Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Jan 16, 2019; 11(1): 61-67
Published online Jan 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i1.61
Published online Jan 16, 2019. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v11.i1.61
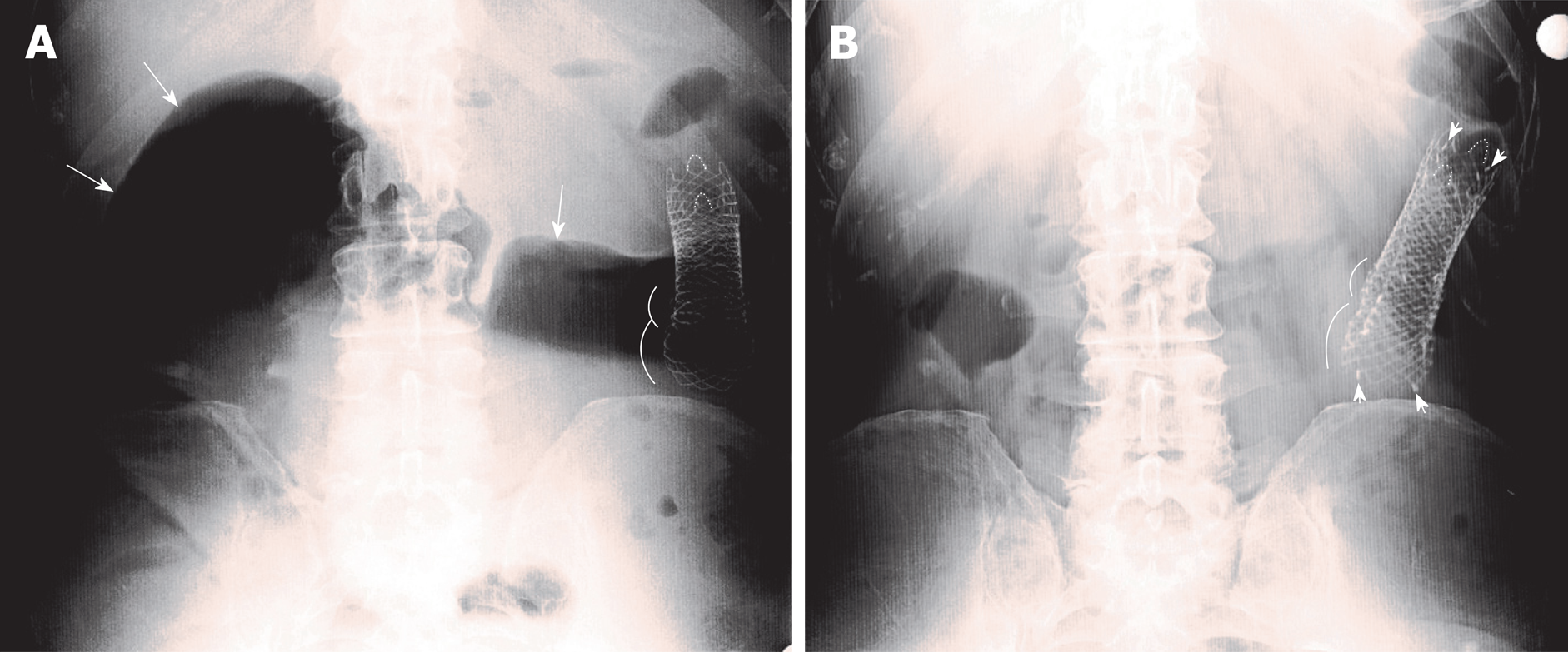
Figure 1 Abdominal X-ray before and after the positioning of the third stent.
A: Large bowel massive distention (long arrows) without apparent stent migration; curves highlight the profiles of the proximal edges of the first and second previously placed stents; B: The third stent placed within the two previously placed stents (short arrows indicating some of the radiopaque markers), with detention of proximal loops.
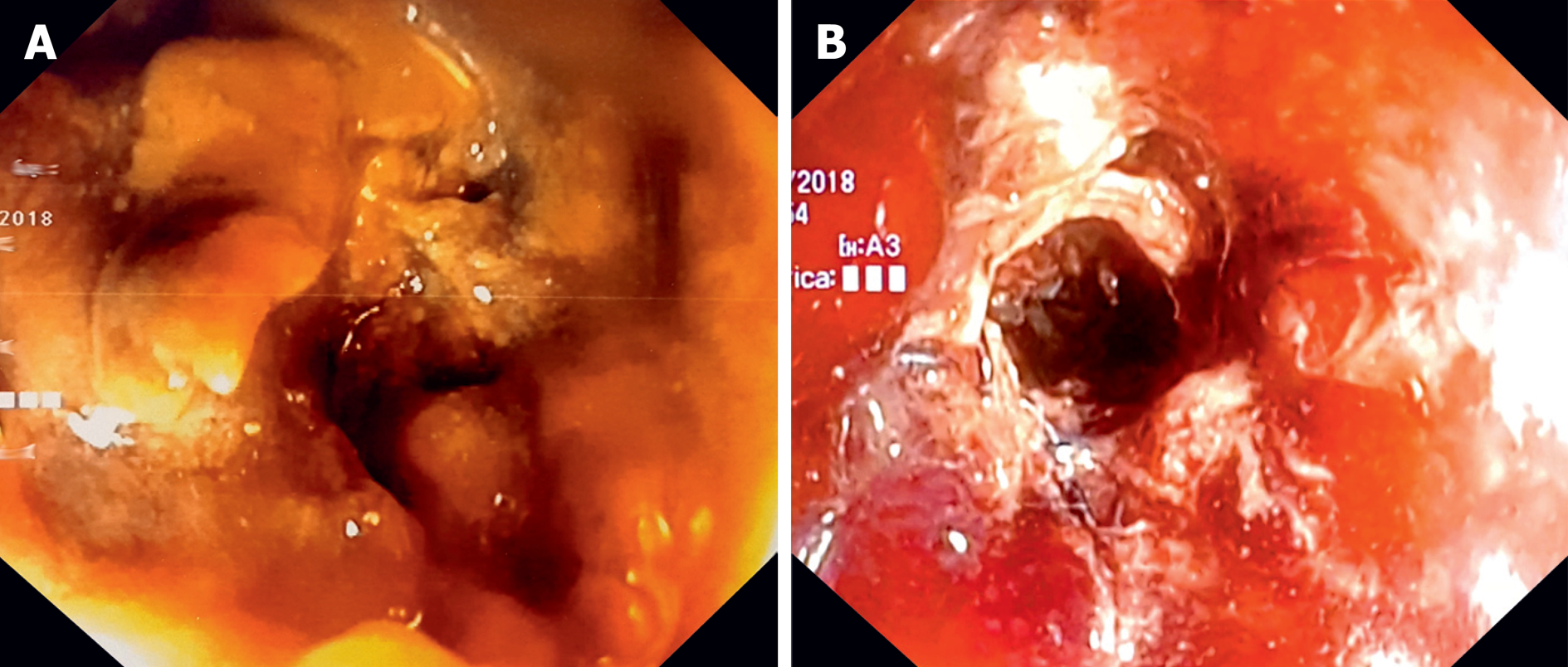
Figure 2 Endoscopic appearance of neoplastic stenosis before and after the third stent.
A: Tumor ingrowth inside the two completely hidden previously placed stents; B: A small diameter hole inside the stenotic tract immediately after deployment of the third stent.
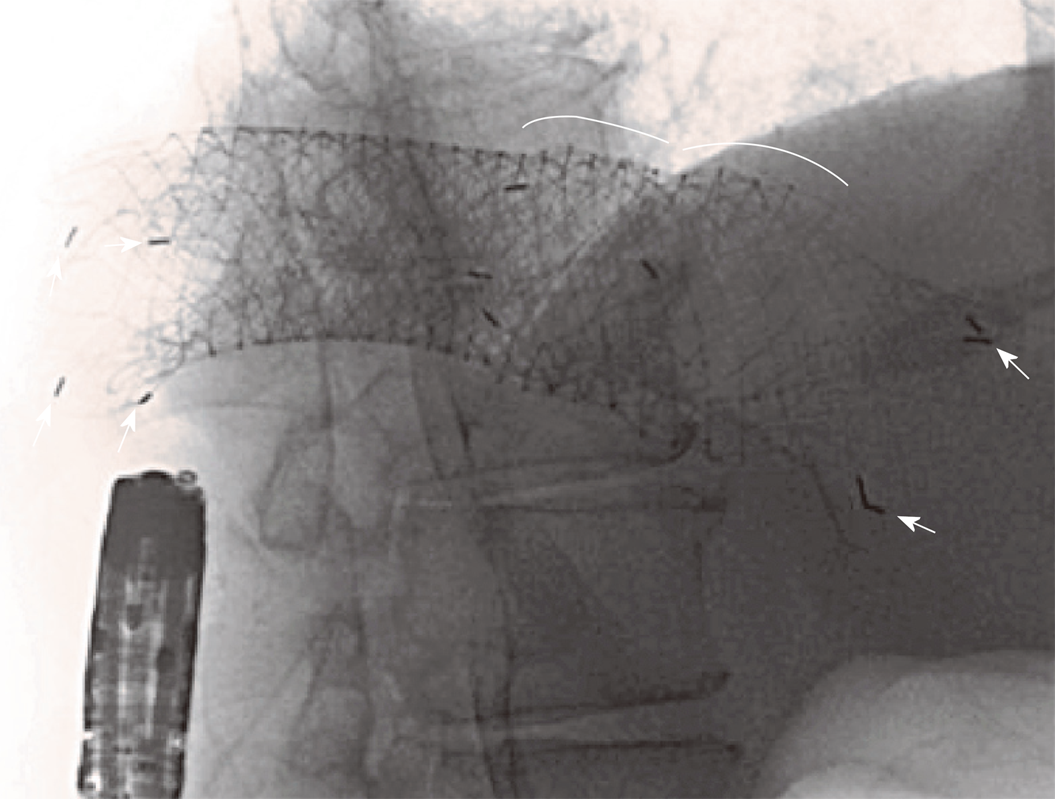
Figure 3 Intraprocedural radiological appearance of the three stents bypassing the lesion above the splenic flexure.
Curves highlight the proximal edges of the first and second previously placed stents; arrows indicate some of the radiopaque markers of the third recently positioned and gradually expanding stent.
- Citation: Vanella G, Coluccio C, Di Giulio E, Assisi D, Lapenta R. Tertiary stent-in-stent for obstructing colorectal cancer: A case report and literature review. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2019; 11(1): 61-67
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v11/i1/61.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v11.i1.61