Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Gastrointest Endosc. Nov 16, 2018; 10(11): 340-347
Published online Nov 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.340
Published online Nov 16, 2018. doi: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.340
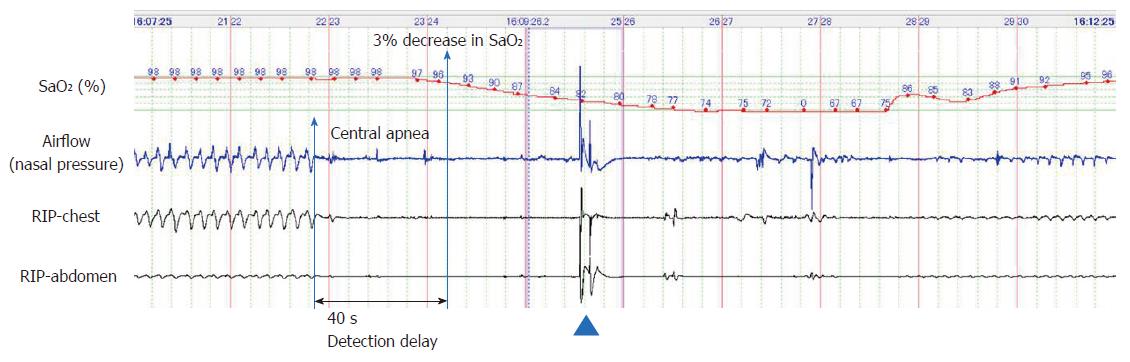
Figure 1 Representative polysomnographic recording of a long central apnea episode occurring soon after a bolus injection of propofol (2 mg/kg) and pentazocine (7.
5 mg), followed by continuous infusion of propofol (2 mg/kg per hour) in a 67-year-old female. Chin-lift airway maneuver (shown by an arrowhead) restored breathing once; however, central apnea redeveloped, resulting in severe hypoxemia (SaO2, 67%); the hypoxemia reversed gradually with improvement in breathing efforts. Polysomnography could detect apnea 40 s before the observed decrease in SaO2 levels.
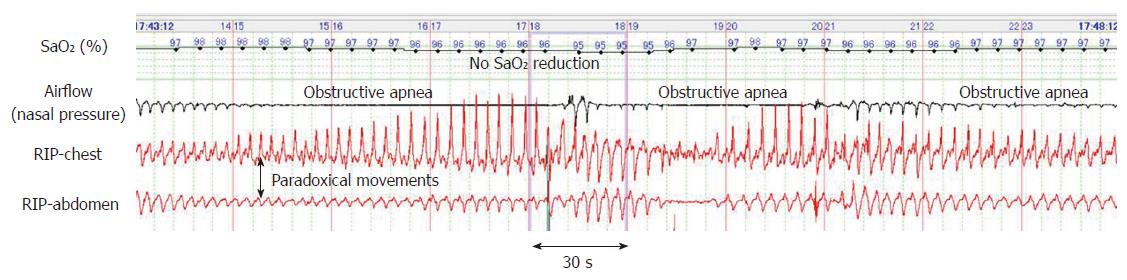
Figure 2 Representative polysomnograph of periodic obstructive apnea that occurred during endoscopic submucosal dissection under propofol sedation.
Thoraco-abdominal respiratory movements showed obstructive disturbance represented by paradoxical movements. Despite these long apneas lasting more than one minute, SaO2 levels remained > 95%.
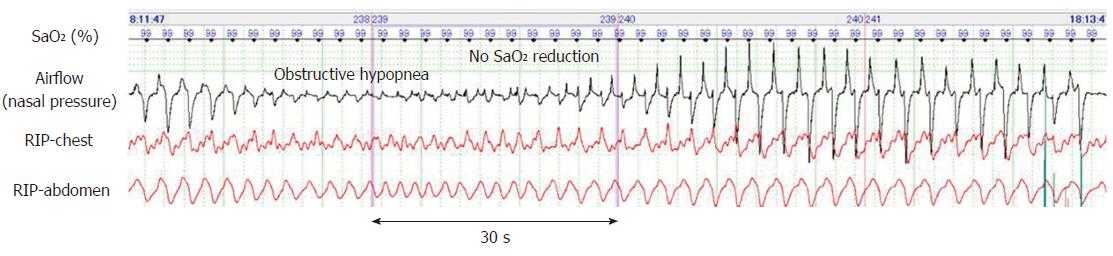
Figure 3 Typical polysomnograph of an obstructive hypopnea that occurred during endoscopic submucosal dissection under propofol sedation.
Obstructive hypopnea episodes were diagnosed based on paradoxical thoraco-abdominal wall movements and flattened nasal pressure waves and resolved spontaneously with gradual increase in airflow caused by an increase in breathing effort.
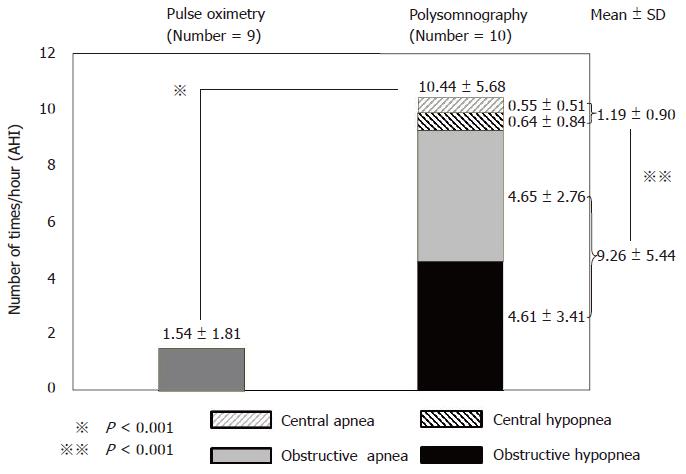
Figure 4 Frequency of respiratory disturbances detected by pulse oximetry and polysomnography.
All patients experienced respiratory disturbances during propofol sedation (total AHI: 10.44 ± 5.68/h). Total apnea hypopnea index (AHI) was significantly greater with polysomnography than with pulse oximetry (1.54 ± 1.81/h, P < 0.001). Obstructive AHI (9.26 ± 5.44/h) was significantly greater than central AHI (1.19 ± 0.90/h, P < 0.001).
- Citation: Urahama R, Uesato M, Aikawa M, Yamaguchi Y, Hayano K, Matsumura T, Arai M, Kunii R, Isono S, Matsubara H. Polysomnographic assessment of respiratory disturbance during deep propofol sedation for endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric tumors. World J Gastrointest Endosc 2018; 10(11): 340-347
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5190/full/v10/i11/340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.340