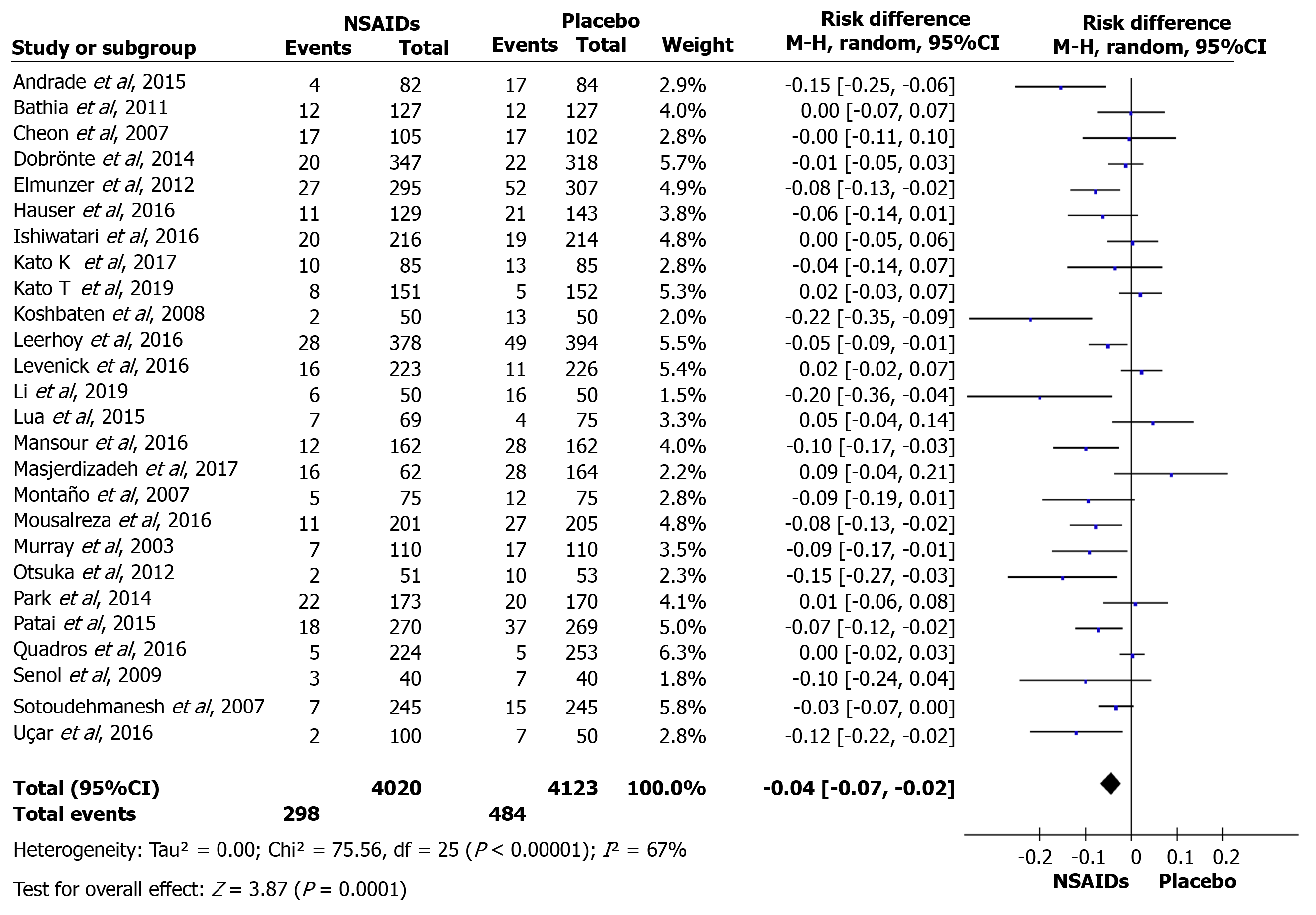
Figure 2 Forest plot of the global incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CI: Confidence interval.
