Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2025; 17(2): 102328
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.102328
Published online Feb 27, 2025. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.102328
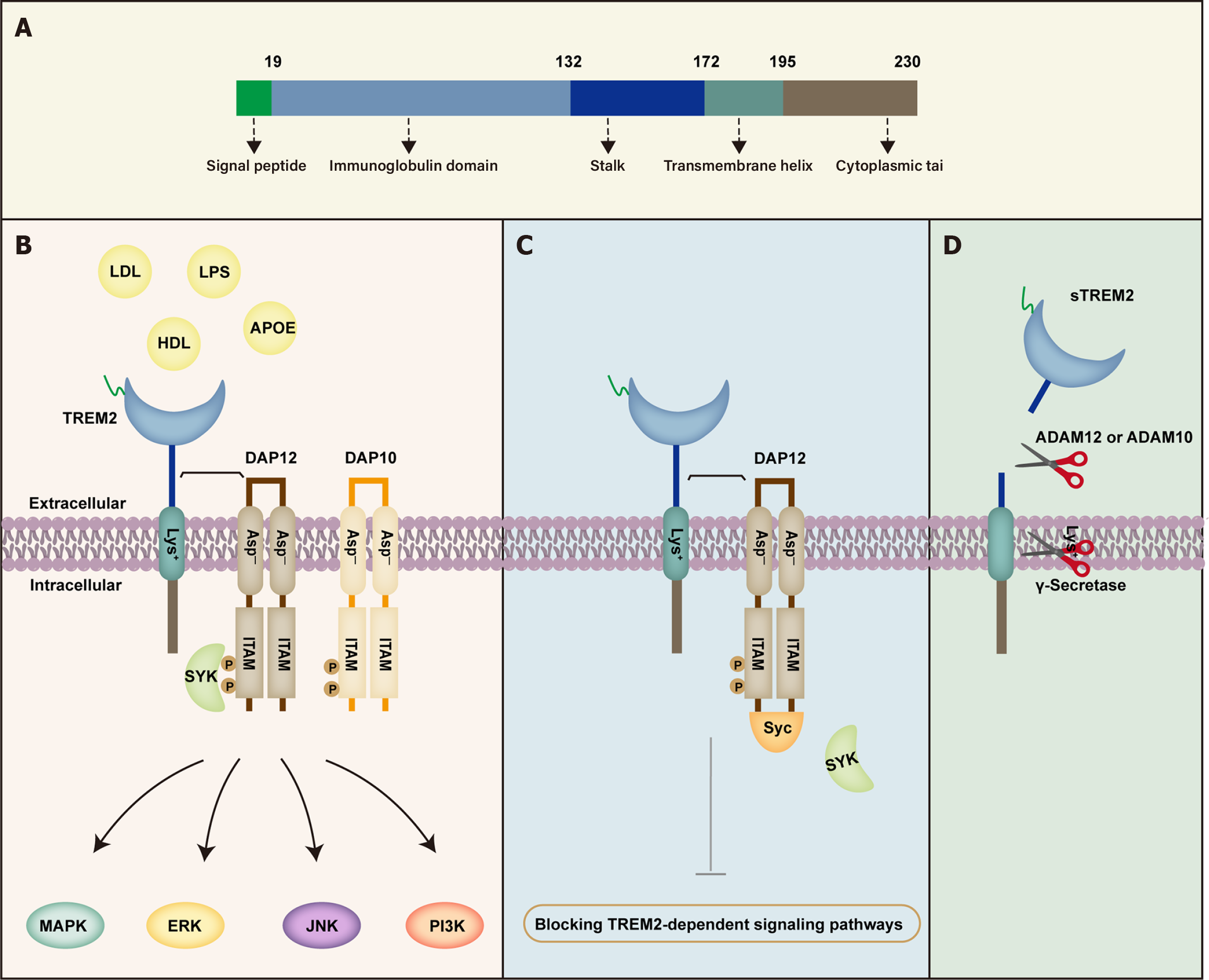
Figure 1 Structure and function of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
A: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM) 2 consists of a signal peptide, an extracellular domain containing a V-type immunoglobulin domain, a short stalk sequence, a transmembrane helix, and a cytoplasmic tail; B: After binding to TREM2, ligands such as high-density lipoprotein, low-density lipoproteins, lipopolysaccharide, apolipoprotein, and other ligands bind to adaptor proteins DNAX-activating proteins (DAP) 12 and DAP10 to form a ligand-receptor complex, which triggers the phosphorylation of the immune receptor tyrosine-based activation motif in the cytoplasmic region of DAP12, recruiting and mediating spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) phosphorylation, thereby activating downstream signaling pathways such as phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, mitogen-activated protein kinase, extracellular regulating kinase, and c-Jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathways; C: During the early formation of the TREM2-DAP12 complex, the recruitment of Syk to DAP12 and the activation of downstream signaling can be blocked by Src homology 2-containing inositol-5'-phosphatase 1; D: TREM2 can also be cleaved by a disintegrin and metalloproteinase (ADAM) 10, ADAM17, and γ-secretase to release soluble TREM2. ADAM: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase; APOE: Apolipoprotein E; DAP: DNAX-activating proteins; ERK: Extracellular regulating kinase; HDL: High-density lipoprotein; ITAM: Immune receptor tyrosine-based activation motif; JNK: C-Jun N-terminal kinase; LDL: Low-density lipoproteins; LPS: Lipopolysaccharide; MAPK: Mitogen-activated protein kinase; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; STREM2: Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; Syk: Spleen tyrosine kinase; TREM2: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
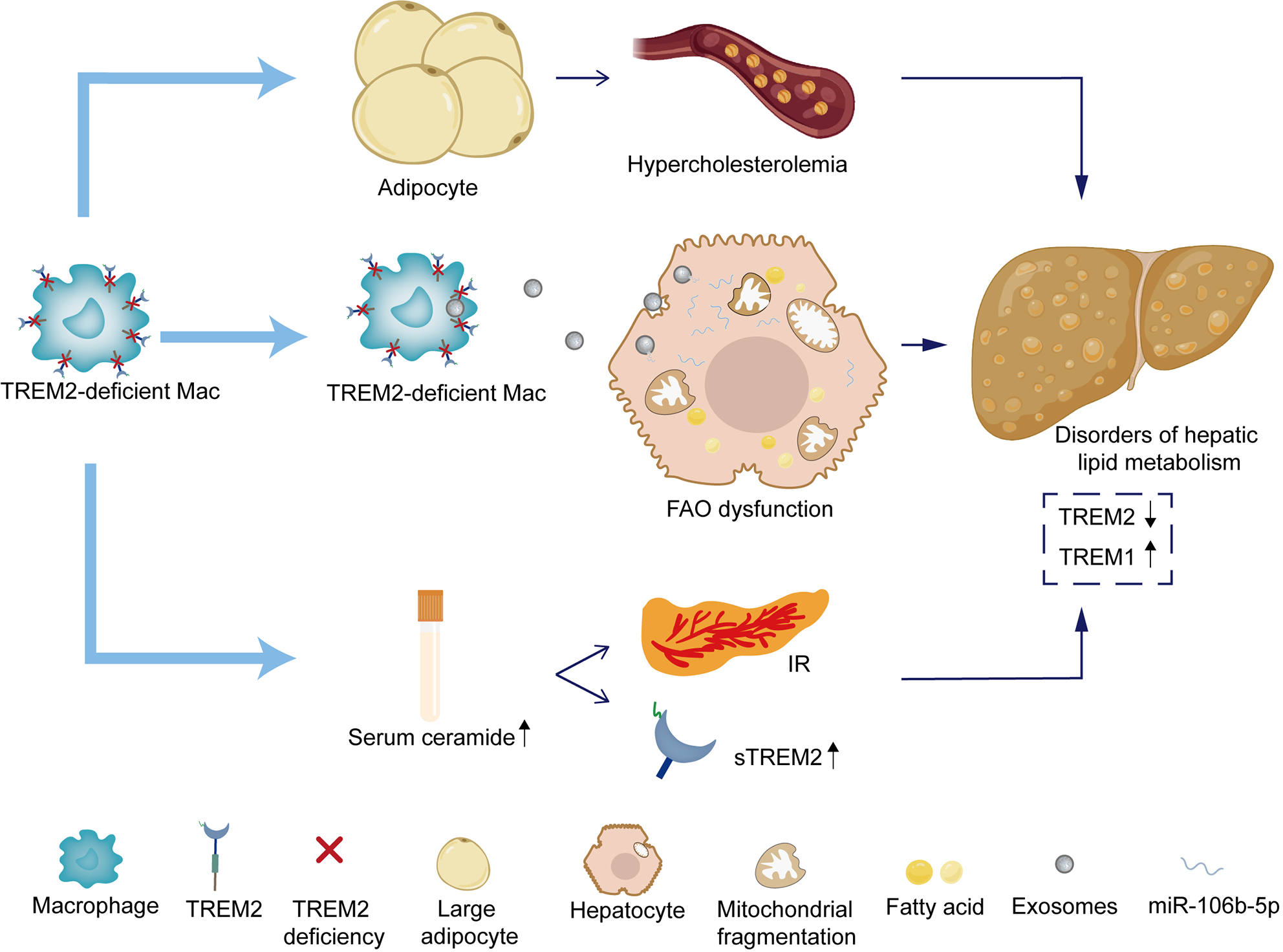
Figure 2 Regulatory role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in liver lipid metabolism.
