Published online Mar 18, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i8.418
Peer-review started: July 13, 2016
First decision: October 10, 2016
Revised: October 28, 2016
Accepted: January 11, 2017
Article in press: January 14, 2017
Published online: March 18, 2017
Processing time: 244 Days and 10.9 Hours
To evaluate the effects of chronic exposure to ethanol in the liver and the expression of inflammatory genes in zebrafish.
Zebrafish (n = 104), wild type, adult, male and female, were divided into two groups: Control and ethanol (0.05 v/v). The ethanol was directly added into water; tanks water were changed every two days and the ethanol replaced. The animals were fed twice a day with fish food until satiety. After two and four weeks of trial, livers were dissected, histological analysis (hematoxilin-eosin and Oil Red staining) and gene expression assessment of adiponectin, adiponectin receptor 2 (adipor2), sirtuin-1 (sirt-1), tumor necrosis factor-alpha (tnf-a), interleukin-1b (il-1b) and interleukin-10 (il-10) were performed. Ultrastructural evaluations were conducted at fourth week.
Exposing zebrafish to 0.5% ethanol developed intense liver steatosis after four weeks, as demonstrated by oil red staining. In ethanol-treated animals, the main ultrastructural changes were related to cytoplasmic lipid particles and droplets, increased number of rough endoplasmic reticulum cisterns and glycogen particles. Between two and four weeks, hepatic mRNA expression of il-1b, sirt-1 and adipor2 were upregulated, indicating that ethanol triggered signaling molecules which are key elements in both hepatic inflammatory and protective responses. Adiponectin was not detected in the liver of animals exposed and not exposed to ethanol, and il-10 did not show significant difference.
Data suggest that inflammatory signaling and ultrastructural alterations play a significant role during hepatic steatosis in zebrafish chronically exposed to ethanol.
Core tip: Excessive alcohol consumption remains one of the most important causes of liver disease worldwide. Alcoholic steatosis results from the deposition of fat in liver cells and is the earliest stage of alcohol-related liver disease. Usually inflammation is associated with steatohepatitis, however our results demonstrate that chronic ethanol exposure increased the expression of the inflammatory gene interleukin-1b. Paradoxically the expression of adiponectin receptor-2 and sirtuin-1 also increased for attenuating the liver injury. Ultrastructural abnormalities were observed showing early alterations in liver cells. Knowledge of alcohol injury mechanisms will contribute to the development of novel therapies in the treatment of alcoholic liver disease.
- Citation: Schneider ACR, Gregório C, Uribe-Cruz C, Guizzo R, Malysz T, Faccioni-Heuser MC, Longo L, da Silveira TR. Chronic exposure to ethanol causes steatosis and inflammation in zebrafish liver. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(8): 418-426
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i8/418.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i8.418
Alcoholic liver disease (ALD) encompasses a wide spectrum of injury, ranging from simple steatosis, leading to steatohepatitis, fibrosis and finally to cirrhosis[1,2]. Hepatic steatosis is the first and most common consequence of alcohol abuse, develops in about 90%-95% of individuals who drink heavily, is usually asymptomatic and self limited; but may also occur in individuals who drink moderately[2]. Several studies have suggested that progression to more severe liver disease occurs in about 5%-20% of alcohol consumers[1]. As a consequence, it is important to better understand the pathogenesis of hepatic steatosis and the relationship between steatosis and liver injury.
Excessive accumulation of triglycerides in hepatocytes is the hallmark of hepatic steatosis. The source of triglyceride in the liver of ethanol consumers may be originated from disturbances of fatty acid oxidation mechanisms, oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum stress, alterations in lipogenic and lipolytic pathways and immune responses to ethanol[3-7]. A number of molecular mediator pathways regulating the synthesis, export, and oxidation of lipids have been discovered to be altered by ethanol: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma, adiponectin, sirtuins and others[8].
Zebrafish is increasingly used as an in vivo model system for translational research, since zebrafish have a high degree of genetic conservation and their morphological and molecular basis of tissue and organ development is either identical or similar to other vertebrates including humans[9,10]. In previous studies regarding to hepatic diseases related to ethanol, zebrafish proved to be a valuable strategy for identifying lipogenic mechanisms, genes and pathways that influence hepatic steatosis[11-14]. Studies focused in inflammatory pathways in steatosis are scarce and the issue is not completely elucidated. Chronic ethanol consumption results in the activation of innate immunity and an inflammatory state, which contributes to the pathogenesis of ethanol-induced liver injury. The expression of tumor necrosis factor - alpha (tnf-a), interleukin-1b (il-1b), interleukin-10 (il-10), adiponectin, adiponectin receptor 2 (adipor2) and sirtuin-1 (sirt-1) were evaluated and histological and ultrastructural evaluations were performed in liver of adult zebrafish after chronic ethanol exposure.
