Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Feb 18, 2016; 8(5): 291-300
Published online Feb 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i5.291
Published online Feb 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i5.291
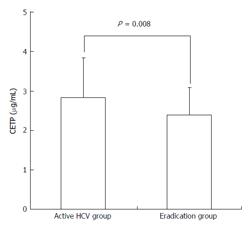
Figure 1 Comparison of the serum cholesteryl ester transfer protein level between the active hepatitis C virus infection group and the hepatitis C virus eradication group.
The serum CETP level was significantly higher in patients with active HCV infection than those in whom HCV eradication was achieved (2.84 ± 1.00 μg/mL vs 2.40 ± 0.70 μg/mL, P = 0.008). CETP: Cholesterol ester transfer protein; HCV: Hepatitis C virus.
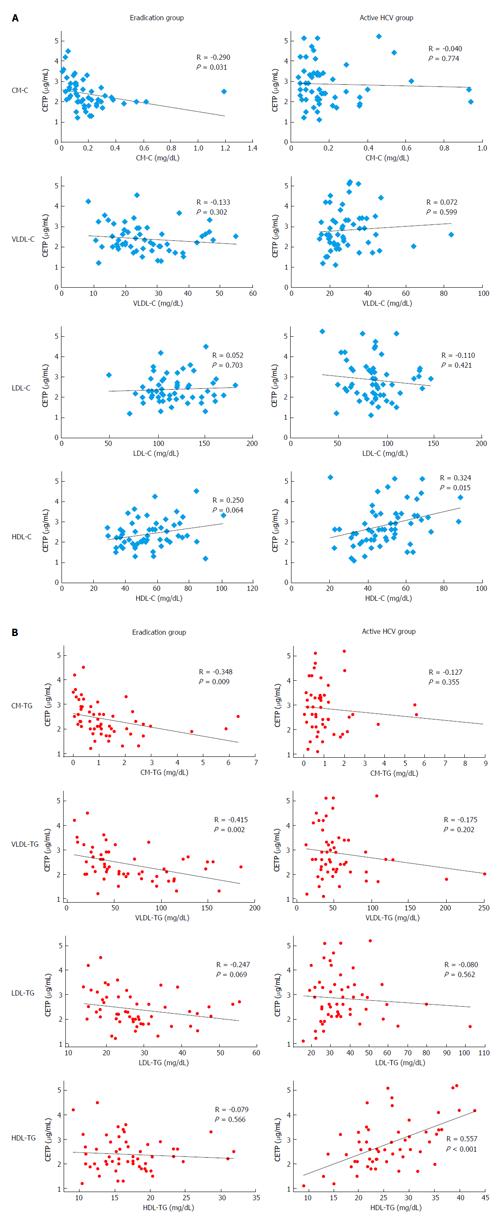
Figure 2 Correlation between the cholesteryl ester transfer protein level and triglyceride concentration in the four major lipoprotein classes in the hepatitis C virus eradication group and the active hepatitis C virus infection group.
A: The CETP level had a weak correlation with HDL cholesterol in the active HCV infection group (R = 0.324, P = 0.015) and a weak, inverse correlation with chylomicron-cholesterol (R = -0.290, P = 0.031); B: The CETP level had a strong correlation with HDL-TG in the active HCV infection group (R = 0.557, P < 0.001). However, significant correlations with TG for other lipoprotein classes were not detected in the active HCV group. HCV: Hepatitis C virus; CM: Chylomicron; VLDL: Very-low-density lipoprotein; LDL: Low-density lipoprotein; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; TG: Triglyceride.
- Citation: Satoh K, Nagano T, Seki N, Tomita Y, Aida Y, Sugita T, Itagaki M, Sutoh S, Abe H, Aizawa Y. High level of serum cholesteryl ester transfer protein in active hepatitis C virus infection. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(5): 291-300
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i5/291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i5.291