Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Hepatol. Jan 18, 2016; 8(2): 92-106
Published online Jan 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i2.92
Published online Jan 18, 2016. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i2.92
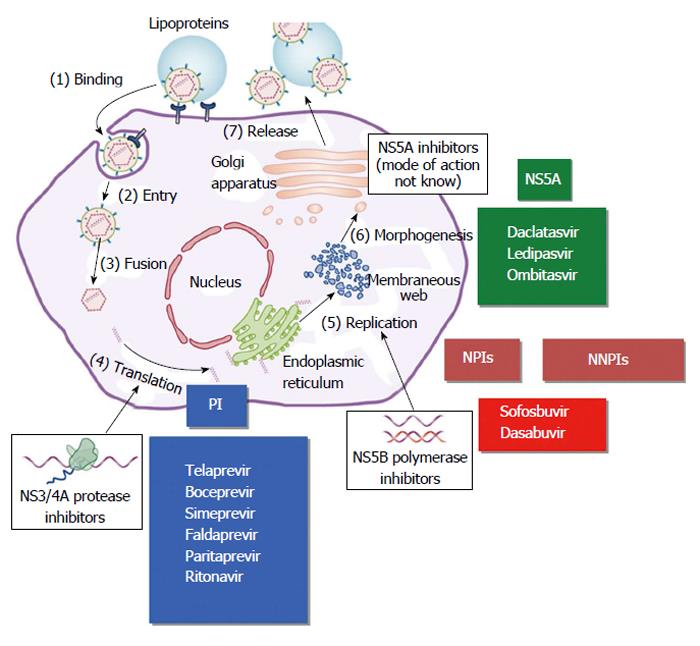
Figure 1 Hepatitis C virus replicative cycle and main targets for direct acting antiviral agents.
Modified from Manns and Cornberg. Lancet Infectious Diseases 2013. PIs: Protease inhibitors; NPIs: Nucleoside polymerase inhibitors; NNPIs: Non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitors.
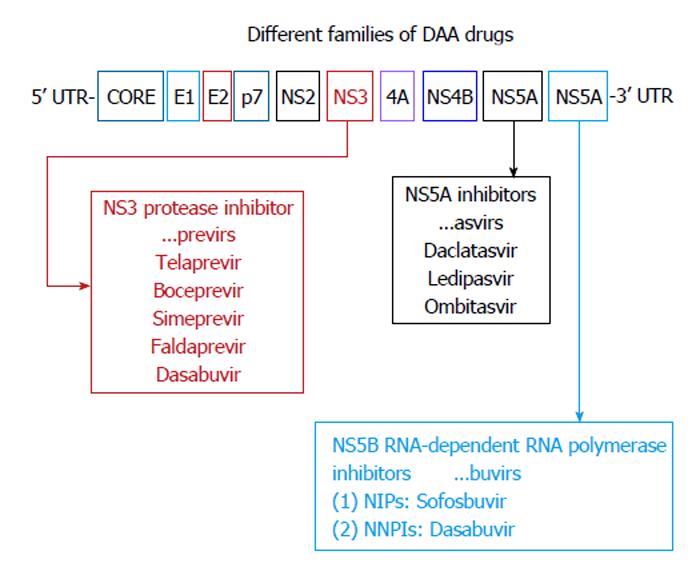
Figure 2 Direct acting antiviral agents.
Modified from Alexopoulou et al[121]. Interferon-based combination treatment for chronic hepatitis C in the era of direct acting antivirals. Annals of Gastroenterology 2015; 28: 55-65. NPIs: Nucleoside polymerase inhibitors; NNPIs: Non-nucleoside polymerase inhibitors; DAA: Direct acting antiviral.
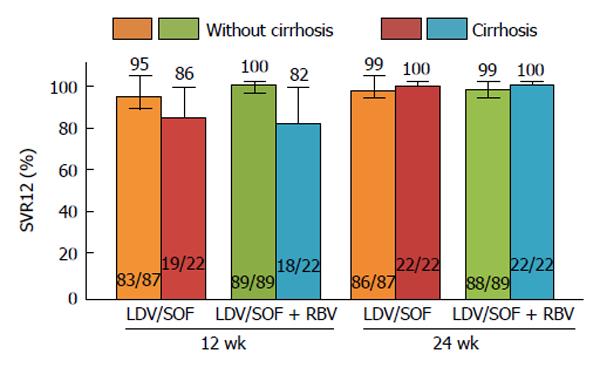
Figure 3 ION-2 sub-analysis of cirrhosis vs without cirrhosis.
Error bars represent 95%CIs. LDV: Ledipasvir; RBV: Ribavirin; SOF: Sofosbuvir; SVR12: Sustained virologic response at 12 wk post-treatment.
- Citation: Bertino G, Ardiri A, Proiti M, Rigano G, Frazzetto E, Demma S, Ruggeri MI, Scuderi L, Malaguarnera G, Bertino N, Rapisarda V, Di Carlo I, Toro A, Salomone F, Malaguarnera M, Bertino E, Malaguarnera M. Chronic hepatitis C: This and the new era of treatment. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(2): 92-106
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i2/92.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i2.92