Published online Dec 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1892
Peer-review started: February 23, 2021
First decision: May 3, 2021
Revised: May 25, 2021
Accepted: October 24, 2021
Article in press: October 24, 2021
Published online: December 27, 2021
Processing time: 306 Days and 8.8 Hours
Hepatic hemangioma is usually detected on a routine ultrasound examination because of silent clinical behaviour. The typical ultrasound appearance of hemangioma is easily recognizable and quickly guides the diagnosis without the need for further investigation. But there is also an entire spectrum of atypical and uncommon ultrasound features and our review comes to detail these particular aspects. An atypical aspect in standard ultrasound leads to the continuation of explorations with an imaging investigation with contrast substance [ultrasound/ computed tomography/or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)]. For a clinician who practices ultrasound and has an ultrasound system in the room, the easiest, fastest, non-invasive and cost-effective method is contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS). Approximately 85% of patients are correctly diagnosed with this method and the patient has the correct diagnosis in about 30 min without fear of malignancy and without waiting for a computer tomography (CT)/MRI appointment. In less than 15% of patients CEUS does not provide a conclusive appearance; thus, CT scan or MRI becomes mandatory and liver biopsy is rarely required. The aim of this updated review is to synthesize the typical and atypical ultrasound aspects of hepatic hemangioma in the adult patient and to propose a fast, non-invasive and cost-effective clinical-ultrasound algorithm for the diagnosis of hepatic hemangioma.
Core Tip: Liver hemangiomas are benign tumors usually found on a routine ultrasound in an asymptomatic adult patient. A high-performance ultrasonographic system equipped with contrast-enhanced ultrasound software, allows the experienced examinator to orient the diagnosis quickly, cost-effectively and non-invasively in most cases. This article reviews the typical and atypical ultrasound features of hepatic hemangioma and proposes a diagnostic algorithm for liver hemangiomas in patients referred to the hepatologist.
- Citation: Sandulescu LD, Urhut CM, Sandulescu SM, Ciurea AM, Cazacu SM, Iordache S. One stop shop approach for the diagnosis of liver hemangioma. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(12): 1892-1908
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i12/1892.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i12.1892
After focal fatty sparing, hepatic hemangioma (HH) is the second most common benign solid lesion of the liver[1]. The rate of detection of HHs has increased as imaging methods have become more effectiveness and accessible. The prevalence depends on the method used for detection: 2%-4% for ultrasonography, up to 5% for computed tomography and up to 7% of cases in autopsy cases[2-5]. HH are more common in women than in men[4]. It can appear at any age but are detected more frequently between 30-50 years[6]. HHs are usually single, small in size, less than 3 cm, but can also be multiple and large in size up to 20 cm.
HHs belong to the group of non-epithelial lesions, consisting of a blood-filled space, fed by hepatic arterial circulation. HH arises from a vascular malformation and increases in size mainly by dilating the vessels inside the tumour.
The pathogenesis of hemangioma is not entirely understood, the theory of congenital disorder[7] with possible hormonal dependence has been taken into account[4]. Macroscopically, HHs are well delineated, described as flat red-blue lesions. Hemangiomas are classified into three types: Cavernous, capillary and sclerosing hemangioma. Capillary hemangiomas are usually small, less than 3 cm, while cavernous hemangiomas reach sizes over 5 cm. Sclerotic hemangioma is small, completely fibrous, therefore it can occasionally be misdiagnosed as a malignant fibrous tumor[9,10]. Microscopically, hemangiomas consist of cavernous vascular spaces padded with a flattened endothelium divided by fibrous septa of varying thicknesses that are often incomplete. Currently, according to newer classification system of the International Society for the Study of Vascular Anomalies ISSVA, last updated in 2018, HH is a vascular tumor, considered as a slow flow venous malformation[11].
Small hemangiomas are usually asymptomatic, detected by chance on imaging evaluation. Multiple or bulky tumors can cause symptoms, as pain in abdominal right upper quadrant secondary to infarction, haemorrhage, torsion or distention of the Glisson’s capsule. Other symptoms like fullness, nausea, vomiting and early satiety may result from compression of adjacent organs[12].
Liver function tests are usually normal. The natural history of hemangiomas is variable: Most of them remain stable, some may grow or involute. In the vast majority of cases does not require treatment or monitoring.
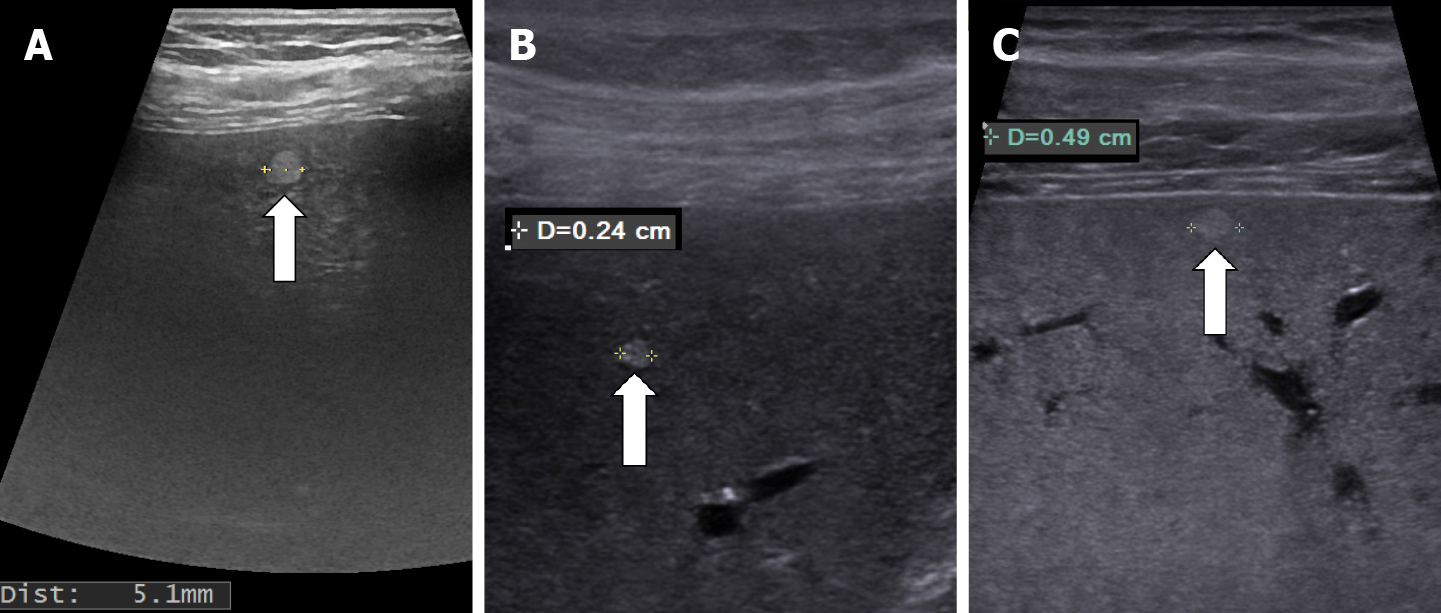
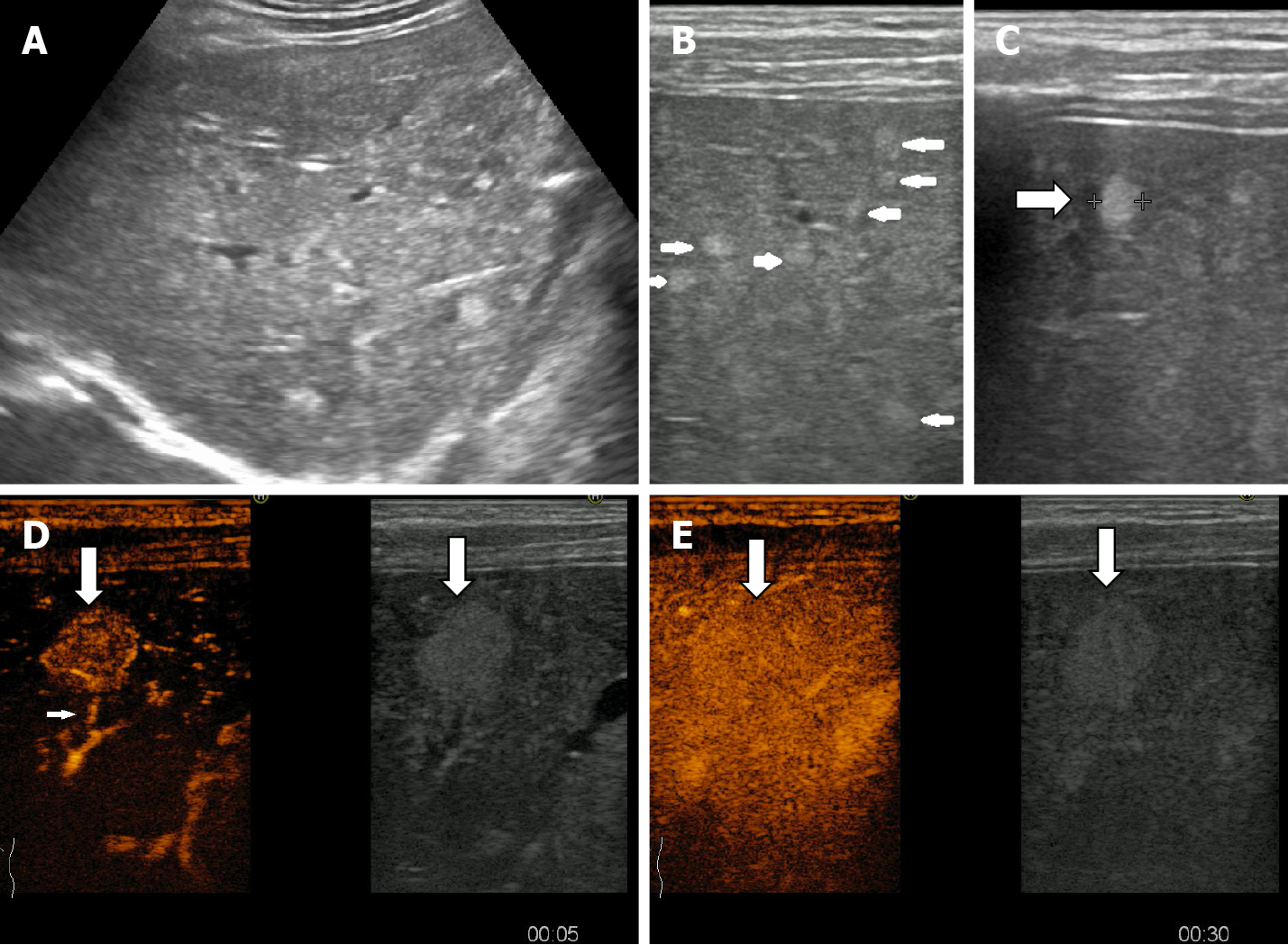
In recent years, ultrasound examination is the main method of detecting HH due to the fact that it is widely available, inexpensive, rapidly performed without exposing the patient to radiation. Because ultrasonography systems are becoming more and more efficient, smaller and smaller masses are detected, from 2-3 mm, especially if a linear probe with a frequency higher than 8 MHz is used (Figure 1).