Wild-type, adult zebrafish (Danio rerio), male and female, were purchased from a commercial distributor (Fish Flower, Porto Alegre, RS). The animals were of heterogeneous wild type stock from the standard short-fin phenotype and were housed for 2 wk before the experiments in order to acclimate to the laboratory facility. The animal protocol was designed to minimize pain or discomfort to the animals. Fish were maintained in aerated water at 28 °C ± 2 °C, 6.8-7 pH, on a 12/12 light/dark photoperiod cycle (lights on at 7:00 am). Biochemical parameters and quality of the water were monitored regularly: pH, presence of nitrates and nitrites, oxygen and ammonia levels. The animals were fed twice a day with fish food until satiety. Experiments were performed using a total of 104 animals. All fish used in this study were healthy and free of any signs of disease.
After acclimation period, the fish were randomly allocated into experimental tanks, density of 1 fish per liter of water. The following groups were performed (n = 52/group): Control (C) and ethanol (E). E group received 0.5% (v/v) of ethanol (Merck KGaA, Germany) directly added into water; tank water was changed every two days and the ethanol replaced[15]. This ethanol dose was chosen due to the liver damage observed by Schneider and coworkers in zebrafish exposed to 0.5% of ethanol[15]. The tank water of C group was also changed in same days of E group. At 2 and 4 wk, fish were euthanized by hypothermal shock[16] and livers were completely removed for molecular and histological analysis.
The protocols were approved by the Research Ethics Committee of Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre, Brazil (No. 10.0327), and conducted in accordance with international guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals.
Livers of zebrafish dissected at 2nd and 4th weeks were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (n = 5/group) or Oil Red (n = 5/group). Livers were fixed in 10% formalin, embedded in paraffin wax, sectioned (5 μm), and slices were stained with hematoxylin and eosin. Livers embedded in Tissue-Tek OCT Compound (Sakura Finetek, United States) were cryosectioned (8 μm thick) and stained with Oil Red (Sigma-Aldrich, United States) to assess fatty droplet accumulation.
For ultrastructural evaluation, livers of 2 animals (male) of each group (C and E) were fixed in 2.5% glutaraldehyde diluted by 0.12 mol/L phosphate buffer (pH 7.2-7.4) for 3 h at 4 °C. The material was washed three times in the same buffer at 30-min intervals and then post-fixed for 30 min in 1% buffered osmium tetroxide followed by a phosphate buffer (0.1 mol/L) wash three times at 15-min intervals. Livers were dehydrated using ascending grades of alcohols and embedded in an epon-araldite mixture. Ultrathin sections (90 nm) were stained with 2% uranyl acetate and 1% lead citrate[17]. The ultrathin sections were examined under JEM 1200 FX II transmission electron microscope.
The liver samples (pool = 3 livers; n = 5/group/period) were immediately immersed in liquid nitrogen and stored in ultrafreezer (-80 °C). Total RNA was extracted using the TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, United States) according to the manufacturer’s protocol and the concentrations were quantified by Nanodrop (Thermo Fisher Scientific, United States) at 260 nm. RNA purity was verified by a 260/280 nm ratio of 1.8 or greater. First-strand cDNA was synthesized from 3 µg of total RNA using the Superscript TM II RT system (Invitrogen, United States). Gene expression analysis of adiponectin, adipor2, sirt-1, tnf-a, il-1b and il-10 were performed from 5 μL of cDNA and run in duplicate using TaqMan Gene Expression Assays (Life Technologies, United States) (Table 1).
| Gene | Assay ID |
| adiponectin | F: 5’-AGG CTT AGA CTG TGA ACG GTG GGA C-3’ |
| R: 5’-AGC AGG TGT GTC CAG ATG TTT CCA G-3’ | |
| adipor2 | dr0342657 |
| sirt-1 | ENSDART00000098209 |
| tnf-a | dr03126848 |
| il-1b | dr03114368 |
| il-10 | dr03103209 |
| ef-1α | dr03432748 |
PCR amplifications were run on a Step One™ Real time PCR System (Applied Biosystems, United States) and performed starting with a 2 min denaturation step at 50 °C, 10 min at 95 °C followed by 40 cycles with 15 s at 95 °C and 1 min at 60 °C.
Gene expression was quantified using the 2-ΔΔCt (threshold cycle) method and normalization was done using the elongation factor-αgene (ef-1α).
Log-transformed data was tested with Kruskal-Wallis test and Dunn as post hoc test for multiple comparisons. Results with P < 0.05 were considered statistically significant. All analysis were performed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS 18.0) software.
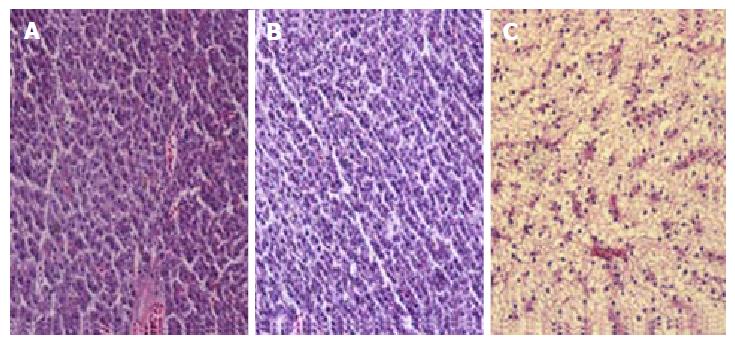
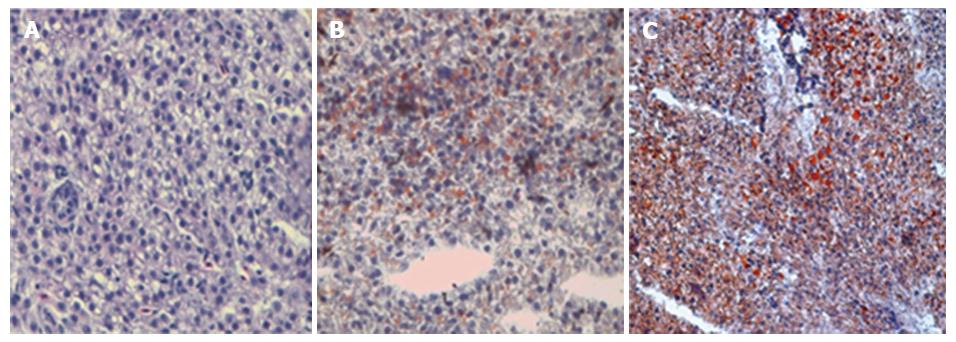
Sections of livers from control animals stained with hematoxylin-eosin showed well-preserved liver cells without signs of fat deposits (Figure 1A). After 2 wk of ethanol exposure, the liver appearance of animals from E group were similar to the C group (Figure 1B), however at 4 wk, the hepatocytes of animals from E group showed an expressive enlargement and presented nuclei displaced to the periphery of the cytoplasm due to fatty infiltration (Figure 1C). Livers of the control animals stained with Oil Red did not present any lipid droplets (Figure 2A). However, ethanol-treated animals presented a light steatosis at 2nd week (Figure 2B) which increased severely in the 4th week (Figure 2C).
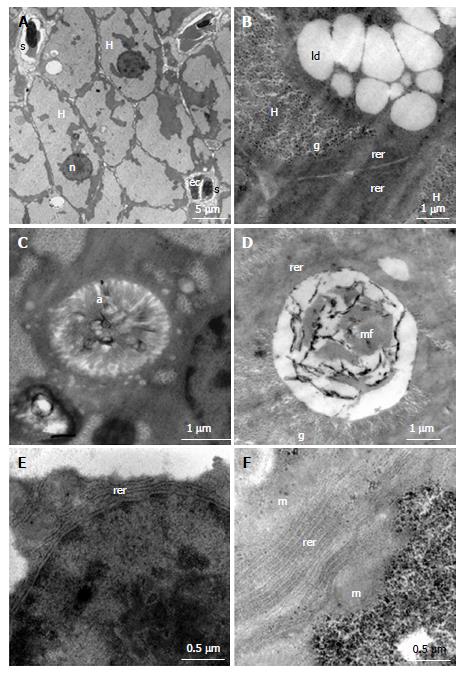
The supplemental file contains the results of ultrastructural evaluations. Control group showed hepatocytes with hexagonal shape, evident nucleoli of moderate size and located in the centre of the spherically shaped nuclei (Figure 3A), intracellular duct with microvilli (Figure 3C), rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) contained few cisternae and were closely associated with mitochondria (Figure 3E). Compared to control group, hepatocytes of ethanol-treated fish showed a large amount of glycogen associated with numerous lipid droplets (Figure 3B); the intracellular canaliculi often showed signs of degeneration with aspects of myelin figures therein (Figure 3D); and augmented number of RER cisterns (Figure 3F).
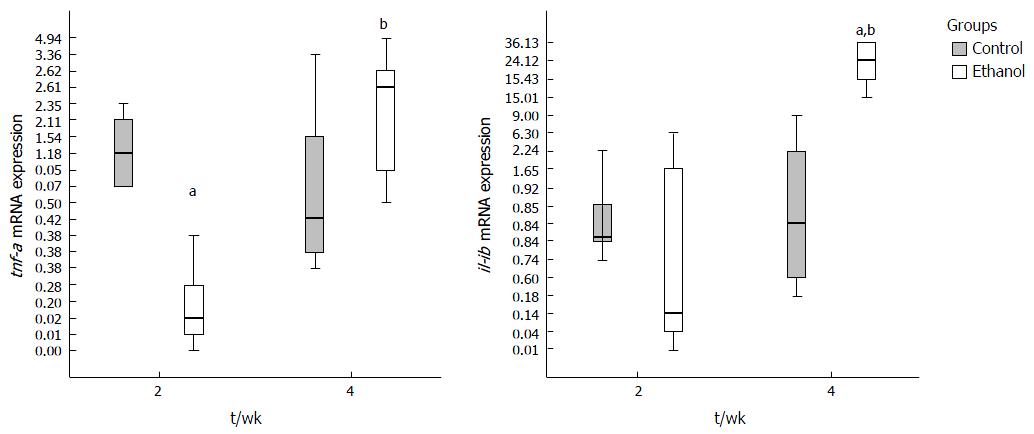
At 2nd week the genes evaluated did not present statistical difference in mRNA expression between E and C groups, except for tnf-a, which was decreased. An increase of expression of tnf-a, il-1b, adipor2 and sirt-1 was observed between two and four weeks in E group, demonstrating that time to ethanol exposure had influence on expression of these genes. The il-10 expression did not reach significant statistical difference between groups at any period (data not shown). Adiponectin mRNA was not detected in liver of animals from C and E groups.
The hepatic tnf-a expression in E group was lower than in C group at 2 wk (P = 0.018). The il1-b expression was significantly increased between C and E groups at 4th week (P = 0.024) (Figure 4).
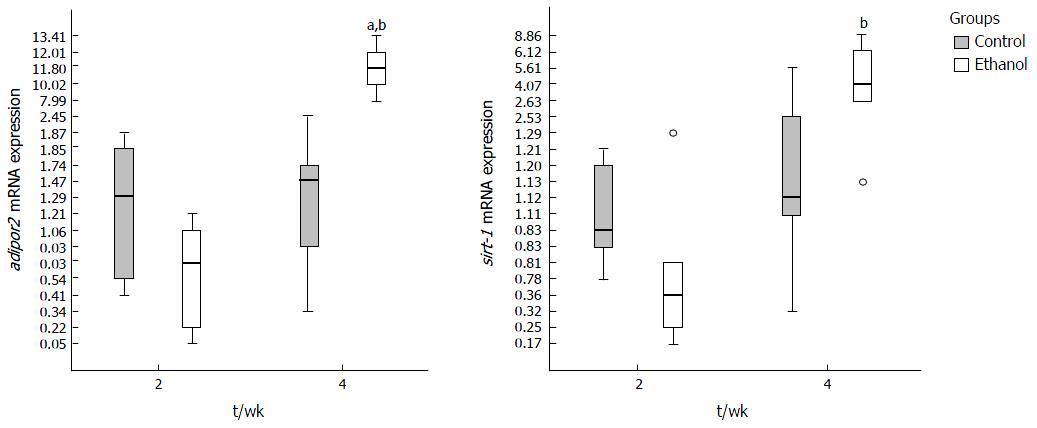
The expression of adipor2 increased in E group between 2 and 4 wk (P < 0.0001) and was higher in E compared to C group (P = 0.006) at 4th week (Figure 5). Sirt-1 showed an increased expression in E group along time until the 4th week (P = 0.001) (Figure 5).
Hepatic metabolic derangements are key components in the development of steatosis, considered the first hit for development of ALD. Until recently, the role of inflammation was linked to the presence of steatohepatitis, and scarce evidences have shown the precocity of inflammatory signaling during steatosis[18].
Important histological and ultrastructural abnormalities in liver of chronic ethanol-exposed zebrafish were seen at 4th week in this study. A light steatosis was detected by oil red staining at 2nd week, which increased severely at 4th week. Electron transmission microscopy revealed concurrent marked accumulation of glycogen and lipid droplets in cytoplasm, committed intracellular canaliculi, and increased RER cisterns. Our findings were similar to those described in alcoholic humans: Increased glycogen and fat deposits in the cytoplasm, abnormalities in endoplasmic reticulum[19]. Howarth et al[13] observed abnormalities of endoplasmic reticulum and biliary canaliculi in acutely ethanol treated zebrafish larvae. Mitochondrial and ER abnormalities were seen in a model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) induced by fructose in zebrafish[20].
In accordance to histological findings, there were changes in hepatic mRNA expression of il-1b, tnf-a, sirt-1 and adipor2. At fourth week, in the presence of more advanced steatosis, il-1b showed an expressive increase. Growing evidence indicates that increased pro-inflammatory cytokines are involved in the progression of alcohol-induced liver injury[21,22]. The activation of innate immunity also stimulates the release of hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory cytokines, which play a compensatory role against liver damage and inflammation[22]. In our study the il-10 expression was not different between C and E groups. The il-10 is produced by macrophages, lymphocytes, and Kupffer cells, and the liver is considered to be the main source of il-10 production in response to lipopolysaccharides (LPS) stimulation[23]. Sepulcre et al[24] demonstrated that zebrafish responds to LPS with much lower sensitivity than mammals, what can explain the absence of difference in hepatic expression of il-10, between C and E groups.
Elevated circulating levels of TNF-α and IL-1b have been observed in human patients and animal models of ethanol-induced liver injury[25,26]. The expression levels of these cytokines correlate well with the progression of the disease. In our study the tnf-a liver expression was initially decreased in E group compared to C at 2nd week and increased significantly along 2nd and 4th week, reaching the C expression levels at 4th week. Liu et al[27] demonstrated that only zebrafish with previous intestinal inflammation presented elevated tnf-a expression in liver compared to healthy animals after LPS exposure. Zebrafish are indeed able to respond to LPS, however with much lower sensitivity than mammals and via a tlr4/myd88-independent signaling pathway[24,28]. Among the few studies that evaluated tnf-a expression in the liver of zebrafish, Sapp observed an elevation of tnf-a in fructose-treated larvae and Hammes in thiocetamide-treated fish[20,29]. Although there was no direct evidence in our study, these cited findings conducted us to the following conclusions: tnf-a is not promptly induced by LPS in zebrafish exposed to ethanol as occurring in mammals and its activation mechanism seems to be associated to more aggressive hepatotoxicants.
Differently, the hepatic expression of il-1b increased significantly over the period considered and at 4th week it was significantly higher in E group compared to C. Interleukin-1, the “gatekeeper” of inflammation, is the apical cytokine in a signaling cascade that drives the early responses to injury or infection[30]. Il-1b production requires caspase-1 activation by inflammasomes-multiprotein complexes that are assembled in response to danger signals. Vojtech et al[31] have described the cleavage of zebrafish il-1b by the caspase-1 homologues caspase-A and caspase-B, implying that the basic facets of the inflammasome platform of immune activation are conserved in zebrafish. The induction of il-1b demonstrated an early response to inflammatory stimuli in the present study. The up regulation of il-1b did not occur synergistically with tnf-a expression, as seen in mammals with ALD[26]. This result may suggest that il-1b is up regulated during chronic alcohol induced steatosis in zebrafish in a LPS independent pathway.
Adiponectin is a hormone that is secreted exclusively by adipocytes and has anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities[32]. Circulating adiponectin is decreased in mammals with alcoholic disease[32,33]. In our study, adiponectin mRNA did not amplify in the livers of animals of both groups. Amali and collaborators observed elevated expression of adiponectin in liver of zebrafish treated with thioacetamide, but not in control animals[34].
In this study, the adipor2, a receptor of adiponectin, was over expressed in liver of animals exposed to ethanol, during the period that hepatic steatosis became more severe. To date, very few data are available regarding the effect of chronic ethanol exposure on hepatic adipor2. Hammes et al[29] observed decreased mRNA expression of hepatic adipor2 and sirt-1 and increased tnf-a in a model of NAFLD induced by thioacetamide in zebrafish. Possibly, thioacetamide, a more aggressive liver toxicant, contributed to down regulate adipor2. In humans, it was observed by Kaser that in presence of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, adiponectin receptor 2 expression was decreased compared to simple steatosis[35]. Neumeier et al[36] showed that animals (rodents) with liver steatosis presented elevated liver expression of adipor2. The increased expression of adipor2 may be related to hepatic protection during steatosis.
SIRT-1 is a NAD+-dependent class III protein deacetylase that regulates lipid metabolism by deacetylation of modified lysine residues on histones, and targets a number of transcription factors involved in the regulation of gluconeogenesis, mitochondrial biogenesis, resistance to oxidative stress, adipogenesis and lipolysis, glycolysis, inflammation, apoptosis, cell differentiation, and angiogenesis[37]. To date, little is known about the function of SIRT-1 in innate immunity and host defense. Studies in mammals have indicated that SIRT-1 suppresses innate inflammatory responses[38]. Other authors have shown an expressive increase of sirt-1 in liver of zebrafish chronically exposed to ethanol (0.5% vv)[39,40]. In our study occurred a significant increase of sirt-1 between second and fourth weeks in fish treated with ethanol. We can speculate that the sirt-1 hepatoprotective role might be involved in this process.
Ethanol effectively induced hepatic lipid accumulation and ultrastructural abnormalities in liver of zebrafish. Augmented expression of il-1b suggests that inflammatory signaling plays a significant role in hepatic steatosis and adipor2 and sirt-1 increased expression appears to represent compensatory efforts to alleviate consequences of ethanol liver injury, probably, indicating a hepatoprotective reaction. Hepatic steatosis is considered the first hit of chronic progressive ALD. The investigation of earliest events linked to ALD requires multiple strategies to reverse the damage effects of ethanol to the liver and to contribute to development of new therapies.
We thank FIPE - HCPA (Fundo de Incentivo à Pesquisa Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre) and CNPq (National Counsel of Technological and Scientific Development) for financial support.
Alcohol abuse is an acute health problem throughout the world and alcohol consumption is related to the occurrence of chronic liver disease. Hepatic steatosis is the first step of liver damage, and in spite of being considered a benign event, may progress to alcoholic steatohepatitis and more severe liver disease. The zebrafish has been proposed for the study of the effects of ethanol on several organs and has been helpful to unravel the pathways of liver damage by alcohol.
The zebrafish (Danio rerio) is increasingly recognized as an important model system for studying liver development and human liver disease. Despite differences in the anatomical architecture of the zebrafish liver from mammals, alcoholic liver damages are similar to those of human beings, including alcoholic steatosis. This animal model will likely be a useful tool to further elucidate the pathogenesis and related disorders of alcoholic liver disease, as well as to discover new treatments.
Proinflammatory cytokines were frequently linked to steatohepatitis, however, this study describes early ultrastructural alterations in hepatocytes and cytokines increase in the onset of ethanol-induced liver damage.
The major advantage of zebrafish as a model system for hepatic processes is the ability to perform screening (genetic or chemical) in a vertebrate organism. The investigation of earliest events linked to alcoholic liver disease can contribute to the development of new strategies to prevent the advance of such disease.
Hepatic steatosis: Or fatty liver. It is caused by an excessive fat deposition in the liver; Steatohepatitis: It is a type of fatty liver disease characterized by the presence of inflammation; Fibrosis: Scars produced in a reparative or reactive process in the liver; Ultrastructure: The detailed structure of a biological specimen, such as a cell, that can be observed by electron microscopy; Histology: The study of the microscopic anatomy of tissues. The cell of the tissue can be observed under a light microscope.
The paper is well-written.
Manuscript source: Invited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: Brazil
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Chattopadhyay A S- Editor: Song XX L- Editor: A E- Editor: Li D
| 1. | O'Shea RS, Dasarathy S, McCullough AJ; Practice Guideline Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; Practice Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology. Alcoholic liver disease. Hepatology. 2010;51:307-328. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 837] [Cited by in RCA: 852] [Article Influence: 56.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 2. | Gao B, Bataller R. Alcoholic liver disease: pathogenesis and new therapeutic targets. Gastroenterology. 2011;141:1572-1585. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1244] [Cited by in RCA: 1489] [Article Influence: 106.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Lieber CS. Alcoholic fatty liver: its pathogenesis and mechanism of progression to inflammation and fibrosis. Alcohol. 2004;34:9-19. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 424] [Cited by in RCA: 449] [Article Influence: 21.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Donohue TM. Alcohol-induced steatosis in liver cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13:4974-4978. [PubMed] |
| 5. | Sozio M, Crabb DW. Alcohol and lipid metabolism. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2008;295:E10-E16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 145] [Cited by in RCA: 153] [Article Influence: 9.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Tilg H, Moschen AR, Kaneider NC. Pathways of liver injury in alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol. 2011;55:1159-1161. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 68] [Cited by in RCA: 81] [Article Influence: 5.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Park BJ, Lee YJ, Lee HR. Chronic liver inflammation: clinical implications beyond alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:2168-2175. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 37] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 3.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Rasineni K, Casey CA. Molecular mechanism of alcoholic fatty liver. Indian J Pharmacol. 2012;44:299-303. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 63] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Lieschke GJ, Currie PD. Animal models of human disease: zebrafish swim into view. Nat Rev Genet. 2007;8:353-367. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1552] [Cited by in RCA: 1527] [Article Influence: 84.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Goldsmith JR, Jobin C. Think small: zebrafish as a model system of human pathology. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:817341. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 102] [Cited by in RCA: 137] [Article Influence: 10.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Passeri MJ, Cinaroglu A, Gao C, Sadler KC. Hepatic steatosis in response to acute alcohol exposure in zebrafish requires sterol regulatory element binding protein activation. Hepatology. 2009;49:443-452. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 168] [Cited by in RCA: 161] [Article Influence: 10.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Howarth DL, Passeri M, Sadler KC. Drinks like a fish: using zebrafish to understand alcoholic liver disease. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2011;35:826-829. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 52] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Howarth DL, Vacaru AM, Tsedensodnom O, Mormone E, Nieto N, Costantini LM, Snapp EL, Sadler KC. Alcohol disrupts endoplasmic reticulum function and protein secretion in hepatocytes. Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 2012;36:14-23. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 3.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Tsedensodnom O, Vacaru AM, Howarth DL, Yin C, Sadler KC. Ethanol metabolism and oxidative stress are required for unfolded protein response activation and steatosis in zebrafish with alcoholic liver disease. Dis Model Mech. 2013;6:1213-1226. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 62] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Schneider AC, Machado AB, de Assis AM, Hermes DM, Schaefer PG, Guizzo R, Fracasso LB, de-Paris F, Meurer F, Barth AL. Effects of Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG on hepatic and serum lipid profiles in zebrafish exposed to ethanol. Zebrafish. 2014;11:371-378. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Wilson JM, Bunte RM, Carty AJ. Evaluation of rapid cooling and tricaine methanesulfonate (MS222) as methods of euthanasia in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2009;48:785-789. [PubMed] |
| 17. | Reynolds ES. The use of lead citrate at high pH as an electron-opaque stain in electron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1963;17:208-212. [PubMed] |
| 18. | Wang Z, Su B, Fan S, Fei H, Zhao W. Protective effect of oligomeric proanthocyanidins against alcohol-induced liver steatosis and injury in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;458:757-762. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 32] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 3.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Lane BP, Lieber CS. Ultrastructural alterations in human hepatocytes following ingestion of ethanol with adequate diets. Am J Pathol. 1966;49:593-603. [PubMed] |
| 20. | Sapp V, Gaffney L, EauClaire SF, Matthews RP. Fructose leads to hepatic steatosis in zebrafish that is reversed by mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibition. Hepatology. 2014;60:1581-1592. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 95] [Article Influence: 8.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Mandrekar P, Szabo G. Signalling pathways in alcohol-induced liver inflammation. J Hepatol. 2009;50:1258-1266. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 396] [Cited by in RCA: 391] [Article Influence: 24.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Gao B. Hepatoprotective and anti-inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012;27 Suppl 2:89-93. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 147] [Cited by in RCA: 155] [Article Influence: 11.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Kawaratani H, Tsujimoto T, Douhara A, Takaya H, Moriya K, Namisaki T, Noguchi R, Yoshiji H, Fujimoto M, Fukui H. The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:495156. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 189] [Cited by in RCA: 181] [Article Influence: 15.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Sepulcre MP, Alcaraz-Pérez F, López-Muñoz A, Roca FJ, Meseguer J, Cayuela ML, Mulero V. Evolution of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) recognition and signaling: fish TLR4 does not recognize LPS and negatively regulates NF-kappaB activation. J Immunol. 2009;182:1836-1845. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 294] [Cited by in RCA: 299] [Article Influence: 18.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Mandrekar P, Ambade A, Lim A, Szabo G, Catalano D. An essential role for monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in alcoholic liver injury: regulation of proinflammatory cytokines and hepatic steatosis in mice. Hepatology. 2011;54:2185-2197. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 201] [Cited by in RCA: 245] [Article Influence: 17.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Bertola A, Park O, Gao B. Chronic plus binge ethanol feeding synergistically induces neutrophil infiltration and liver injury in mice: a critical role for E-selectin. Hepatology. 2013;58:1814-1823. |
| 27. | Liu X, Chang X, Wu H, Xiao J, Gao Y, Zhang Y. Role of intestinal inflammation in predisposition of Edwardsiella tarda infection in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2014;41:271-278. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Meng Z, Zhang XY, Guo J, Xiang LX, Shao JZ. Scavenger receptor in fish is a lipopolysaccharide recognition molecule involved in negative regulation of NF-κB activation by competing with TNF receptor-associated factor 2 recruitment into the TNF-α signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2012;189:4024-4039. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 31] [Cited by in RCA: 38] [Article Influence: 2.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Hammes TO, Pedroso GL, Hartmann CR, Escobar TD, Fracasso LB, da Rosa DP, Marroni NP, Porawski M, da Silveira TR. The effect of taurine on hepatic steatosis induced by thioacetamide in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Dig Dis Sci. 2012;57:675-682. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 21] [Cited by in RCA: 22] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 30. | Ogryzko NV, Hoggett EE, Solaymani-Kohal S, Tazzyman S, Chico TJ, Renshaw SA, Wilson HL. Zebrafish tissue injury causes upregulation of interleukin-1 and caspase-dependent amplification of the inflammatory response. Dis Model Mech. 2014;7:259-264. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 49] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 4.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Vojtech LN, Scharping N, Woodson JC, Hansen JD. Roles of inflammatory caspases during processing of zebrafish interleukin-1β in Francisella noatunensis infection. Infect Immun. 2012;80:2878-2885. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 82] [Cited by in RCA: 80] [Article Influence: 6.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | You M, Rogers CQ. Adiponectin: a key adipokine in alcoholic fatty liver. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2009;234:850-859. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 86] [Cited by in RCA: 84] [Article Influence: 5.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Thakur V, Pritchard MT, McMullen MR, Nagy LE. Adiponectin normalizes LPS-stimulated TNF-alpha production by rat Kupffer cells after chronic ethanol feeding. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2006;290:G998-1007. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 115] [Article Influence: 6.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 34. | Amali AA, Rekha RD, Lin CJ, Wang WL, Gong HY, Her GM, Wu JL. Thioacetamide induced liver damage in zebrafish embryo as a disease model for steatohepatitis. J Biomed Sci. 2006;13:225-232. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 65] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 3.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Kaser S, Moschen A, Cayon A, Kaser A, Crespo J, Pons-Romero F, Ebenbichler CF, Patsch JR, Tilg H. Adiponectin and its receptors in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Gut. 2005;54:117-121. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 327] [Cited by in RCA: 305] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Neumeier M, Hellerbrand C, Gäbele E, Buettner R, Bollheimer C, Weigert J, Schäffler A, Weiss TS, Lichtenauer M, Schölmerich J. Adiponectin and its receptors in rodent models of fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:5490-5494. [PubMed] |
| 37. | Feige JN, Auwerx J. Transcriptional targets of sirtuins in the coordination of mammalian physiology. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2008;20:303-309. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 171] [Cited by in RCA: 172] [Article Influence: 10.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Yoshizaki T, Schenk S, Imamura T, Babendure JL, Sonoda N, Bae EJ, Oh DY, Lu M, Milne JC, Westphal C. SIRT1 inhibits inflammatory pathways in macrophages and modulates insulin sensitivity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;298:E419-E428. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 288] [Cited by in RCA: 326] [Article Influence: 21.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Oliveira GMT, Schimer H, Pereira TCB, Rico EP, Rosemberg DB, Bonan CB, Souto AA, Bogo MR. Análise do padrão transcricional de SIRT1, PGC1α e PPAR-γ influenciado por etanol em fígado de zebrafish. Available from: http://www.pucrs.br/edipucrs/XSalaoIC/Ciencias_Biologicas/Bioquimica/70777-GIOVANNA_MEDEIROS_TAVARES_DE_OLIVEIRA.pdf. |
| 40. | Pereira TC, Rico EP, Rosemberg DB, Schirmer H, Dias RD, Souto AA, Bonan CD, Bogo MR. Zebrafish as a model organism to evaluate drugs potentially able to modulate sirtuin expression. Zebrafish. 2011;8:9-16. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |