Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 106675
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106675
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106675
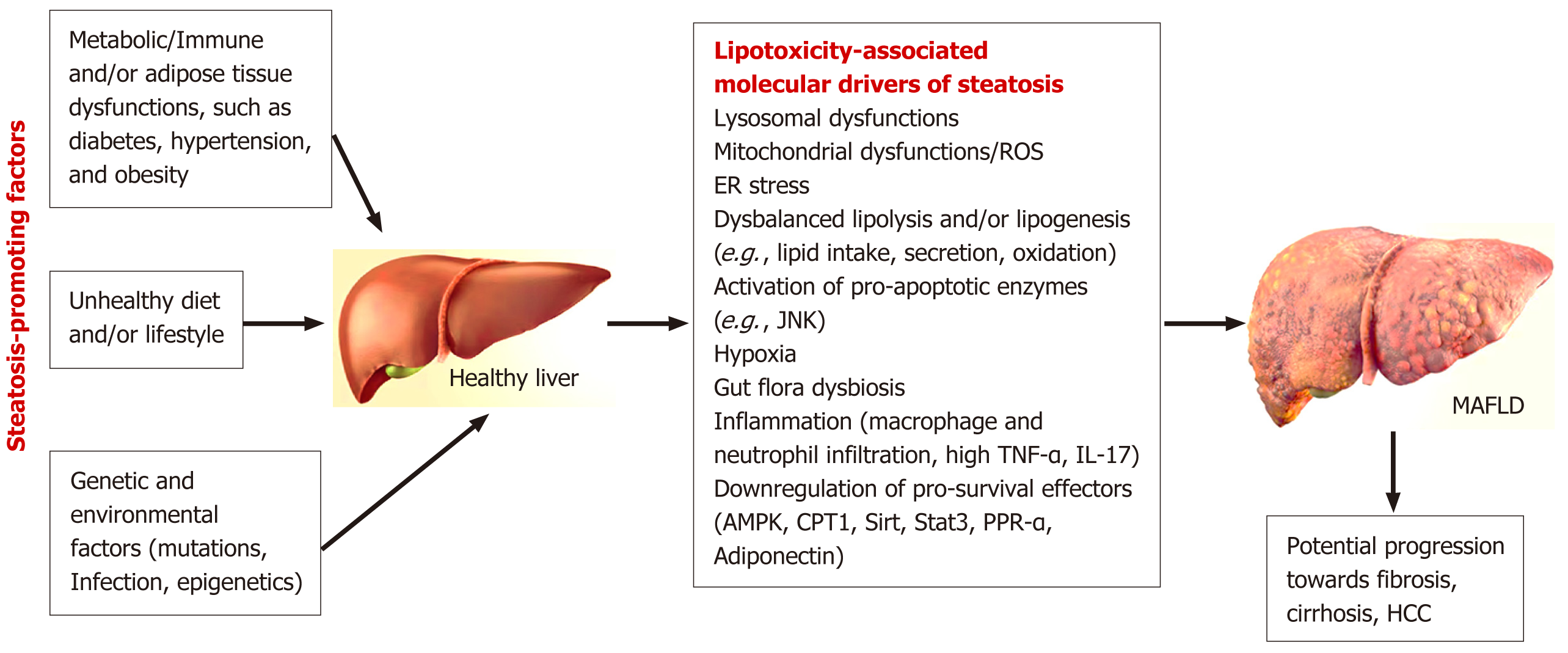
Figure 1 The risk factors and biological mechanisms of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; CPT1: Carnitine palmitoyltransferase I; ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; IL: Interleukin; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; PPR-α: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; Sirt: Sirtuin; Stat3: Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; TNF-α: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha.
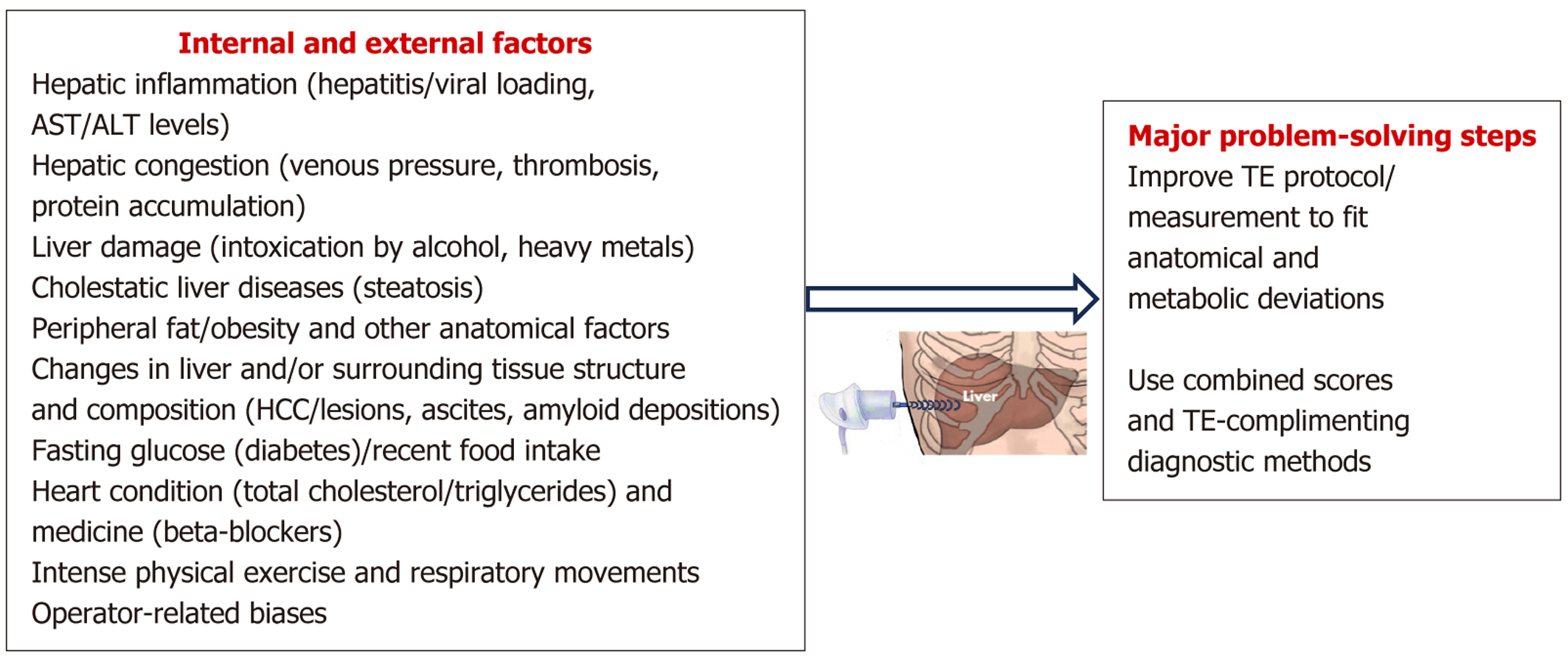
Figure 2 Factors that define transient elastography diagnostic accuracy.
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; TE: Transient elastography.
- Citation: Sukocheva O, Ow TW, Harding D, Le Mire M, Tse E. Liver stiffness measurements in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: Updates on the method effectiveness and perspectives. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(7): 106675
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i7/106675.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106675