Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Aug 27, 2025; 17(8): 109530
Published online Aug 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.109530
Published online Aug 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.109530
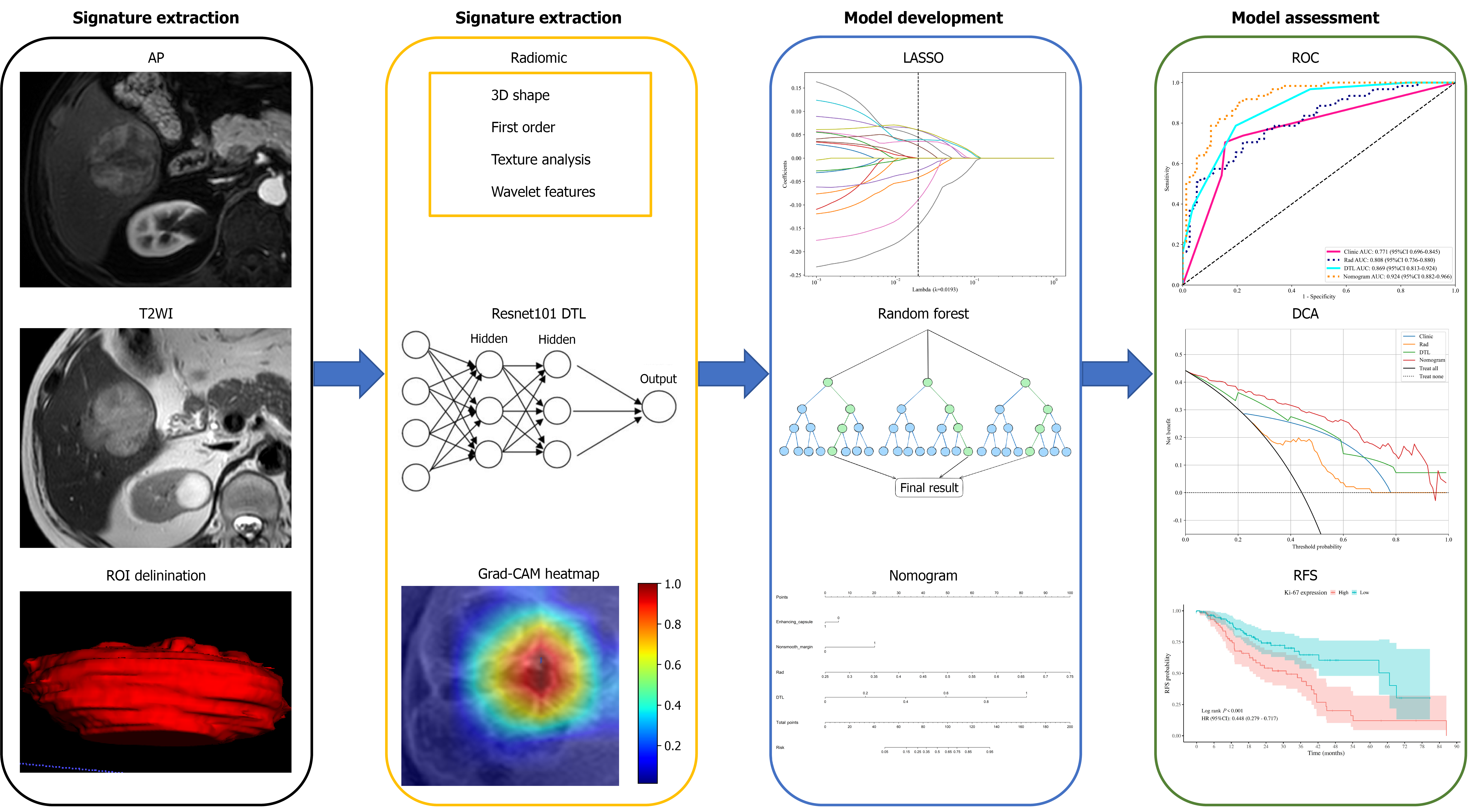
Figure 1 Detailed process from biparametric magnetic resonance imaging acquisition to recurrence-free survival assessment.