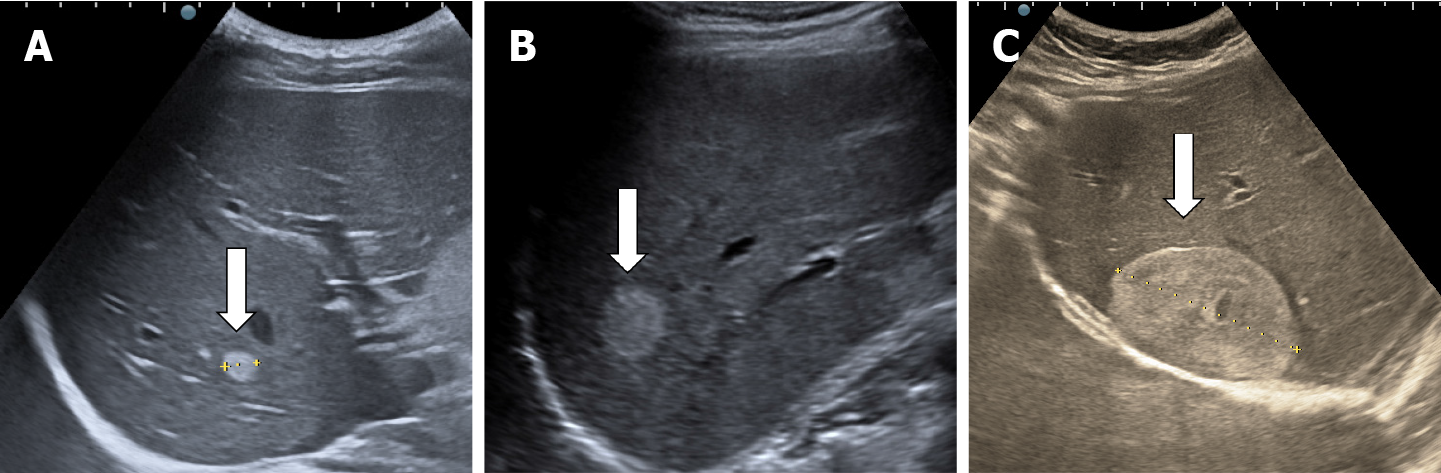
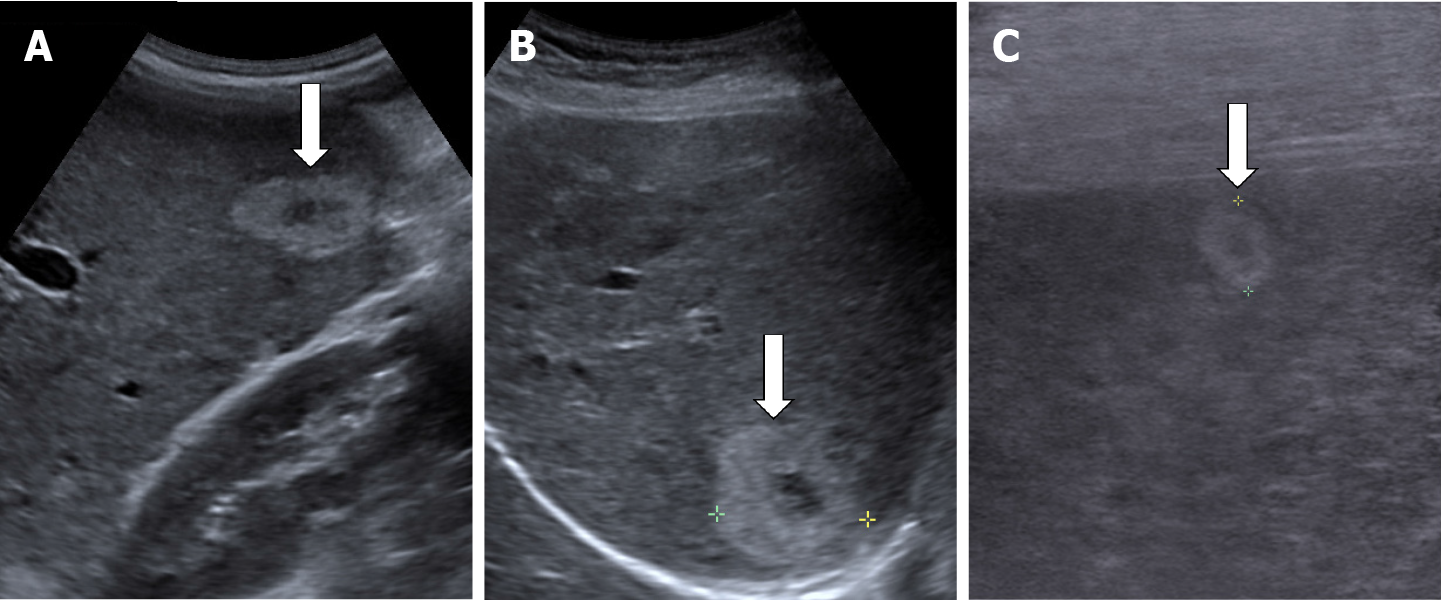
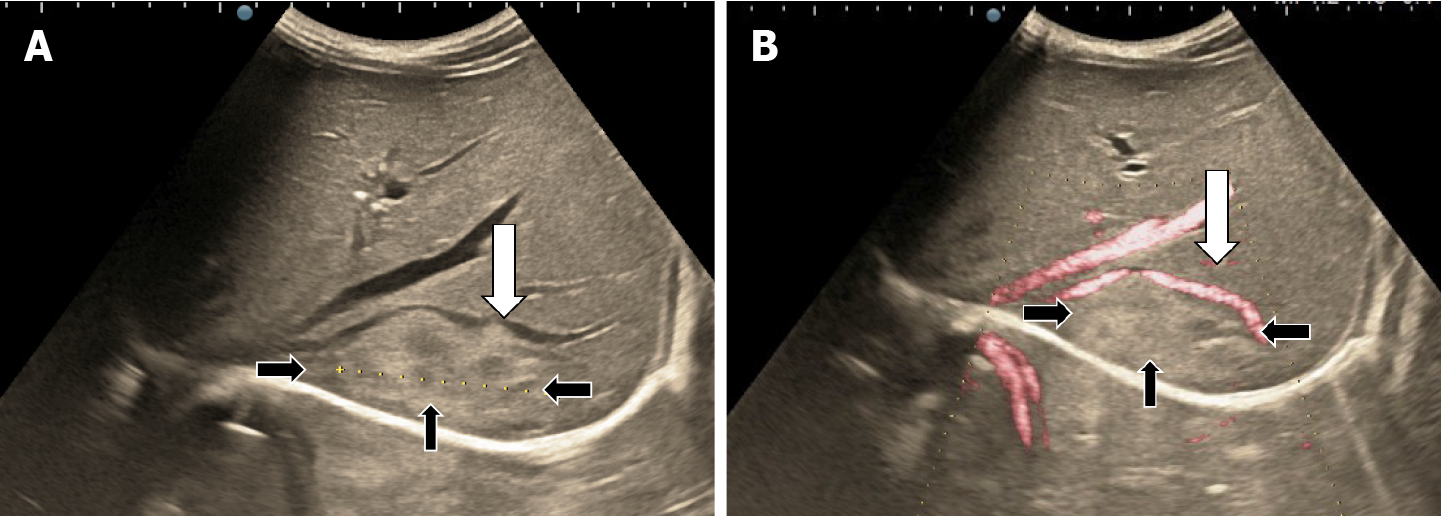
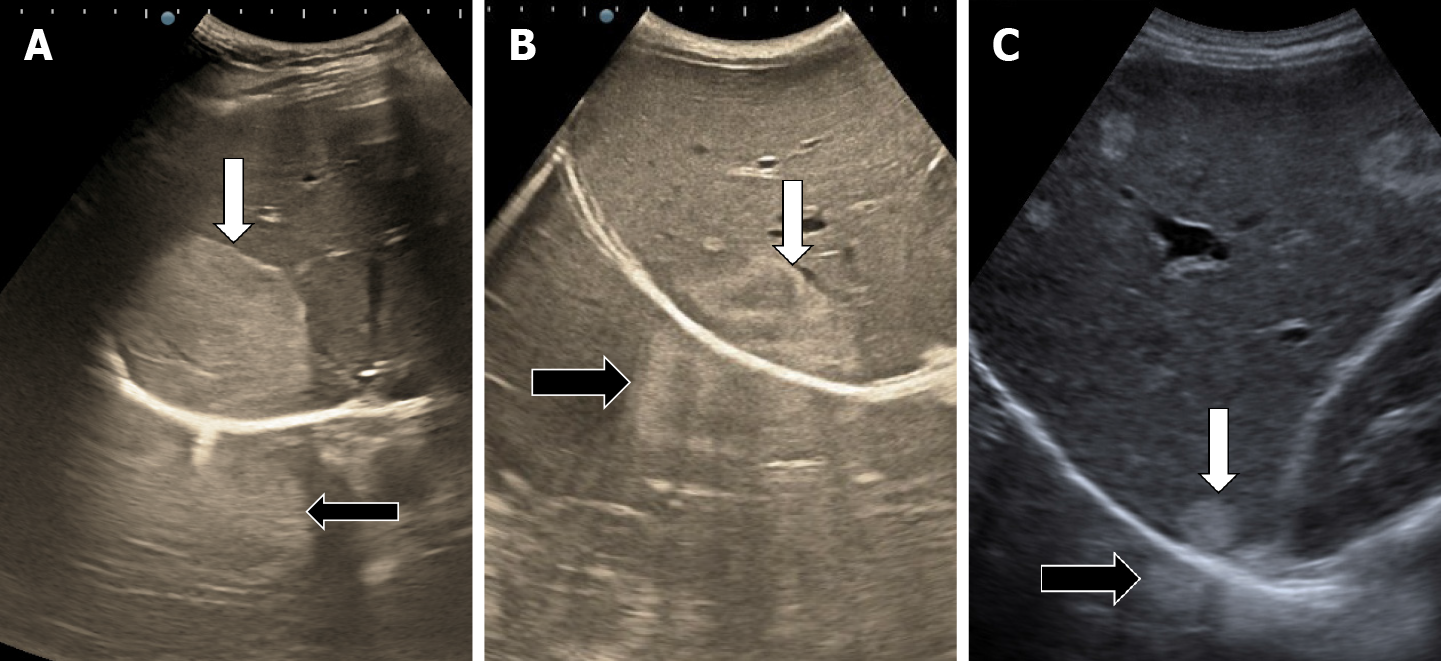
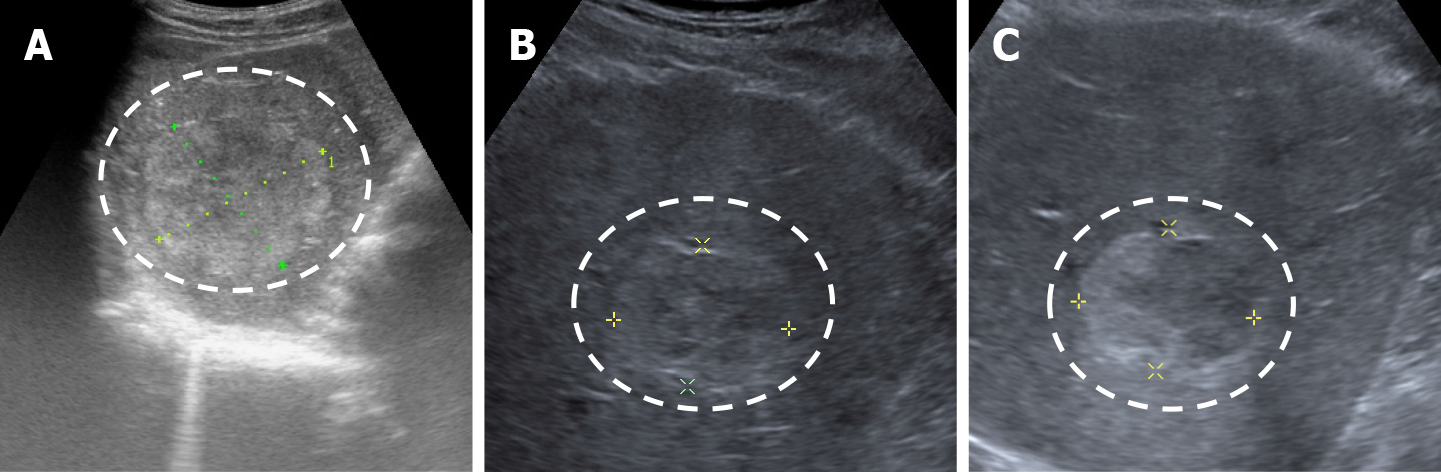
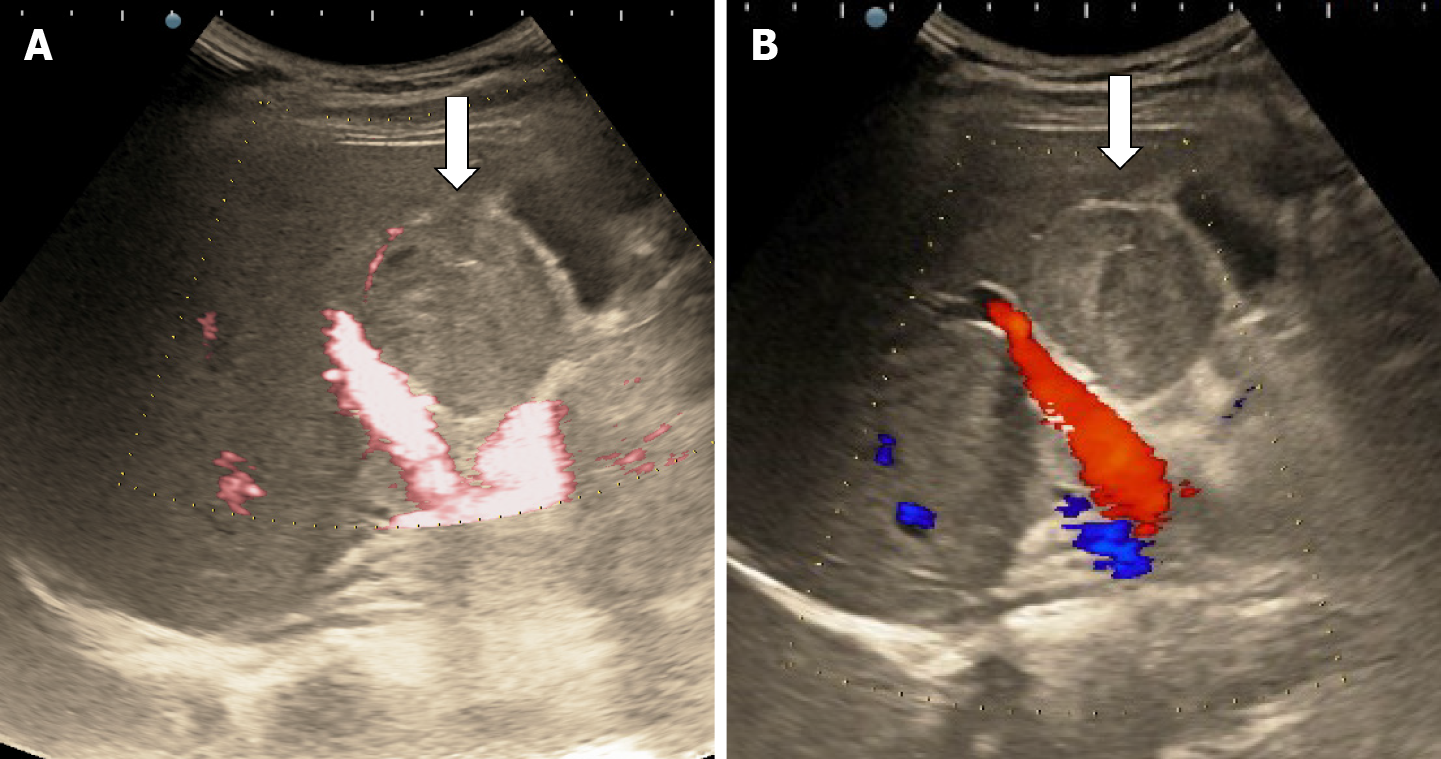
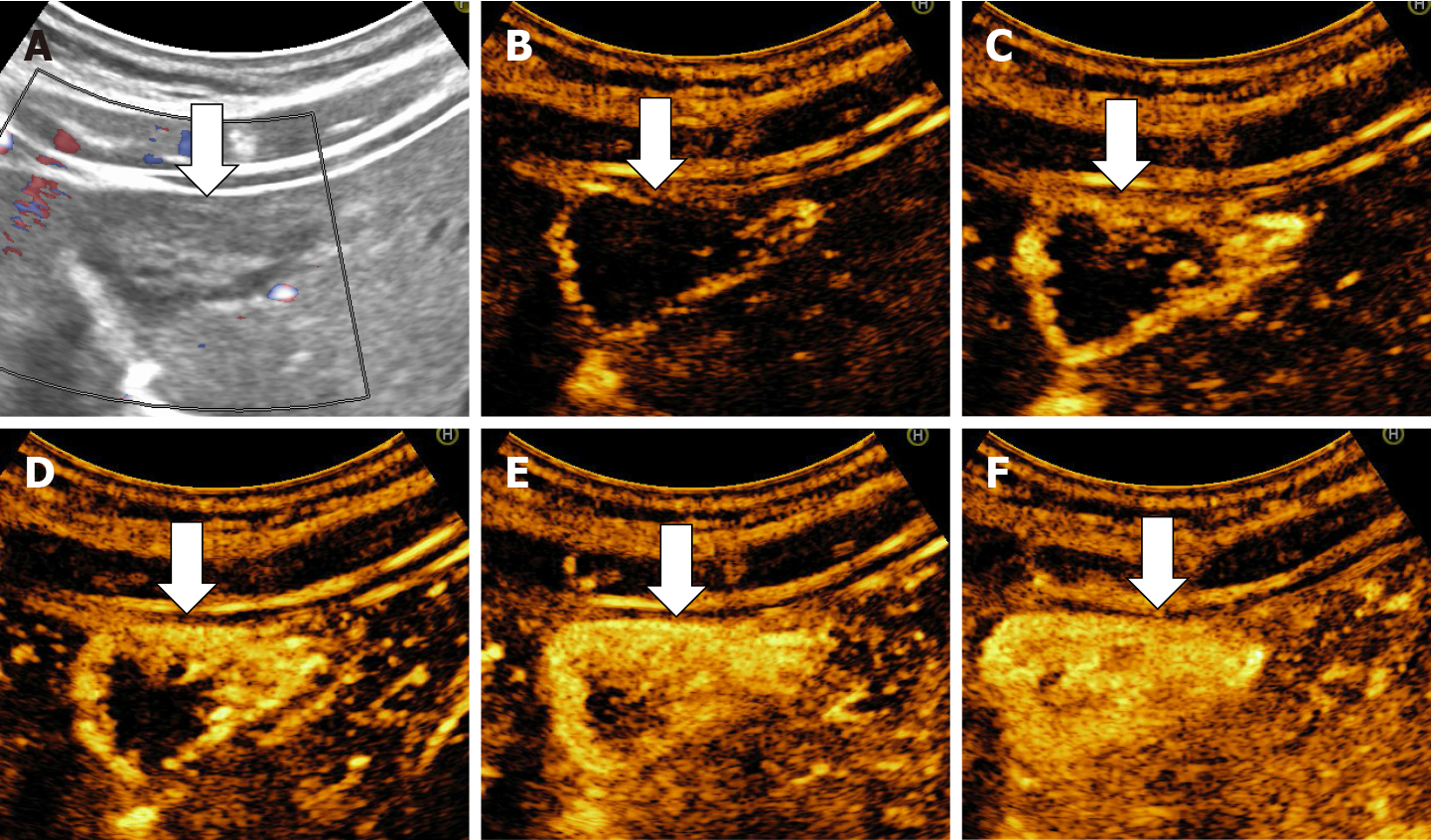
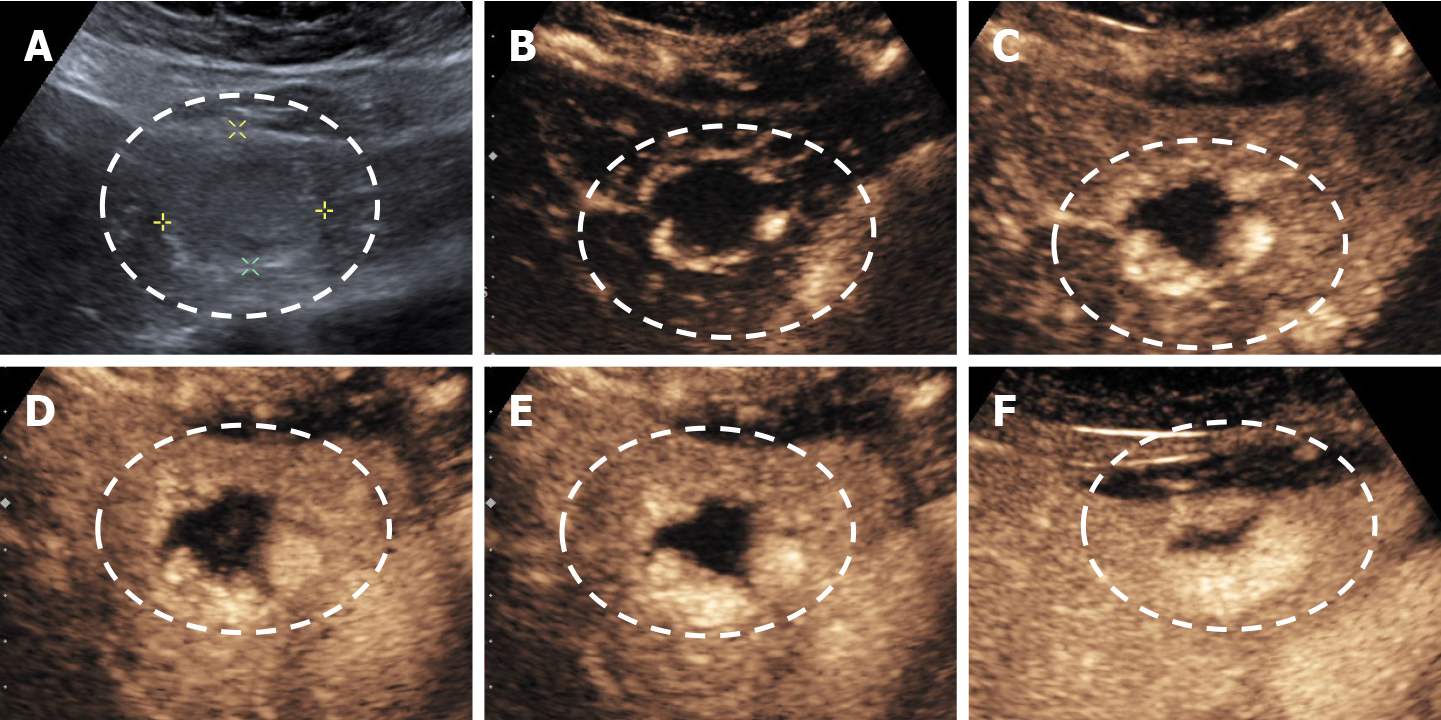
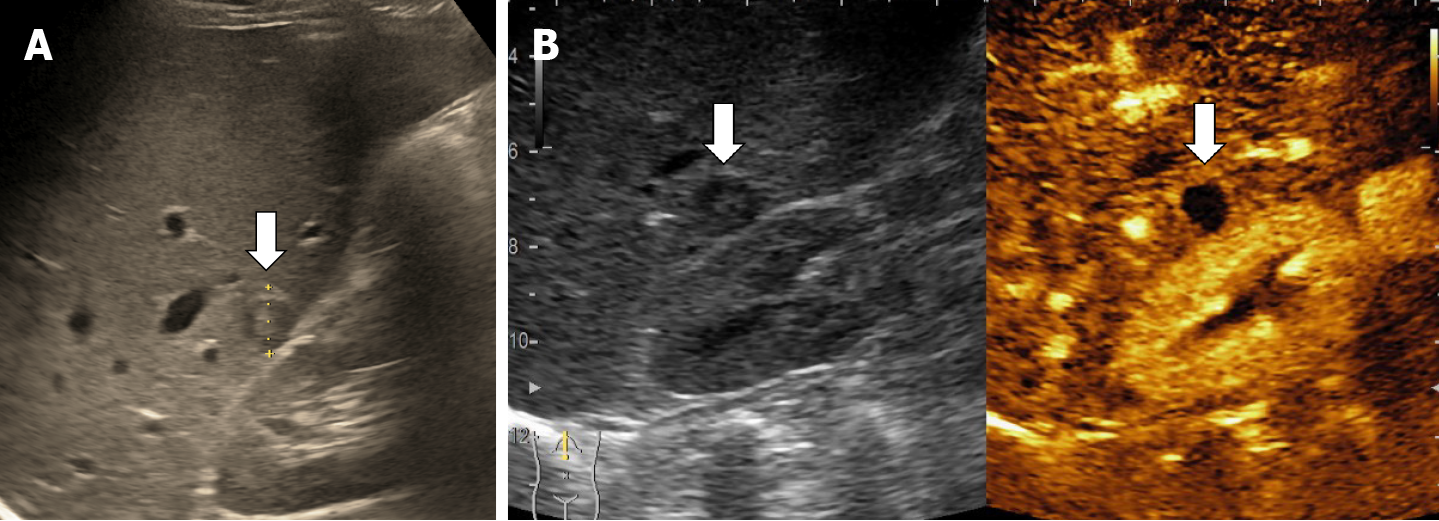
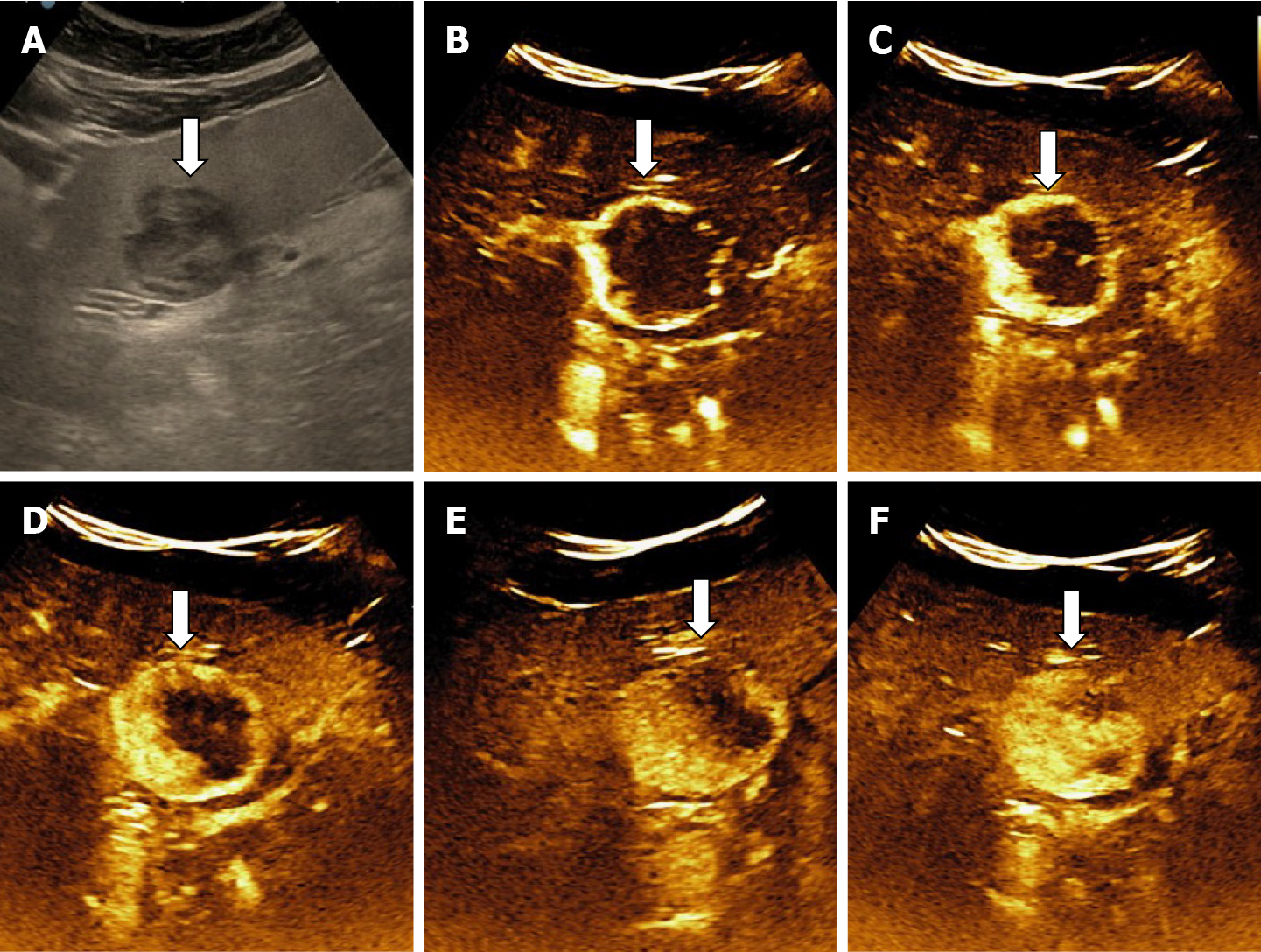
The classic sonographic appearance of hemangioma is that of a homogeneous hyperechoic mass, measuring less than 3 cm in diameter with acoustic enhancement and sharp margins[13] (Figure 2). Sometimes it outlines a central hypoechoic area (Figure 3). HHs does not have a peritumoral halo and pushes the hepatic vessels without their invasion or thrombosis (Figure 4). The acoustic enhancement is due to the blood content. When located subdiaphragmatically it produces the artifact "in the mirror" (Figure 5). The hyperechoic appearance is related to the interfaces between vascular space and the fibrous stroma[13]. HH is usualy homogenous mass, but at dimension > 5 cm may show inhomogeneous echogenicity probably because of intratumorally changes, such as thrombosis or fibrosis[14] (Figure 6). No intra-tumoral vessels are seen at color Doppler exam due very slow intralesional flows, but power Doppler technique is more sensitive in detecting blood flow[13] (Figure 7). This aspect is found in most cases of HHs and corresponds histologically to the cavernous hemangioma[14]. Most typical-looking hemangiomas measure less than 3 cm[13].
