Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Oct 8, 2016; 8(28): 1194-1199
Published online Oct 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i28.1194
Published online Oct 8, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i28.1194
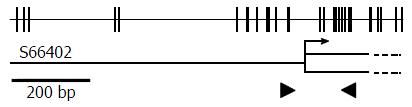
Figure 1 Agtr1a genomic structure.
Each vertical tick on the top line shows an individual CpG site. GenBank accession number is listed at the left end on the bottom line. Open box shows exon 1, and dashed lines show the ambiguous boundary region of exon 1. Quantitative real-time methylation-specific PCR was performed in the region marked with closed arrowheads.
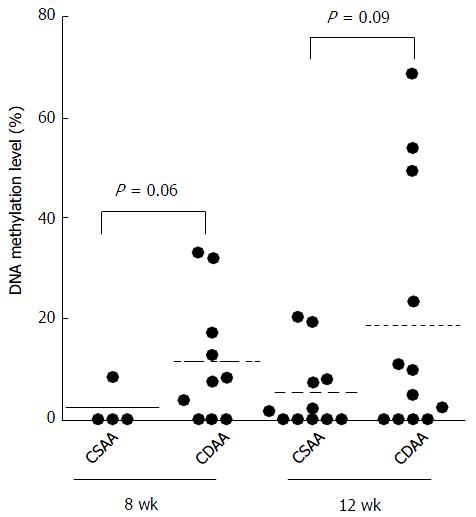
Figure 2 Levels of Agtr1a methylation in the livers of control choline-sufficient amino acid - and choline-deficient amino acid - fed rats.
The livers of choline-deficient amino acid (CDAA) - fed rats show higher Agtr1a methylation than that shown by the livers of choline-sufficient amino acid (CSAA) - fed rats at 8 (mean, 11.5% and 2.1%, P = 0.06) and 12 wk (mean, 18.6% and 5.3%, P = 0.09), respectively.
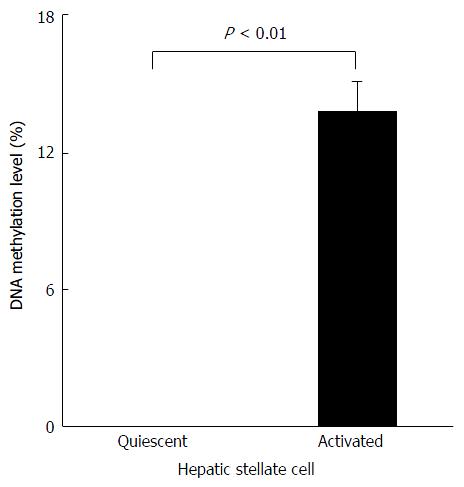
Figure 3 Levels of Agtr1a methylation in the quiescent and activated hepatic stellate cells.
Agtr1a is not methylated at all in quiescent hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) but hypermethylated (13.8%, P < 0.01) in activated HSCs. Data are presented as the mean ± SE.
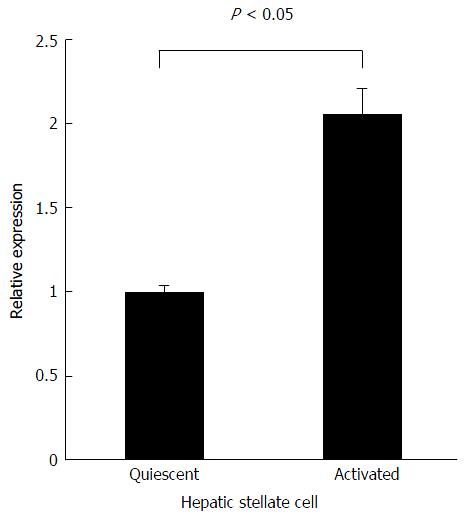
Figure 4 Relative Agtr1a expression normalized to Ppia in quiescent and activated hepatic stellate cells.
Activated hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) show 2.2-fold higher (P < 0.05) Agtr1a expression than that shown by quiescent HSCs. Data are presented as the mean ± SE.
- Citation: Asada K, Aihara Y, Takaya H, Noguchi R, Namisaki T, Moriya K, Uejima M, Kitade M, Mashitani T, Takeda K, Kawaratani H, Okura Y, Kaji K, Douhara A, Sawada Y, Nishimura N, Seki K, Mitoro A, Yamao J, Yoshiji H. DNA methylation of angiotensin II receptor gene in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related liver fibrosis. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(28): 1194-1199
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i28/1194.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i28.1194