Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.393
Peer-review started: November 15, 2023
First decision: November 27, 2023
Revised: December 31, 2023
Accepted: February 23, 2024
Article in press: February 23, 2024
Published online: March 27, 2024
Processing time: 132 Days and 15.2 Hours
Obesity is an independent risk factor for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and may influence its outcomes. However, after diagnosis of HCC, like other malignancies, the obesity paradox may exist where higher body mass index (BMI) may in fact confer a survival benefit. This is frequently observed in patients with advanced HCC and cirrhosis, who often present late with advanced tumor features and cancer related weight loss.
To explore the relationship between BMI and survival in patients with cirrhosis and HCC.
This is a retrospective cohort study of over 2500 patients diagnosed with HCC between 2009-2019 at two United States academic medical centers. Patient and tumor characteristics were extracted manually from medical records of each institutions' cancer registries. Patients were stratified according to BMI classes: < 25 kg/m2 (lean), 25-29.9 kg/m2 (overweight), and > 30 kg/m2 (obese). Patient and tumor characteristics were compared according to BMI classification. We performed an overall survival analysis using Kaplan Meier by the three BMI classes and after adjusting for Milan criteria. A multivariable Cox regression model was then used to assess known risk factors for survival in patients with cirrhosis and HCC.
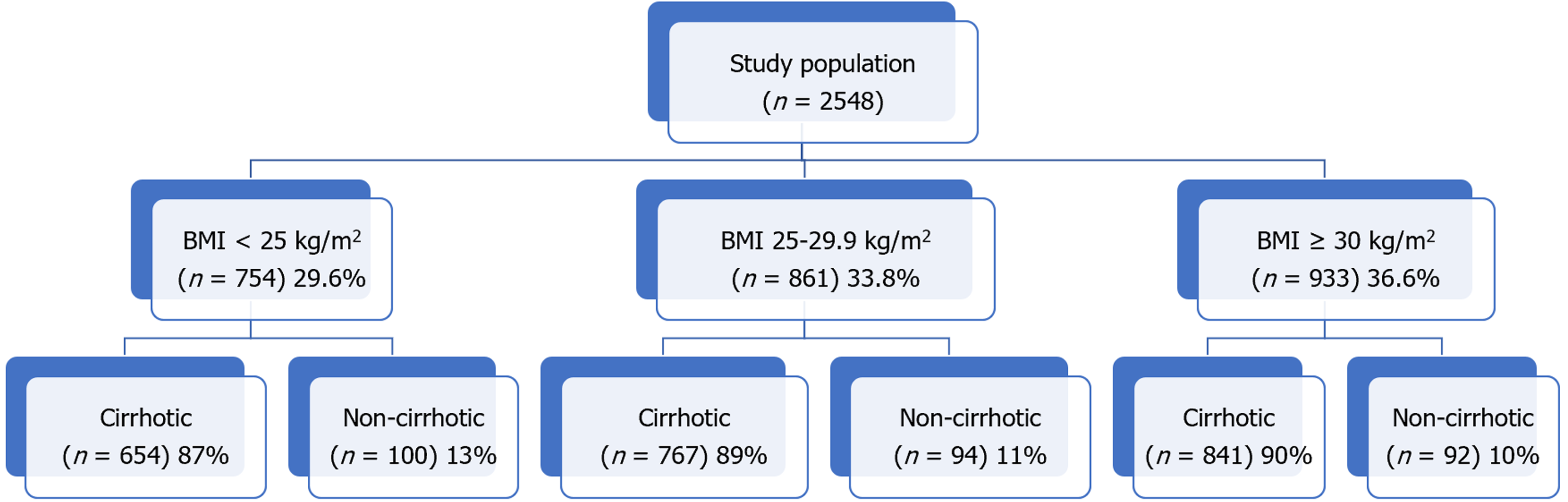
A total of 2548 patients with HCC were included in the analysis of which 11.2% (n = 286) were classified as non-cirrhotic. The three main BMI categories: Lean (n = 754), overweight (n = 861), and obese (n = 933) represented 29.6%, 33.8%, and 36.6% of the total population overall. Within each BMI class, the non-cirrhotic patients accounted for 15% (n = 100), 12% (n = 94), and 11% (n = 92), respectively. Underweight patients with a BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 (n = 52) were included in the lean cohort. Of the obese cohort, 42% (n = 396) had a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2. Out of 2262 patients with cirrhosis and HCC, 654 (29%) were lean, 767 (34%) were overweight, and 841 (37%) were obese. The three BMI classes did not differ by age, MELD, or Child-Pugh class. Chronic hepatitis C was the dominant etiology in lean compared to the overweight and obese patients (71%, 62%, 49%, P < 0.001). Lean patients had significantly larger tumors compared to the other two BMI classes (5.1 vs 4.2 vs 4.2 cm, P < 0.001), were more likely outside Milan (56% vs 48% vs 47%, P < 0.001), and less likely to undergo transplantation (9% vs 18% vs 18%, P < 0.001). While both tumor size (P < 0.0001) and elevated alpha fetoprotein (P < 0.0001) were associated with worse survival by regression analysis, lean BMI was not (P = 0.36).
Lean patients with cirrhosis and HCC present with larger tumors and are more often outside Milan criteria, reflecting cancer related cachexia from delayed diagnosis. Access to care for hepatitis C virus therapy and liver transplantation confer a survival benefit, but not overweight or obese BMI classifications.
Core Tip: This study explores the impact of different body mass index (BMI) strata on patient survival following the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). We stratified patients with cirrhosis by lean (BMI < 25 kg/m2), overweight BMI (25-29.9 kg/m2), and obese (BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2) categories, and analyzed patient and tumor characteristics. Lean patients with HCC presented with significantly larger tumors as well as more advanced tumors. Survival was significantly reduced in lean HCC patients in the overall cohort but was restricted to those patients outside Milan criteria following sub-group analysis. We included a survival analysis by BMI class according to the three most common chronic liver diseases: Chronic hepatitis C, alcoholic liver disease, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Lastly, we found no significant difference in survival comparing the three BMI classes from our sub-group of 286 patients with HCC but without cirrhosis.
