Copyright
©2013 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2013; 5(12): 654-665
Published online Dec 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i12.654
Published online Dec 27, 2013. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v5.i12.654
Figure 1 Primary sclerosing cholangitis in a 54-year-old man.
Magnetic resonance imaging shows multifocal strictures and beading of the bile duct.
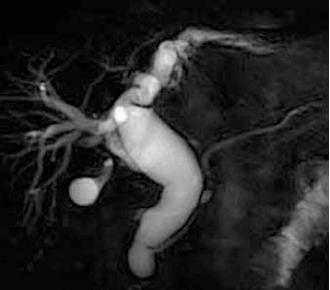
Figure 2 Choledochal cyst Todani IV-A type in a 58-year-old man.
Magnetic resonance imaging shows dilatation both intrahepatic and extrahepatic bile ducts with abnormal arrangement of the pancreato-biliary ductal system.
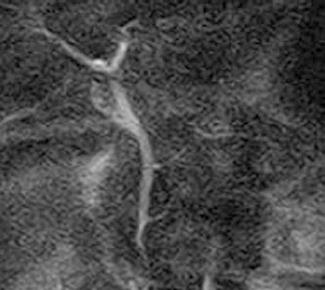
Figure 3 Magnetic resonance image in a 48-year-old woman with abnormal arrangement of the pancreato-biliary ductal system without a choledochal cyst.
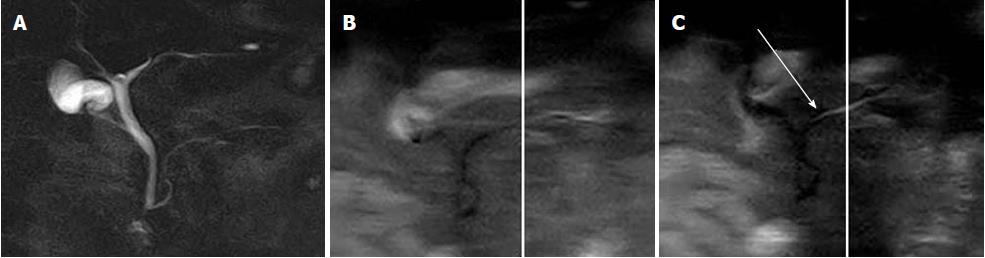
Figure 4 Flow of pancreatic juice by time-spatial labeling inversion pulse imaging.
A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography image; B: Time- spatial labeling inversion pulse image obtained by applying labeling pulse box surrounded by lines to the body and tail portions of the main pancreatic duct, not showing movement; C: Flow of pancreatic juice in duct from body into the head of pancreas is identified by high signal intensity (arrow).
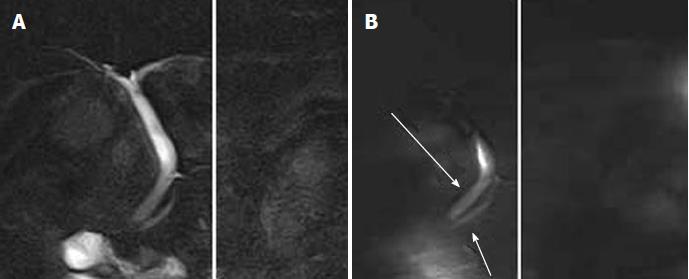
Figure 5 Pancreatic juice reflux into the biliary tree by time-spatial labeling inversion pulse imaging.
A 56-year-old female patient underwent magnetic resonance imaging after abnormal laboratory findings. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed normal morphology, but time- spatial labeling inversion pulse imaging showed pancreatic juice reflux into the biliary tree. A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography image; B: Flow of pancreatic juice from body of the pancreas into the head of the pancreas is identified by high signal intensity (arrows).
Figure 6 Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in a 70-year-old man.
A: Axial T2-weighted image shows high signal intensity liver mass (arrow); B: Diffusion-weighted imaging shows high signal intensity in the lesion (arrow).
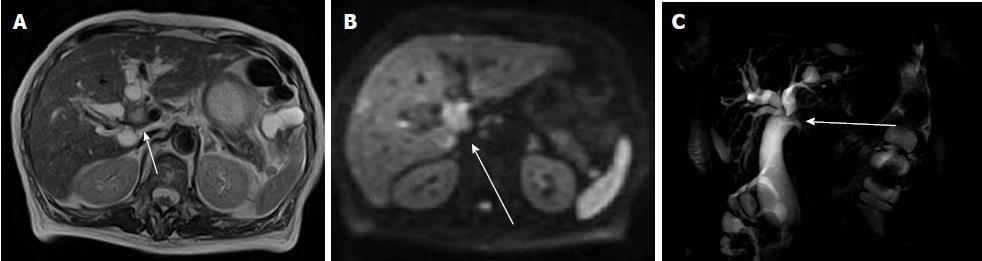
Figure 7 Hilar bile duct cancer in an 84-year-old woman.
A: Axial T2-weighted image shows wall thickening and high signal intensity of hilar bile duct (arrow); B: Diffusion-weighted imaging shows high signal intensity in the lesion (arrow); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows occlusion of the hilar bile duct (arrow).
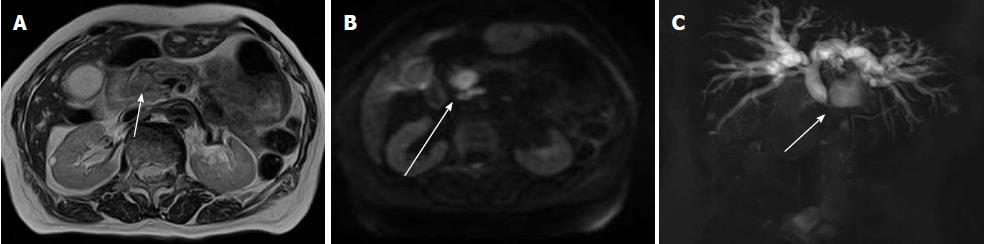
Figure 8 Distal extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma in an 83-year-old woman.
A: Axial T2-weighted image shows wall thickening and slight high mass of the distal common bile duct (arrow); B: Diffusion-weighted imaging shows high signal intensity in the lesion (arrow); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows occlusion of the distal common bile duct (arrow).
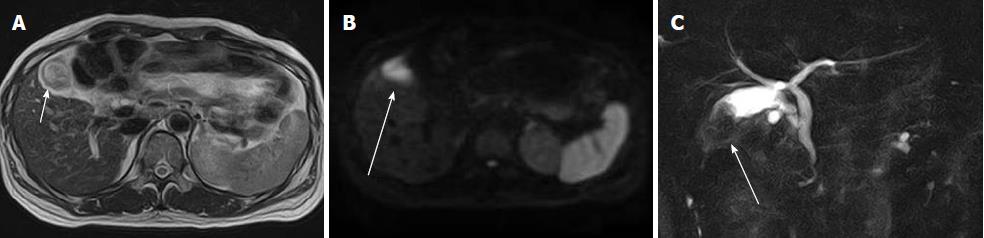
Figure 9 Gallbladder carcinoma in a 56-year-old woman.
A: Axial T2-weighted image shows focal wall thickening (arrow); B: Diffusion-weighted imaging shows high signal intensity in the lesion (arrow); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows a filling defect in the gallbladder (arrow). Abnormal arrangement of the pancreato-biliary ductal system is identified.
Figure 10 Ampullary cancer in an 84-year-old woman.
A: T2-weighted axial image shows a focal mass in the ampullary region (arrow); B: Diffusion-weighted imaging shows high signal intensity within an ampullary cancer (arrow); C: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography shows marked dilatation of the bile duct and slight dilatation of the main pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Sugita R. Magnetic resonance evaluations of biliary malignancy and condition at high-risk for biliary malignancy: Current status. World J Hepatol 2013; 5(12): 654-665
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v5/i12/654.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v5.i12.654