Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1494-1511
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1494
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1494
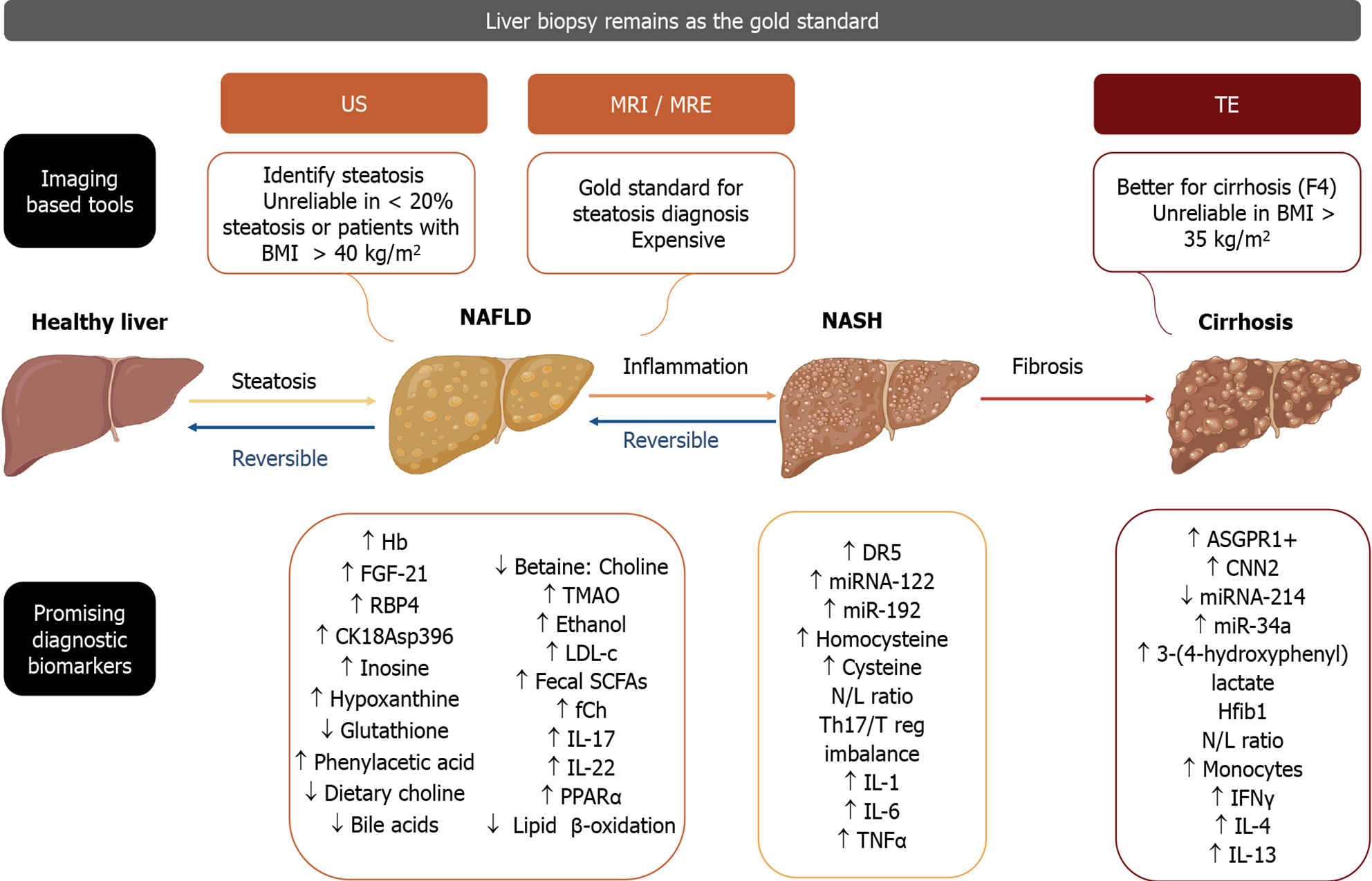
Figure 1 Although liver biopsy remains as the gold standard for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, other current imaging studies are shown, along with promising diagnostic and/or monitoring biomarkers that may be present in each of the stages of hepatic pathology, ranging from reversible steatosis and inflammation to irreversible fibrosis and eventually cirrhosis (Figure 1 created with BioRender.
com). US: Ultrasound; TE: Transient elastography; BMI: Body mass index; Hb: Hemoglobin; FGF-21: Fibroblast growth factor 21; RBP4: Retinol binding protein 4; CK18Asp396: Caspase cleaved cytokeratin-18 fragment; TMAO: Trimethylamine N-oxide; LDL-c: Low density lipoprotein cholesterol; Fecal SCFAs: Fecal Short chain fatty acids; fCh: Ferrochelatase; IL-17: Interleukin-17; IL-22: Interleukin-22; PPARα: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α; DR5: Death receptor 5; miRNA-122: MicroRNA 122; miR-192: MicroRNA 192; N/L ratio: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio; Th17/Treg imbalance: T helper 17/T regulatory cells imbalance; IL-1: Interleukin-1; IL-6: Interleukin-6; TNFα: Tumor necrosis factor alpha; ASGPR1+: Asialoglycoprotein receptor 1; CNN2: Calponin 2; miRNA-214: MicroRNA 214; miR-34a: MicroRNA 34a; Hfib1: Hepatic fibrosis 1; N/L ratio: Neutrophil/lymphocyte ratio; IFNγ: Interferon γ; IL-4: Interleukin-4; IL-13: Interleukin-13.
- Citation: Castillo-Castro C, Martagón-Rosado AJ, Ortiz-Lopez R, Garrido-Treviño LF, Villegas-Albo M, Bosques-Padilla FJ. Promising diagnostic biomarkers of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: From clinical proteomics to microbiome. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1494-1511
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1494.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1494