Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Dec 28, 2015; 7(30): 2980-2991
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i30.2980
Published online Dec 28, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i30.2980
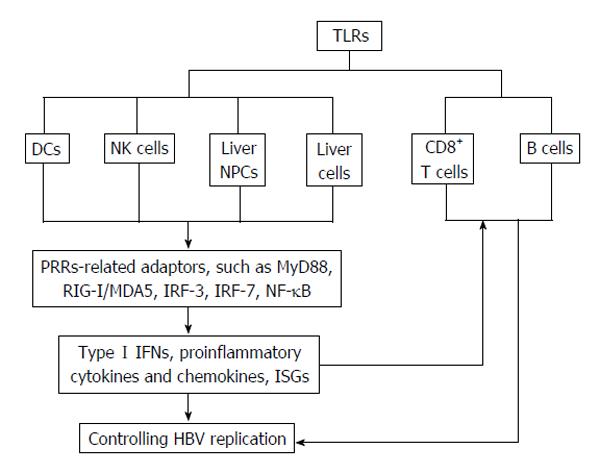
Figure 1 Expressions and activation of toll-like receptors in innate and adaptive immune cells in controlling hepatitis B virus infection.
HBV: Hepatitis B virus; NPCs: Non-parenchymal cells; NK: Natural killer; IFN: Interferon; TLRs: Toll-like receptors; ISG: Interferon-stimulated genes; RIG-I: Retinoic acid inducible gene I; IRF: Interferon-regulatory factors; NF-κB: Nuclear factor κB; PBMCs: Periperal blood mononuclear cells; MDA5: Melanoma differentiation associated gene 5; DCs: Dendritic cells.
- Citation: Wang L, Wang K, Zou ZQ. Crosstalk between innate and adaptive immunity in hepatitis B virus infection. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(30): 2980-2991
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i30/2980.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i30.2980