Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2024; 16(3): 393-404
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.393
Published online Mar 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.393
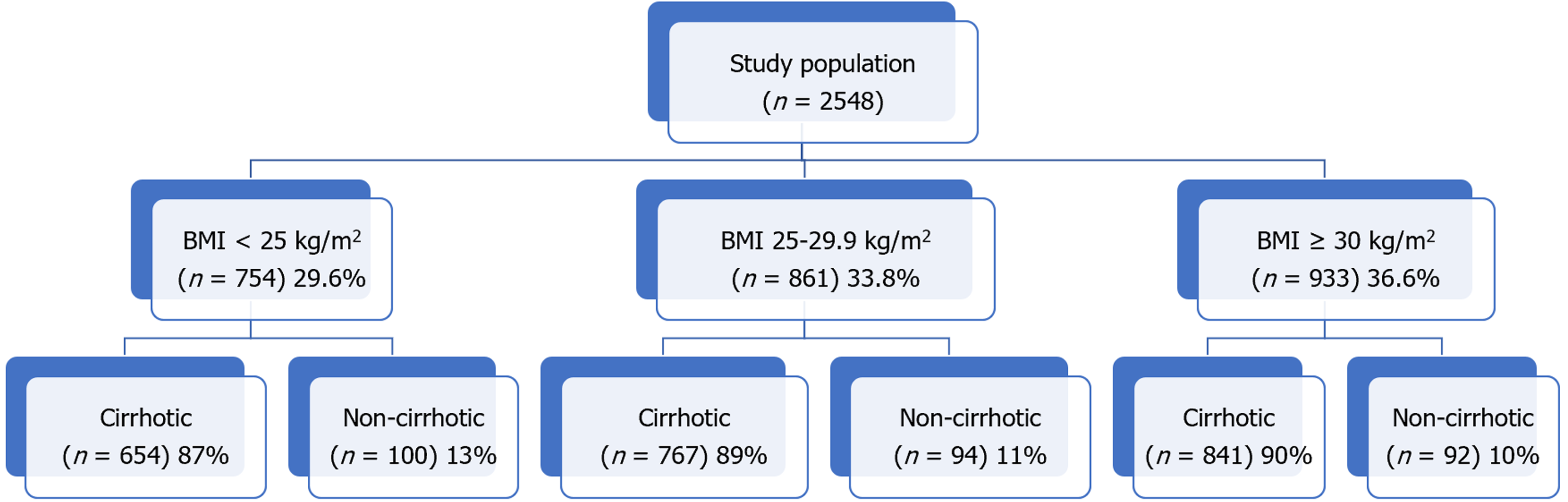
Figure 1 Study cohort by body mass index class.
BMI: Body mass index class.
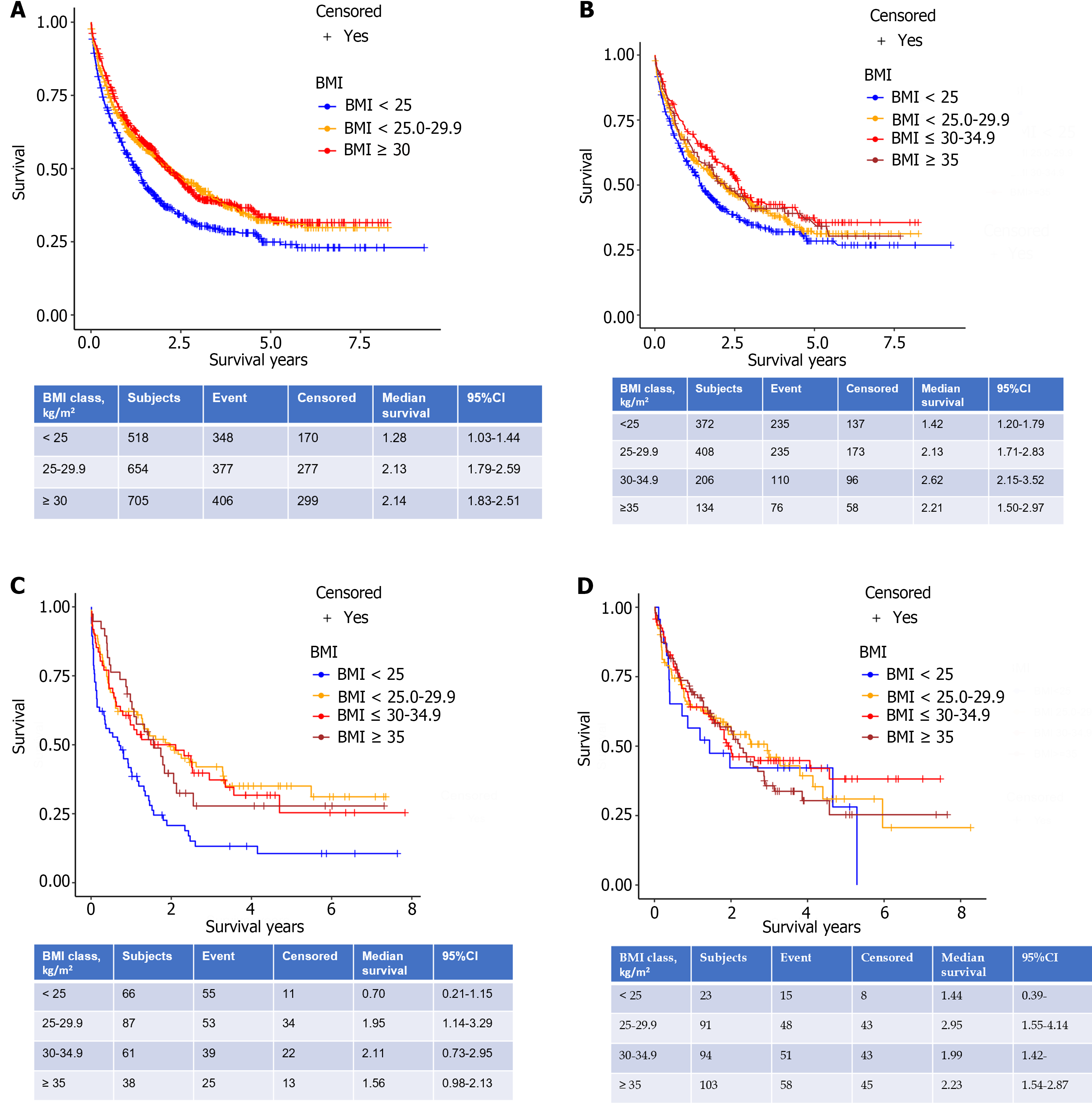
Figure 2 Patient survival.
A: Patient survival with hepatocellular carcinoma according to body mass index class (BMI); B: Overall survival (OS) across four BMI groups by liver disease etiology: Hepatitis C virus; C: OS across four BMI groups by liver disease etiology: Alcohol; D: OS across four BMI groups by liver disease etiology: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. BMI: Body mass index class.
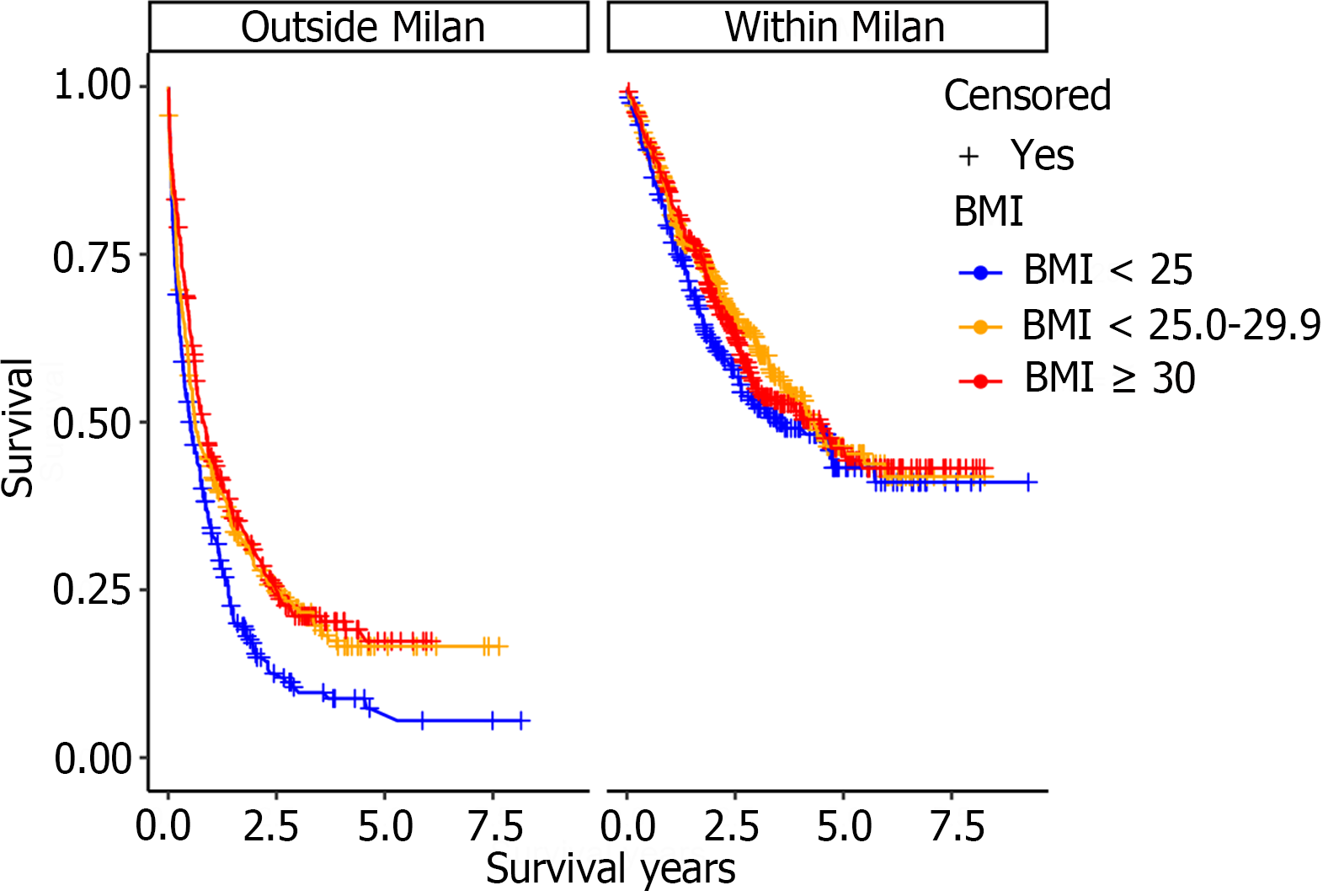
Figure 3 Patient survival after hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis by body mass index class adjusted for Milan criteria.
BMI: Body mass index class.
- Citation: deLemos AS, Zhao J, Patel M, Kooken B, Mathur K, Nguyen HM, Mazhar A, McCarter M, Burney H, Kettler C, Chalasani N, Gawrieh S. Lean body mass index is a marker of advanced tumor features in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(3): 393-404
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i3/393.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i3.393