Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Hepatol. May 8, 2017; 9(13): 635-641
Published online May 8, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i13.635
Published online May 8, 2017. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v9.i13.635
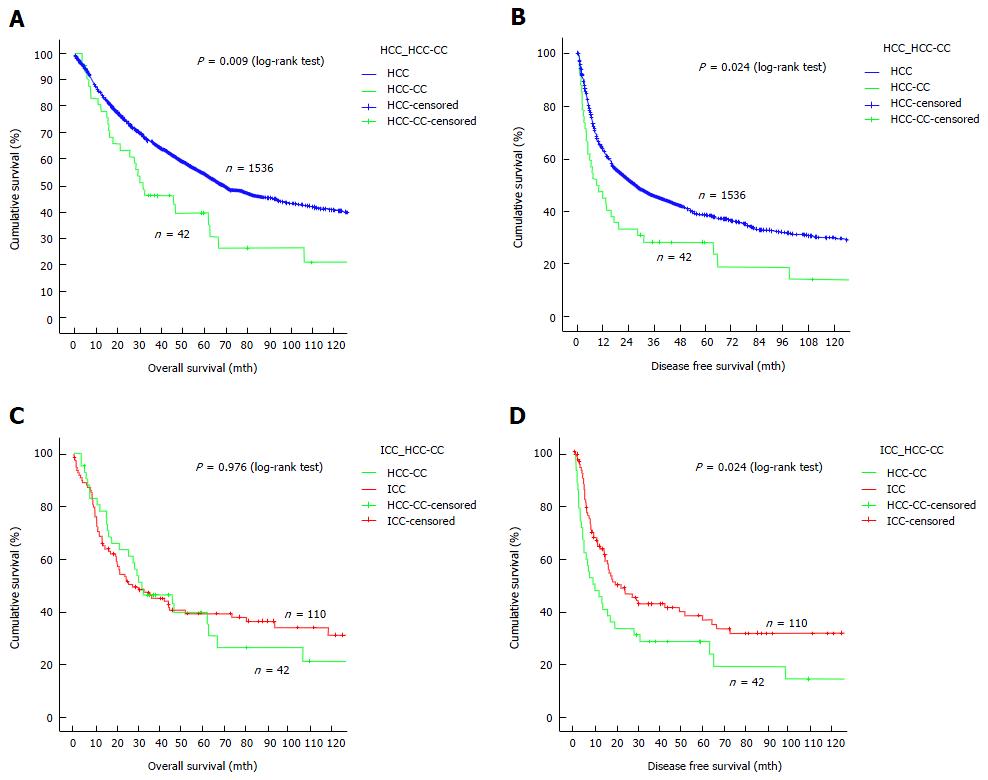
Figure 1 Survival comparisons between different groups of patients.
A: Overall survival of HCC-CC patients and HCC patients; B: Disease-free survival of HCC-CC patients and HCC patients; C: Overall survival of HCC-CC patients and ICC patients; D: Disease-free survival of HCC-CC patients and ICC patients. HCC-CC: Hepatocholangiocarcinoma; ICC: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
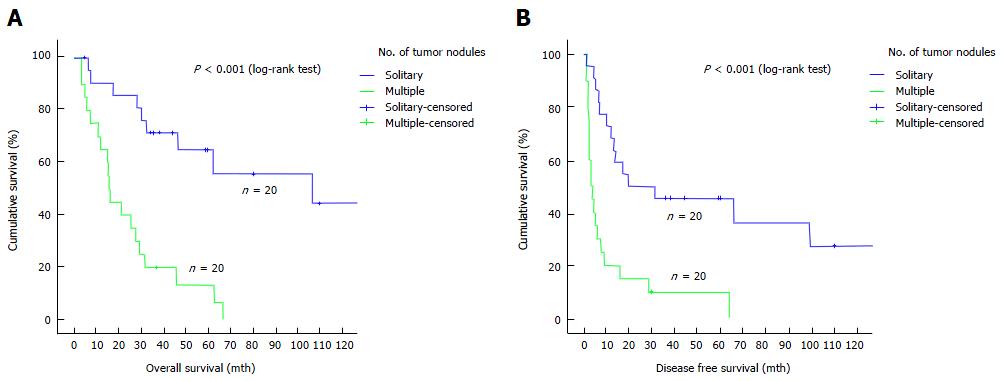
Figure 2 Survival of hepatocholangiocarcinoma patients with solitary vs multiple tumor nodules.
A: Overall survival of HCC-CC patients with solitary tumor nodule and with multiple tumor nodules; B: Disease-free survival of HCC-CC patients with solitary tumor nodule and with multiple tumor nodules. HCC-CC: Hepatocholangiocarcinoma.
Figure 3 Effect of wide resection margin on disease-free survival of patients with multifocal hepatocholangiocarcinoma.
- Citation: Ma KW, Chok KSH. Importance of surgical margin in the outcomes of hepatocholangiocarcinoma. World J Hepatol 2017; 9(13): 635-641
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v9/i13/635.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i13.635