- Citation: deLemos AS, Zhao J, Patel M, Kooken B, Mathur K, Nguyen HM, Mazhar A, McCarter M, Burney H, Kettler C, Chalasani N, Gawrieh S. Lean body mass index is a marker of advanced tumor features in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(3): 393-404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i3/393.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.393
The epidemiology of cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is evolving as the burden of disease shifts toward a future predominated by alcoholic liver disease (ALD) and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). A recent study from Canada projects that 92% of incident cases of cirrhosis will be due to either NAFLD or ALD in 2040[1]. The incidence of NAFLD-related HCC in the United States is predicted to increase by 137% to 12240 cases by 2030[2]. These alarming estimates underscore the present mandate to identify patients at risk for cirrhosis and HCC, presently the third leading cause of cancer death worldwide[3].
While the risk of HCC development varies depending on the underlying etiology of liver disease, ample data now supports a higher risk among chronic liver disease (CLD) patients with superimposed metabolic syndrome[4]. In a retrospective cohort of NAFLD patients, the presence of diabetes, hypertension, and dyslipidemia was shown to confer the highest risk for progression to HCC relative to patients with obesity alone[5]. A report from the International Agency for Research on Cancer, however, clearly establishes a higher body mass index (BMI) as a risk factor for HCC with a relative risk of 1.8 compared to a normal reference BMI[6]. A recent meta-analysis of 22 prospective studies encompassing over 6 million patients followed for liver cancer occurrence found that a higher BMI was associated with an increased risk of HCC, with hazard ratios (HR) that increased from 1.36 to 1.77 to 3.08 in overweight, obese class I, and obese class II/III patients respectively[7].
Although obesity is a recognized risk factor for incident HCC, whether a high BMI translates into poorer survival following the diagnosis of HCC remains unclear. In fact, a survival analysis of a nationwide cancer registry of 10578 patients with HCC from South Korea found that overweight men with a BMI of 25-29.9 kg/m2 had a better prognosis than normal weight men[8]. This “obesity paradox”, or a survival benefit in overweight or mildly obese patients with cancer may in fact be apparent in patients with HCC such as has been shown in other types of cancer[9,10]. The “obesity paradox” may also be applicable in the context of cirrhosis. The presence of obesity was found by multivariate analysis to be associated with a lower risk of inpatient mortality in 32000 cirrhotic patients from the Nationwide Inpatient Sample[11]. Additionally, a BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 was recently identified as a variable associated with improved survival in cirrhotic patients undergoing surgery[12].
This study aims to investigate the relationship between BMI at diagnosis of HCC, tumor characteristics and patient survival. We contrasted patient and tumor characteristics, as well as overall survival across 3 BMIs: BMI < 25 kg/m2 (lean), BMI 25-29.9 kg/m2 (overweight), and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (obese) in over 2500 patients diagnosed with HCC over the last decade. To our knowledge, this is the first United States-based study comprised of individually collected patient data to address the “obesity paradox” in patients with HCC.
This retrospective study included patient data from 2 academic medical centers (Atrium Health in Charlotte, North Carolina and Indiana University School of Medicine in Indianapolis, Indiana). HCC cases diagnosed from January of 2009 through June of 2019 were identified from each institutions’ cancer registries. A detailed explanation of the cohort composition was described previously[13]. A confirmation of the HCC diagnosis based upon histological and/or radiographic evidence consistent with American Association for Study of Liver Disease guidelines was made by direct review of the individual electronic health record (EHR)[14]. Following verification of the HCC diagnosis, patient and tumor characteristics were then manually extracted from the EHR into a shared REDCap database. Tumor variables collected included alpha fetoprotein (AFP), largest tumor diameter, tumor-node-metastasis stage, and whether the HCC was within Milan criteria[15,16]. The method of HCC diagnosis was ascertained whenever possible and categorized as by routine screening, symptom work-up, and/or incidentally. All HCC treatment modalities were recorded from the medical record for analysis as well.
Patients were classified according to 3 BMI classes: BMI < 25 kg/m2 (lean), BMI 25-29.9 kg/m2 (overweight), and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (obese). BMI was individually recorded from each EHR at the nearest timepoint from initial date of HCC diagnosis. Provider documentation, again through manual chart review was used in concert with confirmatory laboratory testing to assess for the presence of co-morbid metabolic risk factors including diabetes, dyslipidemia, coronary artery disease and hypertension. Patients were classified as either cirrhotic or non-cirrhotic according to criteria published previously by Mittal et al[17] and externally validated by our group[17,18]. The underlying etiology of CLD was determined by review of hepatology provider notes and supportive clinical testing. A patient with combined chronic hepatitis C (CHC) and alcohol abuse was categorized as CHC and we captured whether a sustained virologic response (SVR) was known to have occurred. Laboratory testing for a model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) calculation closest to the time of HCC diagnosis was recorded. The presence or absence of liver-related complications (ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, varices, and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis was collected through the last documentation in the EHR.
Patient survival was established from cancer registries and medical records. For patients who are still alive or died with an unknown date of death, the date of last contact available in the medical record was used to define the time of censoring for the survival analysis. Each participating site had local Institutional Review Board approval to conduct the study.
BMI group differences of patient and tumor characteristics were compared using analysis of variance, Kruskal-Wallis test, chi-square test, and Fisher's Exact test, as appropriate. Cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic cases were analyzed separately. Survival curves among BMI classes was estimated through the Kaplan-Meier method. Subgroup analyses by Milan criteria as well as etiology of CLD were conducted and included a subgroup of patients with BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2. To better evaluate potential survival differences, multivariable Cox regression models were conducted to assess risk factors for survival with HR and 95%CI presented. Risk factors included gender, race, diabetes, alcohol use, etiology of CLD, AFP, Milan criteria, screening within 2 years before HCC diagnosis, liver transplantation, and BMI categories. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS statistical software (version 9.4; SAS Institute, Cary, NC, United States).