Contrast enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) can be performed immediately after standard ultrasound exam while focal liver lesion (FLL) is found, in the same session, using a dedicated contrast software. Currently, four contrast agents are used in the imaging assessment of FLLs[15,16].
Traditionally CEUS reveals tissue perfusion in real time, in all arterial, portal and late phases but a new contrast agent (Sonazoid) allows the assessment of an additional postvascular phase (Kupffer)[17].
The aspect of the capture in the arterial phase orients on the tumor type while the presence or absence of the wash-out in the late phase differentiates the benign tumors from the malignant masses[15,16]. For the diagnosis of HH the arterial phase is the most important. The typical CEUS feature of a hemangioma, regardless of the injected contrast agent, is peripheral nodular enhancement in the arterial phase with progressive centripetal partial or complete fill-in[16] in portal venous phase and complete enhancement in late phase (Figures 8 and 9). In the postvascular phase (specific for Levovist) hemangioma is isoenhancement or slight hypoenhancement relative to surrounding liver parenchyma[18]. The described appearance is highly suggestive of hemangioma. When the two hallmarks of haemangioma, peripheral pools and centripetal progression, are present the diagnosis of HH is most likely, the specificity of the method approaching 100% in most studies[19,20].
Not all hemangiomas have typical enhancement, thus, the overall sensitivity of CEUS for diagnosis of hemangioma is lower than specificity, approximately 86% (95% confidence interval: 81%-92%) according to a meta-analysis including 612 cases from 20 studies[20]. As the years passed, the equipment evolved, and the examiners gained more experience. Recent multicenter European studies, each with over 1000 examined FLL, reveal that CEUS correctly diagnosed 85%-90% of hemangiomas[21-24] and if a computerized image analysis is added the diagnostic accuracy reaches 93.3%[25]. Moreover, there are studies that demonstrate CEUS to be approximately equal to the computed tomography (CT)-scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) regarding to assessment of tumor differentiation and specification of newly discovered liver tumors in clinical practice, including for HH[26,27].
Because it is a proven method, WFUMB (World Federation for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology) Guidelines for CEUS in the liver — update 2020 recommends CEUS as the first line imaging technique for the characterization of incidentally, indeterminate FLLs at ultrasound in patients with non-cirrhotic liver and no history or clinical suspicion of malignancy[15]. Similarly, the EASL (European Association for the Study of the Liver) Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of benign liver tumors recommends CEUS or another contrast imaging method (CT, MR) when in B-mode ultrasound the appearance is atypical, or when the lesion occurs in cancer patients or those with underlying liver disease[1].
The advantages of CEUS are related to the immediate availability in the ultrasound room where the lesion was detected, the real-time visualization of the tumor perfusion, non-ionizing technique and low financial costs[28,29]. Moreover, sonographic contrast agents have only a few contraindications and precautions, can be used regardless of renal and thyroid impairment and have excellent safety profiles[30].
There are few disadvantages of CEUS as compared to other imaging techniques: the dependence on the experience of the sonographer and providing only limited information in patients with high body mass index or bowel gas overlay. As a specific disadvantage for the diagnosis of hemangioma, CEUS with SonoVue cannot appreciate the very late phase of HH because the contrast substance is eliminated by breathing in about 5-6 min after injection.
In some cases, the phenomenon of pseudo-washout in the late phase observed due to hyperinsonation may induce differential diagnosis issues with malignant lesions but the typical appearance of the arterial phase is enough in clinical practice for a correct diagnosis of hemangioma (Figure 10).
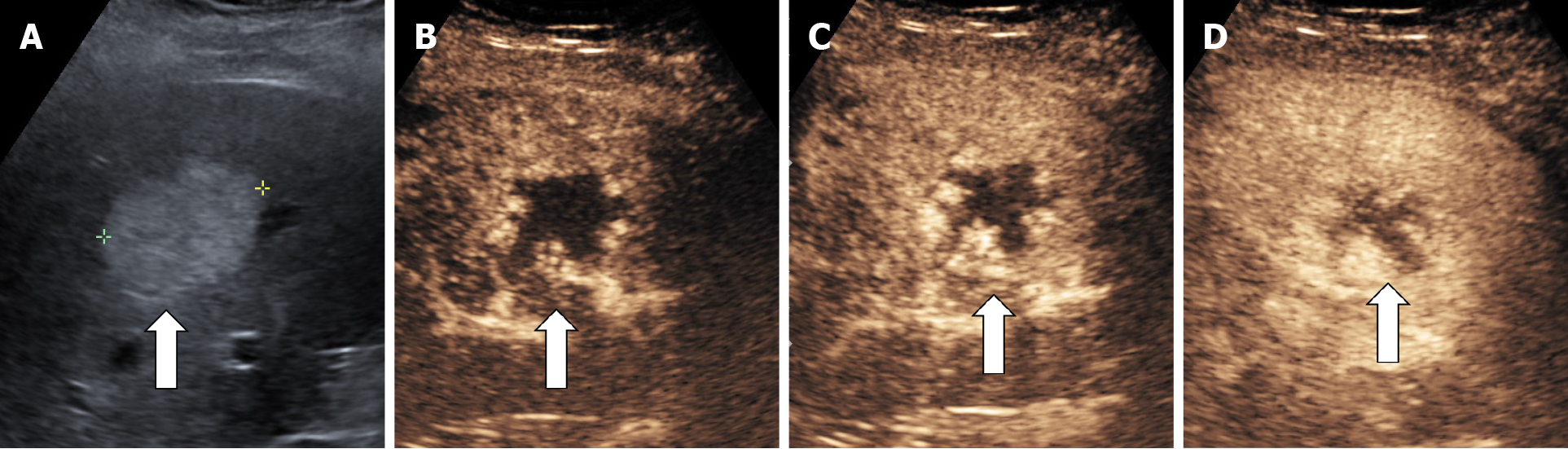
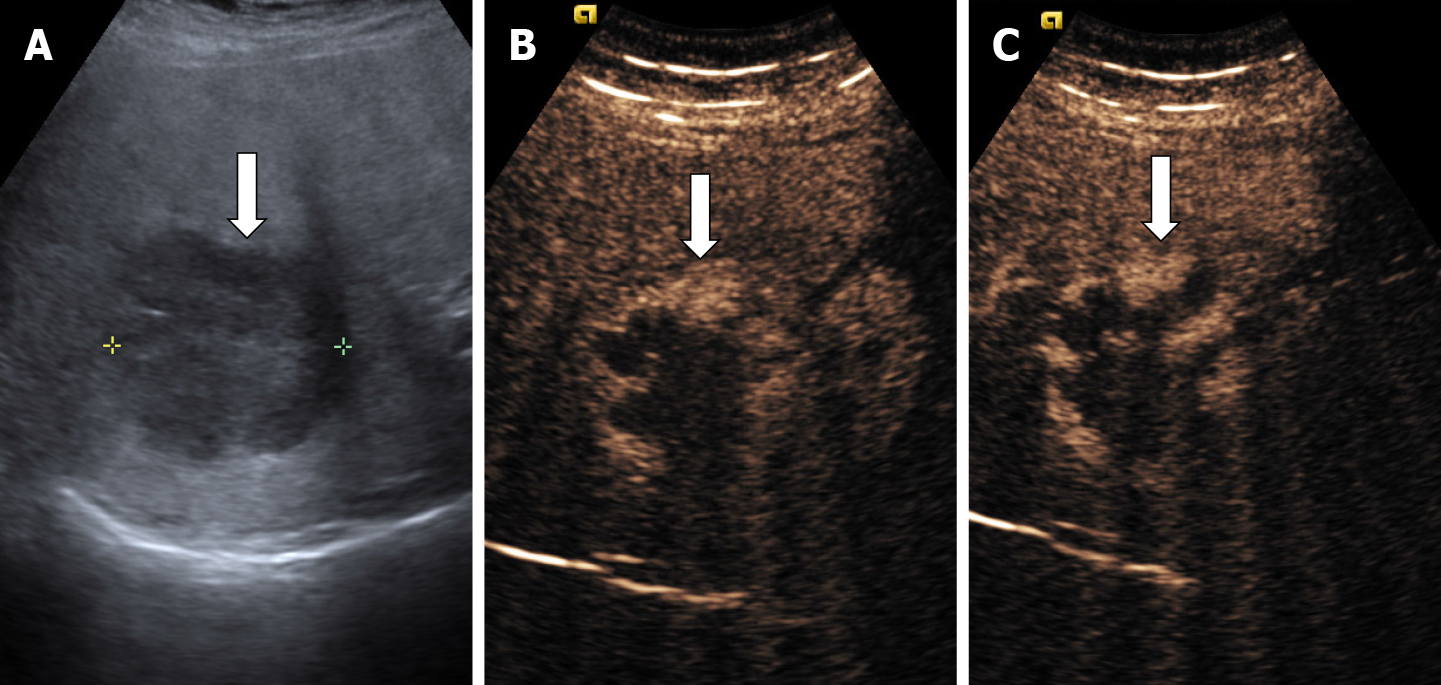
The diagnosis of HH is relatively easy if typical peripheral nodular enhancement with subsequent central fill-in is present. In about 16% of all hemangiomas, however, there is a rapid, uniform and intense homogeneous enhancement in the arterial phase, more often in small hemangiomas (42% are under 1 cm in size)[13,31]. The homogeneous enhancement persists into the portal and late phases (Figure 11).
The mechanism of the enhancement is not clearly understood. The large proportion of small-sized hemangiomas with this type of loading suggests that this pattern may be due to a difference between blood spaces: the smaller the lesion, the more rapid is the spread of contrast agent within[31-33].
Rapidly filling hemangiomas could be difficult to be differentiated from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and hypervascular liver metastases because they exhibit hypervascularity during the hepatic arterial phase. In the late phase, HH remains isoenhanced while metastases and most HCC show a typical washout of contrast agent during the portal and delayed phases. Differentiation remains difficult between small and well-differentiated HH and HCC, which do not show wash-out in the late phase[34].