On the one hand, macrophages lacking triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells (TREM) 2 lead to the accumulation of hypertrophic adipocytes, causing systemic hypercholesterolemia. On the other hand, macrophages lacking TREM2 release exosomes, leading to mitochondrial fragmentation in hepatocytes and fatty acid oxidation dysfunction, accelerating the progression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The deficiency of TREM2 may aggravate insulin resistance (IR) by increasing serum ceramide, leading to hepatic steatosis. The amount of soluble TREM2 in serum and IR are positively correlated. The increase of TREM1 and the decrease of TREM2 are involved in the pathological process of NAFLD. FAO: fatty acid oxidation; IR: insulin resistance; STREM2: Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; TREM: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
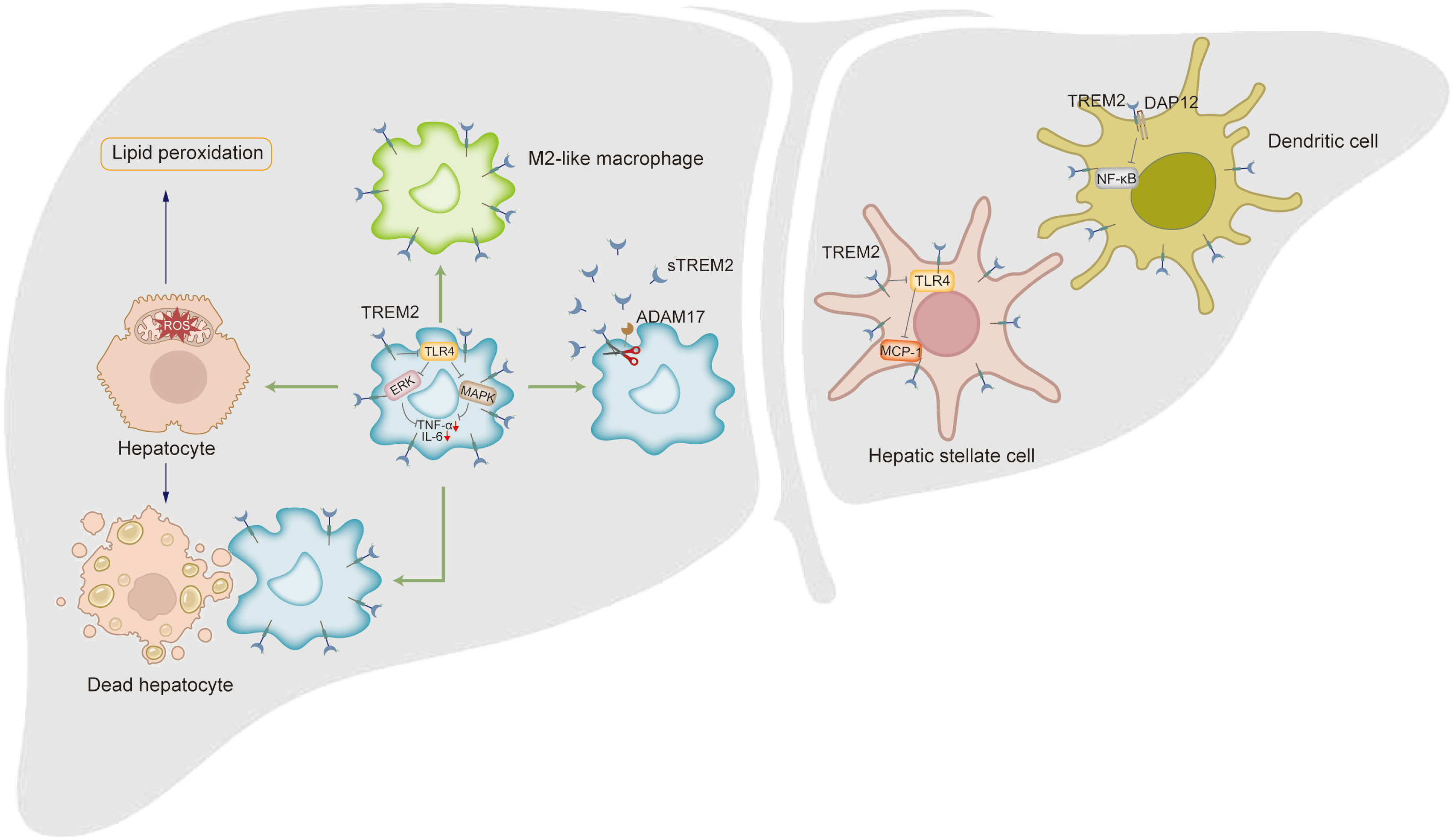
Figure 3 Regulatory role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related inflammatory injury.
