Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Hepatol. Jan 27, 2024; 16(1): 91-102
Published online Jan 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i1.91
Published online Jan 27, 2024. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v16.i1.91
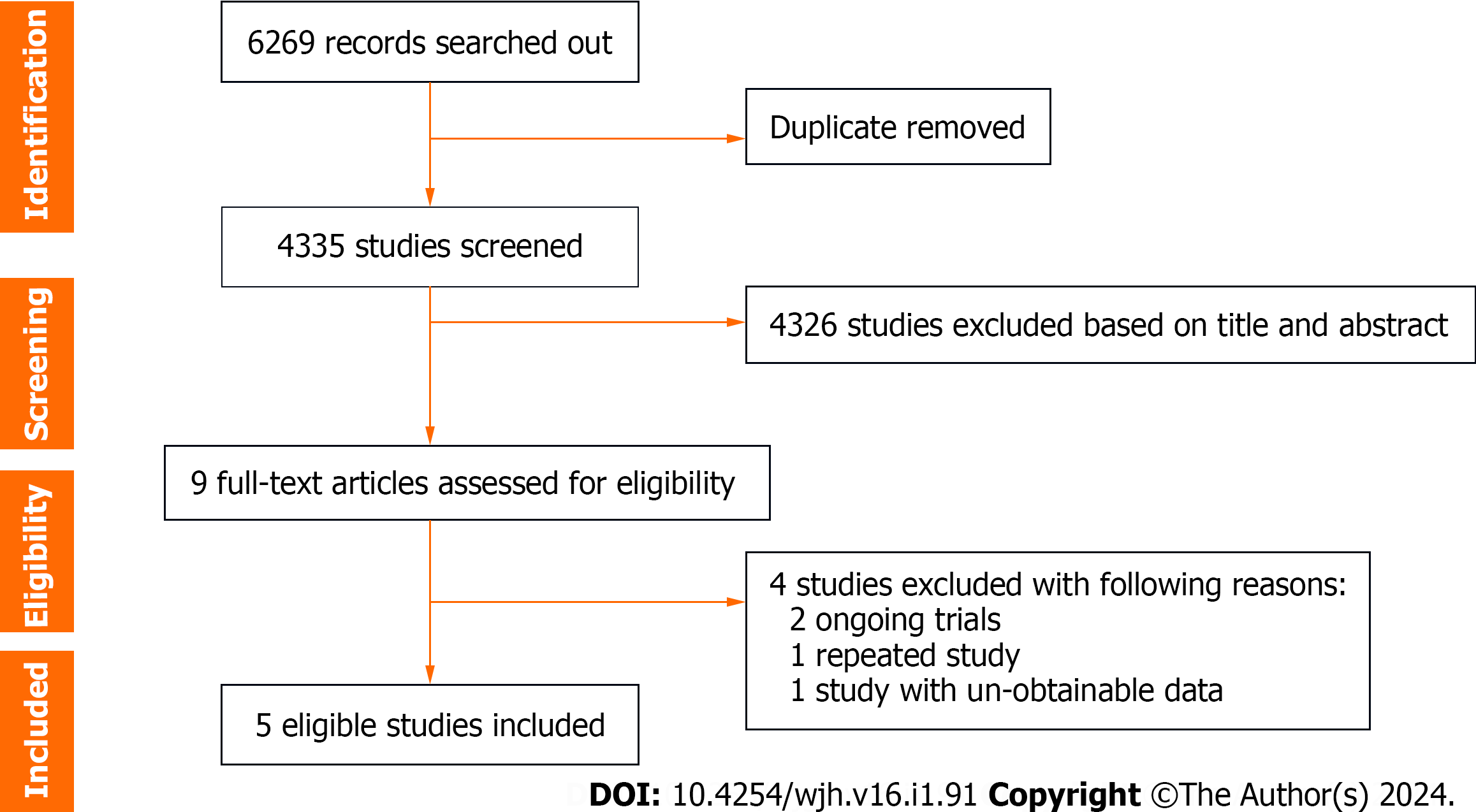
Figure 1 Flowchart of study selection.
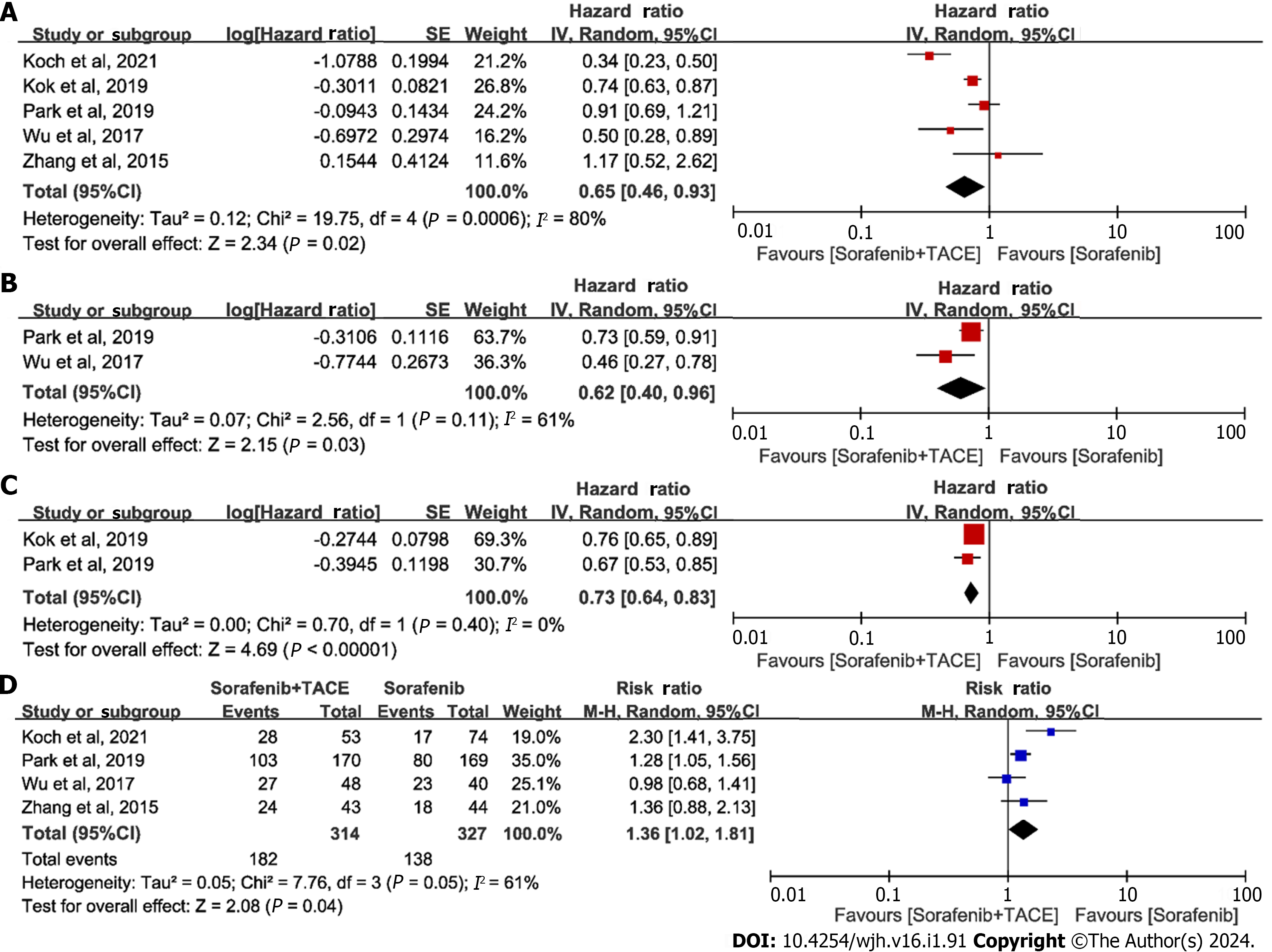
Figure 2 Meta-analysis of efficacy outcomes in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving sorafenib plus transarterial chemoembolization or sorafenib alone.
A: Forest plot of overall survival; B: Forest plot of progression free survival; C: Forest of time to progression; D: Forest plot of disease control rate. The pooled results were calculated by using a random-effects model. 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
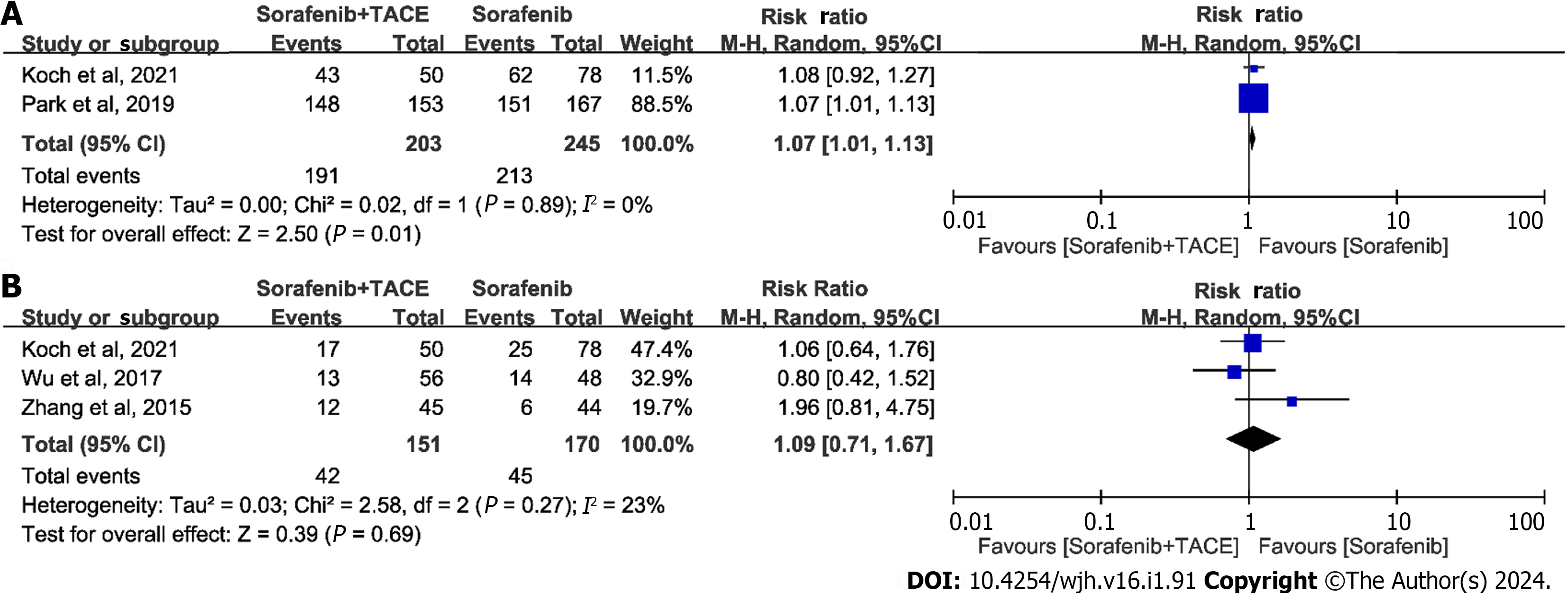
Figure 3 Meta-analysis of safety outcomes in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving sorafenib plus transarterial chemoembolization or sorafenib alone.
A: Forest plot of any adverse event (AE); B: Forest plot of grade ≥ 3 AEs. 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
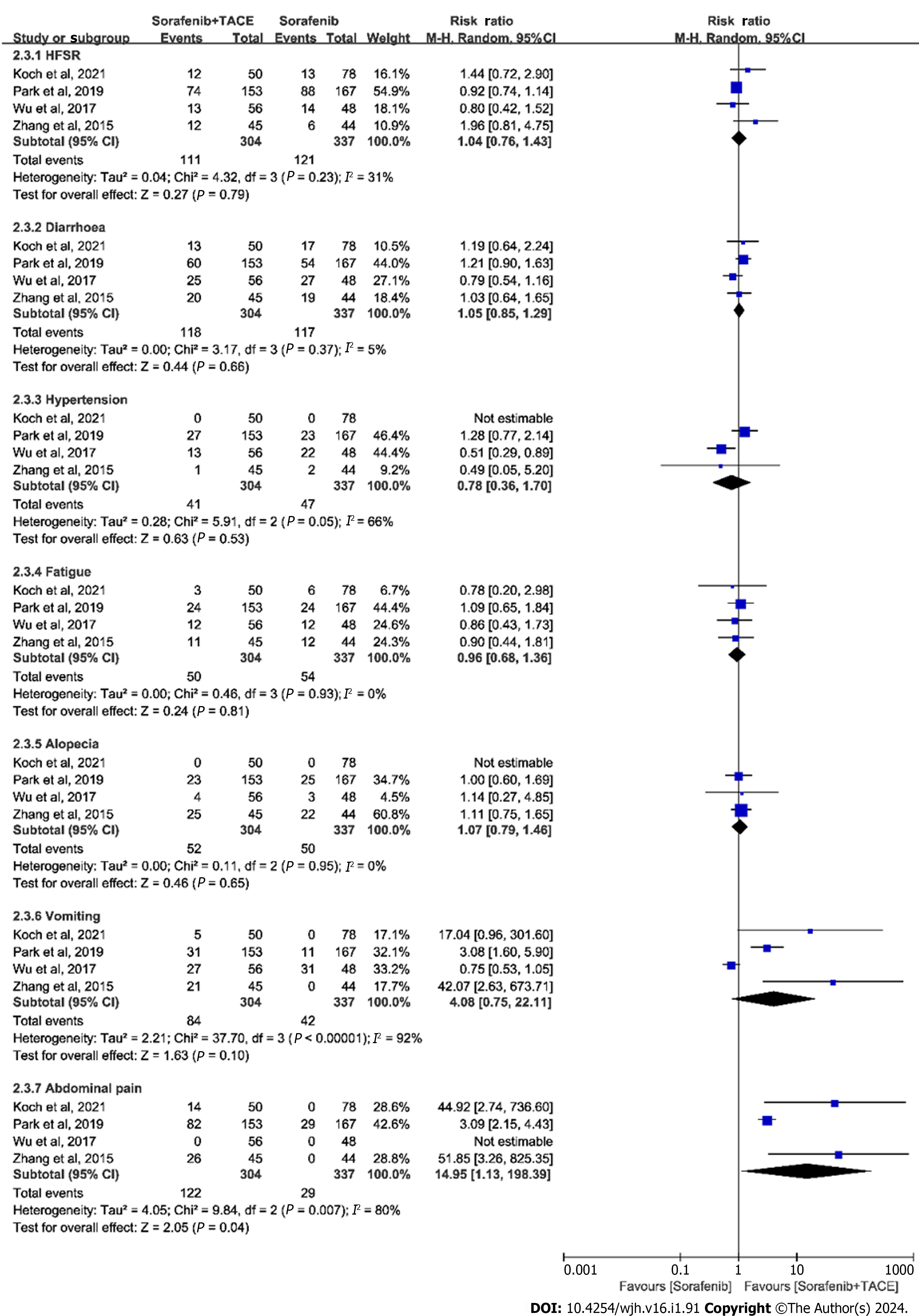
Figure 4 Meta-analysis of incidence of typical AEs in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma receiving sorafenib plus transarterial chemoembolization or sorafenib alone.
AE: Adverse event; HFSR: Hand-foot skin reaction; 95%CI: 95% confidence interval; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization.
- Citation: Yang HJ, Ye B, Liao JX, Lei L, Chen K. Sorafenib plus transarterial chemoembolization vs sorafenib alone for patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Hepatol 2024; 16(1): 91-102
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v16/i1/91.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v16.i1.91