Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
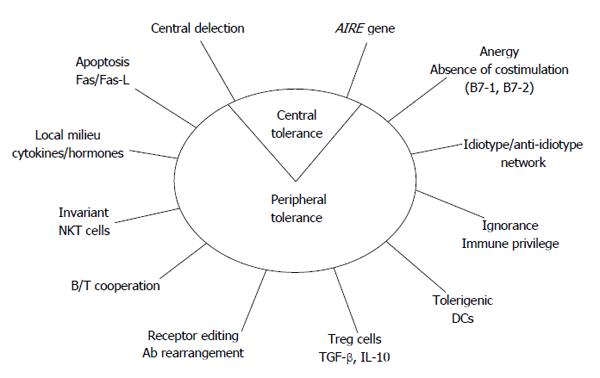
Figure 1 Potential mechanisms for self-tolerance control.
AIRE: Autoimmune regulator gene; DCs: Dendritic cells; TGF: Transforming growth factor; IL: Interleukin; Ab: Antibody; NKT cells: Natural killer T cells.
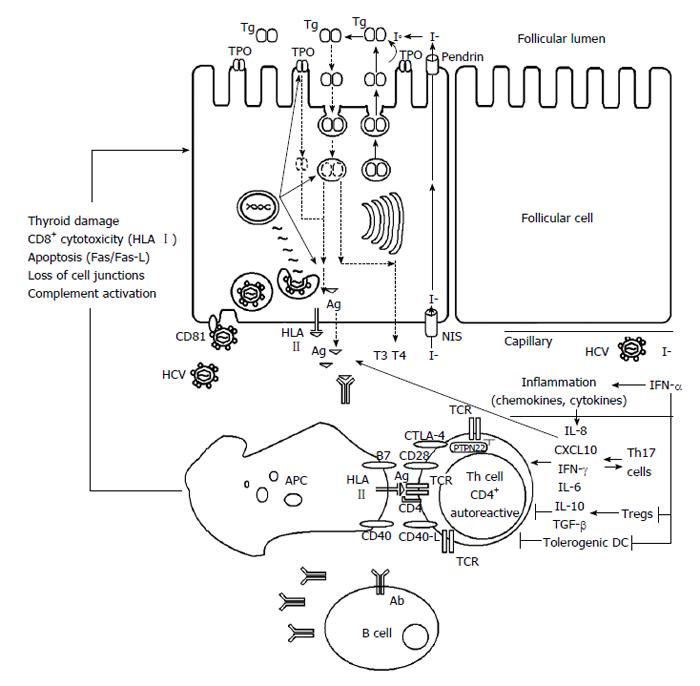
Figure 2 Development of thyroid autoimmunity in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection during interferon-α treatment.
Ab: Antibody; Ag: Antigen; APC: Antigen presenting cell; CD: Cluster of differentiation; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte antigen 4; CXCL10: C-X-C motif chemokine; DC: Dendritic cell; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; I-: Iodide; IFN: Interferon; IL: Interleukin; NIS: Sodium/iodide symporter; PTPN22: Protein tyrosine phosphatase nonreceptor-type 22; T3 and T4: Thyroid hormones; TCR: T cell receptor; Tg: Thyroglobulin; TGF: Transforming growth factor; Th: T helper; TPO: Thyroid peroxidase; Tregs: T regulatory cells.
- Citation: Pastore F, Martocchia A, Stefanelli M, Prunas P, Giordano S, Toussan L, Devito A, Falaschi P. Hepatitis C virus infection and thyroid autoimmune disorders: A model of interactions between the host and the environment. World J Hepatol 2016; 8(2): 83-91
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v8/i2/83.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v8.i2.83