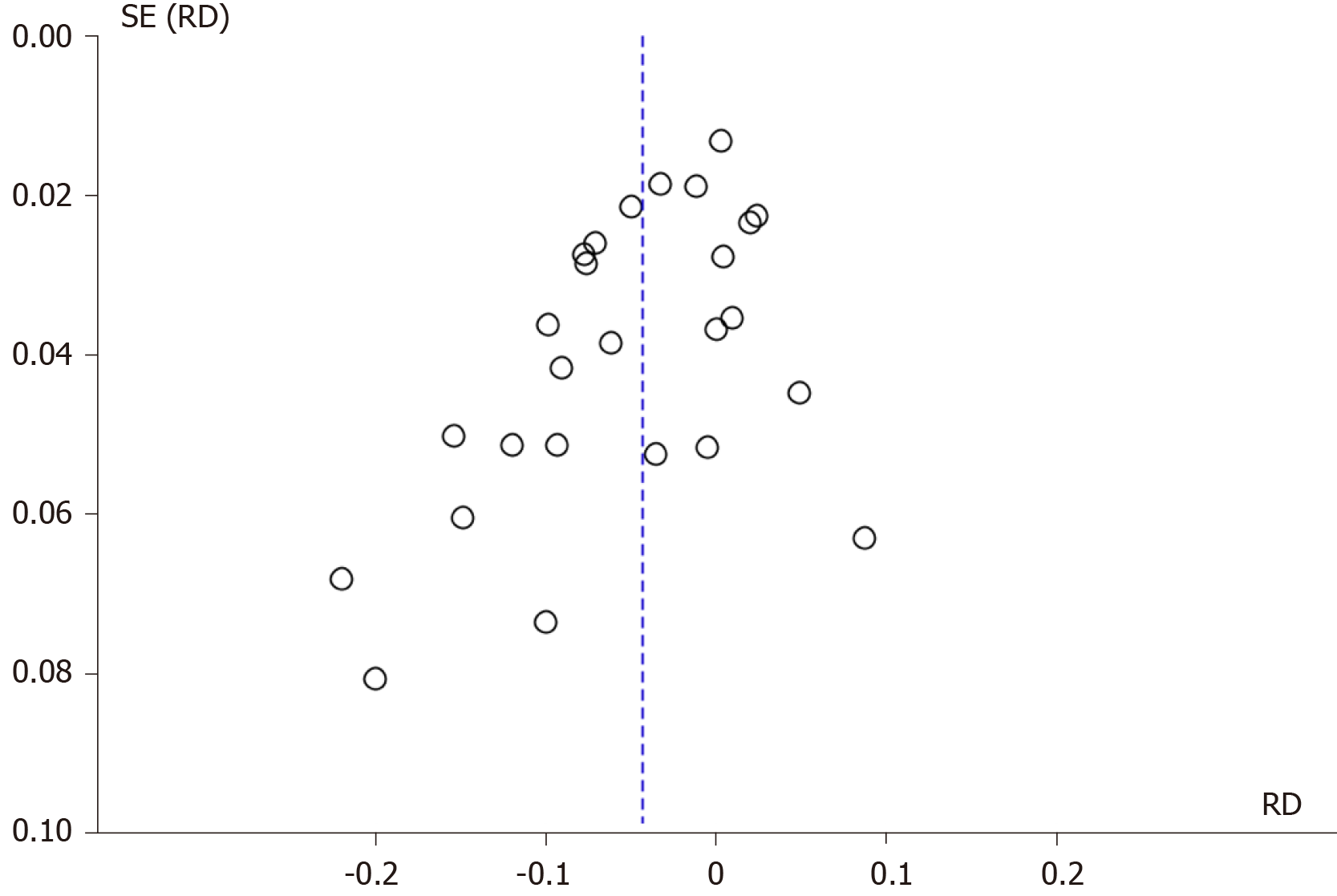
Figure 3 Funnel plot of the global incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis.
SE: Standard error; RD: Risk difference.
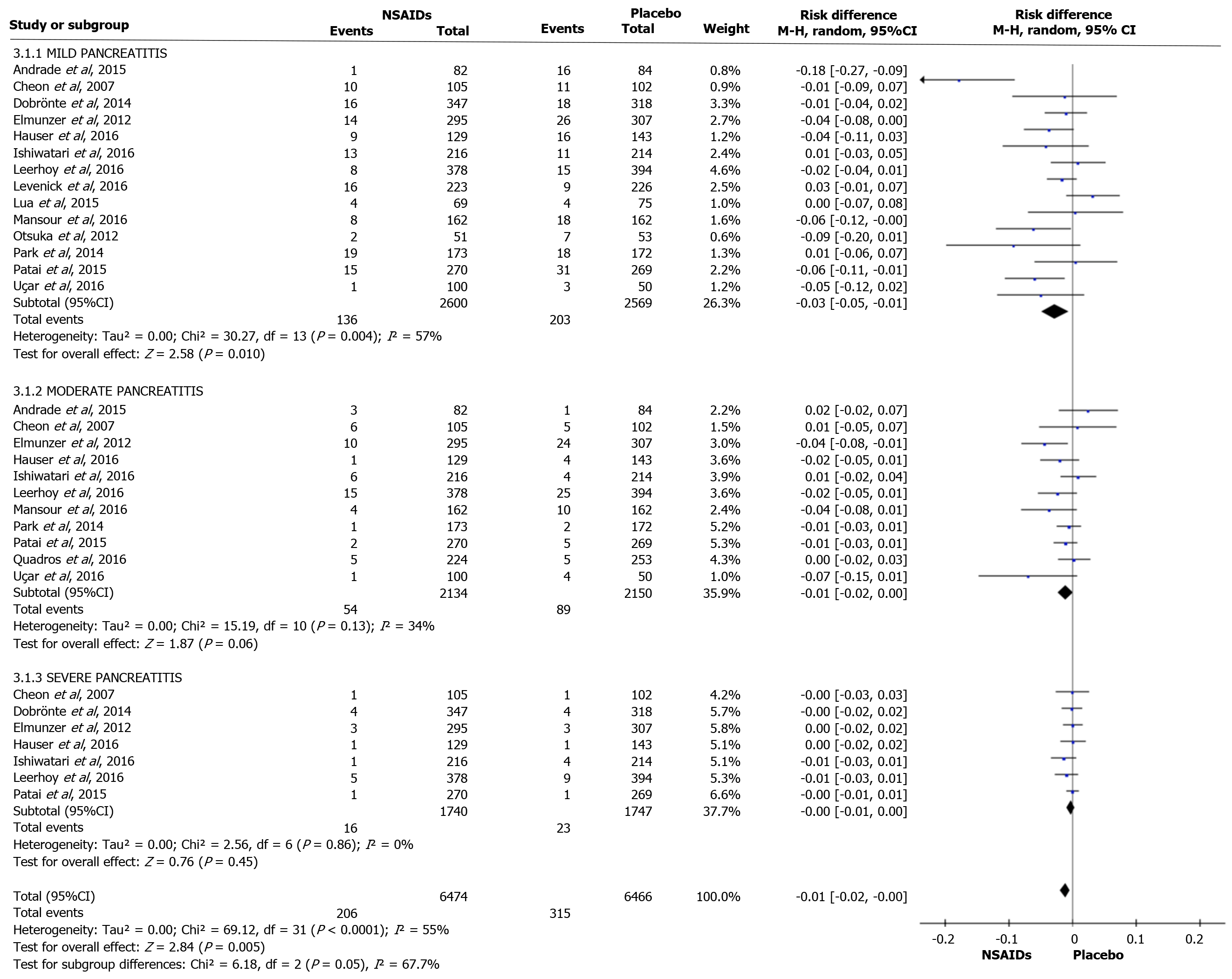
Figure 4 Forest plot of the incidence according to post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis severity.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CI: Confidence interval.
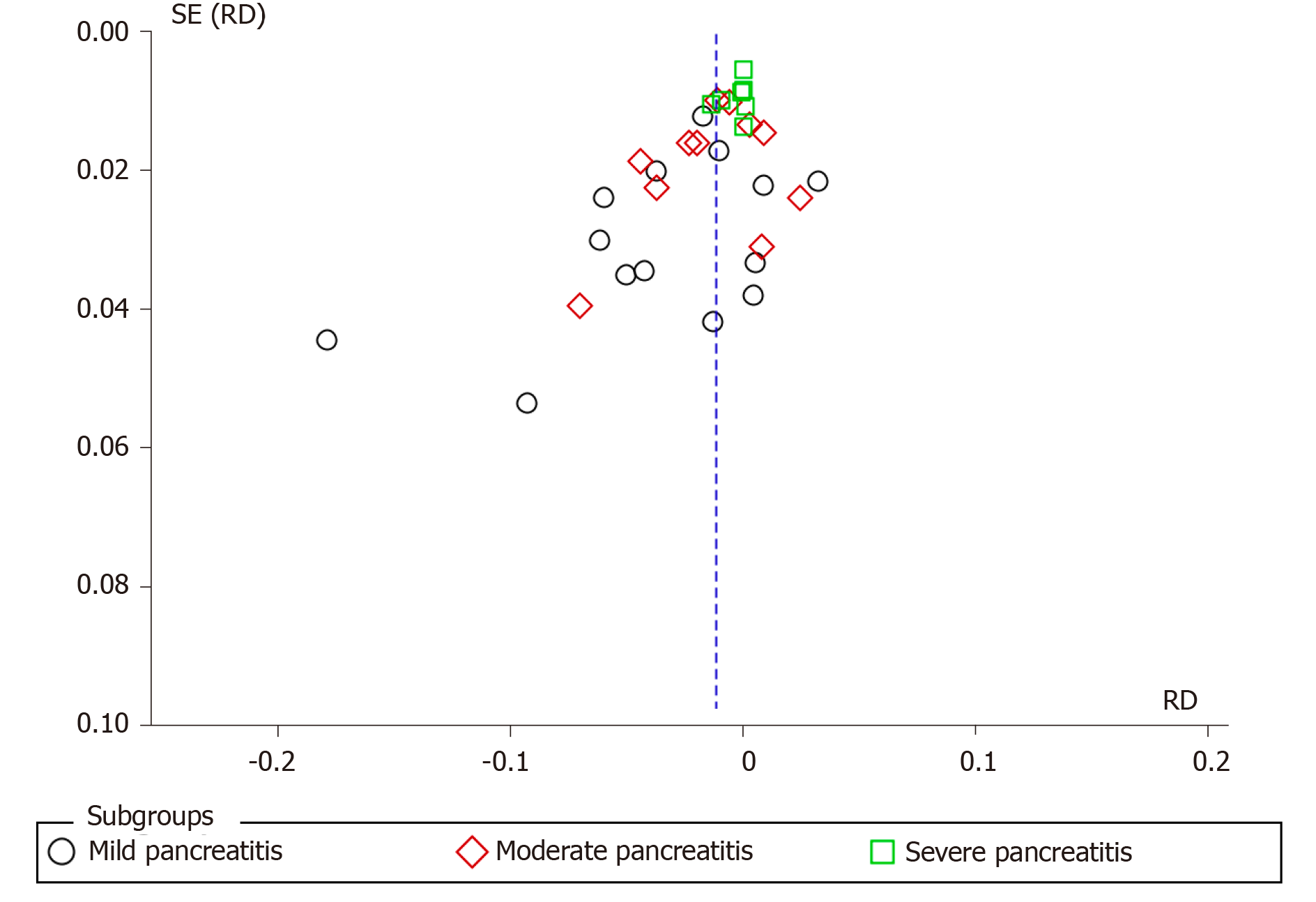
Figure 5 Funnel plot of the incidence according to post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis severity.