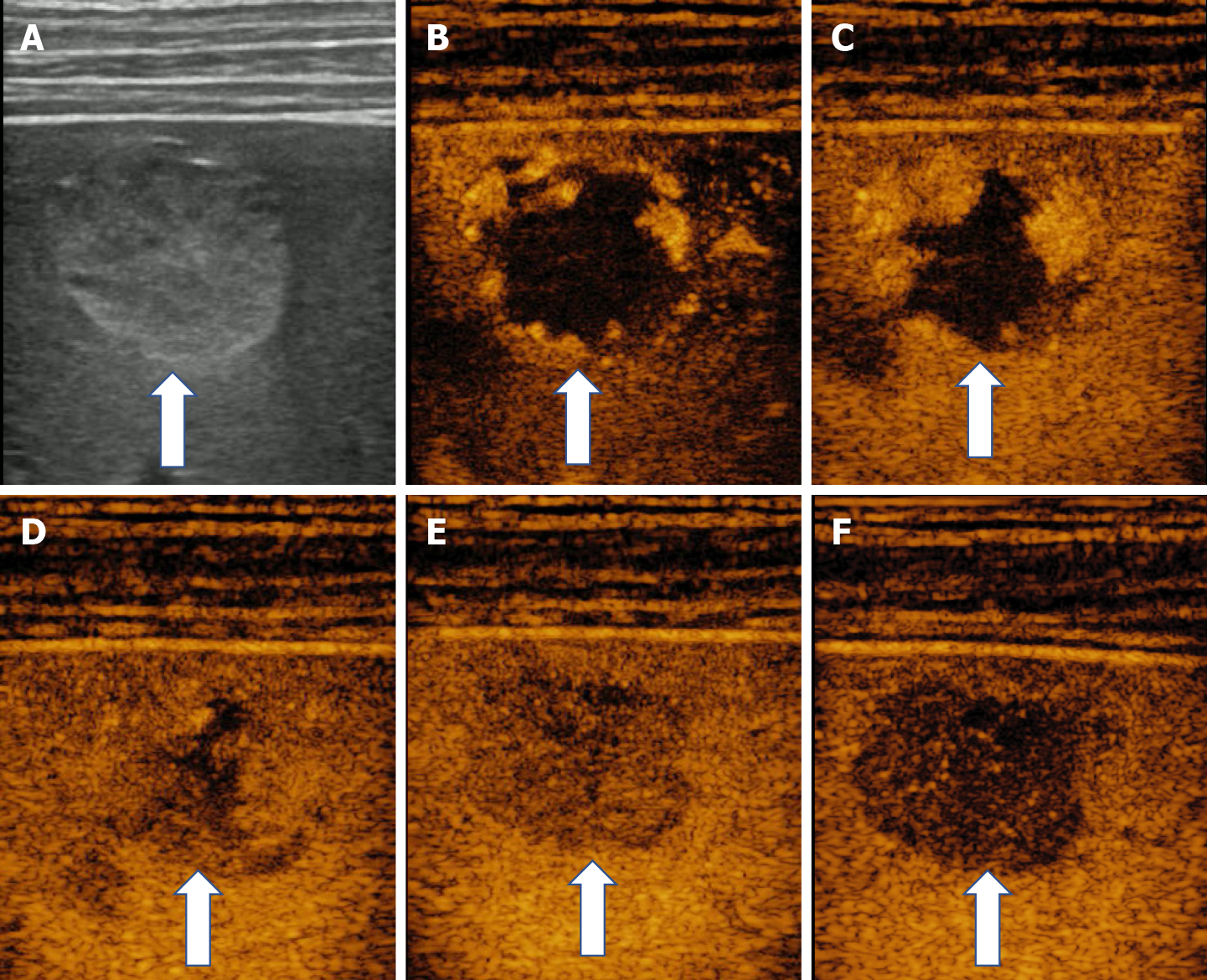
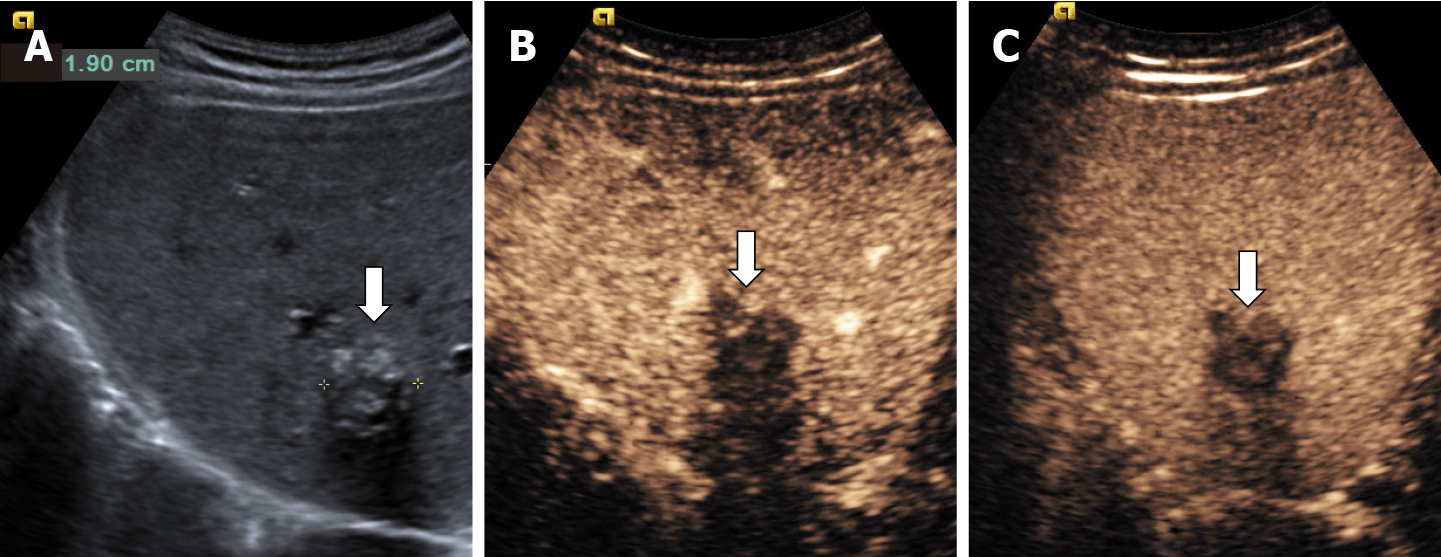
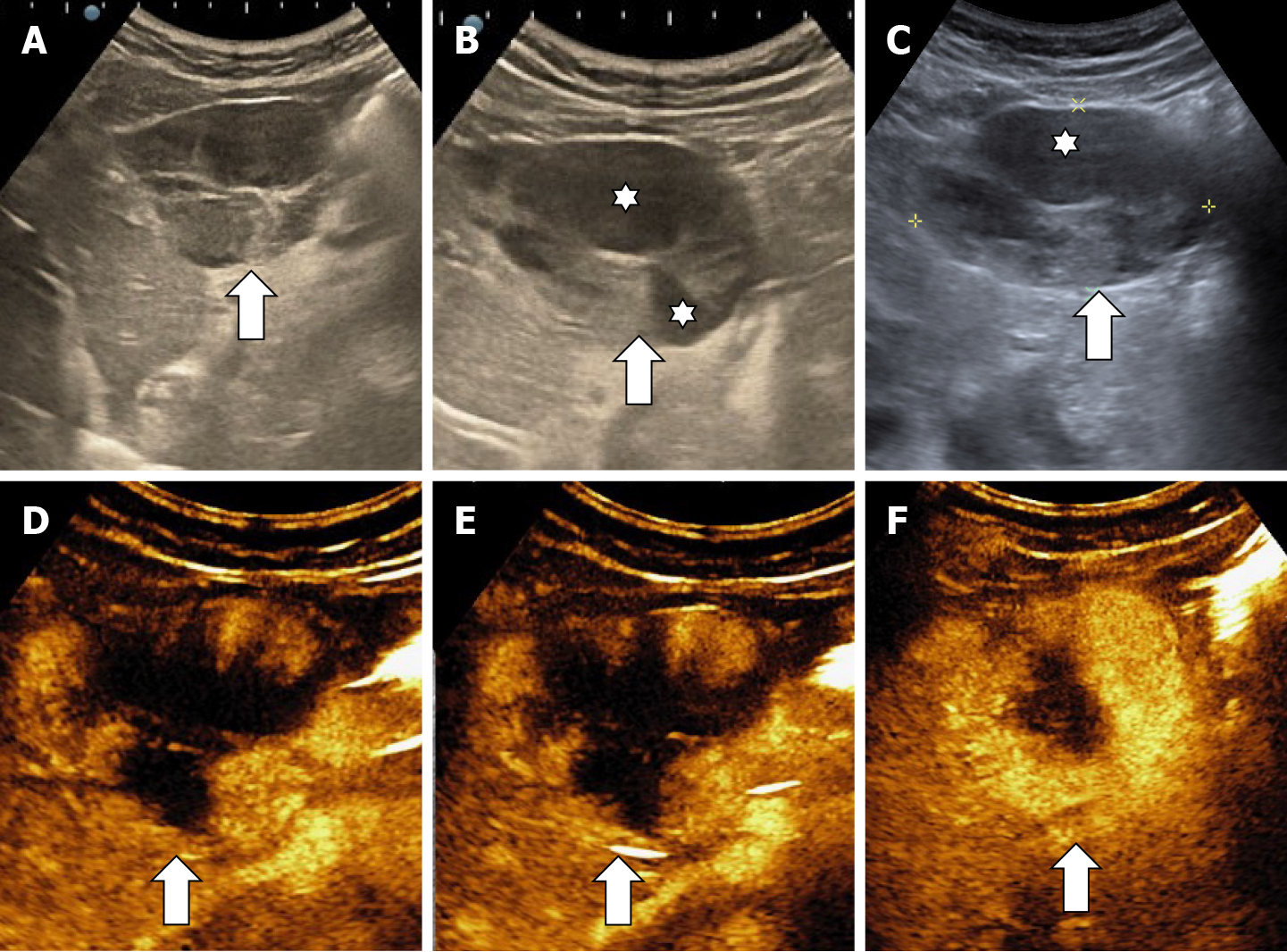
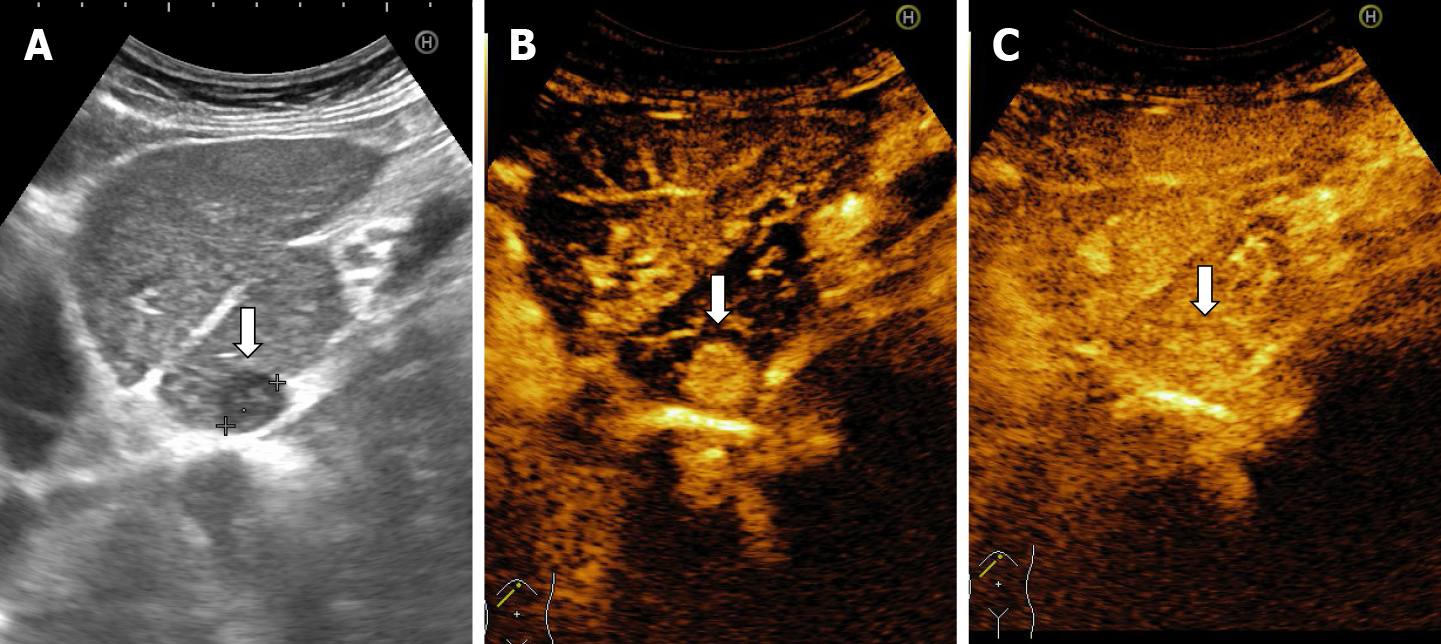
In some cases (up to 15% of cases) HH has an echoic border, which is seen as a thick echoic rind or a thin echoic rim (Figure 12)[35]. The central part of the lesion has low echogenicity due to previous hemorrhagic necrosis, scarring, or myxomatous changes. On CEUS this type of HH often shows the typical pattern of enhancement so that the diagnosis can be made easily (Figure 13)[32,36].
When the HH is predominantly fibrosed with near complete loss of the vascular spaces it is called ‘sclerosed/hyalinized’ while partially affected lesions are called ‘sclerosing/hyalinizing’ hemangiomas[13,32].
At ultrasound exam, sclerosed hemangioma are heterogeneous in echotexture with predominantly hypoechoic areas from sclerosis and geographic pattern [37]. When placed subcapsular HH causes capsular retraction. If the patient has been known for several years with HH and the images are evaluated dynamically, a reduction in size of the lesion over time can be observed[37].
