Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2024; 16(12): 1429-1440
Published online Dec 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1429
Published online Dec 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1429
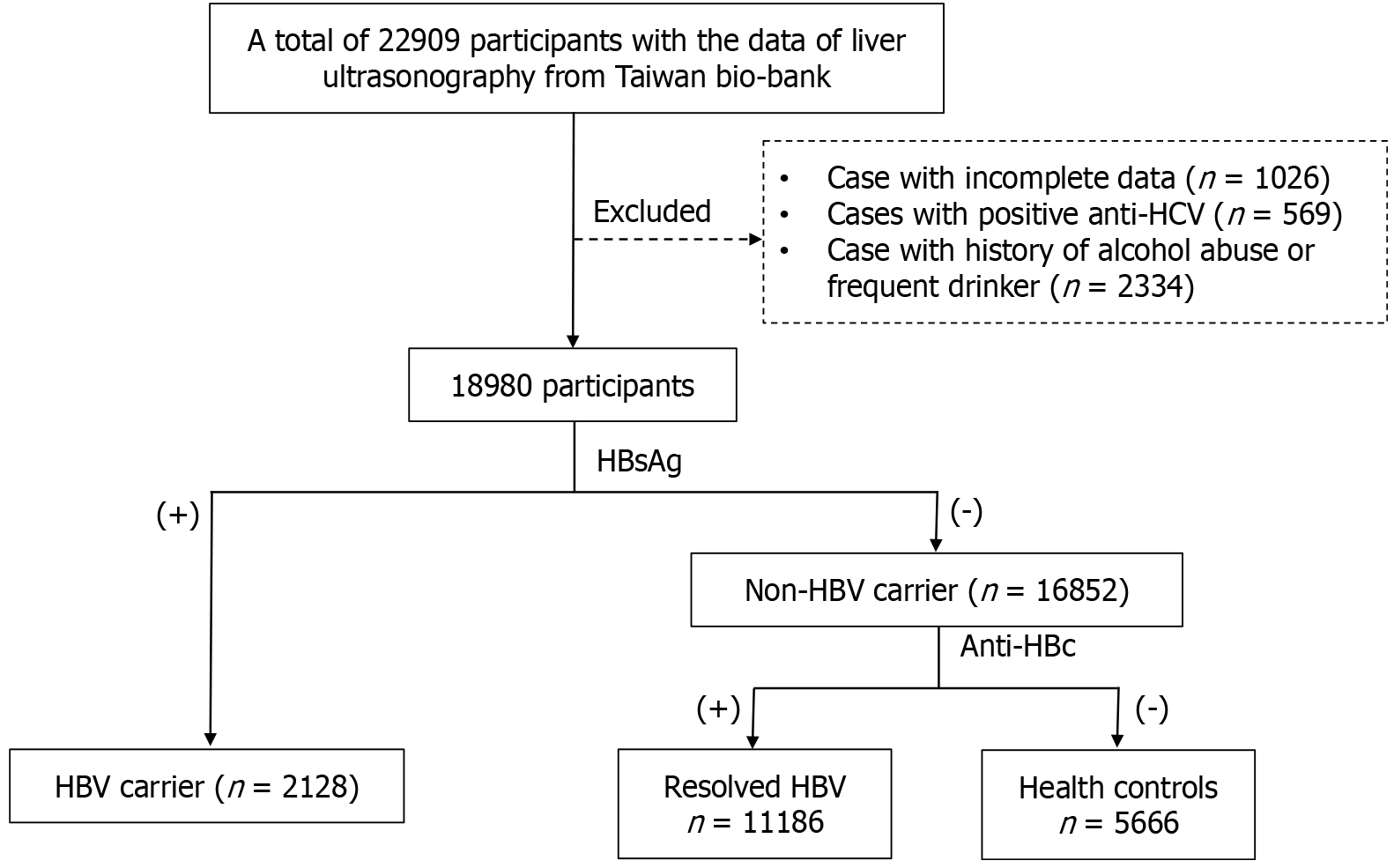
Figure 1 Patients were distributed to three groups according to the results of hepatitis B surface antigen and hepatitis B core antibodies.
anti-HBc: Hepatitis B core antibodies; anti-HCV: Antibodies against hepatitis C virus; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV: Hepatitis B virus.
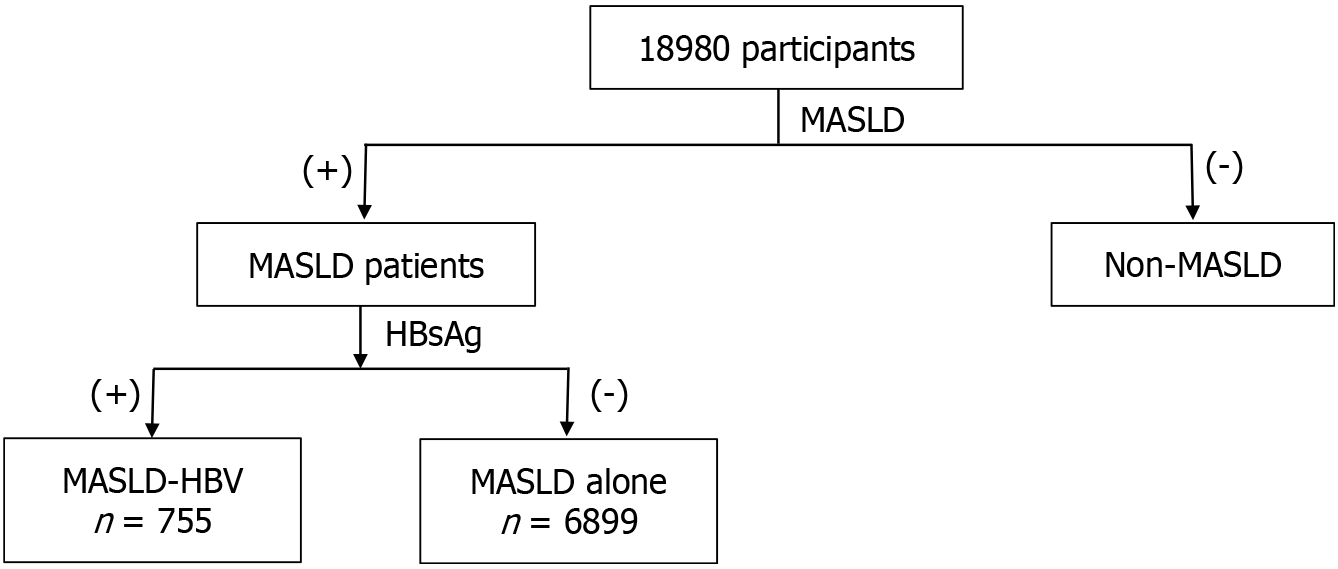
Figure 2 Metabolic associated steatotic liver disease patients were distributed to two groups based on the status of hepatitis B surface antigen.
HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
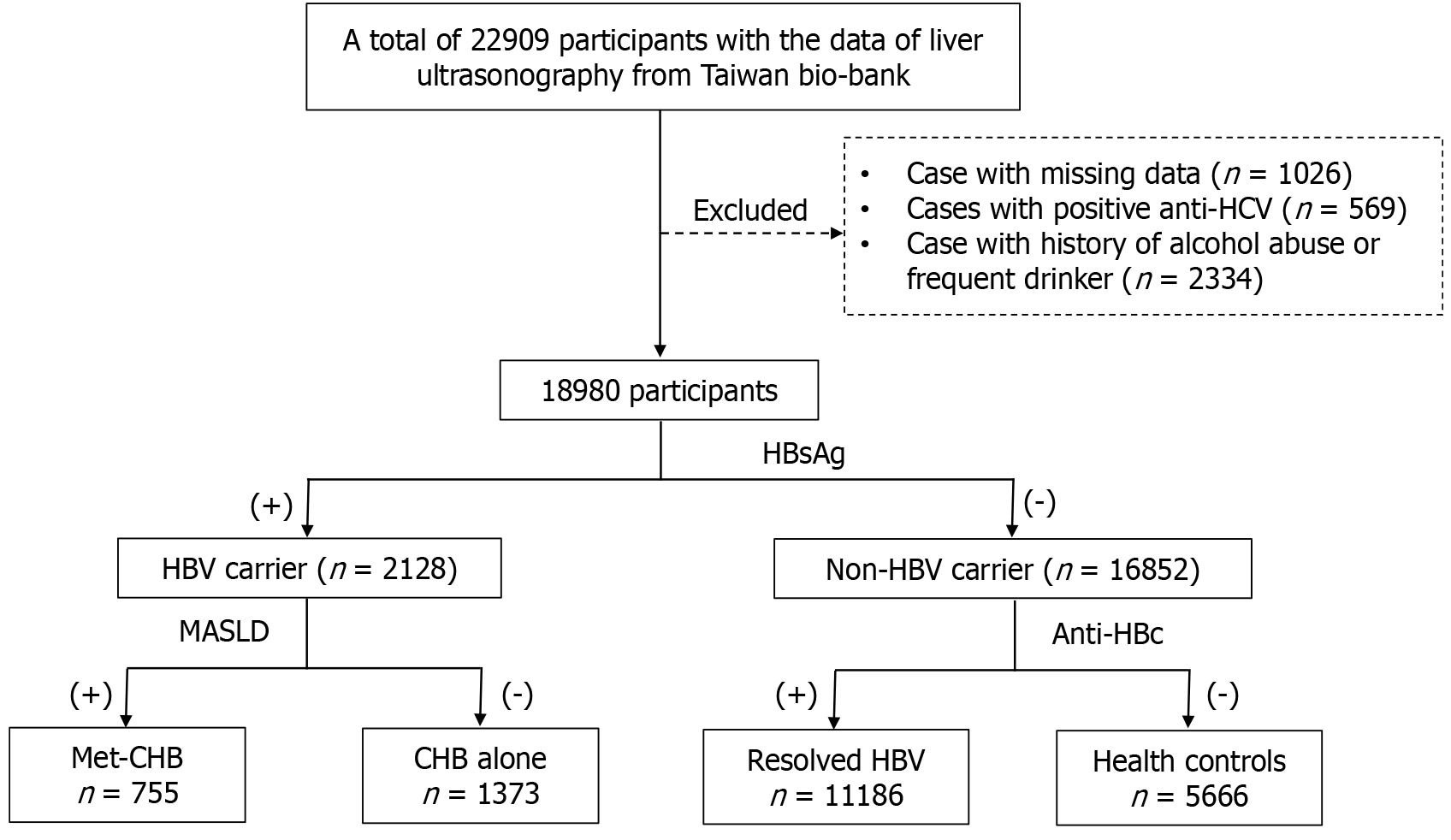
Figure 3 Patients with positive hepatitis B surface antigen were distributed to two groups based on the status of metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
anti-HBc: Hepatitis B core antibodies; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; HBV: Hepatitis B virus; MASLD: Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease.
- Citation: Wang SW, Chang YW, Wang C, Cheng YM, Hsieh TH, Wang CC, Kao JH. Clinical profiles and their interaction of concurrent metabolic associated steatotic liver disease and hepatitis B virus infection. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(12): 1429-1440
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i12/1429.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i12.1429