AP: Arterial phase; T2WI: T2-weighted imaging; ROI: Region of interest; DTL: Deep transfer learning; CAM: Class activation mapping; ROC: Receiver operating characteristic; DCA: Decision curve analyses; RFS: Recurrence-free survival.
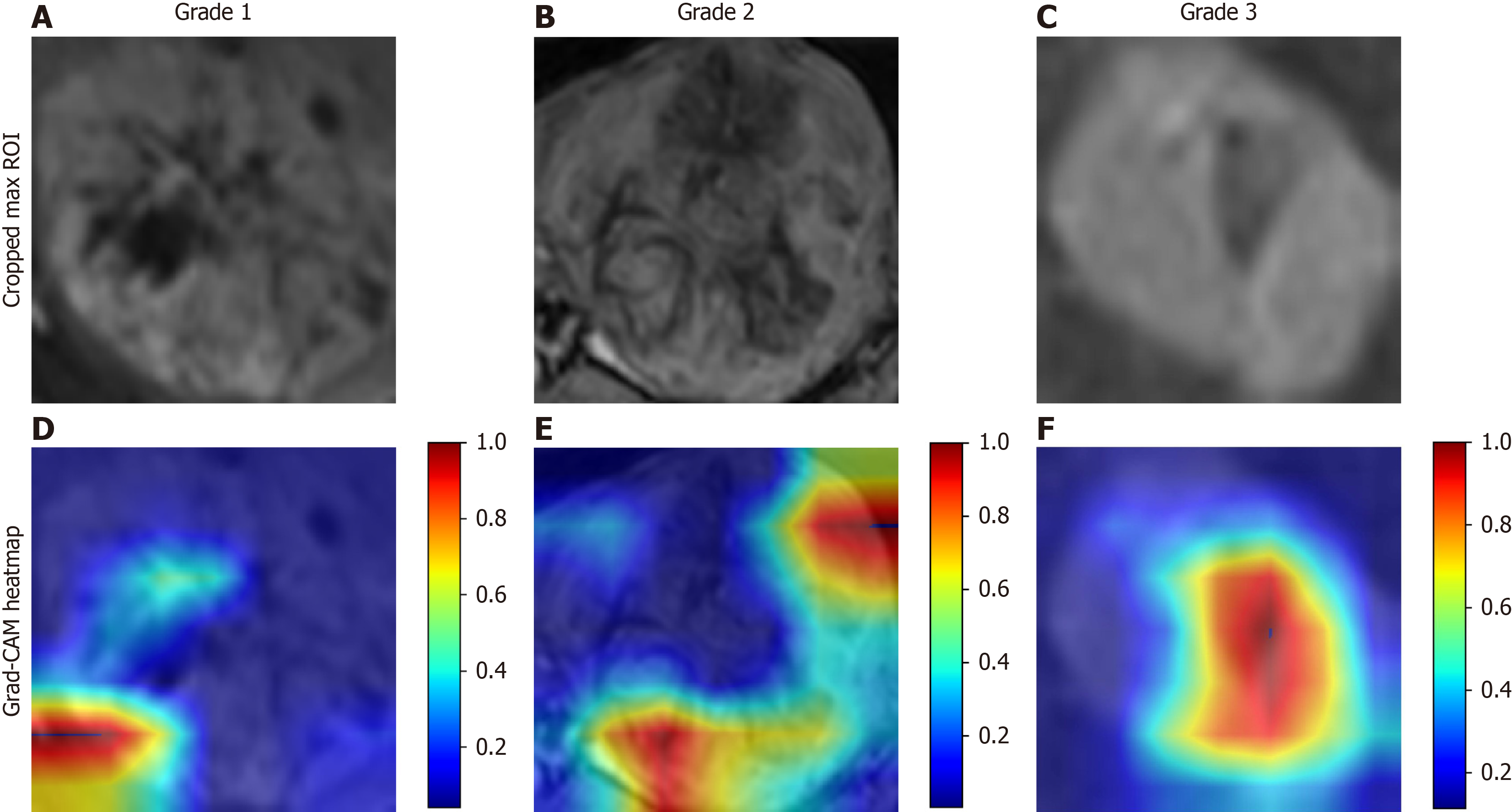
Figure 2 The cropped maximum region of interest and gradient-weighted class activation mapping heatmap were analyzed for varying levels of Ki-67 expression, ranging from Grade 1 to Grade 3.
