Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2013; 5(6): 340-344
Published online Jun 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i6.340
Published online Jun 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i6.340
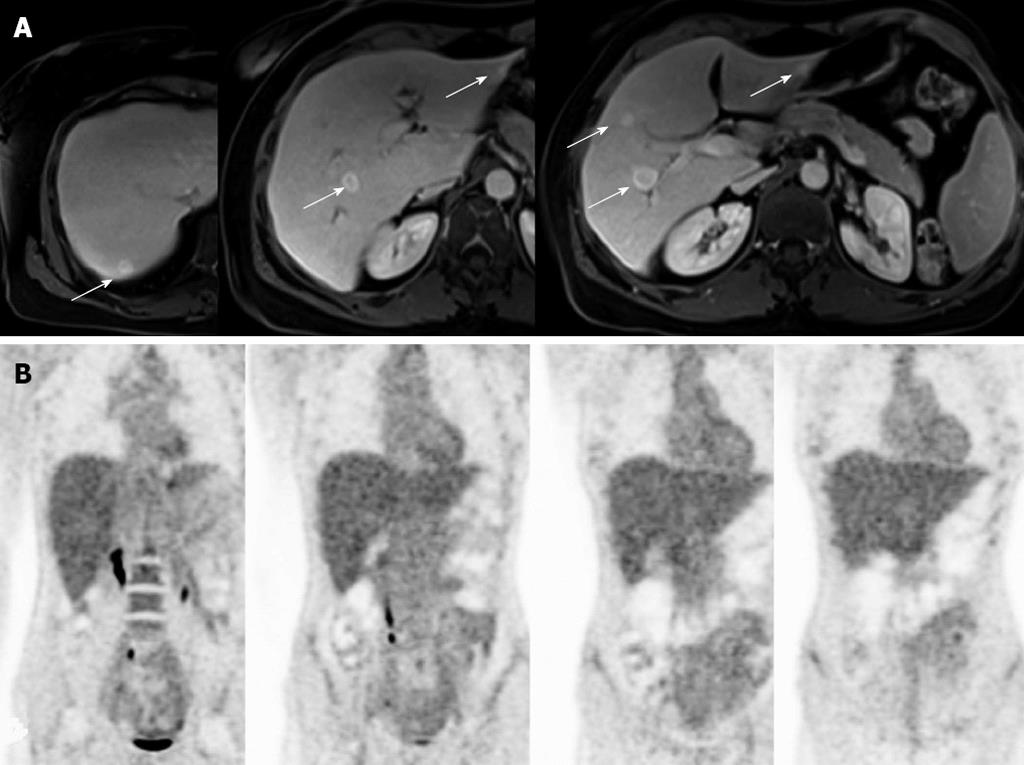
Figure 1 Radiological imaging of case 1.
A: The abdominal contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed multiple bilateral focal liver lesions (arrows); B: The fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scan did not show any pathological uptake of the trace.
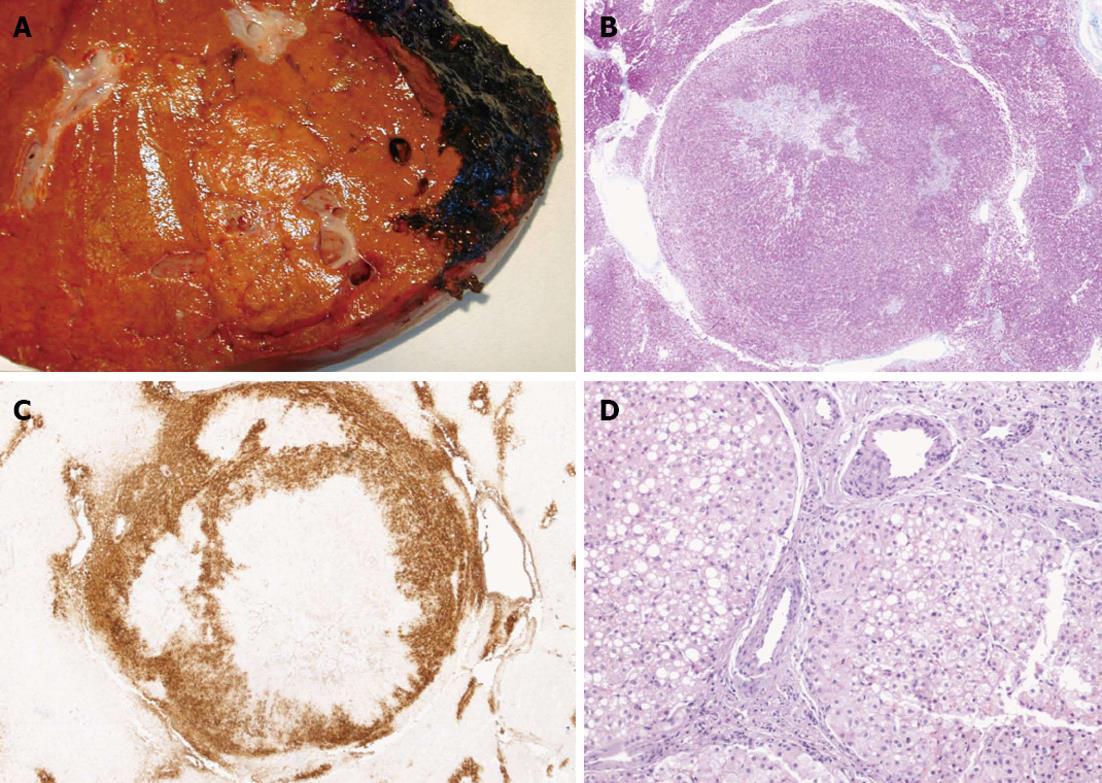
Figure 2 Histology of case 1.