The liver macrophages expressing Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) exhibit inhibition of the pro-inflammatory response caused by toll like receptor (TLR) 4-driven extracellular regulating kinase and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation activation, as well as reactive oxygen species-mediated lipid peroxidation and hepatocyte death. High expression of TREM2 ensures that macrophages can effectively clear apoptotic hepatocytes through efferocytosis in a timely manner, thereby inhibiting the transformation of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease into non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). TREM2 can induce macrophage differentiation towards M2 macrophages and inhibit inflammatory response. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1β can induce a disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 to cleave TREM2, leading to an increase in soluble TREM2 levels and aggravation of inflammation in NASH. TREM2 can also inhibit the production of TLR4-dependent monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in hepatic stellate cells. The TREM2 receptor expressed in dendritic cells inhibits nuclear factor-kappa B through binding with DNAX-activating proteins 12, thereby alleviating liver inflammation. ADAM: A disintegrin and metalloproteinase; DAP: DNAX-activating proteins; STREM2: Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; TREM: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
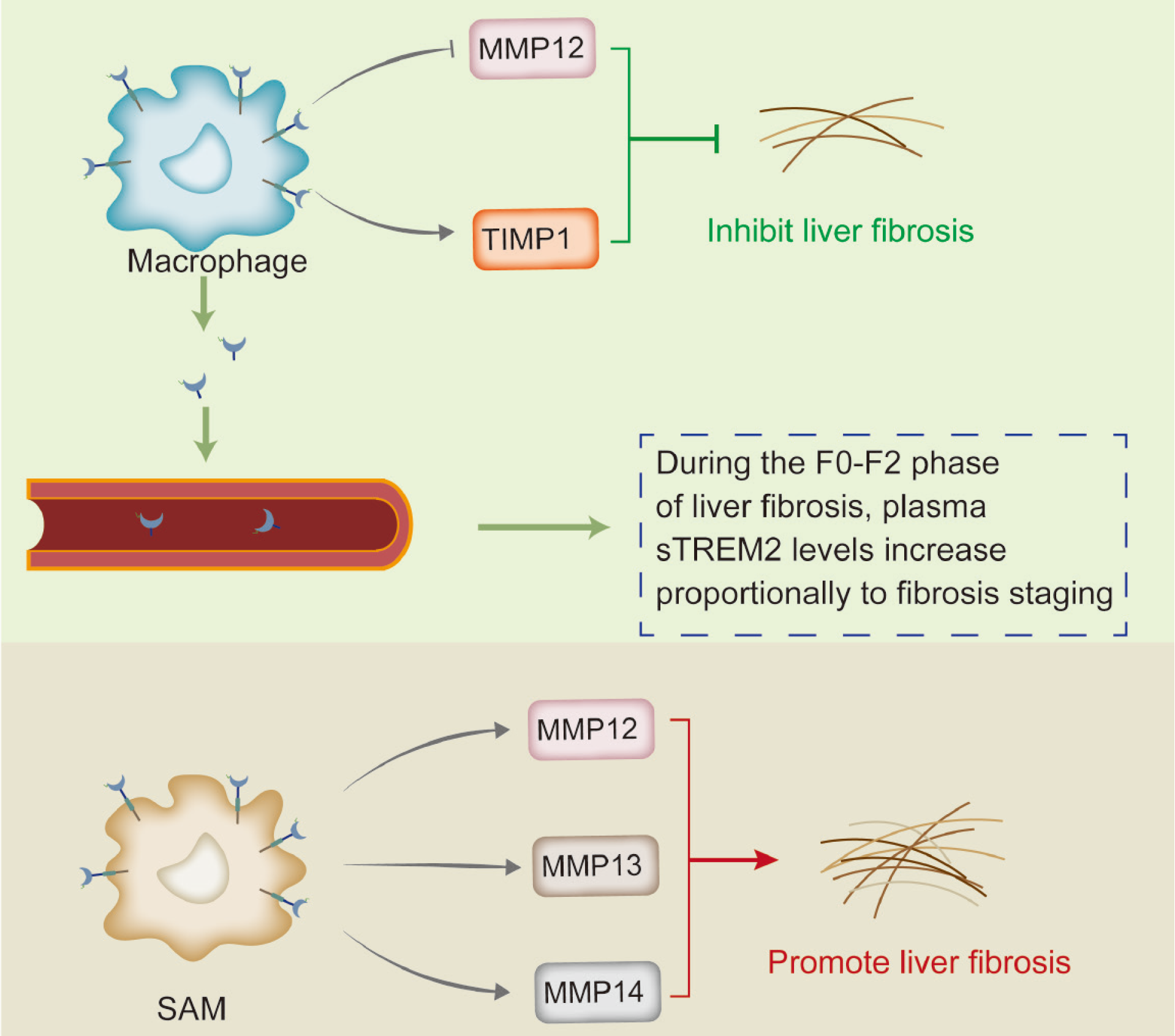
Figure 4 Bidirectional regulation of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related liver fibrosis.
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) can promote the reduction of mitochondrial membrane potential (MMP) 12 and increase the expression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 1, thereby exerting an anti-fibrotic effect. The level of plasma soluble TREM2 can be used as a biomarker to monitor the progression of liver fibrosis in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Conversely, studies have shown that CD9+TREM2+ non-alcoholic steatohepatitis-associated macrophages or scar-associated macrophages accumulate in the liver and promote liver fibrosis by enhancing the expression of MMP12, MMP13, and MMP14. MMP: Mitochondrial membrane potential; SAM: S-adenosyl methionine; STREM2: Soluble triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2; TIMP1: Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 1.
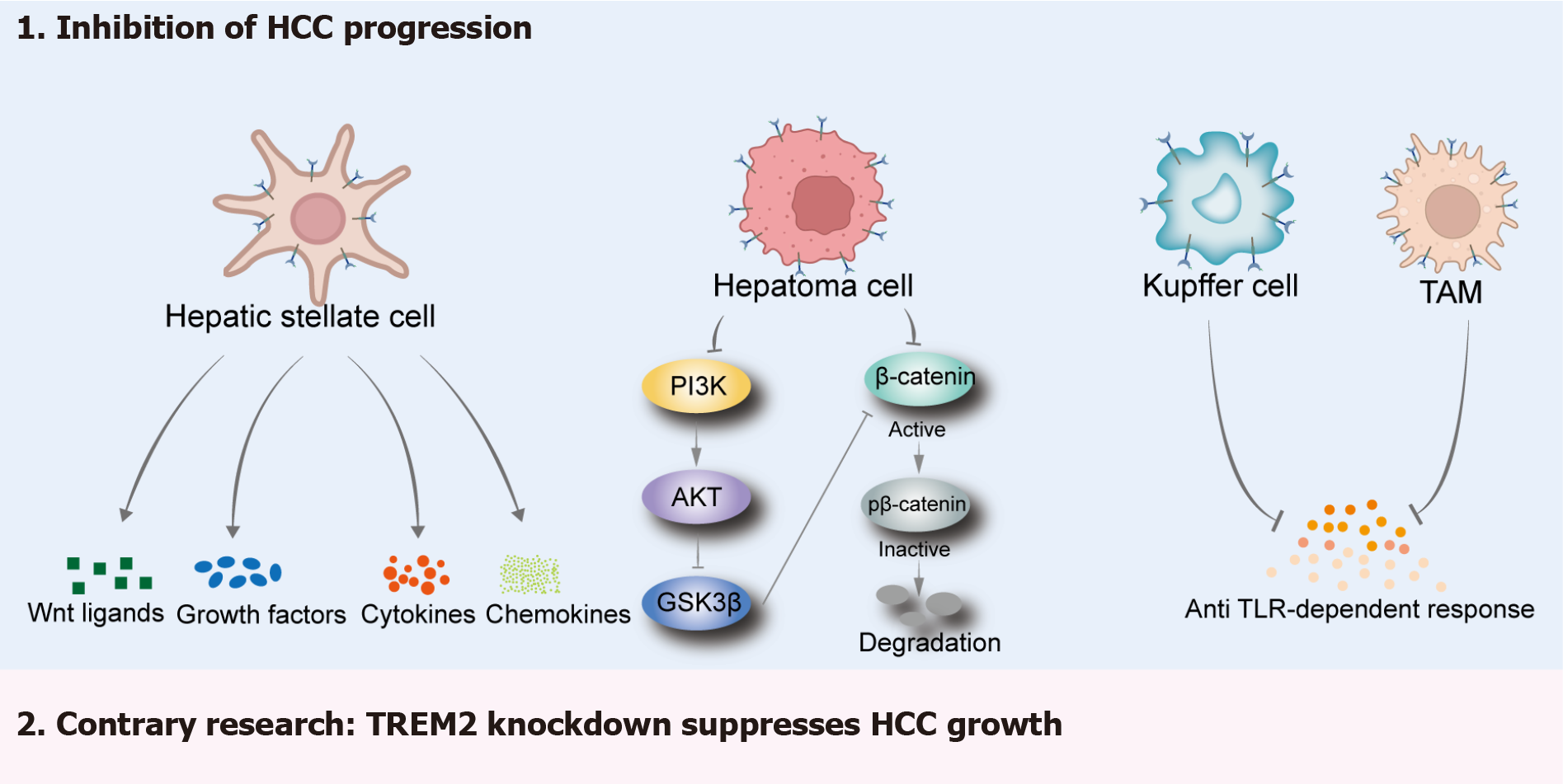
Figure 5 Bidirectional regulatory role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-related hepatocellular carcinoma.
Overexpressed triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) in hepatic stellate cells can regulate the secretion of Wnt ligands and protect the liver from hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Overexpressed TREM2 in HCC cells can inhibit HCC progression by regulating the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B/β-catenin pathway. During the development of end-stage HCC, TREM2 in Kupffer cells and tumor-associated macrophages may inhibit the occurrence of liver tumors by preventing toll like receptor-1 receptor-dependent responses. Another study revealed that TREM2 is a carcinogenic gene in the development of HCC. AKT: Protein kinase B; GSK3β: Glycogen synthase kinase-3β; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; TAMs: Tumor-associated macrophages; TLR: Toll like receptor; TREM2: Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2.
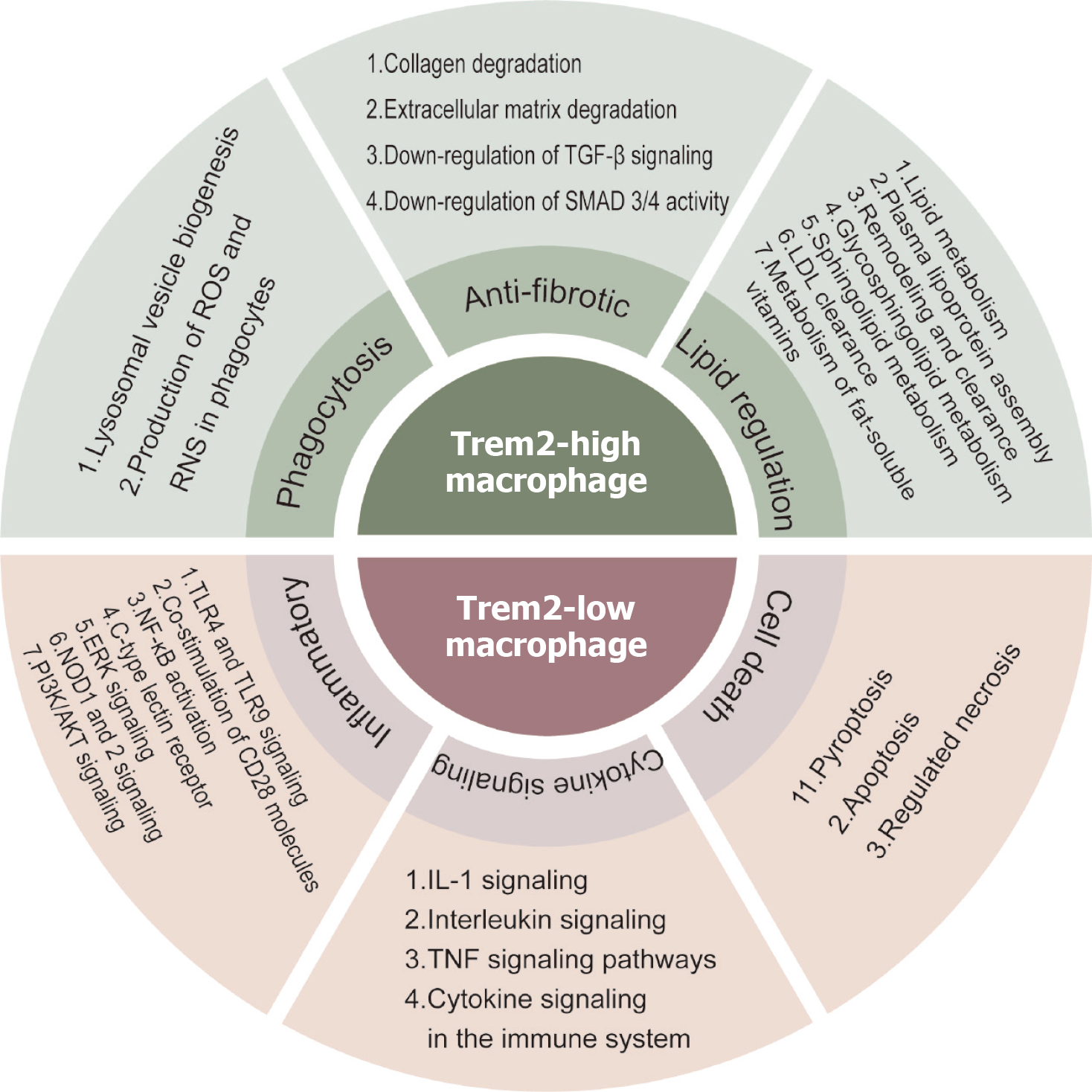
Figure 6 Interaction of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 with other molecular pathways in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
Triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 (TREM2) high-expressing macrophages have phagocytosic and anti-fibrotic functions, and improve lipid/lipoprotein processing. TREM2 Low-expressing macrophages are enriched in metapathways associated with inflammation, enhanced cytokine signaling, and cell death. AKT: Protein kinase B; ERK: Extracellular regulating kinase; IL: Interleukin; NF-κB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; NOD: Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain; PI3K: Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; ROS: Reactive oxygen species; TGF: Transforming growth factor; TLR: Toll like receptor; TNF: Tumor necrosis factor.
- Citation: Zhang LH, Liu ST, Zhao Q, Liu XY, Liu T, Zhang Q, Liu MH, Zhao WX. Role of triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 2 in the pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Hepatol 2025; 17(2): 102328
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v17/i2/102328.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v17.i2.102328