SE: Standard error; RD: Risk difference.
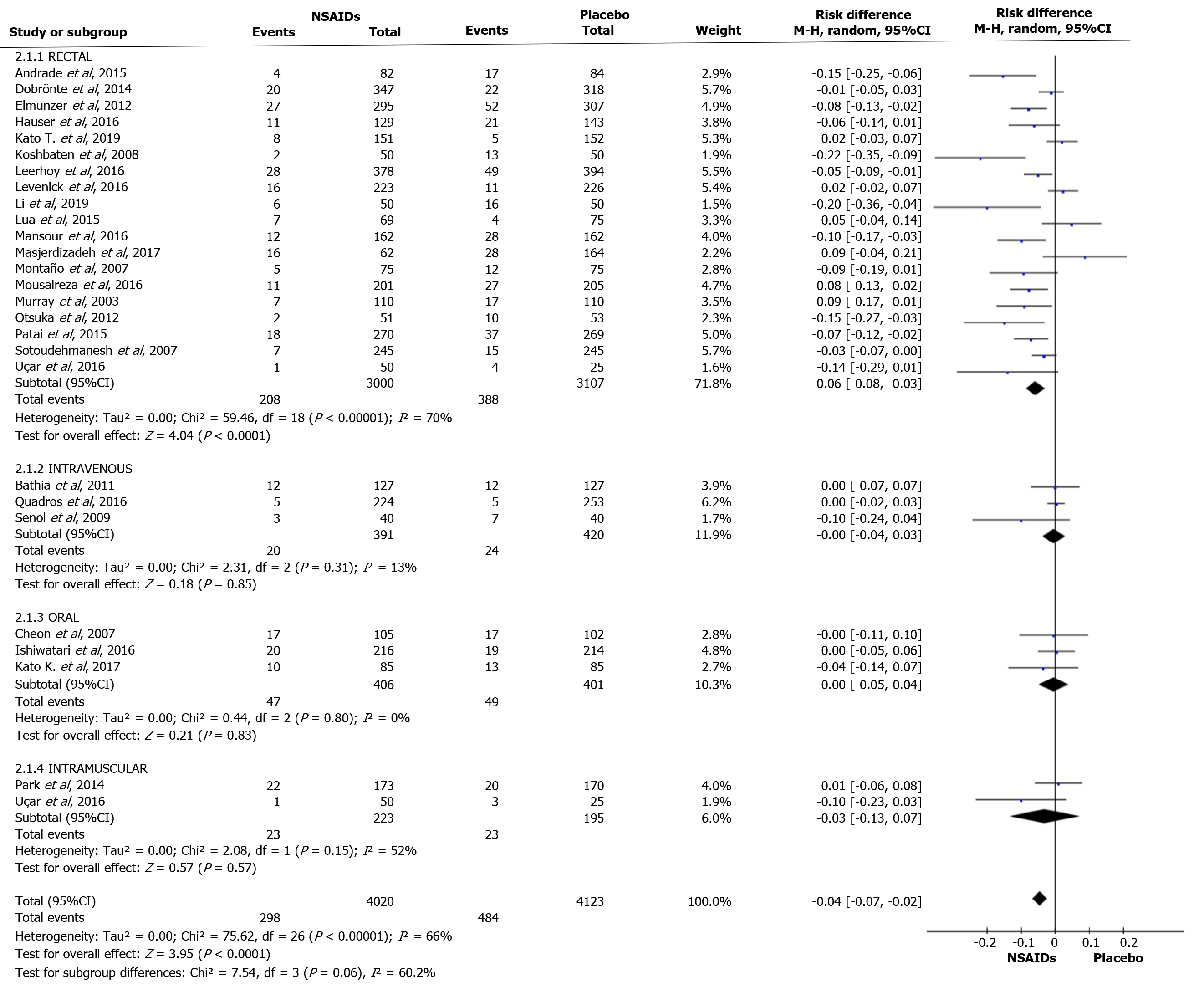
Figure 6 Forest plot of the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis according to different routes of administration.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CI: Confidence interval.