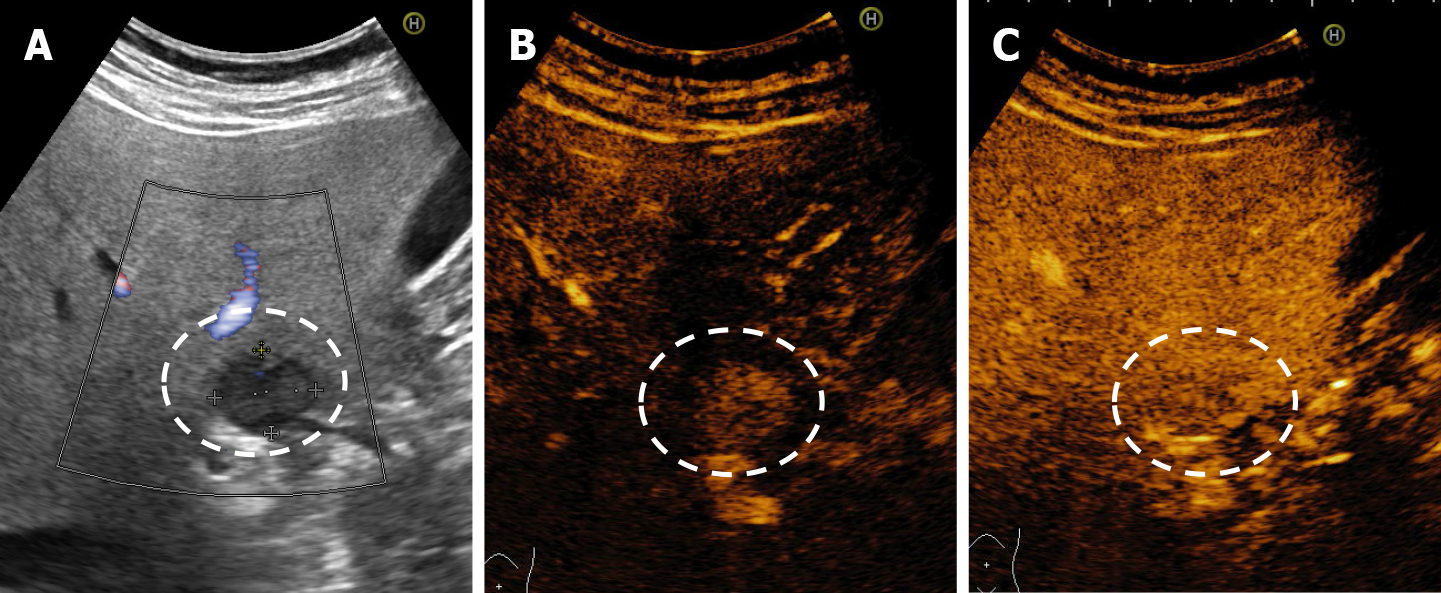
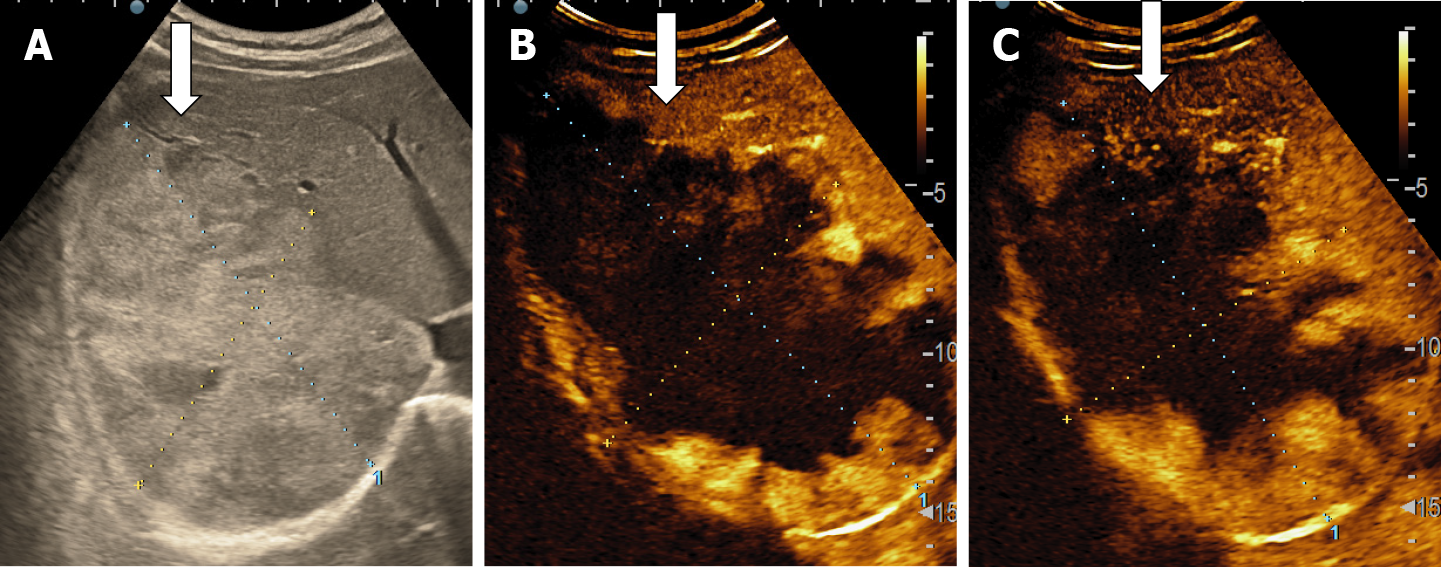
In CEUS three patterns may be observed: no enhancement, persistent irregular ring enhancement and lack of early enhancement with slight peripheral enhancement in the late phase[33,38,39] (Figure 14). These enhancement patterns create differential diagnosis issues with the intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and liver metastasis[40]. In a case report, reinjection of Sonasoid helped in the discriminate between the two entities[41].
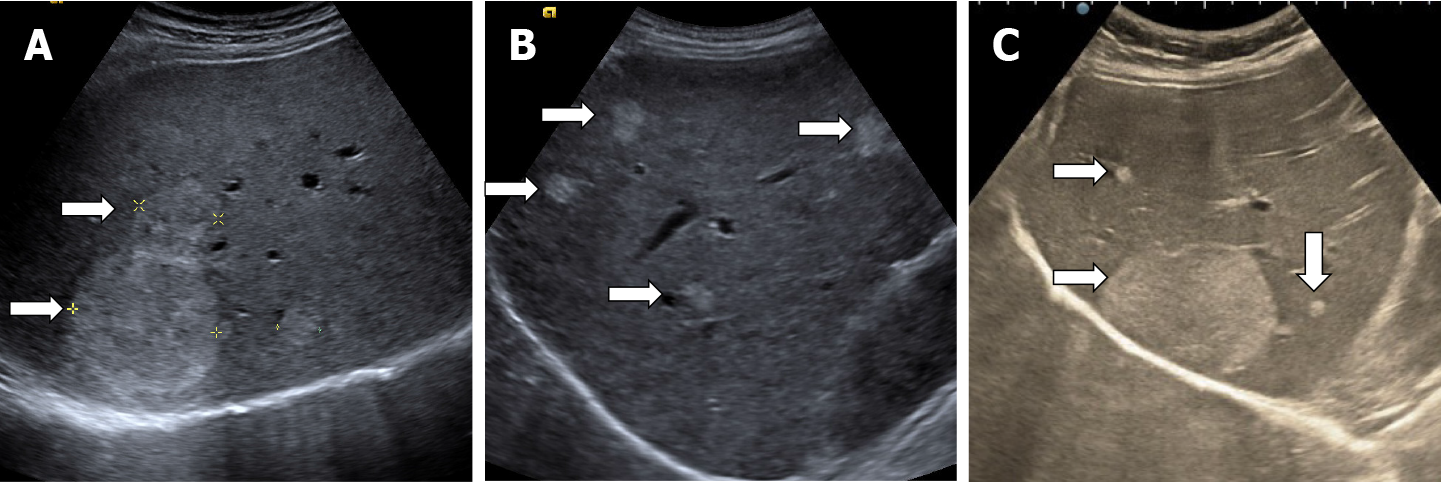
In very rare cases, although the tissue is soft, HHs may have calcifications. It can appear in the marginal or central part of the lesion. There may be several spotted calcifications, which correspond to phleboliths or large coarse calcifications[13]. On post-contrast administration, calcified hemangiomas may appear poorly or no enhanced as the calcifications do not show enhancement[37] (Figure 15).
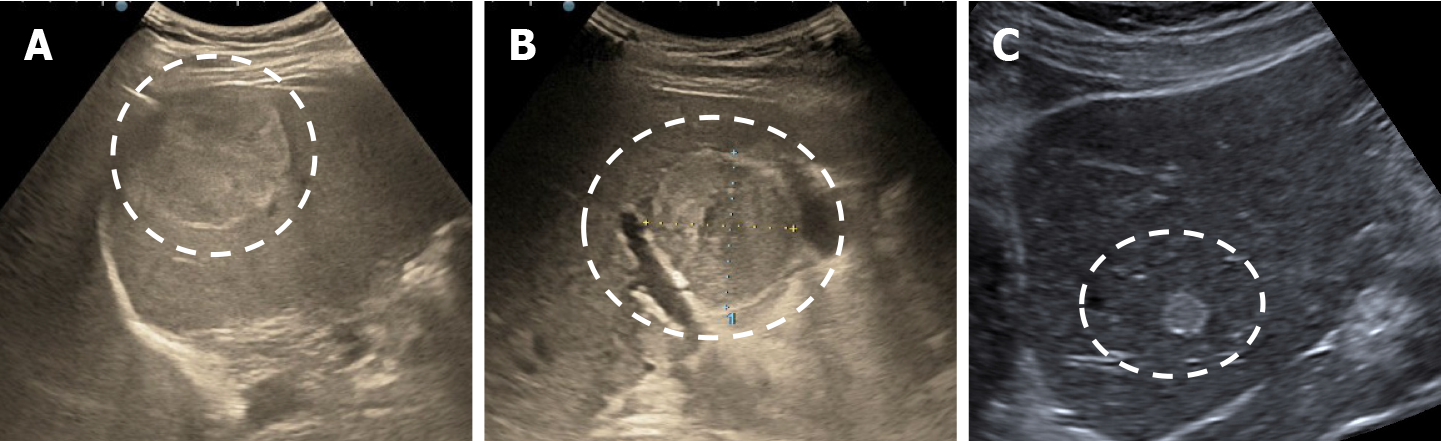
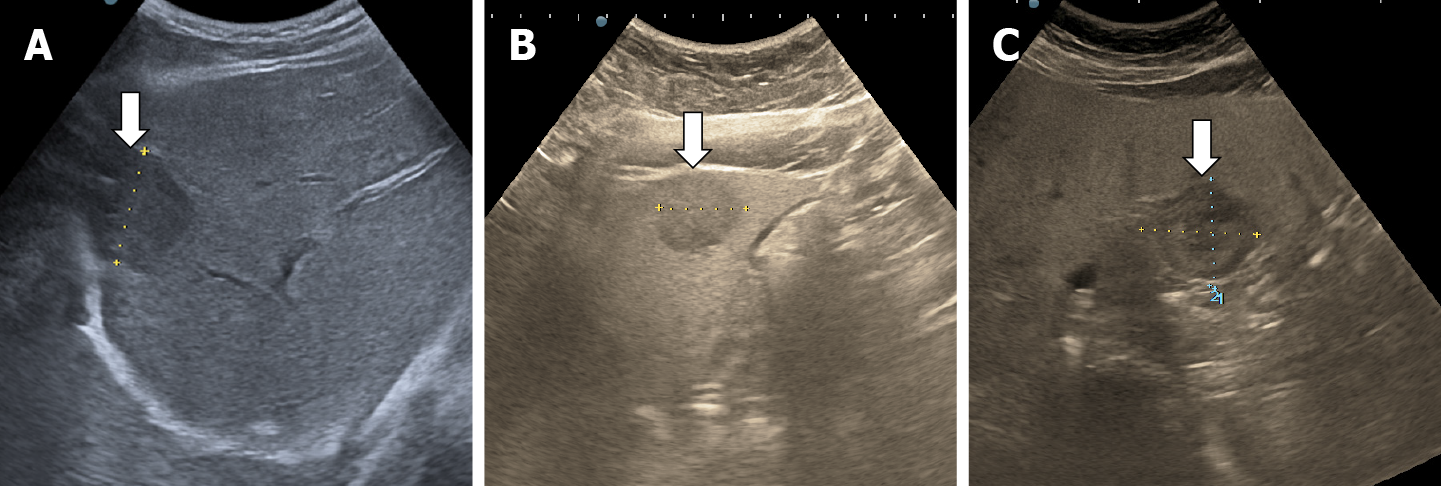
The majority of the authors define giant hemangiomas as lesions greater 12 cm in diameter[32,33,37]. On B-mode ultrasound, large hemangiomas often appear intense heterogeneous. After intravenous administration of contrast agent, the typical early, peripheral, globular enhancement is observed. However, during the venous and delayed phases, the progressive centripetal enhancement of the lesion is present but does not lead to complete filling[13,42] (Figure 16).
Represents a very rare aspect of HH, cited in only few case reports[43-45]. On B-mode ultrasound appears as inhomogeneous lesion with a large central cavity that contains fluid and possible septa[13,46]. This type of hemangioma could originate from cystic degeneration caused by central thrombosis and hemorrhage[32]. The fluid cystic cavities appear anechoic on US or with hyperechoic material suggesting previous internal hemorrhage. In our experience, the typical early, peripheral, globular enhancement is observed, without centripetal progression of enhancement and the septa could have contrast enhancement as well (Figure 17). Although the appearance of B-mode ultrasound creates differential diagnosis issues with mucinous cystic neoplasm (biliary cystadenoma or cystadenocarcinoma)[47], epithelioid hemangioendothelioma[48] or angiosarcoma[49], CEUS directs the diagnosis to hemangioma.
HHs may be multiple in 10%-50% of cases[13]. In standard ultrasound multiple HH has hyperechoic, variable in size, well delimited (Figure 18). The presence of multiple FLLs in B-mode ultrasound has to be differentiated from liver metastases or other multiple malignancies.
Hemangiomatosis, also called diffuse hepatic hemangiomatosis (DHH), is a rare condition characterized by innumerable HHs distributed in the liver parenchyma[13]. In B-mode ultrasound the lesions appear frequently hyperechoic or hypoechoic and the boundary of the lesions is usually ill-defined as compared to multiple HH where the lesions are well delineated. DHH is more frequently seen in newborns where the entire liver is usually involved but uncommon cases of isolated DHH without extrahepatic involvement may be seen in the adult population (about 17 cases in the literature)[14,50].