A: The gross inspection of the specimen showed lesions sized between 0.5 and 2 cm, with well-defined margins, and a central scar; B, C: At microscopy the lesions were characterized by several fibrous septa highlighted by special stains (Masson staining), and they showed a typical patter at glutamine synthetase immunostaining; D: At higher magnification they contained several dystrophic vessels.
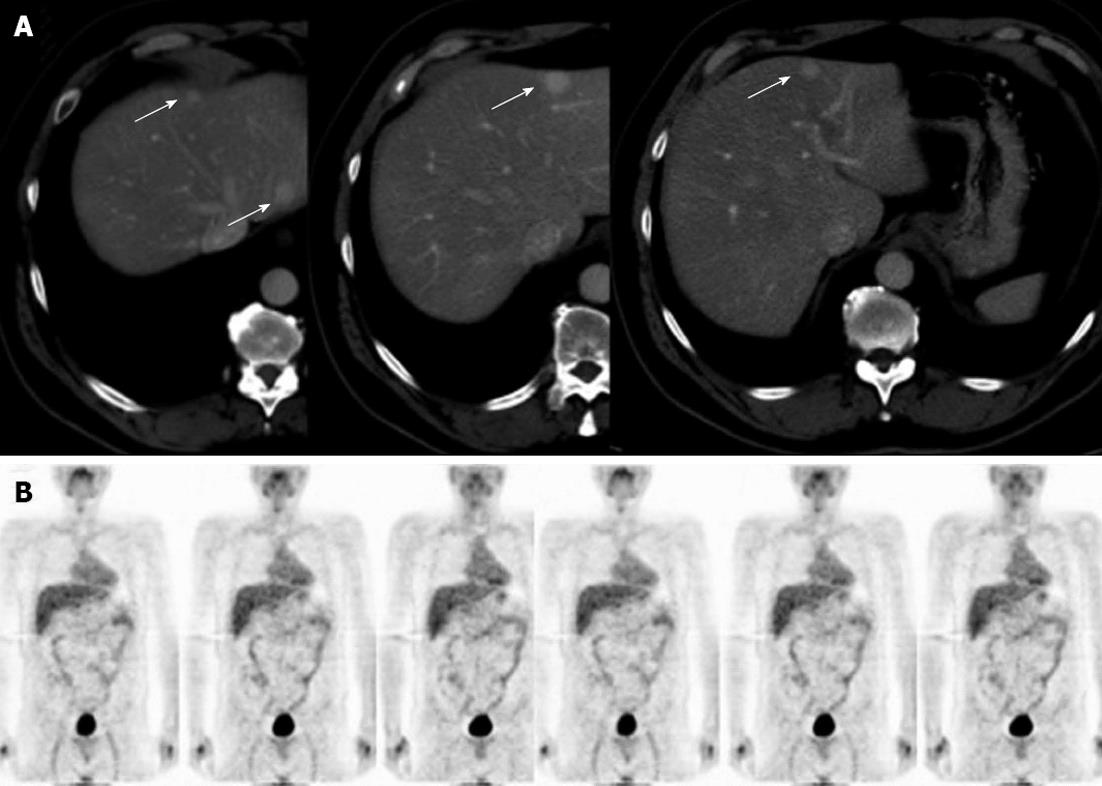
Figure 3 Radiological imaging of case 2.
A: The abdominal contrast-enhanced computed tomography showed multiple focal liver lesions (arrows); B: The fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography scan did not show any pathological uptake of the trace.
- Citation: Donadon M, Di Tommaso L, Roncalli M, Torzilli G. Multiple focal nodular hyperplasias induced by oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(6): 340-344
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i6/340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i6.340