A: The cropped maximum region of interest for Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) with Ki-67 expression index was 10% (Grade 1); B: Gradient-weighted class activation mapping identifying only a few regions on the heatmap; C: The cropped maximum region of interest for HCC with Ki-67 expression index was 45% (Grade 2); D: Gradient-weighted class activation mapping confirming moderate peritumoral heatmap activity; E: The cropped maximum region of interest for HCC with Ki-67 expression index was 55% (Grade 3); F: Gradient-weighted class activation mapping confirming more pronounced intratumoral heatmap activity. ROI: Region of interest; CAM: Class activation mapping.
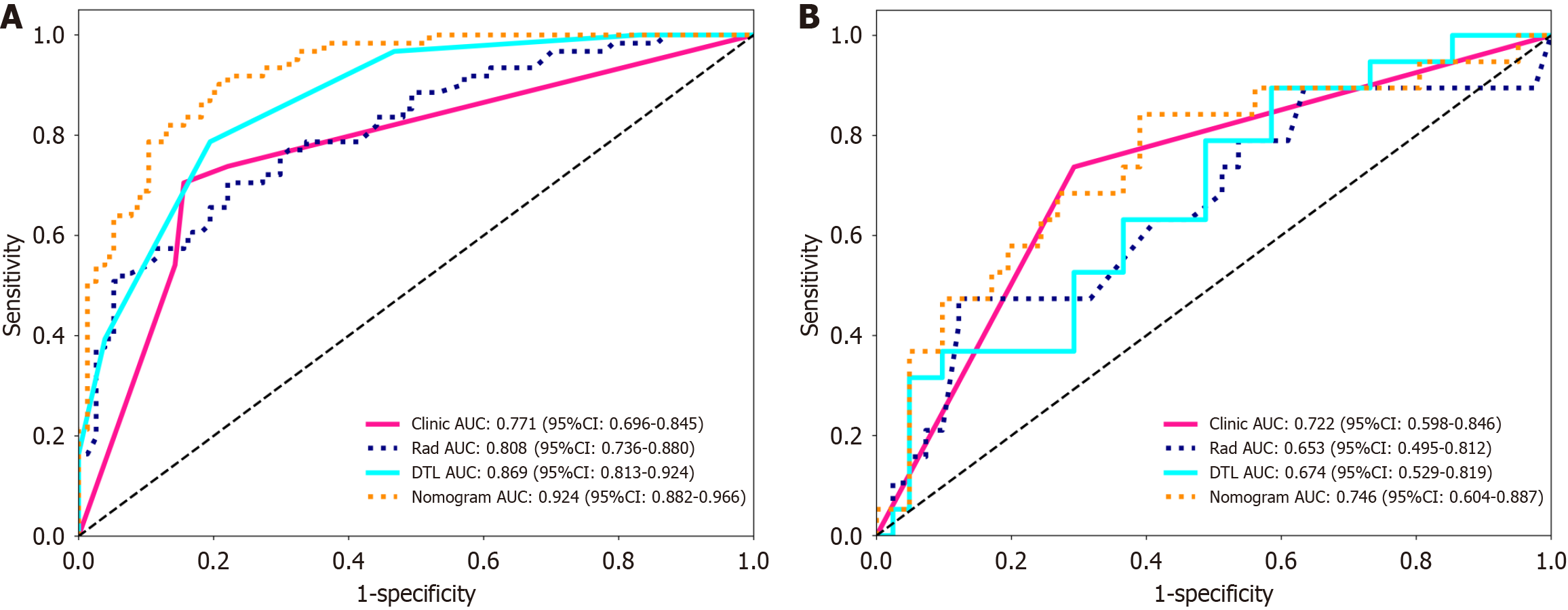
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis of different models in predicting high Ki-67 risk stratification in both groups.
A: Training groups; B: Validation groups. DTL: Deep transfer learning; AUC: Area under the curve.
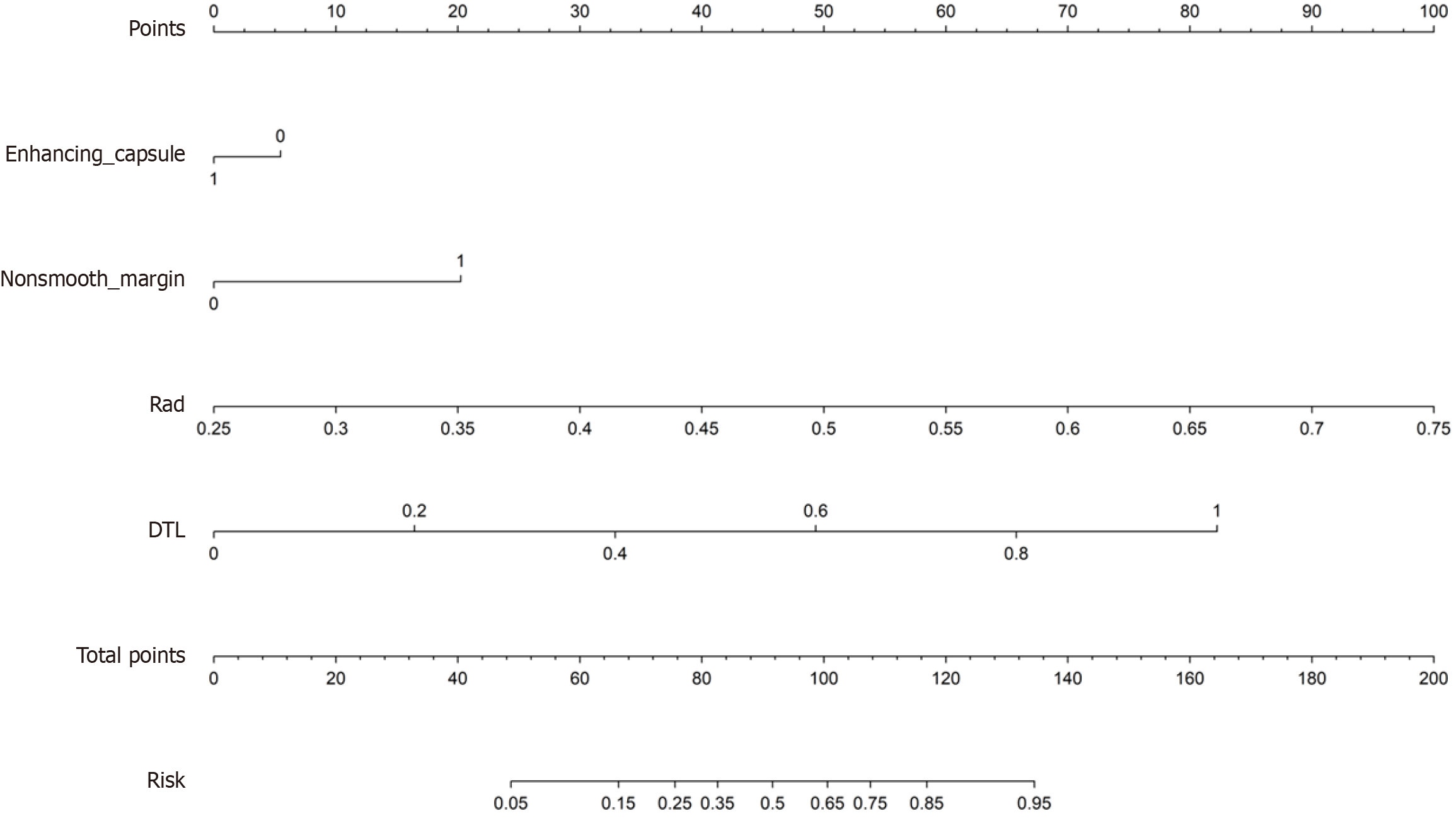
Figure 4 Nomogram model for predicting high Ki-67 risk stratification in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.
DTL: Deep transfer learning.
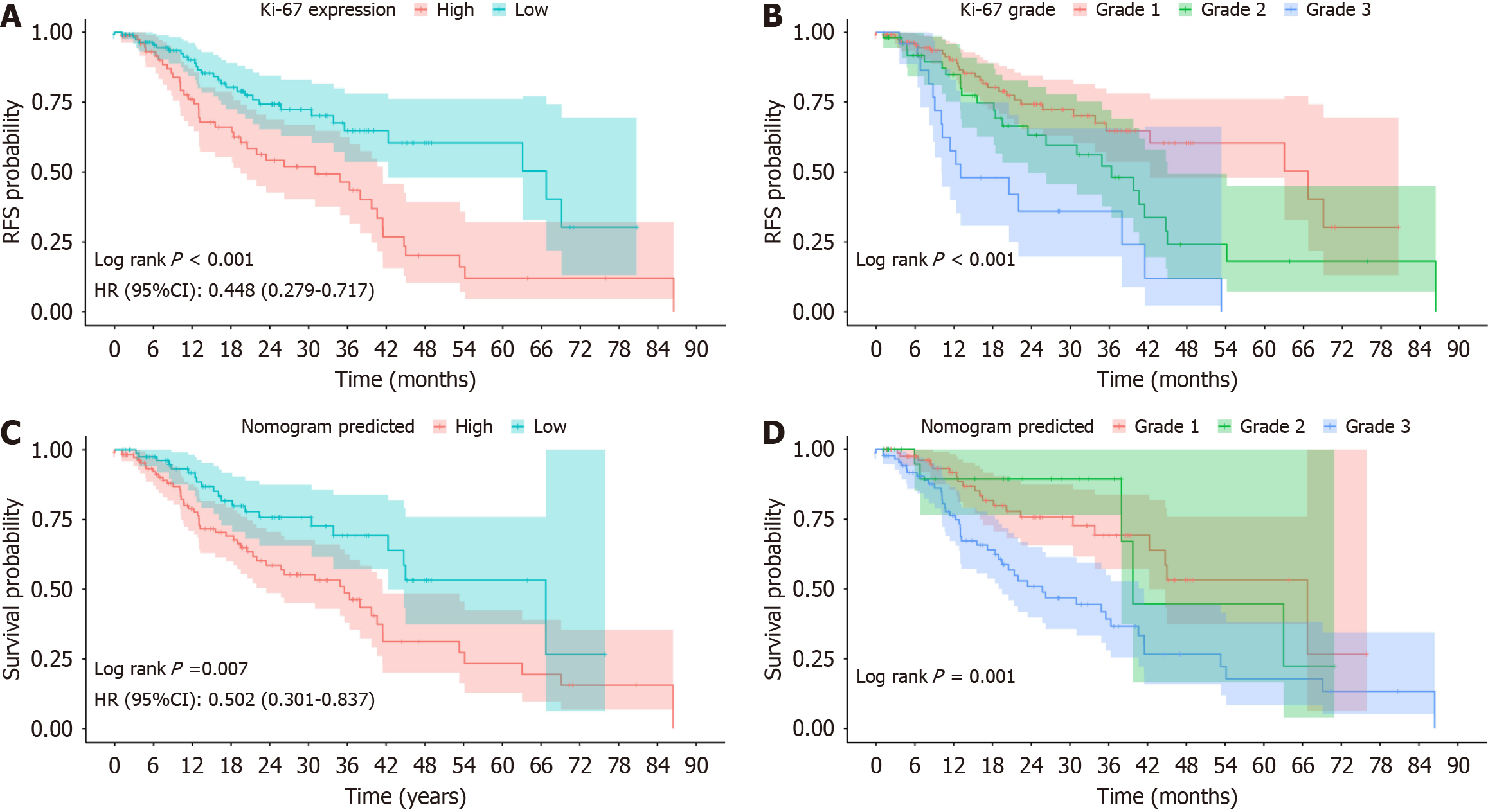
Figure 5 Recurrence-free survival curves obtained from Kaplan-Meier analysis were scaled for high Ki-67 risk stratification.
A: High Ki-67 expression was confirmed by histopathology; B: High Ki-67 expression was predicted by the nomogram model; C: Ki-67 risk stratification was further diagnosed by histopathology; D: Ki-67 risk stratification was further predicted by the nomogram model.
- Citation: Zuo XY, Liu HF. Biparametric magnetic resonance imaging-based radiomic and deep learning models for predicting Ki-67 risk stratification in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(8): 109530
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i8/109530.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i8.109530