Hepatic hemangiomatosis may present as two forms, a multinodular pattern consisting of multiple small discrete and coalescent nodules, and a diffuse pattern consisting of innumerable poorly defined lesions, with a tendency to confluence, replacing almost all of the liver[14]. To our knowledge, the appearance of DHH in contrast ultrasound has not yet been reported. In our experience, in DHH with multiple, small LFHs, the loading is of the “flashfilling” type (Figure 19).
The incidence of liver steatosis has increased in recent years and HHs no longer have the typical ultrasound appearance in a hyperechoic liver. Most often they are isoechoic, or hypoechoic relative to a hyperechoic, fatty liver[13]. In some cases, the area surrounding the hemangioma appears hypoechoic and resembles a halo, an appearance termed a ''pseudohalo''[51] (Figure 20). Fortunately, in CEUS HH in fatty liver show a typical enhancement pattern of cavernous or flash-filling hemangioma[52-54] (Figure 21).
HHs in cirrhotic liver are uncommon compared to their incidence in non-cirrhotic liver[55]. It appears that the process of cirrhosis (necrosis and fibrosis) obliterates existing hemangiomas. In B-mode ultrasound, HH in cirrhotic liver had an atypical appearance, are often solitary and small in size[13,37,55] difficult to be differentiated from dysplastic nodules and HCC. In CEUS, the enhancement pattern of a cavernous hemangiomas (Figure 22) is enough for diagnosis but flash-filling enhancement of a HH is similar to the enhancement of an HCC in the arterial phase (Figure 23)[56]. Therefore, in the case of an FLL with a hyperenhancement appearance in the arterial phase, it is necessary to complete the imaging assessment.
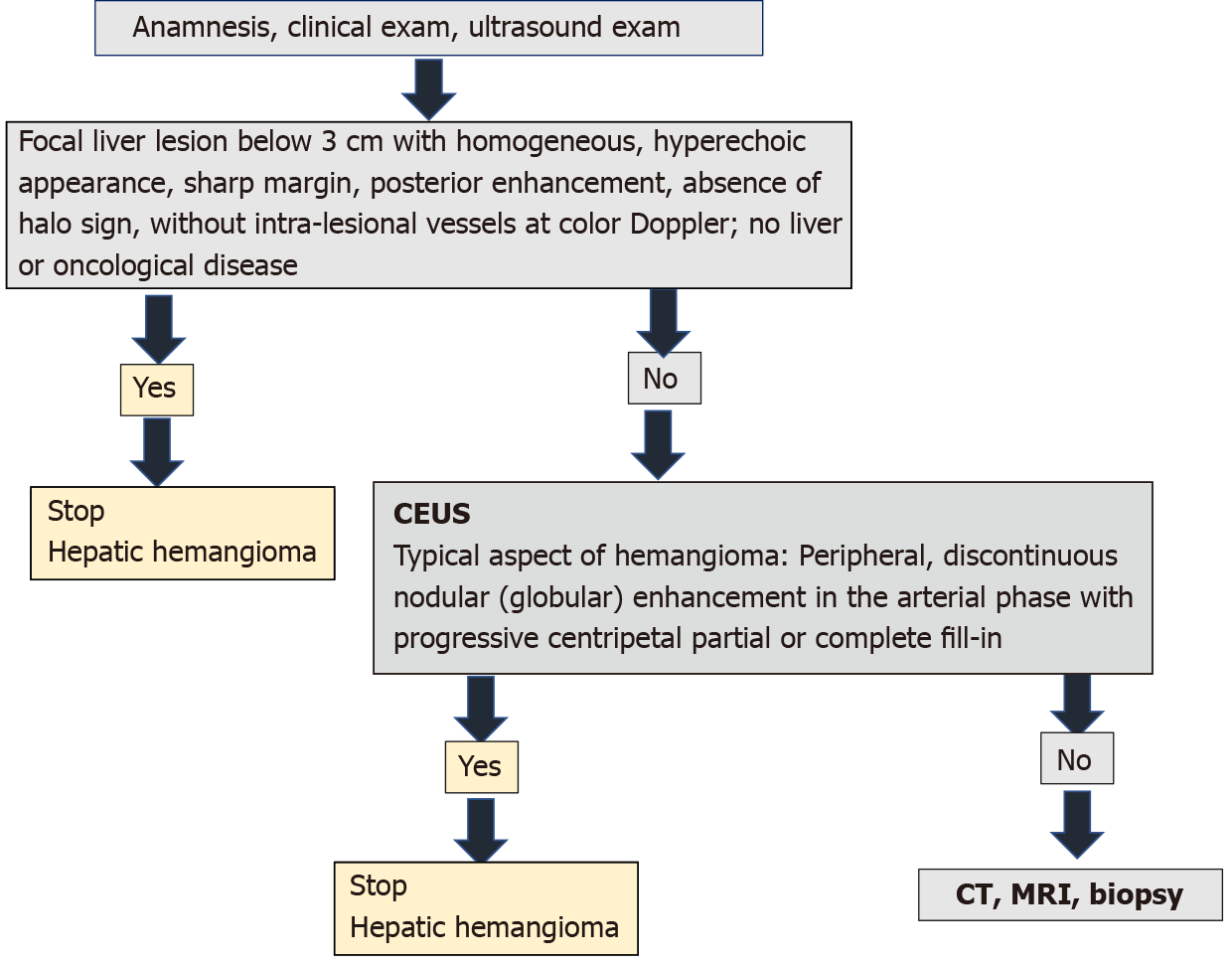
Ultrasound has been introduced into clinical practice for over 50 years. Contrast ultrasound after more than 15 years of use has been shown to provide more information than standard ultrasound in the diagnosis of liver tumors. In several countries, the hepatologist also practices ultrasonography. Thus, it has the possibility to complete on the spot the information obtained through anamnesis and clinical examination with imaging data. In an asymptomatic adult patient, without liver or oncological disease, the detection on standard ultrasound of a FLL below 3 cm with homogeneous hyperechoic appearance, sharp margin, posterior enhancement, absence of halo sign, without intra-tumoral vessels at colour Doppler directs the diagnosis to HH and does not require further investigation[1,16]. However, if ultrasound shows a lesion with features other than those described, measures over 3 cm or has been detected in oncology patients or those with underlying liver disease, contrast enhanced imaging (CEUS, CT or MRI) is required[1]. EFSUMB Guidelines for CEUS in the liver — update 2020 recommends CEUS as the first step[16]. CEUS can be performed immediately after standard ultrasound in the consulting room, without the need to assess renal function as needed in the administration of contrast agents for CT/MRI. Studies to date have shown that CEUS has similar performance to computed tomography or MRI in the diagnosis of HH. The cost is lower[28,29,57,58], no irradiation and the contrast agent administered has lower toxic and allergic effects. A typical aspect of hemangioma in contrast ultrasound (peripheral and globular enhancement on arterial phase followed by a central enhancement on delayed phases) guides the diagnosis in a maximum of 30 min, stops further investigations and provides mental comfort to the patient. According to studies, this strategy includes approximately 85%-90% of patients[21-24]. If the appearance in the CEUS is not typical, the patient must be scheduled for further investigations. This diagnostic algorithm is applicable to the adult patient in countries where the hepatologist has an ultrasonography system equipped with CEUS software in the consulting room. CEUS saves time, is cost effective and non-invasive.
To our knowledge it is the first article to illustrate the typical and atypical aspects of HH in the adult patient by B-mode ultrasound along with CEUS. It is also for the first time when an algorithm for diagnosing HH is proposed in the consulting room, adapted according to the latest guidelines of EASL and WFUMB (Figure 24).
In conclusion, standard and contrast-enhanced ultrasound examination in a clinical context guides the diagnosis of HH in most patients.
Provenance and peer review: Invited article; Externally peer reviewed.
Peer-review model: Single blind
Specialty type: Gastroenterology and hepatology
Country/Territory of origin: Romania
Peer-review report’s scientific quality classification
Grade A (Excellent): A
Grade B (Very good): 0
Grade C (Good): 0
Grade D (Fair): 0
Grade E (Poor): 0
P-Reviewer: Shi GQ S-Editor: Gao CC L-Editor: A P-Editor: Gao CC
| 1. | European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL). EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines on the management of benign liver tumours. J Hepatol. 2016;65:386-398. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 286] [Cited by in RCA: 325] [Article Influence: 36.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (2)] |
| 2. | Rungsinaporn K, Phaisakamas T. Frequency of abnormalities detected by upper abdominal ultrasound. J Med Assoc Thai. 2008;91:1072-1075. [PubMed] |
| 3. | Kaltenbach TE, Engler P, Kratzer W, Oeztuerk S, Seufferlein T, Haenle MM, Graeter T. Prevalence of benign focal liver lesions: ultrasound investigation of 45,319 hospital patients. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016;41:25-32. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 81] [Cited by in RCA: 97] [Article Influence: 10.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 4. | Kamyab AA, Rezaei-Kalantari K. Hepatic Hemangioma in a Cluster of Iranian Population. J Med Ultrasound. 2019;27:97-100. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 5. | Horta G, López M, Dotte A, Cordero J, Chesta C, Castro A, Palavecino P, Poniachik J. [Benign focal liver lesions detected by computed tomography: Review of 1,184 examinations]. Rev Med Chil. 2015;143:197-202. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 17] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 6. | Reddy KR, Kligerman S, Levi J, Livingstone A, Molina E, Franceschi D, Badalamenti S, Jeffers L, Tzakis A, Schiff ER. Benign and solid tumors of the liver: relationship to sex, age, size of tumors, and outcome. Am Surg. 2001;67:173-178. [PubMed] |
| 7. | Moser C, Hany A, Spiegel R. [Familial giant hemangiomas of the liver. Study of a family and review of the literature]. Praxis (Bern 1994). 1998;87:461-468. [PubMed] |
| 8. | Glinkova V, Shevah O, Boaz M, Levine A, Shirin H. Hepatic haemangiomas: possible association with female sex hormones. Gut. 2004;53:1352-1355. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 103] [Cited by in RCA: 96] [Article Influence: 4.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 9. | Mori H, Ikegami T, Imura S, Shimada M, Morine Y, Kanemura H, Arakawa Y, Kanamoto M, Hanaoka J, Sugimoto K, Tokunaga T. Sclerosed hemangioma of the liver: Report of a case and review of the literature. Hepatol Res. 2008;38:529-533. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 20] [Cited by in RCA: 21] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 10. | Wakasugi M, Ueshima S, Tei M, Tori M, Yoshida K, Tsujimoto M, Akamatsu H. Multiple hepatic sclerosing hemangioma mimicking metastatic liver tumor successfully treated by laparoscopic surgery: Report of a case. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015;8C:137-140. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 12] [Article Influence: 1.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 11. | Sadick M, Müller-Wille R, Wildgruber M, Wohlgemuth WA. Vascular Anomalies (Part I): Classification and Diagnostics of Vascular Anomalies. Rofo. 2018;190:825-835. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 59] [Cited by in RCA: 104] [Article Influence: 14.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 12. | Gandolfi L, Leo P, Solmi L, Vitelli E, Verros G, Colecchia A. Natural history of hepatic haemangiomas: clinical and ultrasound study. Gut. 1991;32:677-680. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 153] [Cited by in RCA: 124] [Article Influence: 3.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 13. | Vilgrain V, Brancatelli G. Liver hemangioma. In: Cioni LL, Bartolozzi C. Focal Liver Lesions. Detection, Characterization, Ablation. Springer: Verlag Berlin Heidelberg, 2005: 101-117. |
| 14. | Mamone G, Di Piazza A, Carollo V, Cannataci C, Cortis K, Bartolotta TV, Miraglia R. Imaging of hepatic hemangioma: from A to Z. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020;45:672-691. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 13] [Article Influence: 2.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 15. | Dietrich CF, Nolsøe CP, Barr RG, Berzigotti A, Burns PN, Cantisani V, Chammas MC, Chaubal N, Choi BI, Clevert DA, Cui X, Dong Y, D'Onofrio M, Fowlkes JB, Gilja OH, Huang P, Ignee A, Jenssen C, Kono Y, Kudo M, Lassau N, Lee WJ, Lee JY, Liang P, Lim A, Lyshchik A, Meloni MF, Correas JM, Minami Y, Moriyasu F, Nicolau C, Piscaglia F, Saftoiu A, Sidhu PS, Sporea I, Torzilli G, Xie X, Zheng R. Guidelines and Good Clinical Practice Recommendations for Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) in the Liver-Update 2020 WFUMB in Cooperation with EFSUMB, AFSUMB, AIUM, and FLAUS. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2020;46:2579-2604. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 291] [Cited by in RCA: 287] [Article Influence: 57.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 16. | Lee JY, Minami Y, Choi BI, Lee WJ, Chou YH, Jeong WK, Park MS, Kudo N, Lee MW, Kamata K, Iijima H, Kim SY, Numata K, Sugimoto K, Maruyama H, Sumino Y, Ogawa C, Kitano M, Joo I, Arita J, Liang JD, Lin HM, Nolsoe C, Gilja OH, Kudo M. The AFSUMB Consensus Statements and Recommendations for the Clinical Practice of Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound using Sonazoid. Ultrasonography. 2020;39:191-220. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 29] [Cited by in RCA: 73] [Article Influence: 14.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 17. | Barr RG, Huang P, Luo Y, Xie X, Zheng R, Yan K, Jing X, Xu H, Fei X, Lee JM. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of the liver: a review of the clinical evidence for SonoVue and Sonazoid. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2020;45:3779-3788. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 55] [Cited by in RCA: 49] [Article Influence: 9.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 18. | Sugimoto K, Moriyasu F, Saito K, Yoshiara H, Imai Y. Kupffer-phase findings of hepatic hemangiomas in contrast-enhanced ultrasound with sonazoid. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2014;40:1089-1095. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 14] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 1.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 19. | Soussan M, Aubé C, Bahrami S, Boursier J, Valla DC, Vilgrain V. Incidental focal solid liver lesions: diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound and MR imaging. Eur Radiol. 2010;20:1715-1725. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 51] [Cited by in RCA: 42] [Article Influence: 2.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 20. | Friedrich-Rust M, Klopffleisch T, Nierhoff J, Herrmann E, Vermehren J, Schneider MD, Zeuzem S, Bojunga J. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for the differentiation of benign and malignant focal liver lesions: a meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2013;33:739-755. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 83] [Cited by in RCA: 93] [Article Influence: 7.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 21. | Sporea I, Săndulescu DL, Şirli R, Popescu A, Danilă M, Spârchez Z, Mihai C, Ioaniescu S, Moga T, Timar B, Brisc C, Nedelcu D, Săftoiu A, Enăchescu V, Badea R. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound for the Characterization of Malignant vs Benign Focal Liver Lesions in a Prospective Multicenter Experience - The SRUMB Study. J Gastrointestin Liver Dis. 2019;28:191-196. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 22. | Tranquart F, Le Gouge A, Correas JM, Ladam Marcus V, Manzoni P, Vilgrain V, Aube C, Bellin MF, Chami L, Claudon M, Cuilleron M, Drouillard J, Gallix B, Lucidarme O, Marion D, Rode A, Tasu JP, Trillaud H, Fayault A, Rusch E, Giraudeau B. Role of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in the blinded assessment of focal lesions in comparison with MDCT and CEMRI: Results from a multicentre clinical trial. EJC Suppl. 2008;6:9-15. |
