Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2014; 6(3): 114-129
Published online Mar 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i3.114
Published online Mar 27, 2014. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v6.i3.114
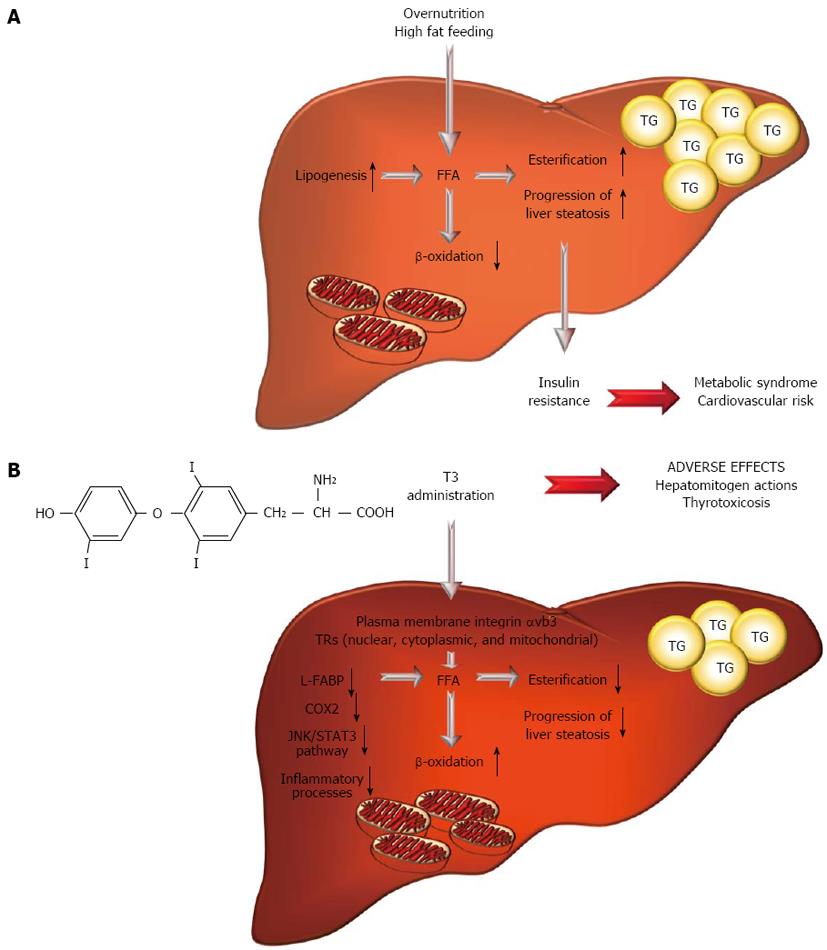
Figure 1 Hepatic lipid partitioning and liver and systemic metabolic damages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (A) and a schematic representation of the anti-steatotic effect of 3,3’,5-triiodo-L-thyronine (B).
A: Hepatic lipid partitioning and liver and systemic metabolic damages in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Chronic overnutrition/hyperlipidemic feeding causes fat retention in hepatocytes that, in turn, results in alteration of fat uptake, de novo synthesis (lipogenesis) and oxidation with a significant imbalance of lipid homeostasis. This can subsequently induce insulin-resistance, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases; B: A schematic representation of the anti-steatotic effect of T3: An update. T3-administration associated adverse effects are also highlighted (for details see the text). T3: 3,3’,5-triiodo-L-thyronine; TRs: Thyroid hormone receptor isoforms; FFA: Free fatty acid; TG: Triglyceride; L-FABP: Liver-type fatty acid-binding protein; COX2: Cyclooxygenase 2; JNK: c-Jun N-terminal kinases; STAT3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3.
