Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Hepatol. Dec 18, 2015; 7(29): 2880-2889
Published online Dec 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i29.2880
Published online Dec 18, 2015. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i29.2880
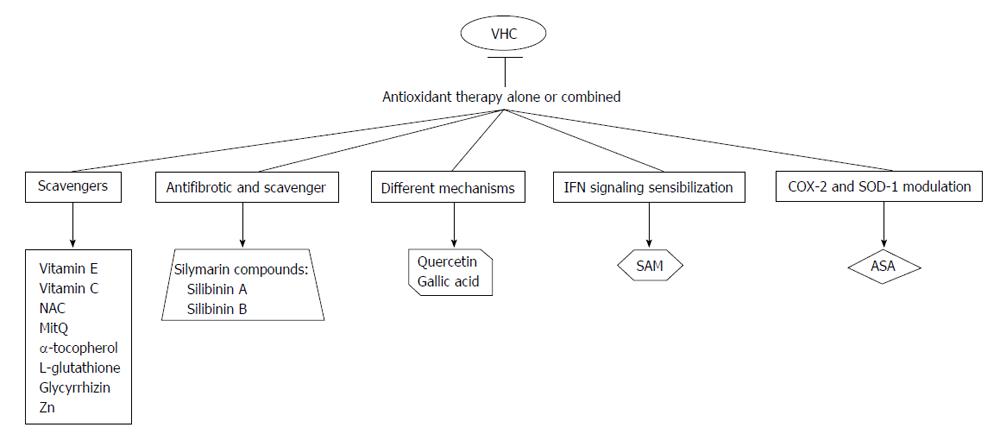
Figure 1 Possible interactions/mechanisms of antioxidant agents with reported anti-hepatitis C virus effect.
SOD: Superoxide dismutase; SAM: S-adenosylmethionine; ASA: Acetylsalicylic acid; Zn: Zinc; IFN: Interferon.
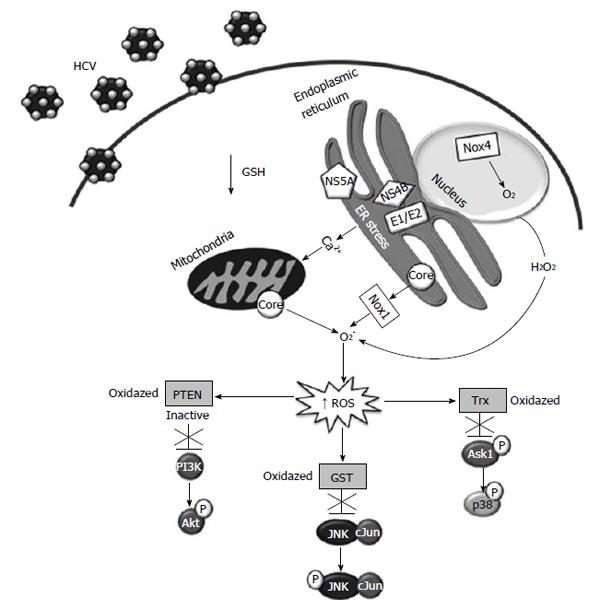
Figure 2 Cell signaling pathways modulated by increased reactive oxygen species levels in hepatitis C virus infected cells.
ROS: Reactive oxygen species; HCV: Hepatitis C virus; GSH: Glutathione system; Trx: Thioredoxin; PI3K: Phosphoinositide-3 kinase.
- Citation: Lozano-Sepulveda SA, Bryan-Marrugo OL, Cordova-Fletes C, Gutierrez-Ruiz MC, Rivas-Estilla AM. Oxidative stress modulation in hepatitis C virus infected cells. World J Hepatol 2015; 7(29): 2880-2889
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v7/i29/2880.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v7.i29.2880