Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2023; 15(11): 1196-1209
Published online Nov 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i11.1196
Published online Nov 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i11.1196
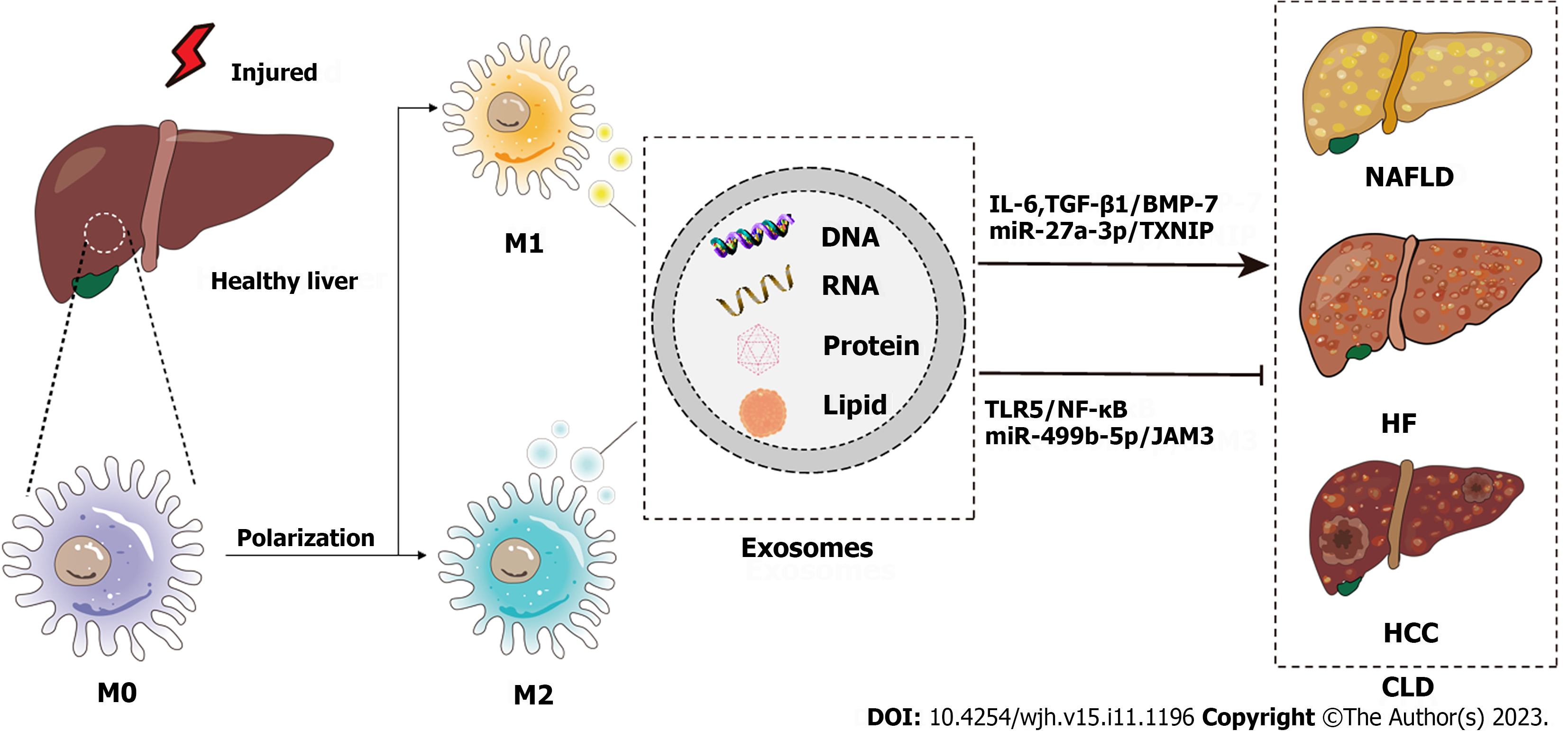
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of the pathogenesis of chronic liver disease from the perspective of macrophage-derived exosomes.
Injured livers activate macrophages to secrete exosomes that encapsulate RNAs, DNAs, lipids, proteins, etc., which influence the development of chronic liver disease through various signaling pathways. CLD: Chronic liver disease; NAFLD: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HF: Hepatic fibrosis; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TGF: Transforming growth factor; BMP: Bone morphogenetic protein; TXNIP: Thioredoxin-interacting protein; TLR: Toll-like receptor.
- Citation: Xiang SY, Deng KL, Yang DX, Yang P, Zhou YP. Function of macrophage-derived exosomes in chronic liver disease: From pathogenesis to treatment. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(11): 1196-1209
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i11/1196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i11.1196