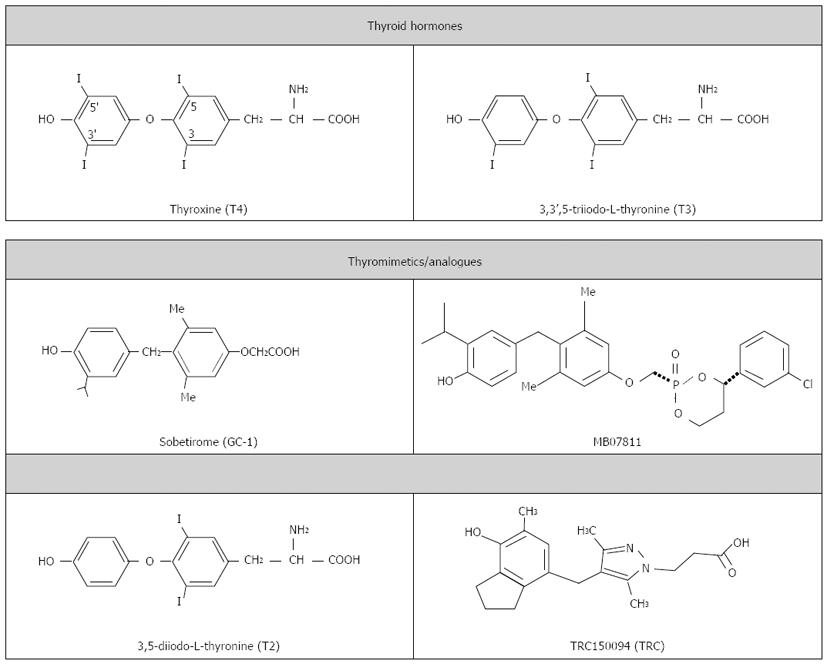
Figure 2 Chemical structure of thyroid hormones and thyromimetics/analogues with reported anti-steatotic effects.
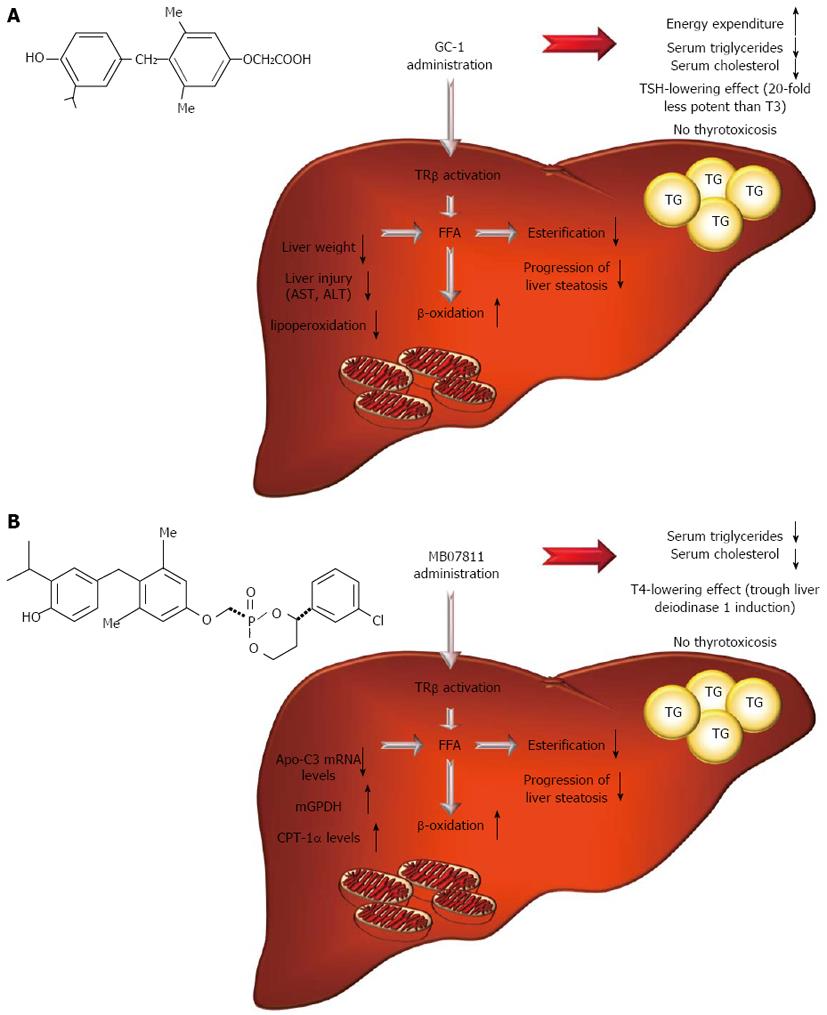
Figure 3 A summary of key events and molecular pathways underlying GC-1 (A) and MB07811 (B) anti-steatotic and hypolipidemic effects (for details see the text).