A total of 2548 patients with HCC were included in the analysis of which 11.2% (n = 286) were classified as non-cirrhotic (Figure 1). The three main BMI categories: Lean (n = 754), overweight (n = 861), and obese (n = 933) represented 29.6%, 33.8%, and 36.6% of the total population overall. Within each BMI class, the non-cirrhotic patients accounted for 15% (n = 100), 12% (n = 94), and 11% (n = 92), respectively. Underweight patients with a BMI < 18.5 kg/m2 (n = 52) were included in the lean cohort. Of the obese cohort, 42% (n = 396) had a BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2.
Out of 2262 patients with cirrhosis and HCC, 654 (29%) were lean, 767 (34%) were overweight, and 841 (37%) were obese (Table 1). The mean age at HCC diagnosis for cirrhotic patients was 62 years and did not differ among the three BMI classes (P = 0.43). Although women represented a minority of HCC cases overall (21%), they were overrepresented in the obese cohort accounting for 26% of cases. By comparison, men accounted for a higher percentage of cases in the lean (80%) and overweight (85%) groups (P < 0.001). Lean patients with HCC were less frequently white or Hispanic and more frequently Black or Asian. As expected, the rate of diabetes, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and coronary artery disease was highest in the obese cohort compared to the overweight and lean groups (P < 0.001 for each risk factor; Table 1). There were no significant or clinical differences in laboratory tests or MELD-Na score across the three groups.
| Variable | BMI < 25 kg/m2 (n = 654) | BMI 25.0-29.9 kg/m2 (n = 767) | BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2 (n = 841) | P value |
| Age (yr) | 62.0 ± 8.9 | 62.6 ± 8.7 | 62.5 ± 8.4 | 0.43 |
| Male | 522 (79.8) | 650 (84.7) | 620 (73.7) | < 0.001 |
| Race | ||||
| White | 437 (66.8) | 599 (78.6) | 697 (83.1) | < 0.001 |
| Black | 166 (25.4) | 110 (14.4) | 98 (11.7) | |
| Hispanic | 14 (2.1) | 27 (3.5) | 31 (3.7) | |
| Asian | 24 (3.7) | 14 (1.8) | 9 (1.1) | |
| Other | 13 (2.0) | 12 (1.6) | 4 (0.48) | |
| Diabetes | 144 (22.1) | 256 (33.5) | 440 (52.3) | < 0.001 |
| Hypertension | 325 (49.8) | 450 (58.8) | 579 (68.8) | < 0.001 |
| Dyslipidemia | 127 (19.4) | 192 (25.1) | 252 (30.0) | < 0.001 |
| Coronary artery disease | 105 (16.1) | 110 (14.4) | 181 (21.5) | < 0.001 |
| Peripheral vascular disease | 74 (11.3) | 76 (9.9) | 83 (9.9) | 0.6 |
| ALT (Units/L) | 63.0 ± 67.9 | 64.3 ± 68.8 | 56.8 ± 112.1 | 0.19 |
| AST (Units/L) | 103.5 ± 147.4 | 94.3 ± 99.0 | 90.6 ± 183.2 | 0.25 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dL) | 2.1 ± 3.0 | 2.3 ± 3.7 | 2.2 ± 3.2 | 0.62 |
| Alkaline phosphatase (Units/L) | 161.3 ± 142.8 | 144.7 ± 108.2 | 146.6 ± 104.6 | 0.017 |
| Albumin (g/dL) | 3.15 ± 0.67 | 3.24 ± 0.69 | 3.16 ± 0.63 | 0.015 |
| Platelets (k/cumm) | 146.9 ± 96.8 | 122.4 ± 74.5 | 123.5 ± 76.1 | < 0.001 |
| Creatinine (md/dL) | 1.03 ± 0.84 | 1.02 ± 0.63 | 1.07 ± 0.71 | 0.37 |
| Sodium (mEq/L) | 135.7 ± 4.1 | 136.6 ± 3.9 | 136.8 ± 3.8 | < 0.001 |
| INR | 1.3 ± 0.31 | 1.3 ± 0.41 | 1.3 ± 0.39 | 0.1 |
| MELD-Na score | 14.3 ± 5.6 | 14.0 ± 5.5 | 14.3 ± 5.4 | 0.72 |
| Alcohol abuse | 342 (53.4) | 380 (50.1) | 312 (37.8) | < 0.001 |
| Etiology of chronic liver disease | ||||
| All HCV | 465 (71.2) | 474 (61.8) | 409 (48.6) | < 0.001 |
| HCV with known SVR | 158 (34) | 183 (38.6) | 167 (40.8) | 0.07 |
| Alcohol alone | 82 (12.5) | 106 (13.8) | 123 (14.6) | 0.51 |
| NAFLD | 34 (5.2) | 108 (14.1) | 230 (27.3) | < 0.001 |
| AIH/PBC/PSC | 7 (1.1) | 12 (1.6) | 14 (1.7) | 0.61 |
| HBV | 32 (4.9) | 35 (4.6) | 19 (2.3) | 0.01 |
| HC/A1AT | 4 (0.61) | 7 (0.91) | 15 (1.8) | 0.08 |
| Child-Pugh classification | ||||
| Child A | 277 (43.0) | 328 (43.5) | 336 (40.8) | 0.58 |
| Child A-B | 15 (2.3) | 26 (3.4) | 25 (3.0) | |
| Child B | 263 (40.8) | 284 (37.7) | 345 (41.9) | |
| Child C | 89 (13.8) | 116 (15.4) | 118 (14.3) | |
| Complications | ||||
| Ascites | 300 (54.1) | 383 (49.9) | 404 (48.0) | 0.31 |
| Encephalopathy | 170 (26.0) | 252 (32.9) | 302 (35.9) | < 0.001 |
| Varices | 259 (39.6) | 368 (48.0) | 427 (50.8) | < 0.001 |
| Portal vein thrombus | 148 (22.6) | 164 (21.4) | 181 (21.5) | 0.83 |
Lean patients with HCC had the highest frequency of alcohol abuse (53%), followed by overweight (50%) and obese patients (38%, P < 0.001). As anticipated, NAFLD was the etiology of cirrhosis in 27% of obese patients with HCC and accounted for 14% and 5% in the overweight and lean groups, (P < 0.001). Correspondingly, CHC accounted for 49%, 62%, and 71% of cases across the three BMI classes (P < 0.001). SVR rates were similar across the 3 CHC BMI groups, ranging from 34% to 41% (P = 0.07). The prevalence of ALD as the only etiology of liver disease was also similar across the 3 BMI classes (13%-15%, P = 0.51).
