Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2025; 17(7): 106291
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106291
Published online Jul 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106291
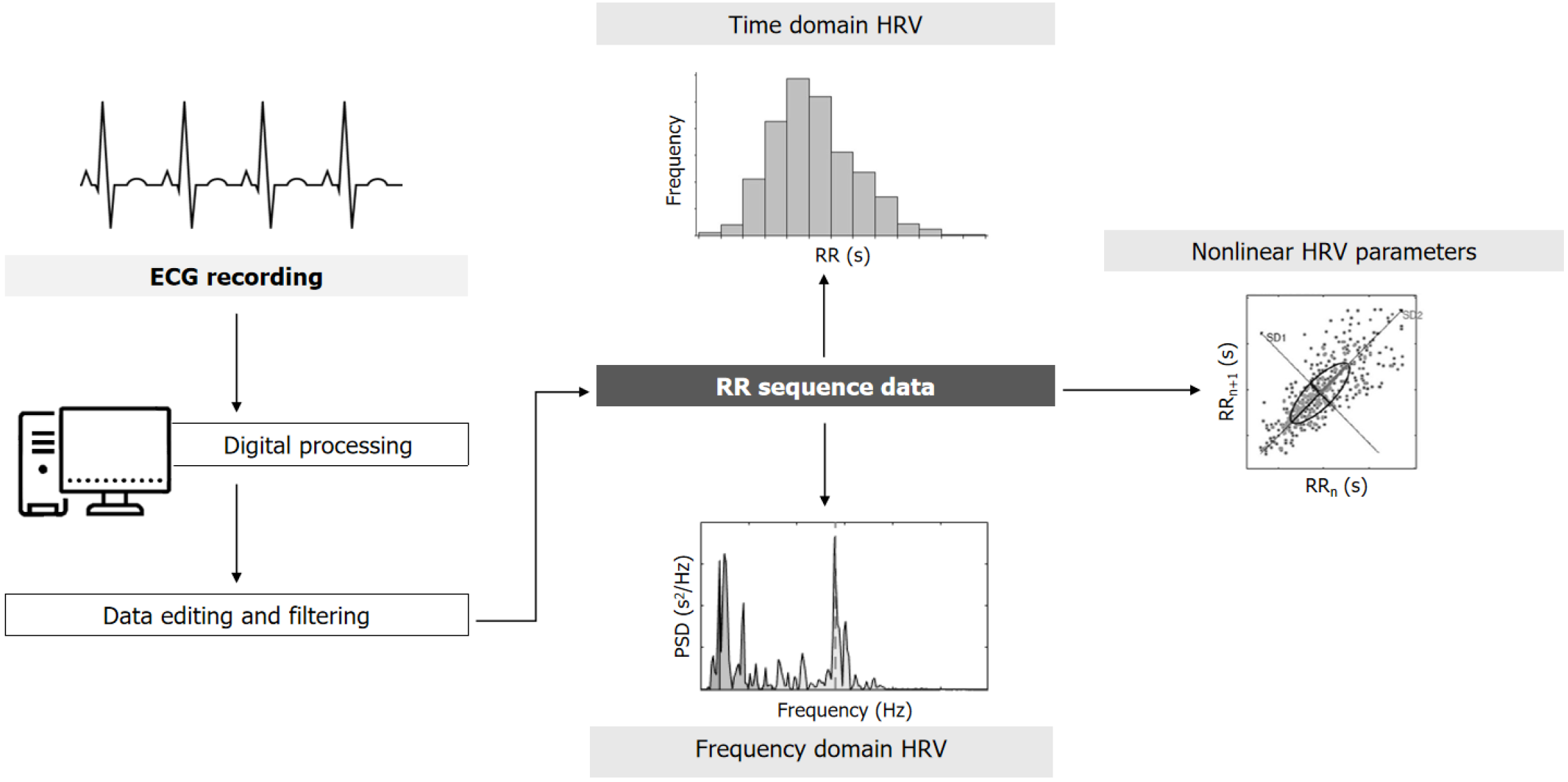
Figure 1 Typical electrocardiogram recording and obtention of heart rate variability measurements.
Starting from a typical electrocardiogram (ECG) recorded using a Holter monitor, after digitalization and edition, the R waves (RR intervals) file or inter-beat interval is obtained, which is used to determine the variation in RR with time and for creating the heart rate variability (HRV) waveform. Three different measurements can be obtained: (1) Time domain HRV: Based on different descriptive statistics and distribution of RR data; (2) Frequency domain HRV: The original HRV trace is separated into a spectrum of frequencies as described in Table 1 (very low frequencies, low frequencies, and high frequencies); and (3) Nonlinear parameters: Based on the complexity and regularity of RR data. ECG: Electrocardiogram; HRV: Heart rate variability; IBI: Inter-beat interval.
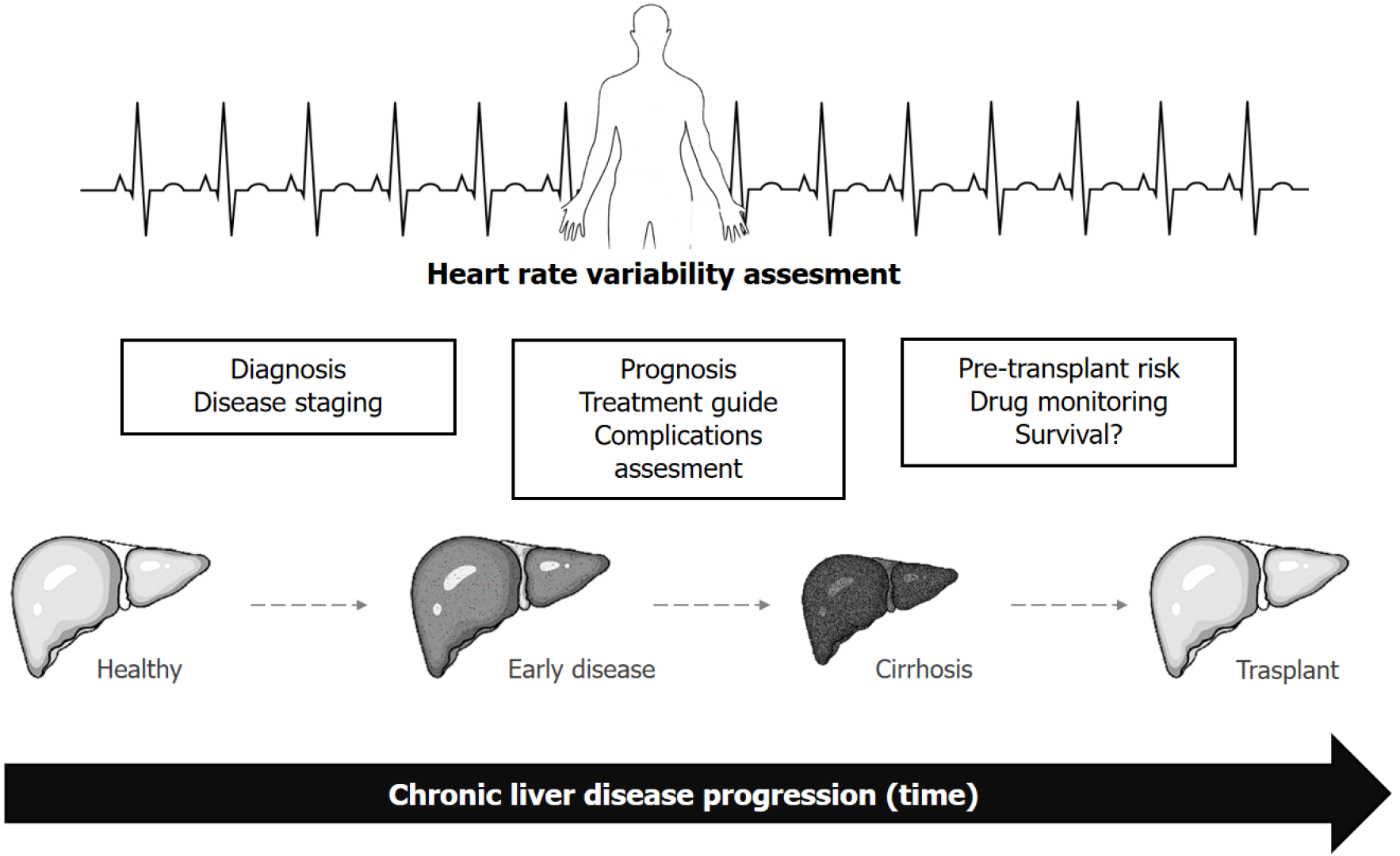
Figure 2 Proposed utility of heart rate variability in chronic liver disease.
Heart rate variability can be assessed across different stages of chronic liver disease progression with different aims at each stage.
- Citation: Bustos N, Giubergia F, Mora C, Lara C, Urzúa Á, Cattaneo M, Poniachik J, Vera DB, Gajardo AI. Heart rate variability in the clinical assessment of patients with chronic liver disease. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(7): 106291
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i7/106291.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i7.106291