| 23. | Strobel D, Seitz K, Blank W, Schuler A, Dietrich C, von Herbay A, Friedrich-Rust M, Kunze G, Becker D, Will U, Kratzer W, Albert FW, Pachmann C, Dirks K, Strunk H, Greis C, Bernatik T. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the characterization of focal liver lesions--diagnostic accuracy in clinical practice (DEGUM multicenter trial). Ultraschall Med. 2008;29:499-505. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 194] [Cited by in RCA: 176] [Article Influence: 10.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 24. | Strobel D, Seitz K, Blank W, Schuler A, Dietrich CF, von Herbay A, Friedrich-Rust M, Bernatik T. Tumor-specific vascularization pattern of liver metastasis, hepatocellular carcinoma, hemangioma and focal nodular hyperplasia in the differential diagnosis of 1,349 Liver lesions in contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS). Ultraschall Med. 2009;30:376-382. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 133] [Cited by in RCA: 118] [Article Influence: 7.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 25. | Sugimoto K, Shiraishi J, Moriyasu F, Doi K. Computer-aided diagnosis of focal liver lesions by use of physicians' subjective classification of echogenic patterns in baseline and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Acad Radiol. 2009;16:401-411. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 23] [Article Influence: 1.4] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 26. | Schwarze V, Lindner F, Marschner C, Negrão de Figueiredo G, Rübenthaler J, Clevert DA. Single-center study: The diagnostic performance of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) for assessing focal splenic lesions compared to CT and MRI. Clin Hemorheol Microcirc. 2019;73:65-71. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 10] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 27. | Seitz K, Bernatik T, Strobel D, Blank W, Friedrich-Rust M, Strunk H, Greis C, Kratzer W, Schuler A. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) for the characterization of focal liver lesions in clinical practice (DEGUM Multicenter Trial): CEUS vs. MRI--a prospective comparison in 269 patients. Ultraschall Med. 2010;31:492-499. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 99] [Cited by in RCA: 103] [Article Influence: 6.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 28. | Westwood M, Joore M, Grutters J, Redekop K, Armstrong N, Lee K, Gloy V, Raatz H, Misso K, Severens J, Kleijnen J. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound using SonoVue® (sulphur hexafluoride microbubbles) compared with contrast-enhanced computed tomography and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for the characterisation of focal liver lesions and detection of liver metastases: a systematic review and cost-effectiveness analysis. Health Technol Assess. 2013;17:1-243. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 54] [Cited by in RCA: 109] [Article Influence: 9.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 29. | Sirli R, Sporea I, Martie A, Popescu A, Dănilă M. Contrast enhanced ultrasound in focal liver lesions--a cost efficiency study. Med Ultrason. 2010;12:280-285. [PubMed] |
| 30. | Piscaglia F, Bolondi L; Italian Society for Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology (SIUMB) Study Group on Ultrasound Contrast Agents. The safety of Sonovue in abdominal applications: retrospective analysis of 23188 investigations. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2006;32:1369-1375. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 596] [Cited by in RCA: 533] [Article Influence: 28.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 31. | Hanafusa K, Ohashi I, Himeno Y, Suzuki S, Shibuya H. Hepatic hemangioma: findings with two-phase CT. Radiology. 1995;196:465-469. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 107] [Cited by in RCA: 91] [Article Influence: 3.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 32. | Vilgrain V, Boulos L, Vullierme MP, Denys A, Terris B, Menu Y. Imaging of atypical hemangiomas of the liver with pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2000;20:379-397. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 319] [Cited by in RCA: 257] [Article Influence: 10.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 33. | Klotz T, Montoriol PF, Da Ines D, Petitcolin V, Joubert-Zakeyh J, Garcier JM. Hepatic haemangioma: common and uncommon imaging features. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2013;94:849-859. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 77] [Cited by in RCA: 71] [Article Influence: 5.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (1)] |
| 34. | Kim TK, Lee E, Jang HJ. Imaging findings of mimickers of hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2015;21:326-343. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 23] [Cited by in RCA: 25] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 35. | Moody AR, Wilson SR. Atypical hepatic hemangioma: a suggestive sonographic morphology. Radiology. 1993;188:413-417. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 67] [Cited by in RCA: 67] [Article Influence: 2.1] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 36. | Bartolotta TV, Midiri M, Quaia E, Bertolotto M, Galia M, Cademartiri F, Lagalla R. Liver haemangiomas undetermined at grey-scale ultrasound: contrast-enhancement patterns with SonoVue and pulse-inversion US. Eur Radiol. 2005;15:685-693. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 39] [Cited by in RCA: 43] [Article Influence: 2.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 37. | Mathew RP, Sam M, Raubenheimer M, Patel V, Low G. Hepatic hemangiomas: the various imaging avatars and its mimickers. Radiol Med. 2020;125:801-815. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 27] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 6.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 38. | Doyle DJ, Khalili K, Guindi M, Atri M. Imaging features of sclerosed hemangioma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:67-72. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 66] [Cited by in RCA: 75] [Article Influence: 4.2] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 39. | Akahoshi S, Yamamura K, Sato N, Oda E, Kinoshita K, Yuki H, Motohara T, Deguchi A, Komohara Y, Beppu T. A hepatic sclerosed hemangioma with drastic changes in contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2020;13:1252-1257. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 4] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 40. | Li T, Klar MM, Alawad M, Abdul R, Zahiruddin A, Salifu MO, McFarlane IM. Hepatic Sclerosing Hemangioma Mimicking Malignancy: A Case and Literature Review. Am J Med Case Rep. 2021;9:144-146. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 3] [Cited by in RCA: 3] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 41. | Ando Y, Ishigami M, Ishizu Y, Kuzuya T, Honda T, Hirooka Y. Utility of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography with perflubutane in evaluating indications for diagnostic percutaneous tumor biopsy in a case of hepatic sclerosed hemangioma. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2018;11:514-520. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 4] [Cited by in RCA: 7] [Article Influence: 1.0] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 42. | Maruyama M, Isokawa O, Hoshiyama K, Hoshiyama A, Hoshiyama M, Hoshiyama Y. Diagnosis and management of giant hepatic hemangioma: the usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. Int J Hepatol. 2013;2013:802180. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 13] [Cited by in RCA: 18] [Article Influence: 1.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 43. | Park JS, Kim GA, Shim JJ, Kim BS, Park SJ, Kim YW. Hepatic hemangioma presenting as a large cystic tumor. Korean J Intern Med. 2021;36:473-474. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 1] [Cited by in RCA: 1] [Article Influence: 0.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 44. | Hussain MZ, Ohtomo K, Hihara T, Uchiyama G, Ainoda T, Yamamoto M, Suda K. Multilocular cystic hemangioma: CT and MR appearance. Radiat Med. 1992;10:206-209. [PubMed] |
| 45. | Cha EY, Kim KW, Choi YJ, Song JS, Cho KJ, Lee MG. Multicystic cavernous haemangioma of the liver: ultrasonography, CT, MR appearances and pathological correlation. Br J Radiol. 2008;81:e37-e39. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 18] [Cited by in RCA: 15] [Article Influence: 0.9] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 46. | Hanazaki K, Koide N, Kajikawa S, Ushiyama T, Watanabe T, Adachi W, Amano J. Cavernous hemangioma of the liver with giant cyst formation: degeneration by apoptosis? J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2001;16:352-355. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 19] [Cited by in RCA: 19] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 47. | Uchiyama T, Akahane T, Watanabe M, Kitayama T, Ise H. [Case of giant liver cyst with angiogenesis mimicking hemangioma that was difficult to differentiate from cystadenocarcinoma of the liver]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi. 2008;105:1634-1639. [PubMed] |
| 48. | Arai J, Shimozuma Y, Otoyama Y, Sugiura I, Nakajima Y, Hayashi E, Kajiwara A, Omori R, Uozumi S, Miyashita M, Uchikoshi M, Doi H, Sakaki M, Wang T, Eguchi J, Ito T, Kurihara T, Munechika J, Gokan T, Saito K, Miura S, Tate G, Takimoto M, Yoshida H. Three cases of histologically proven hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma evaluated using a second-generation microbubble contrast medium in ultrasonography: case reports. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019;19:187. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 5] [Cited by in RCA: 5] [Article Influence: 0.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 49. | Raunkilde L, Brodersen LR, Rafaelsen SA. [Imaging of hepatic angiosarcoma]. Ugeskr Laeger. 2014;176:V01140046. [PubMed] |
| 50. | Batista A, Matos AP, Neta JO, Ramalho M. Diffuse Hepatic Hemangiomatosis in the Adult without Extra-hepatic Involvement: An Extremely Rare Occurrence. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2014;4:43. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Full Text (PDF)] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 8] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 51. | Ito H, Tsujimoto F, Nakajima Y, Igarashi G, Okamura T, Sakurai M, Nobuoka S, Otsubo T. Sonographic characterization of 271 hepatic hemangiomas with typical appearance on CT imaging. J Med Ultrason (2001). 2012;39:61-68. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 6] [Cited by in RCA: 6] [Article Influence: 0.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 52. | Liu GJ, Wang W, Xie XY, Xu HX, Xu ZF, Zheng YL, Liang JY, Moriyasu F, Lu MD. Real-time contrast-enhanced ultrasound imaging of focal liver lesions in fatty liver. Clin Imaging. 2010;34:211-221. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 12] [Cited by in RCA: 11] [Article Influence: 0.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 53. | Liu LP, Dong BW, Yu XL, Liang P, Zhang DK, An LC. Focal hypoechoic tumors of Fatty liver: characterization of conventional and contrast-enhanced ultrasonography. J Ultrasound Med. 2009;28:1133-1142. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 11] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 0.6] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 54. | Martie A, Bota S, Sporea I, Sirli R, Popescu A, Danila M. The contribution of contrast enhanced ultrasound for the characterization of benign liver lesions in clinical practice - a monocentric experience. Med Ultrason. 2012;14:283-287. [PubMed] |
| 55. | Dodd GD 3rd, Baron RL, Oliver JH 3rd, Federle MP. Spectrum of imaging findings of the liver in end-stage cirrhosis: Part II, focal abnormalities. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1999;173:1185-1192. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 85] [Cited by in RCA: 65] [Article Influence: 2.5] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 56. | Renzulli M, Brocchi S, Ierardi AM, Milandri M, Pettinari I, Lucidi V, Balacchi C, Muratori P, Marasco G, Vara G, Tovoli F, Granito A, Carrafiello G, Piscaglia F, Golfieri R. Imaging-based diagnosis of benign lesions and pseudolesions in the cirrhotic liver. Magn Reson Imaging. 2021;75:9-20. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 9] [Cited by in RCA: 9] [Article Influence: 2.3] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 57. | Romanini L, Passamonti M, Aiani L, Cabassa P, Raieli G, Montermini I, Martegani A, Grazioli L, Calliada F. Economic assessment of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for evaluation of focal liver lesions: a multicentre Italian experience. Eur Radiol. 2007;17 Suppl 6:F99-106. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 44] [Cited by in RCA: 46] [Article Influence: 2.7] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |
| 58. | Faccioli N, D'Onofrio M, Comai A, Cugini C. Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in the characterization of benign focal liver lesions: activity-based cost analysis. Radiol Med. 2007;112:810-820. [RCA] [PubMed] [DOI] [Full Text] [Cited by in Crossref: 34] [Cited by in RCA: 33] [Article Influence: 1.8] [Reference Citation Analysis (0)] |