There were no differences in the distribution of Child-Pugh classes, presence of ascites or portal vein thrombosis across the 3 groups. In contrast, the presence of encephalopathy (36% vs 33% vs 26%, P < 0.001) and varices (51% vs 48% vs 40%, P < 0.001) were significantly higher in the obese relative to the overweight and lean groups.
The lean HCC cohort presented with significantly larger tumors than the overweight and lean cohorts (mean 5.1 vs 4.2 vs 4.2 cm, P < 0.001). An AFP level > 200 ng/mL was also more frequently encountered in the lean HCC group in comparison to the other two groups (36% vs 23% vs 26%, P < 0.001). The lean cohort presented with more aggressive tumors as evidenced by the lowest rate of single tumors (35% vs 43% vs 46%) and highest rate of vascular invasion or extrahepatic spread (30% vs 22% vs 22%, P < 0.001 for overall clinical tumor stage). Predictably, the lean cohort was least likely to fall within Milan criteria (44% vs 52% vs 53%, P = 0.003) and to undergo liver transplantation (9% vs 18% vs 18%, P < 0.001). Lastly, the lean HCC group was most likely to be diagnosed as part of a symptom workup (48% vs 42% vs 38%, P = 0.003) and least likely by screening (46% vs 49% vs 55%, P = 0.007), compared to the overweight and obese groups (Table 2).
| Variable | BMI < 25 kg/m², (n = 654) | BMI 25.0-29.9 kg/m², (n = 767) | BMI ≥ 30 kg/m², (n = 841) | P value |
| Tumor size (cm) | 5.1 ± 4.2 | 4.2 ± 3.0 | 4.2 ± 3.2 | < 0.001 |
| AFP (ng/mL) category | ||||
| < 20 | 269 (43.7) | 399 (54.8) | 417 (51.9) | < 0.001 |
| 20-200 | 125 (20.3) | 164 (22.5) | 178 (22.1) | |
| > 200 | 221 (35.9) | 165 (22.7) | 209 (26.0) | |
| Tumor stage | ||||
| Single | 230 (35.2 | 331 (43.2) | 386 (46.0) | < 0.001 |
| 3 tumors < 3 cm | 88 (13.5) | 97 (12.7) | 116 (13.8) | |
| Large multinodular | 142 (21.7) | 173 (22.6) | 153 (18.2) | |
| Vascular invasion or extrahepatic spread | 193 (29.6) | 165 (21.5) | 184 (21.9) | |
| Anatomic stage | ||||
| Stage I | 173 (32.8) | 239 (41.0) | 293 (43.3) | < 0.001 |
| Stage II | 147 (27.9) | 169 (29.0) | 179 (26.5) | |
| Stage IIIA | 36 (6.8) | 38 (6.5) | 49 (7.2) | |
| Stage IIIB | 55 (10.4) | 38 (6.5) | 65 (9.6) | |
| Stage IIIC + IVA + IVB | 116 (22.0) | 99 (17.0) | 90 (13.3) | |
| Tumor outside of Milan criteria | 363 (55.6) | 370 (48.3) | 397 (47.3) | 0.003 |
| Tumor differentiation | ||||
| Well | 70 (27.1) | 109 (31.5) | 116 (32.6) | 0.15 |
| Moderate | 128 (49.6) | 175 (50.6) | 184 (51.7) | |
| Poor | 53 (20.6) | 59 (17.0) | 54 (15.2) | |
| Undifferentiated/anaplastic | 7 (2.7) | 3 (0.9) | 2 (0.5) | |
| How was HCC diagnosed? | ||||
| Part of screening | 236 (45.8) | 285 (48.6) | 350 (54.8) | 0.007 |
| Incidental | 120 (23.3) | 120 (20.5) | 116 (18.2) | 0.098 |
| Symptoms work up | 246 (47.8) | 244 (41.6) | 241 (37.7) | 0.003 |
| Evidence of screening within 2 years | 190 (36.8) | 259 (44.0) | 334 (52.1) | < 0.001 |
| Liver transplantation | 61 (9.3) | 134 (17.5) | 150 (17.8) | < 0.001 |
| Palliative care/hospice | 268 (41.0) | 271 (35.3) | 265 (31.5) | < 0.001 |
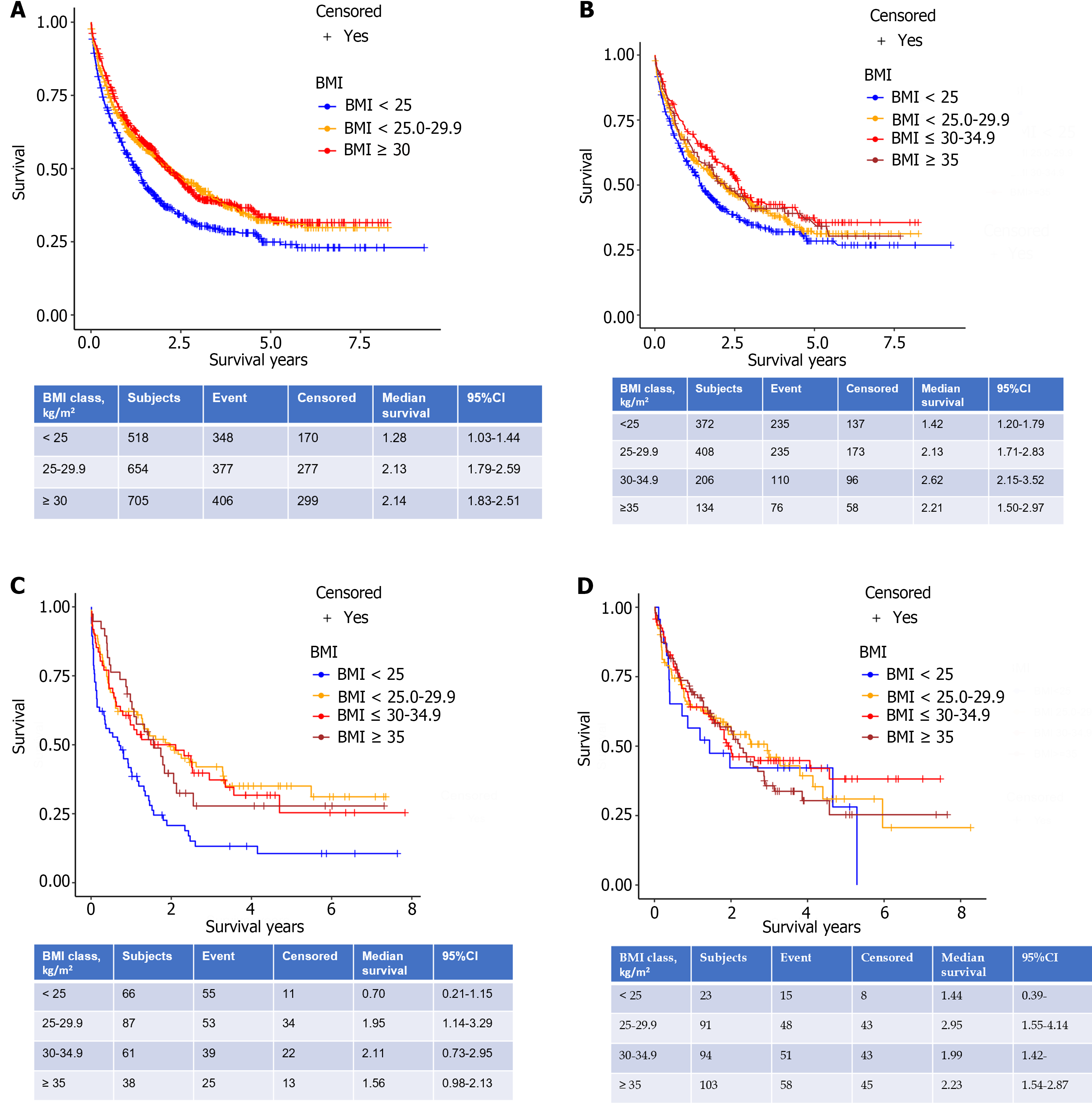
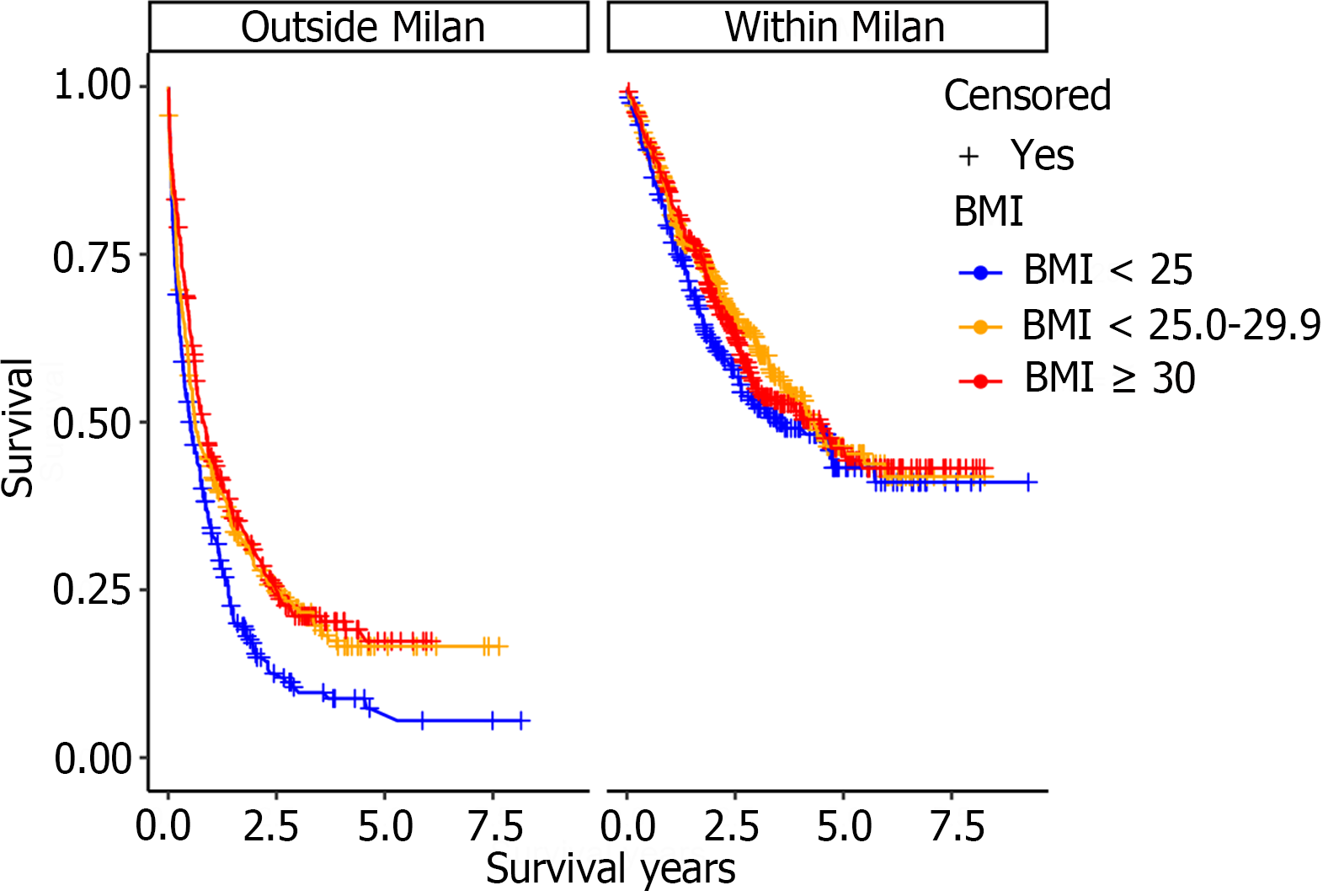
Median survival in the lean HCC cohort was 1.28 years (P < 0.0001, 95%CI 1.03-1.44) and was significantly lower compared to the overweight; 2.13 years (95%CI 1.79-2.59) and obese; 2.14 years (95%CI 1.83-2.51) cohorts (Figure 2A). The reduction in overall survival for lean cirrhotic HCC patients did not persist upon multivariate analysis (P = 0.36; Table 3). Although there was no difference in survival by BMI class when adjusting for patients with HCCs within Milan criteria (P = 0.35), there was a significantly increased mortality for lean cohort patients with HCCs outside Milan criteria compared to the other 2 BMI groups (P < 0.0001; Figure 3). This observation remained significant on multivariate analysis as patients with tumors within Milan criteria had a significant survival benefit (HR = 0.59, 95%CI 0.48-0.72, P < 0.0001) as did those patients undergoing liver transplantation (HR = 0.10, 95%CI 0.06-0.17, P < 0.0001). A SVR from CHC infection was also associated with a survival benefit (HR = 0.27, 95%CI 0.21-0.35, P < 0.0001) while an AFP > 200 ng/mL (HR = 1.93, 95%CI 1.61-2.32, P < 0.0001) and tumor size (cm) (HR = 1.08, 95%CI 1.05-1.12) were associated with worse survival (Table 3).