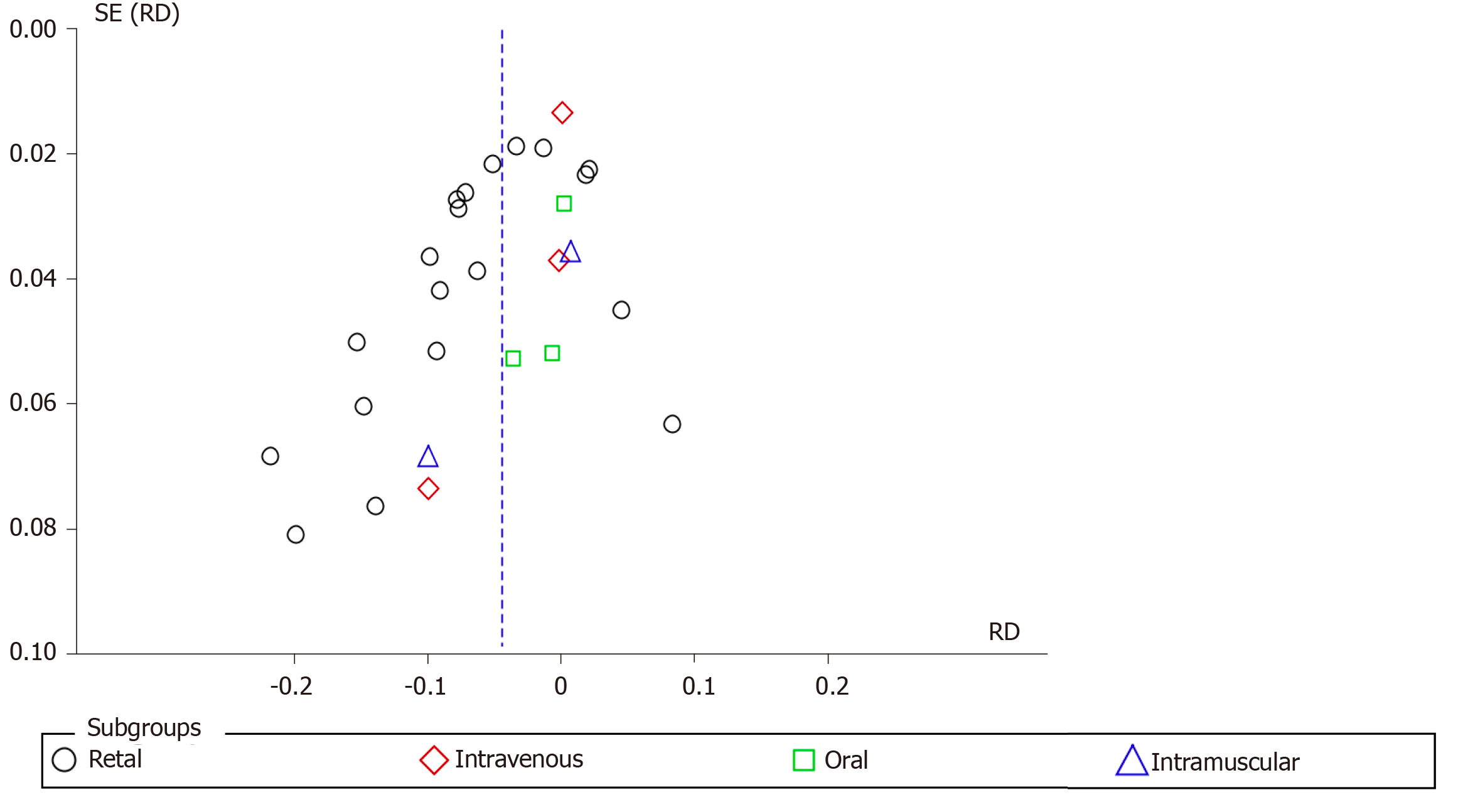
Figure 7 Funnel plot of the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis according to different routes of administration.
SE: Standard error; RD: Risk difference.
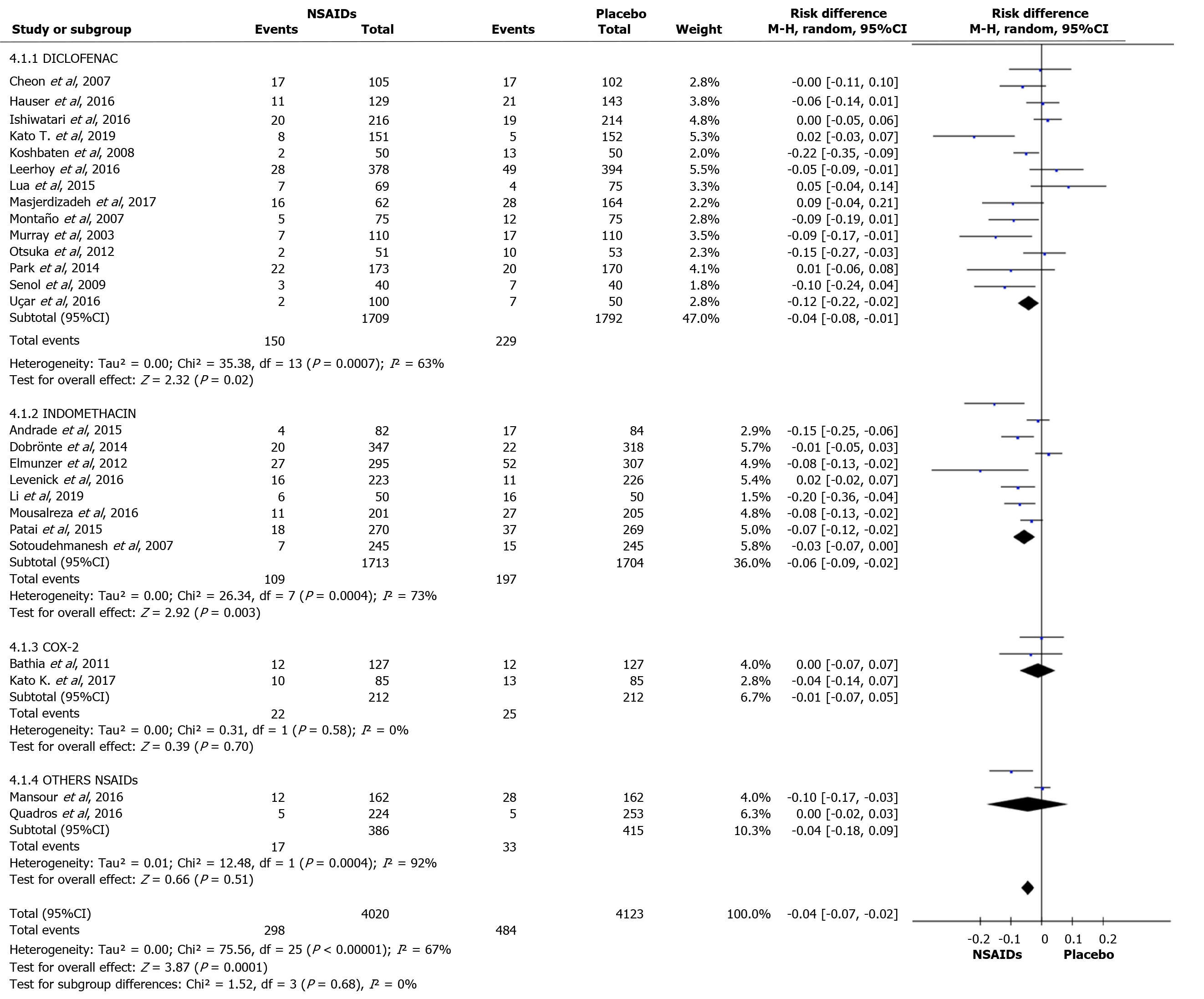
Figure 8 Forest plot showing the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis with different types of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CI: Confidence interval.
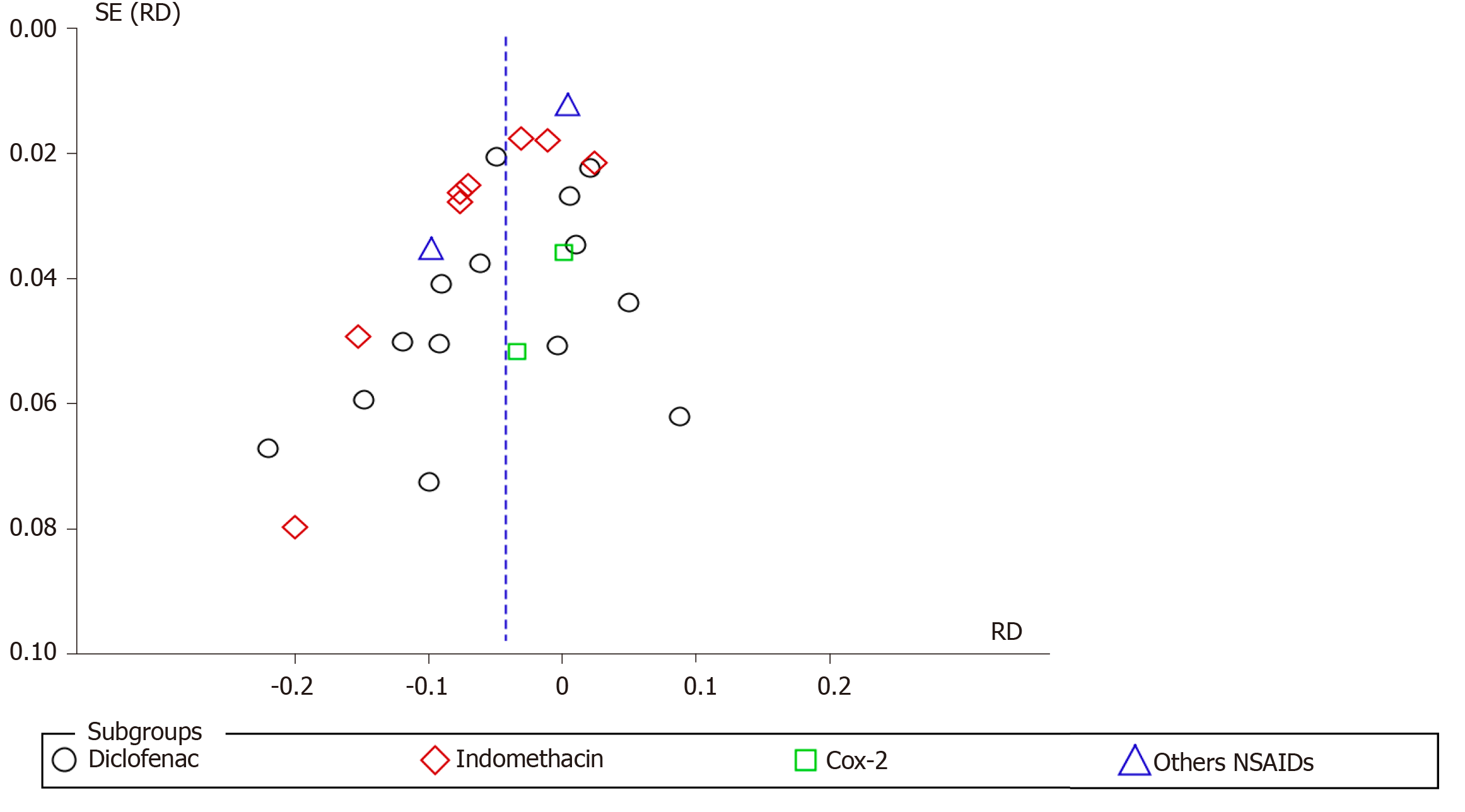
Figure 9 Funnel plot showing the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis with different types of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
SE: Standard error; RD: Risk difference; NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
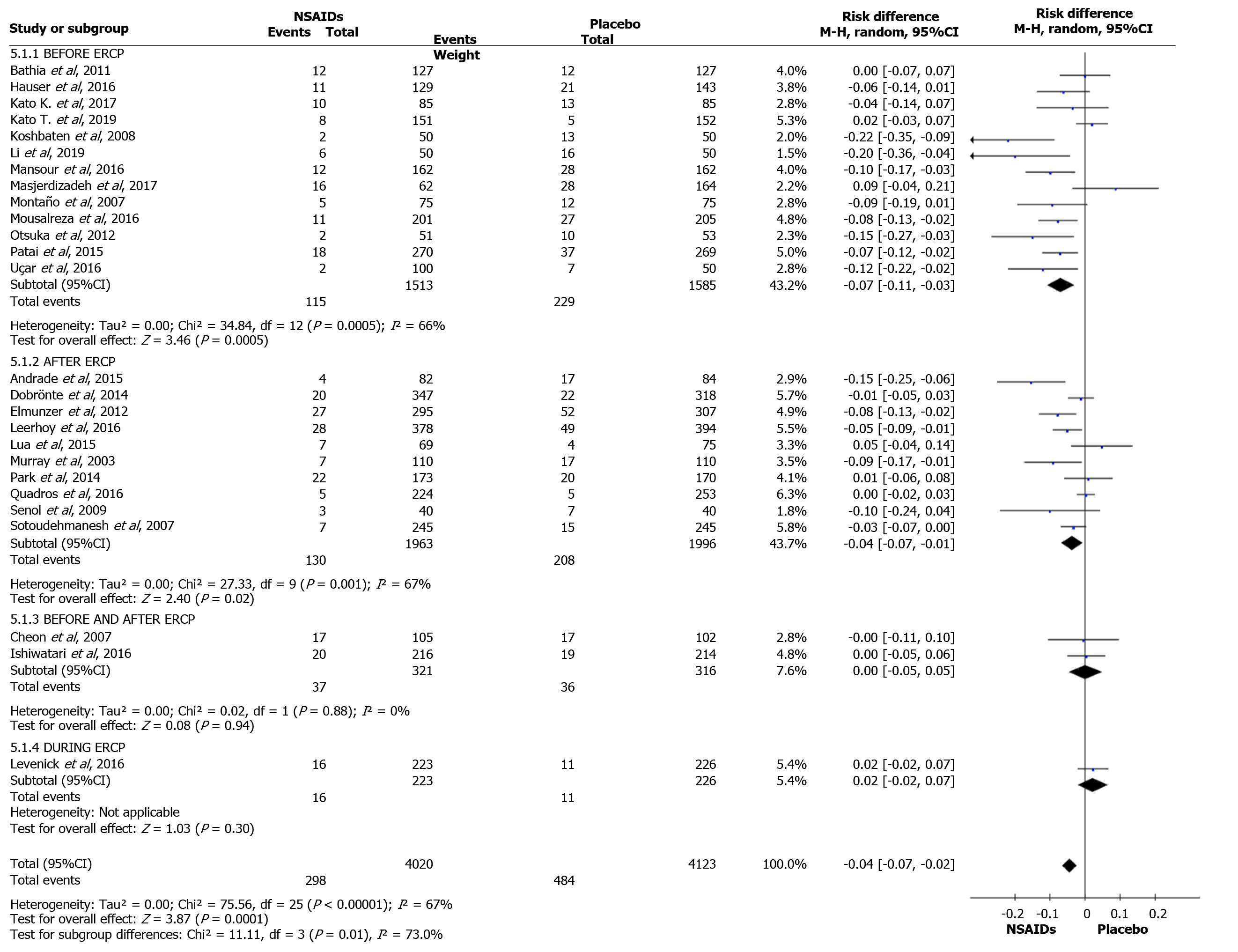
Figure 10 Forest plot showing the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in relation to the timing of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration.
NSAIDs: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; CI: Confidence interval.
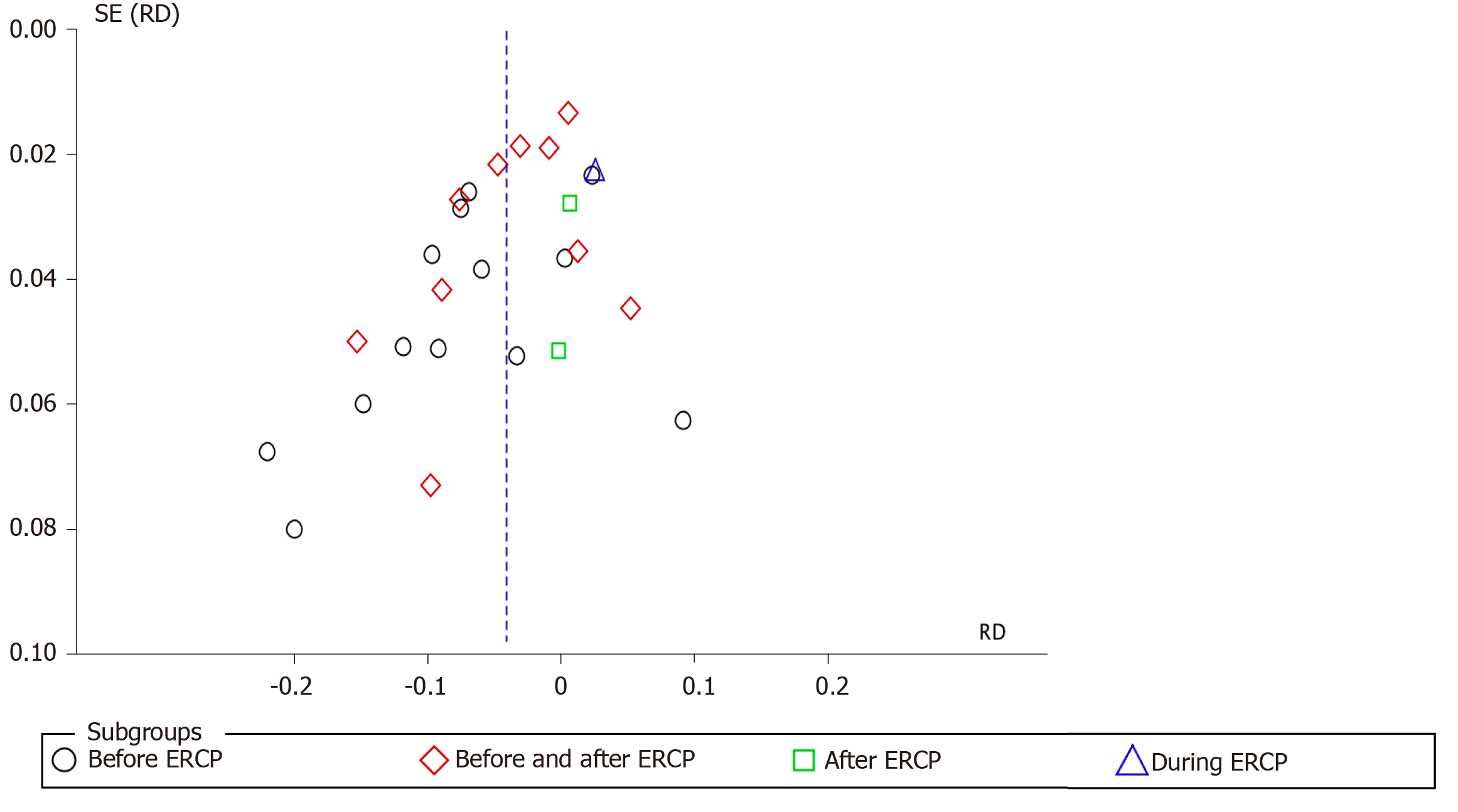
Figure 11 Funnel plot showing the incidence of post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis in relation to the timing of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug administration.
SE: Standard error; RD: Risk difference; ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
- Citation: Román Serrano JP, Jukemura J, Romanini SG, Guamán Aguilar PF, Castro JSL, Torres IT, Sanchez Pulla JA, Micelli Neto O, Taglieri E, Ardengh JC. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug effectivity in preventing post-endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography pancreatitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2020; 12(11): 469-487
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v12/i11/469.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v12.i11.469