TSH: Thyroid-stimulating hormone; T3: 3,3’,5-triiodo-L-thyronine; TRβ: Thyroid hormone receptor β isoform; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; FFA: Free fatty acid; TG: Triglyceride; T4: Thyroxine; Apo-C3: Apolipoprotein C3; mGPDH: Mitochondrial glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase; CPT-1α: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase-1α.
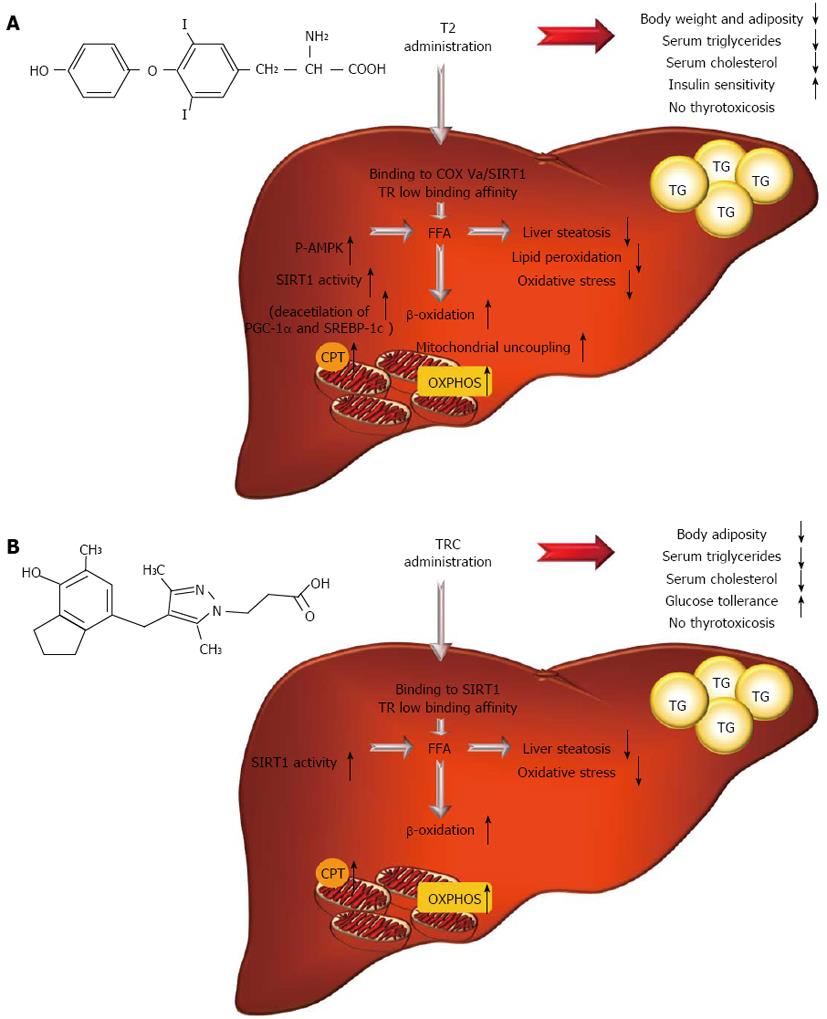
Figure 4 A summary of key events and molecular pathways underlying T2 (A) and TRC (B) anti-steatotic and hypolipidemic effects (for details see the text).
T2: 3,5-diiodo-L-thyronine; TR: Thyroid hormone receptor; COX Va: Cytochrome-c oxidase Va subunit; FFA: Free fatty acid; TG: Triglyceride; P-AMPK: Phosphorylated AMP-activated protein kinase; SIRT1: NAD+-dependent deacetylase sirtuin 1; PGC-1α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator; SREBP-1c: Sterol response element binding protein-1c; CPT: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase system; OXPHOS: Oxidative phosphorylation system.
- Citation: Coppola M, Glinni D, Moreno M, Cioffi F, Silvestri E, Goglia F. Thyroid hormone analogues and derivatives: Actions in fatty liver. World J Hepatol 2014; 6(3): 114-129
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v6/i3/114.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v6.i3.114