| Characteristic | Adjusted HR (95%CI) | P value |
| Age | 1.0 (0.99-1.01) | 0.58 |
| Female (Ref.: Male) | 0.94 (0.76-1.16) | 0.57 |
| Race (Ref.: White) | 0.72 | |
| Asian | 0.98 (0.55-1.76) | |
| Black | 0.87 (0.70-1.08) | |
| Hispanic | 0.94 (0.57-1.55) | |
| Other | 0.81 (0.45-1.45) | |
| BMI classification (kg/m²) (Ref.: BMI < 25) | 0.36 | |
| BMI 25.0-29.9 | 0.87 (0.72-1.06) | |
| BMI ≥ 30 | 0.90 (0.73-1.11) | |
| Diabetes | 0.96 (0.81-1.14) | 0.64 |
| Alcohol abuse | 1.10 (0.90-1.34) | 0.35 |
| HCV SVR | 0.27 (0.21-0.35) | < 0.0001 |
| Tumor size (cm) | 1.08 (1.05-1.12) | < 0.0001 |
| AFP (ng/mL) (Ref.: < 20) | < 0.0001 | |
| 20-200 | 1.51 (1.23-1.85) | |
| > 200 | 1.93 (1.61-2.32) | |
| Tumor within Milan criteria | 0.59 (0.48-0.72) | < 0.0001 |
| Liver transplantation | 0.10 (0.06-0.16) | < 0.0001 |
| Any method of screening within 2 years before HCC diagnosis (Ref.: No) | 0.0634 | |
| Yes | 1.01 (0.85-1.21) | |
| Unknown | 0.79 (0.63-0.99) |
A final survival analysis was performed after stratifying by the three most common etiologies of CLD: Hepatitis C virus (HCV), alcohol, and NAFLD (Figure 2B-D). For each etiology, the obese HCC cohort was further subdivided into Class I obese (BMI: 30-34.9 kg/m2) and Class II & III (BMI ≥ 35 kg/m2). Median survival was significantly lower for the lean HCC cohort with underlying HCV (1.42 years, P = 0.01, 95%CI 1.2-1.79) and alcohol (0.7 years, P = 0.0007, 95%CI 0.21-1.15) compared to the three other BMI groups. The lean NAFLD-related HCC cohort patients were predictably low in number (n = 23) and their median survival, while lower at 1.44 years (95%CI: 0.39-) did not reach statistical significance compared to the overweight (2.95 years, 95%CI 1.5-4.14), obese class I (1.99 years 1.42-) and obese class II (2.23 years, 95%CI 1.54-2.87) (P overall = 0.84 among 4 BMI classes).
The 286 patients with HCC but without cirrhosis were evaluated according to BMI classification (Supplementary Table 1). Patients with non-cirrhotic HCC presented at a mean age of 66, 69, and 67 years old in the lean, overweight, and obese cohorts respectively (P = 0.22). Interestingly, women accounted for 30% of the non-cirrhotic HCC cohort (compared to 21% in the cirrhotic HCC cohort) though there was no significant difference in gender distribution across the three BMI strata. As observed in cirrhotic HCC (Table 1), the non-cirrhotic obese group was more often white than in the overweight or lean groups (88% vs 79% vs 72%, respectively) and less often Black (9% vs 10% vs 21%, respectively, P = 0.015). As expected, 78% of the cases had Aspartate aminotransferase to platelet ratio index scores < 1.0% and 76% had no record of undergoing HCC screening. No CLD etiology could be ascertained in 48% (137/286) of the cases, while the remaining were either NAFLD or viral hepatitis. HCC tumor size on presentation tended to be larger in the lean cohort (9.2 cm) compared to the overweight (7.6 cm) and obese (7.7 cm) cohorts respectively (P = 0.06) though there was no difference among the BMI classes in clinical tumor stage with 51% of the tumors presenting as single lesions and 23% presenting with vascular invasion or extrahepatic spread. Median survival in non-cirrhotic HCC patients in the lean (2.95 years, 95%CI 1.12-6.52), overweight (2.14 years 95%CI 0.96-2.96), and obese (2.77 years 95%CI 1.33-3.17) cohorts was not significantly different.
Our analysis of over 2500 patients diagnosed with HCC over the last decade focused on the differences between overweight and obese BMI classifications relative to a cohort of lean patients. The lean group, at the time of HCC diagnosis was enriched with hepatitis C and alcohol abuse and presented with significantly larger tumors as well as more aggressive tumors which resulted in lower frequency of liver transplantation compared to the overweight and obese groups. By multivariate analysis, however, the impact of BMI classification on patient survival was eclipsed by established survival outcomes such as presenting within Milan criteria and achieving a cure of CHC infection.
Our results should be interpreted within the context of emerging evidence demonstrating the significance of sarcopenia in survival following the diagnosis of HCC. In a Japanese study of over 1200 patients with HCC who underwent computed tomography for body composition assessment; sarcopenia, intramuscular fat deposition, and high visceral adiposity, but not BMI were significant predictors of survival by multivariate analysis[19]. Progressive skeletal muscle volume loss as measured by the psoas muscle index in patients undergoing locoregional therapy for HCC has also recently been associated with poor prognosis[20,21]. We acknowledge that the use of BMI as a variable to evaluate survival in patients with HCC has its limitations. However, our findings reinforce what one would anticipate contrasting BMI classes. The lean cohort, presenting more often without prior HCC screening and with more advanced tumors as we found in our analysis, likely comprises patients with cancer related cachexia. Rich et al[22] investigated the impact of cachexia defined as > 5% weight loss in the six months prior to HCC diagnosis compared to pre-cachexia (2%-5% weight loss) and stable/increased weight patients[22]. Approximately 25% of 600 patients met criteria for cachexia. Notably, BMI in the cachexia cohort was significantly lower than in the pre-cachexia and stable weight groups (25.4 vs 28.3 vs 28.5, P < 001). The authors found that cachexia was independently associated with increased mortality with a median overall survival of 11.3 months which is comparable to the 15.4 months we found in our lean cohort. Thus BMI, while not an ideal surrogate of cachexia, is still of consequence particularly when evaluated in a considerably larger cohort such as ours.
A strength of our study was including a sub-group survival analysis of BMI classes according to HCV, ALD, and NAFLD etiologies. Since 53% of the patients from the lean HCC cohort were classified as having a history of alcohol abuse, the interaction between alcohol use and HCV could have led to more aggressive tumors in the lean cohort which was comprised of 71% HCV-related HCCs. The differences in screening rates preceding HCC diagnosis among the three BMI cohorts is a natural limitation from a retrospective study and highlights the fundamental challenge in routine cirrhosis management, namely access to screening and the diagnostic accuracy of our screening methodology. A recent detailed investigation of the limitations of screening found that just over a third of patients diagnosed with HCC had regular outpatient care in the year before presenting with HCC[23]. Furthermore, the adequacy of ultrasound visualization for HCC screening was reported to be sub-optimal in nearly 20% of cirrhosis patients, particularly in obese patients with NAFLD and ALD[24]. While newer blood-based biomarkers hold promise and may improve upon ultrasound for surveillance[25,26], issues surrounding access to testing will undoubtedly persist.
Reconsidering the use of the term “obesity paradox” in patients with advanced HCC outside the Milan criteria is a salient conclusion to draw from our study. In fact, our results reinforce the larger impact of cancer related weight loss which is at least in part a result of delayed diagnoses. The present focus on creating a robust screening apparatus for our liver disease patients at risk for HCC is of critical importance to prevent the past from repeating itself[27].
This study examines a large cohort of patients diagnosed with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) at two academic medical centers where liver transplantation is offered. Extensive data collection on patient and tumor variables were obtained to investigate the relationship between body mass index (BMI) classification and outcomes of patients with HCC.
The motivation for our research study is to explore how different BMI strata impact survival in patients with HCC.
It is apparent that a lean BMI in patients at the time of HCC diagnosis reflects advanced tumor burden but is not independently associated with worse survival.
Patient and tumor characteristics were compared according to BMI < 25 kg/m2 (lean), BMI 25-29.9 kg/m2 (overweight), and BMI ≥ 30 kg/m2. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to estimate survival by BMI categories. A multivariable model was performed to investigate risk factors (including the three BMI strata) associated with survival following HCC diagnosis.
Our research demonstrates interesting differences when comparing patients across BMI categories. For example, women with HCC were more likely to be in a higher BMI classification than men. Chronic hepatitis C infection was by far the most common reason for chronic liver disease in our cohort, and achieving sustained virologic response, not unexpectedly was associated with improved survival. We did not see significant differences in the Child-Pugh class or model for end stage liver disease scores according to the three different BMI. We did not see a survival difference by BMI class in our large cohort of 286 non-cirrhotic HCC cases patients.
The relevant conclusion that one can draw from this study is the importance of identifying patients early in their presentation as our results confirm well established risk factors for reduced survival in patients with HCC trump the perceived protection of the "obesity paradox".
The future research in this field needs to focus on improving patient access to screening for HCC to prevent a delay in diagnosis.
The following individuals have contributed to the data extraction: Keaton R Jones, MD, Lara Dakhoul, MD and Chelsey McShane, MD (Indiana University School of Medicine), and Patrick Roche (Atrium Health).
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: United States
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): 0
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): C
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Kalinowski P, Poland S-Editor: Li L L-Editor: A P-Editor: Cai YX
| 1. | Flemming JA, Djerboua M, Groome PA, Booth CM, Terrault NA. NAFLD and Alcohol-Associated Liver Disease Will Be Responsible for Almost All New Diagnoses of Cirrhosis in Canada by 2040. Hepatology. 2021;74:3330-3344. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 61] [Article Influence: 15.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 2. | Estes C, Razavi H, Loomba R, Younossi Z, Sanyal AJ. Modeling the epidemic of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease demonstrates an exponential increase in burden of disease. Hepatology. 2018;67:123-133. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1028] [Cited by in RCA: 1701] [Article Influence: 243.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 3. | Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209-249. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 75126] [Cited by in RCA: 64436] [Article Influence: 16109.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (176)] |
| 4. | McGlynn KA, Petrick JL, El-Serag HB. Epidemiology of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology. 2021;73:4-13. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 820] [Cited by in RCA: 1330] [Article Influence: 332.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 5. | Kanwal F, Kramer JR, Li L, Dai J, Natarajan Y, Yu X, Asch SM, El-Serag HB. Effect of Metabolic Traits on the Risk of Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Cancer in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology. 2020;71:808-819. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 108] [Cited by in RCA: 215] [Article Influence: 43.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Lauby-Secretan B, Scoccianti C, Loomis D, Grosse Y, Bianchini F, Straif K; International Agency for Research on Cancer Handbook Working Group. Body Fatness and Cancer--Viewpoint of the IARC Working Group. N Engl J Med. 2016;375:794-798. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2163] [Cited by in RCA: 2410] [Article Influence: 267.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 7. | Sohn W, Lee HW, Lee S, Lim JH, Lee MW, Park CH, Yoon SK. Obesity and the risk of primary liver cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2021;27:157-174. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 101] [Article Influence: 20.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 8. | Cha B, Yu JH, Jin YJ, Suh YJ, Lee JW. Survival Outcomes According to Body Mass Index in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient: Analysis of Nationwide Cancer Registry Database. Sci Rep. 2020;10:8347. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 15] [Cited by in RCA: 20] [Article Influence: 4.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Shachar SS, Williams GR. The Obesity Paradox in Cancer-Moving beyond BMI-Response. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26:981. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 17] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Greenlee H, Unger JM, LeBlanc M, Ramsey S, Hershman DL. Association between Body Mass Index and Cancer Survival in a Pooled Analysis of 22 Clinical Trials. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2017;26:21-29. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 135] [Cited by in RCA: 139] [Article Influence: 17.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Karagozian R, Bhardwaj G, Wakefield DB, Baffy G. Obesity paradox in advanced liver disease: obesity is associated with lower mortality in hospitalized patients with cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2016;36:1450-1456. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 57] [Article Influence: 6.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Mahmud N, Fricker Z, Hubbard RA, Ioannou GN, Lewis JD, Taddei TH, Rothstein KD, Serper M, Goldberg DS, Kaplan DE. Risk Prediction Models for Post-Operative Mortality in Patients With Cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2021;73:204-218. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 73] [Cited by in RCA: 108] [Article Influence: 27.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Mathur K, Mazhar A, Patel M, Dakhoul L, Burney H, Liu H, Nephew L, Chalasani N, deLemos A, Gawrieh S. Changing Trends of Cirrhotic and Noncirrhotic Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Era of Directly-Acting Antiviral Agents. Clin Transl Gastroenterol. 2021;12:e00420. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 14. | Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, Roberts LR, Heimbach JK. Diagnosis, Staging, and Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: 2018 Practice Guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;68:723-750. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 2121] [Cited by in RCA: 3232] [Article Influence: 461.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 15. | Edge SB, Compton CC. The American Joint Committee on Cancer: the 7th edition of the AJCC cancer staging manual and the future of TNM. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17:1471-1474. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5537] [Cited by in RCA: 6457] [Article Influence: 430.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Mazzaferro V, Regalia E, Doci R, Andreola S, Pulvirenti A, Bozzetti F, Montalto F, Ammatuna M, Morabito A, Gennari L. Liver transplantation for the treatment of small hepatocellular carcinomas in patients with cirrhosis. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:693-699. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5110] [Cited by in RCA: 5305] [Article Influence: 182.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Mittal S, El-Serag HB, Sada YH, Kanwal F, Duan Z, Temple S, May SB, Kramer JR, Richardson PA, Davila JA. Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Absence of Cirrhosis in United States Veterans is Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016;14:124-31.e1. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 373] [Cited by in RCA: 490] [Article Influence: 54.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 18. | Gawrieh S, Dakhoul L, Miller E, Scanga A, deLemos A, Kettler C, Burney H, Liu H, Abu-Sbeih H, Chalasani N, Wattacheril J. Characteristics, aetiologies and trends of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients without cirrhosis: a United States multicentre study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2019;50:809-821. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 86] [Article Influence: 14.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Fujiwara N, Nakagawa H, Kudo Y, Tateishi R, Taguri M, Watadani T, Nakagomi R, Kondo M, Nakatsuka T, Minami T, Sato M, Uchino K, Enooku K, Kondo Y, Asaoka Y, Tanaka Y, Ohtomo K, Shiina S, Koike K. Sarcopenia, intramuscular fat deposition, and visceral adiposity independently predict the outcomes of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2015;63:131-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 571] [Cited by in RCA: 564] [Article Influence: 56.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Vallati GE, Trobiani C, Teodoli L, Lai Q, Cappelli F, Ungania S, Catalano C, Lucatelli P. Sarcopenia Worsening One Month after Transarterial Radioembolization Predicts Progressive Disease in Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Biology (Basel). 2021;10. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 8] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Fujita M, Takahashi A, Hayashi M, Okai K, Abe K, Ohira H. Skeletal muscle volume loss during transarterial chemoembolization predicts poor prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatol Res. 2019;49:778-786. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 26] [Cited by in RCA: 45] [Article Influence: 7.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Rich NE, Phen S, Desai N, Mittal S, Yopp AC, Yang JD, Marrero JA, Iyengar P, Infante RE, Singal AG. Cachexia is Prevalent in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Associated With Worse Prognosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:e1157-e1169. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 24] [Article Influence: 8.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 23. | Marquardt P, Liu PH, Immergluck J, Olivares J, Arroyo A, Rich NE, Parikh ND, Yopp AC, Singal AG. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening Process Failures in Patients with Cirrhosis. Hepatol Commun. 2021;5:1481-1489. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 44] [Article Influence: 11.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Schoenberger H, Chong N, Fetzer DT, Rich NE, Yokoo T, Khatri G, Olivares J, Parikh ND, Yopp AC, Marrero JA, Singal AG. Dynamic Changes in Ultrasound Quality for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening in Patients With Cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:1561-1569.e4. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 46] [Cited by in RCA: 79] [Article Influence: 26.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Chalasani NP, Porter K, Bhattacharya A, Book AJ, Neis BM, Xiong KM, Ramasubramanian TS, Edwards DK 5th, Chen I, Johnson S, Roberts LR, Kisiel JB, Reddy KR, Singal AG, Olson MC, Bruinsma JJ. Validation of a Novel Multitarget Blood Test Shows High Sensitivity to Detect Early Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:173-182.e7. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 94] [Article Influence: 31.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Singal AG, Tayob N, Mehta A, Marrero JA, El-Serag H, Jin Q, Saenz de Viteri C, Fobar A, Parikh ND. GALAD demonstrates high sensitivity for HCC surveillance in a cohort of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2022;75:541-549. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 24] [Cited by in RCA: 122] [Article Influence: 40.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Singal AG, Lok AS, Feng Z, Kanwal F, Parikh ND. Conceptual Model for the Hepatocellular Carcinoma Screening Continuum: Current Status and Research Agenda. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022;20:9-18. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 45] [Cited by in RCA: 74] [Article Influence: 24.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |