Published online Aug 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.994
Peer-review started: March 14, 2016
First decision: April 20, 2016
Revised: May 9, 2016
Accepted: July 14, 2016
Article in press: July 18, 2016
Published online: August 18, 2016
Processing time: 156 Days and 21.6 Hours
This report describes a patient that developed recurrent metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) to a suprapancreatic lymph node four years after being treated for primary HCC via complete left hepatectomy. Metastatic HCC was proven by pathologic confirmation. The report addresses the role of surgical resection as a treatment modality for recurrent HCC to solitary lymph nodes. The role of biological chemotherapy as adjuvant treatment is also addressed.
Core tip: Recurrence of primary hepatocellular carcinoma to a solitary extracellular site is a rare occurrence, especially after complete hepatic lobectomy for the primary tumor. In this report we describe a case of recurrence to a solitary suprapancreatic lymph node four years after initial resection. This is the only report to describe such a recurrence this long after the primary resection.
- Citation: Caparelli ML, Roberts NJ, Braverman TS, Stevens RM, Broun ER, Allamaneni S. Metastatic recurrence to a solitary lymph node four years after hepatic lobectomy for primary hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(23): 994-998
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i23/994.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i23.994
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer in the world, with the highest prevalence rates occurring in the eastern hemisphere. However, there has been a rise in prevalence in the Western hemisphere. It has been postulated that this pattern is due to higher incidence of hepatitis B and C virus seen outside of the United States[1]. Tumor staging and strategies for treatment of HCC have been well described with current guidelines following the recommendations of the 2010 AHPBA/SSO/SSAT consensus conference on HCC[2]. Current guidelines are primarily geared toward patients with primary resectable and non-resectable HCC. However, data is lacking with regard to the treatment of recurrent extrahepatic HCC. Systemic chemotherapy has proven to be of minimal benefit for patients with advanced, and recurrent extrahepatic HCC. There are current studies being conducted that support the use of multikinase inhibitors, including Sorafenib, as a viable option for patients with advanced and extrahepatic HCC[3].
It is well known that the most common type of recurrence of HCC is intrahepatic. The most common sites for hematogenous spread are the lung, followed by the adrenal gland, and bone[4]. Metastases of HCC to lymph nodes (LN) are quite rare. In one report that included a subset of Japanese patients who underwent hepatic resection, the prevalence of lymphatic involvement was as low as 2.2%[5]. Another study showed that the 5-year survival rate for patients with lymph node metastasis is approximately 20%[6]. There have been few reports describing metastasis to LN that have been treated with surgical resection, and their results have been varied[7-11]. With this in mind, the importance of surgical resection of extrahepatic HCC recurrent to lymph nodes cannot be understated as a viable treatment modality. Interestingly, this is the first reported case where isolated lymph node metastasis has occurred greater than 3 years after initial hepatic resection. We describe a case of HCC recurrent to a solitary suprapancreatic lymph node treated by complete surgical resection.
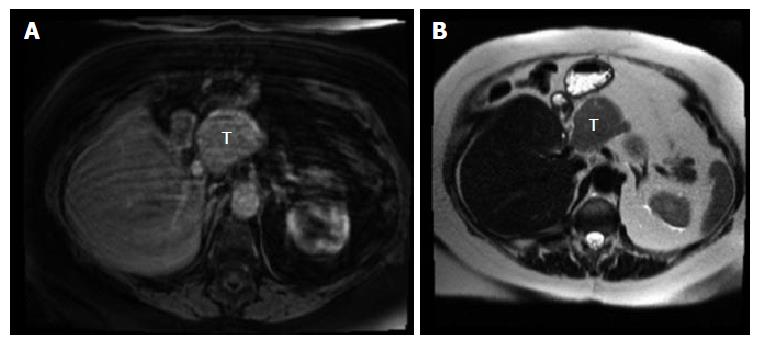
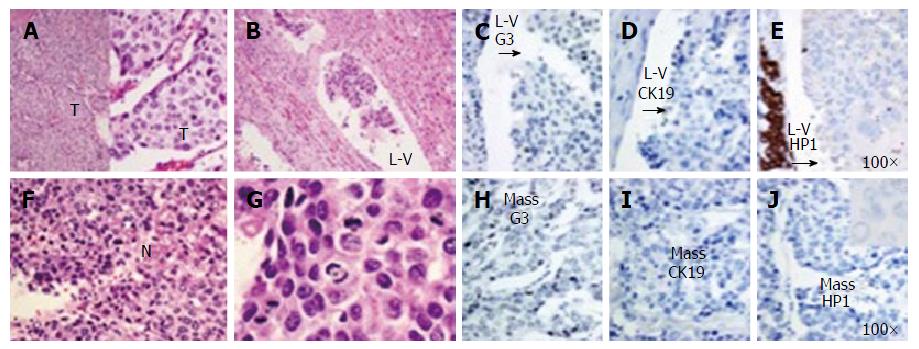
The patient is a 67-year-old woman who presented with a suprapancreatic mass on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). She initially presented 4 years prior with HCC of the left lobe of the liver measuring 10.8 cm × 7.4 cm × 9.5 cm. She was asymptomatic at the time of the discovery and the tumor was found due to imaging studies prior to a recent thoracic aortic aneurysm repair. Interestingly she did not have known risk factors for developing HCC such as cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis, tobacco use, diabetes, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hemochromatosis, or alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency. Laboratory findings at that time showed a alpha fetoprotein (AFP) level of 119000 ng/mL. She subsequently underwent complete left hepatic lobectomy and had no complications post procedure. The patient was in remission for almost 4 years, but had a steady increase in AFP, 177-883 ng/mL, from year 3 to 4. Serial computed tomography (CT) imaging showed no evidence of recurrence over that time period. Subsequent MRI showed a soft tissue mass medial to the right hepatic lobe/porta hepatis measuring 4.6 cm × 5.6 cm (Figure 1). CT guided biopsy of the mass revealed a poorly differentiated malignant neoplasm, favoring HCC. The patient had no history of viral hepatitis, alcoholic liver disease, jaundice, abdominal pain, weight loss, chronic cough, bloody stools, bone pain, or any other signs to suggest metastatic disease. She was subsequently taken to the operating room for en bloc resection of a large suprapancreatic retroperitoneal mass, celiac and portal lymphadenectomy. Pathology showed the suprapancreatic mass to be consistent with HCC, high grade within a lymph node structure. Portal and celiac axis lymph nodes were negative for metastasis. Interestingly, immunohistochemical stains for the recurrent carcinoma showed not only tumor markers that confirm hepatocellular origin, but might suggest a more aggressive tumor - staining positive for cytokeratin 19 (CK19), glypican 3 (G3) and hepatocyte paraffin 1 (HP1). Microscopic pathologic figures are shown in Figures 2 and 3. The patient’s post-operative course has been uncomplicated and at eight months post op she is disease free. Current AFP level is 2.2 ng/mL.
The recurrence of HCC can be classified as early or late phase[12]. Early phase recurrence typically occurs within the first two years post-resection, and is related to aggressive features of the primary tumor such as high tumor grade, local invasion, and multifocal tumors. Late recurrence occurs more than two years after resection and is related to de novo tumor formation, typically in patients with cirrhotic liver disease. The fact that our patient recurred to an extrahepatic LN nearly four years post-surgery is remarkable, and of the first to be reported this late, post-resection. The initial tumor was without aggressive characteristics, as it was moderately differentiated and without local invasion. Additionally, the initial tumor stained negative for CK19, G3 and was only weakly positive for HP1 in the lympho-vascular invasive sample as seen in Figure 1. Interestingly, the recurrent tumor was positive for these three biomarkers, suggesting hepatocellular origin and a more aggressive tumor[13]. Clonal selection, therapeutic selection, or possibly both may explain this finding.
LN status is essential to the staging of cancers, including HCC. The presence of LN metastasis is associated with poorer survival and higher risk of tumor recurrence[4]. Although the most common intra- and extra-hepatic recurrence is to liver and lung respectively, metastases to LNs are not that uncommon. There have been two reports that showed LN metastases in 28% and 25% of autopsied cases of HCC, respectively[14,15]. However, a more recent study of surgical patients in Japan showed only 2.2% LN involvement in patients that underwent hepatic resection[5]. This discrepancy may be due to the fact that more advanced HCC cases that are more likely to have extrahepatic metastases are less likely to undergo resection. This finding illuminates the importance LN dissection in hepatic surgery. LN dissection is not the current standard when performing hepatic resection for HCC. In a study by Ercolani et al[16] the role of lymphadenectomy was addressed. In 40 patients with HCC the incidence of LN metastases was 7.5%. It was also found that the most common site of LN metastases from HCC is the hepatic pedicle node, followed by the retropancreatic space, and common hepatic artery station. The authors concluded that regional lymphadenectomy is a safe procedure after liver resection; however, this is yet to become common practice.
Several case reports have been published on the findings of metastatic HCC to LNs[7-11]. Patients in these reports often had cirrhosis, and all but one of these patients underwent resection with varied short-term survival results. One report described a patient with a solitary suprapancreatic LN mestastasis that underwent pancreaticoduodenectomy and had reported disease free survival for 27 mo. Another patient with LN metastases to two paraaortic mediastinal LNs underwent complete resection, but had recurrence and died 13 mo later[10]. It is reasonable to argue liver disease, and multiple LN involvement may be factors for worse prognosis post LN resection.
Our patient appears to be an excellent candidate for resection, as she had a solitary LN, and is without cirrhotic, viral or alcoholic liver disease. In addition, adjuvant treatment with sorafenib - an oral multikinase inhibitor that has been shown to suppress tumor growth and angiogenesis by inhibiting the Raf/MEK/ERK signaling pathway and receptor kinases, such as VEGFR-1, VEGFR-2, VEGFR-3, and PDGFβ - should be considered[3]. Sorafenib was shown to increase survival in patients with advanced HCC in the SHARP (Sorafenib HCC Assessment Randomized Protocol) trial. However, data is lacking on whether this multikinase inhibitor is useful in the treatment of recurrent extrahepatic HCC. One recent study showed that the therapeutic effect of sorafenib was comparable in advanced HCC with or without extrahepatic metastasis[3]. It may be beneficial to initiate adjuvant treatment in patients with recurrent LN involvement, but further studies need to be performed prior to this becoming standard.
A 67-year-old woman who presented with a suprapancreatic mass on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The patient was asymptomatic at the time of presentation. Imaging studies were performed because of increased serum alpha fetoprotein levels led to increase suspicion for recurrence of primary hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) resected four years prior.
The patient was asymptomatic at the time of presentation.
Recurrent primary HCC, metastatic cancer, reactive lymphadenopathy, primary tumor of unknown origin, lymphoma.
Elevated alpha fetoprotein level of 883 ng/mL.
MRI showed a soft tissue mass medial to the right hepatic lobe/porta hepatis measuring 4.6 cm × 5.6 cm.
HCC, high grade within a lymph node structure.
Surgical resection of lesion.
HCC is a primary liver cancer. HCC typically does not recur to an extrahepatic solitary lymph node after primary resection.
HCC is a primary liver cancer. It is the fifth most common human cancer worldwide.
Surgical resection of HCC recurrence to a solitary lymph node is a viable option and may also be curative. Long term follow-up of this patient will further illuminate the possibility of cure.
An interesting case presentation with a long period disease-free up to 4 years. It should be benefit to the knowledge of the hepatologists and keep in mind for the importance of clinical follow-up after extensive hepatectomy.
Manuscript source: Unsolicited manuscript
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country of origin: United States
Peer-review report classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): B, B
Grade C (Good): C, C, C
Grade D (Fair): D
Grade E (Poor): 0
P- Reviewer: Chetty R, Chiu KW, Delladetsima IK, Mihaila RG, Pan JJ, Zhu X S- Editor: Qiu S L- Editor: A E- Editor: Li D
| 1. | Chen KW, Ou TM, Hsu CW, Horng CT, Lee CC, Tsai YY, Tsai CC, Liou YS, Yang CC, Hsueh CW. Current systemic treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review of the literature. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:1412-1420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 42] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 4.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Munene G, Vauthey JN, Dixon E. Summary of the 2010 AHPBA/SSO/SSAT Consensus Conference on HCC. Int J Hepatol. 2011;2011:565060. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 14] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Nakano M, Tanaka M, Kuromatsu R, Nagamatsu H, Tajiri N, Satani M, Niizeki T, Aino H, Okamura S, Iwamoto H. Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma with extrahepatic metastasis: a prospective multicenter cohort study. Cancer Med. 2015;4:1836-1843. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 35] [Cited by in RCA: 50] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Katyal S, Oliver JH, Peterson MS, Ferris JV, Carr BS, Baron RL. Extrahepatic metastases of hepatocellular carcinoma. Radiology. 2000;216:698-703. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 483] [Cited by in RCA: 515] [Article Influence: 20.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Liver Cancer Study Group of Japan. Primary liver cancer in Japan. Clinicopathologic features and results of surgical treatment. Ann Surg. 1990;211:277-287. [PubMed] |
| 6. | Xiaohong S, Huikai L, Feng W, Ti Z, Yunlong C, Qiang L. Clinical significance of lymph node metastasis in patients undergoing partial hepatectomy for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Surg. 2010;34:1028-1033. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Shoji F, Shirabe K, Yano T, Maehara Y. Surgical resection of solitary cardiophrenic lymph node metastasis by video-assisted thoracic surgery after complete resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10:446-447. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Taniai N, Yoshida H, Mamada Y, Mizuguchi Y, Fujihira T, Akimaru K, Tajiri T. A case of recurring hepatocellular carcinoma with a solitary Virchow’s lymph node metastasis. J Nippon Med Sch. 2005;72:245-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Kurokawa T, Yamazaki S, Moriguchi M, Aoki M, Watanabe Y, Higaki T, Takayama T. Resection of solitary metachronous lymph node metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma following transarterial chemotherapy with cisplatin: a case report. Anticancer Res. 2011;31:3991-3993. [PubMed] |
| 10. | Utsumi M, Matsuda H, Sadamori H, Shinoura S, Umeda Y, Yoshida R, Satoh D, Hashimoto M, Yagi T, Fujiwara T. Resection of metachronous lymph node metastases from hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy: report of four cases. Acta Med Okayama. 2012;66:177-182. [PubMed] |
| 11. | Ueda J, Yoshida H, Mamada Y, Taniai N, Mineta S, Yoshioka M, Kawano Y, Shimizu T, Hara E, Kawamoto C. Surgical resection of a solitary para-aortic lymph node metastasis from hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 2012;18:3027-3031. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Colecchia A, Schiumerini R, Cucchetti A, Cescon M, Taddia M, Marasco G, Festi D. Prognostic factors for hepatocellular carcinoma recurrence. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20:5935-5950. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in CrossRef: 104] [Cited by in RCA: 133] [Article Influence: 12.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Feng J, Zhu R, Chang C, Yu L, Cao F, Zhu G, Chen F, Xia H, Lv F, Zhang S. CK19 and Glypican 3 Expression Profiling in the Prognostic Indication for Patients with HCC after Surgical Resection. PLoS One. 2016;11:e0151501. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 5.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Edmondson HA, Steiner PE. Primary carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900 necropsies. Cancer. 1954;7:462-503. [PubMed] |
| 15. | Anthony PP. Hepatocellular carcinoma: an overview. Histopathology. 2001;39:109-118. [PubMed] |
| 16. | Ercolani G, Grazi GL, Ravaioli M, Grigioni WF, Cescon M, Gardini A, Del Gaudio M, Cavallari A. The role of lymphadenectomy for liver tumors: further considerations on the appropriateness of treatment strategy. Ann Surg. 2004;239:202-209. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 111] [Cited by in RCA: 119] [Article Influence: 5.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |