Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2023; 15(6): 786-796
Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786
Published online Jun 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786
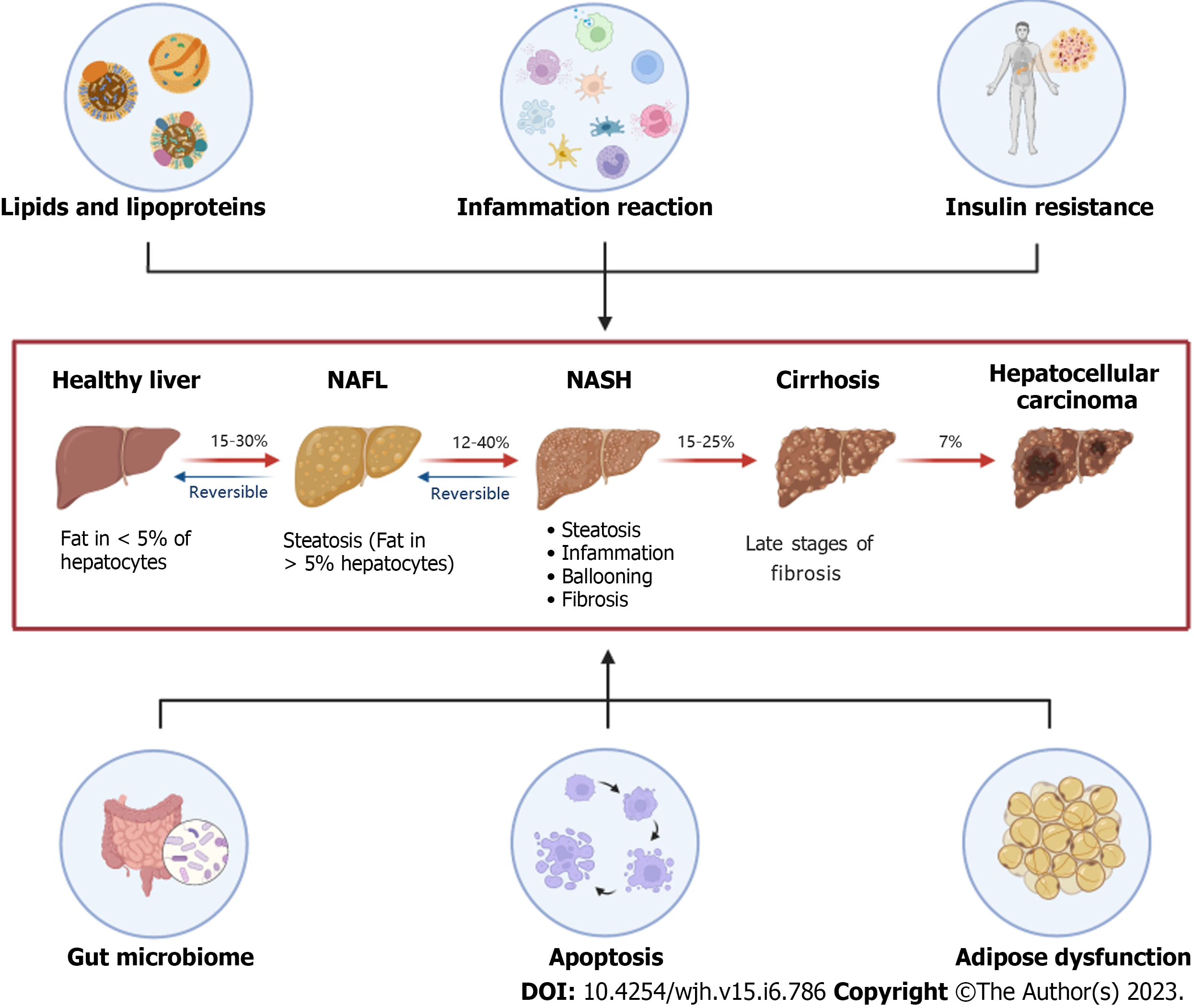
Figure 1 The “multiple-hit” theories are involved in the progress of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Lipids and lipoproteins represent the “first-hit”, while the inflammation reaction illustrates the “second-hit” in the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Six aspects including lipids and lipoproteins, inflammation reaction, insulin resistance, gut microbiome, apoptosis, and adipose dysfunction have a common influence on the pathophysiological mechanism of NAFLD. NAFL: Non-alcoholic fatty liver; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
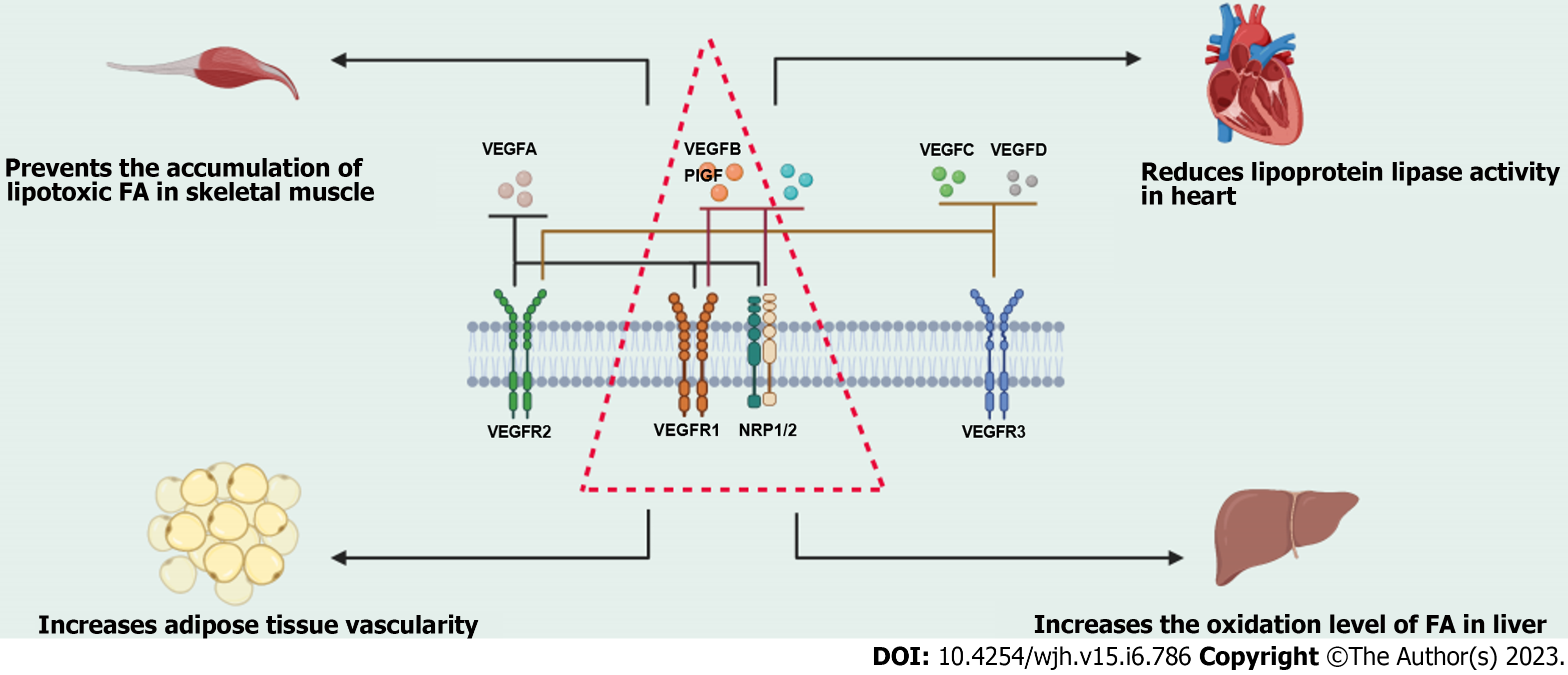
Figure 2 The vascular endothelial growth factor family and its receptors, and the biological function of vascular endothelial growth factor B.
The vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) family includes VEGFA, vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB), VEGFC, VEGFD, and so on. The VEGF receptor family includes VEGFR1, VEGFR2, VEGFR3, and neuropilin 1/2 (NRP1/2). VEGFA combines with VEGFR1, VEGFR2, or NRP1/2. VEGFB and placental growth factor combine with VEGFR1 or NRP1/2. VEGFC and VEGFD combine with VEGFR2 or VEGFR3 to exert their biological functions. VEGFB can prevent the accumulation of lipotoxic free fatty acid (FFA) in skeletal muscle, reduce lipoprotein activity in the heart, increase adipose tissue vascularity, and increase the oxidation level of FFA in the liver. PIGF: Placental growth factor; FA: Fatty acid; NRP1/2: Neuropilin 1/2; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFB: Vascular endothelial growth factor B.
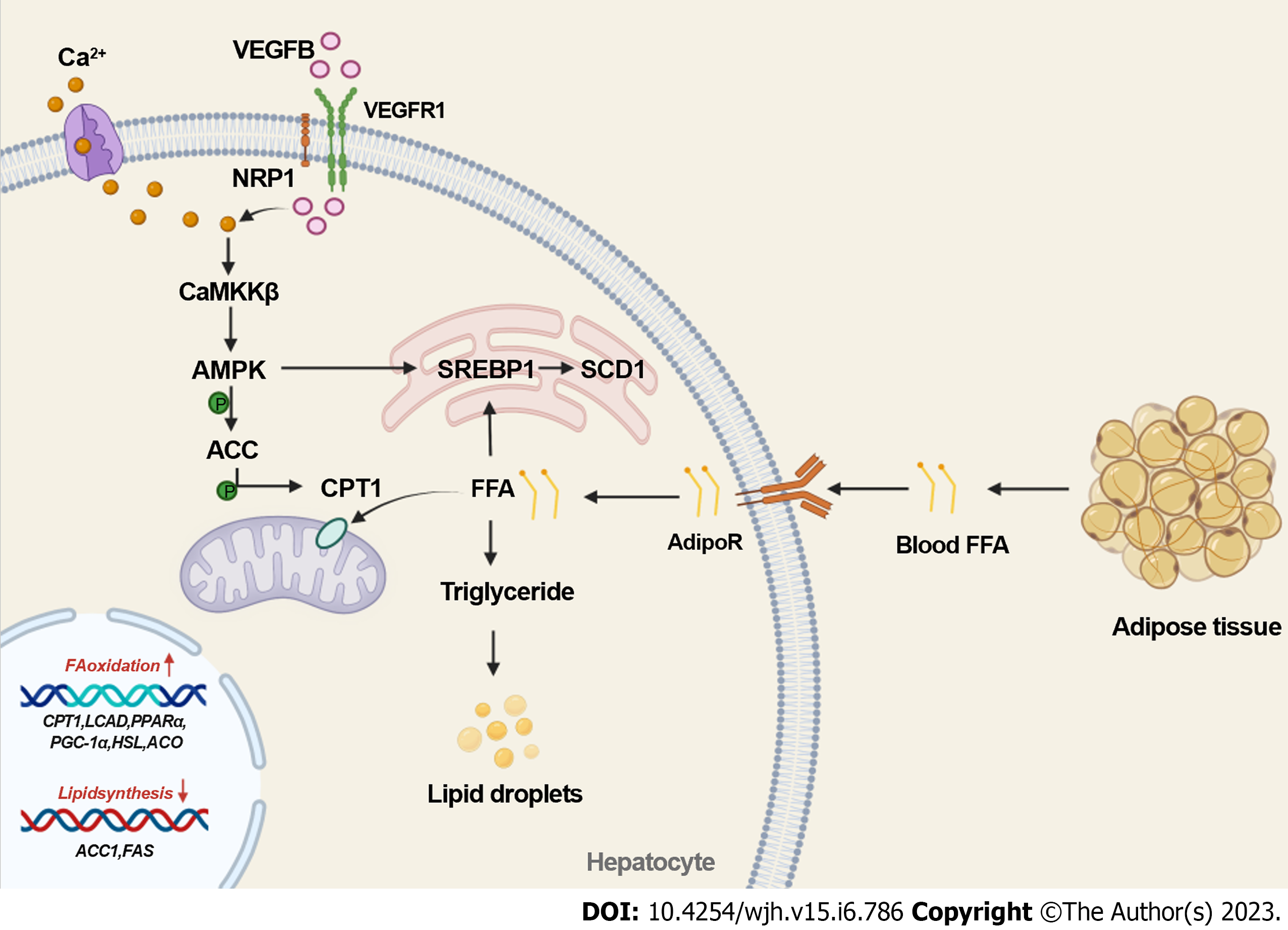
Figure 3 Vascular endothelial growth factor B regulates lipid metabolism in the “first hit” of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via the activated protein kinase signaling pathway.
Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB) performs its biological function by combining with VEGFR1. Once it enters the cell, it activates Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase β (CaMKKβ), which is induced by an increase in intracellular Ca2+ content. VEGFB activates the CaMKKβ-mediated activated protein kinase (AMPK)/A carboxylase (ACC)/carnitine palmitate transferase (CPT1) signaling pathway and related genes, such as CPT1 and long-chain acyl coenzyme A dehydrogenase, which regulate FFA oxidation in mitochondria. VEGFB activates AMPK/SREBP1/SCD1 and related genes, such as ACC1 and FAS, to inhibit lipid synthesis in the endoplasmic reticulum. CaMKKβ: Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase β; AMPK: Adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; ACC: A carboxylase; CPT1: Carnitine palmitate transferase-1; FFA: Free fatty acid; NRP1/2: Neuropilin 1/2; SCD1: Stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1; SREBP1: Sterol-regulatory element-binding protein-1; VEGFB: Vascular endothelial growth factor B; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor; VEGFB: Vascular endothelial growth factor B; FAS: fatty acid synthase; ACO: Acyl Coenzyme A Oxidase; HSL: hormone-sensitive lipase; LCAD: long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; PPARα: proliferator-activated receptor-α; PGC-1α: peroxidase proliferator activator receptor γ coactivator 1α.
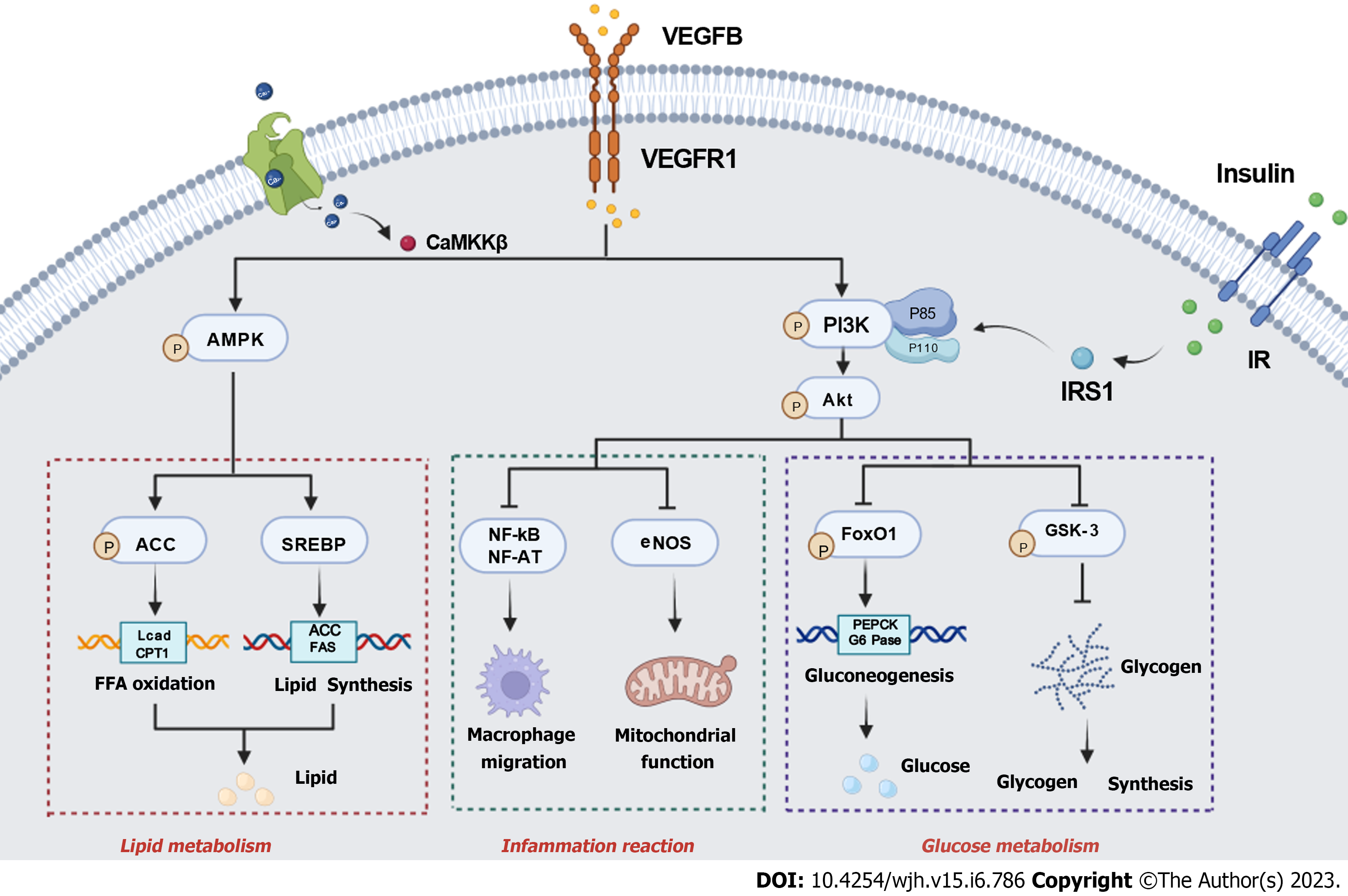
Figure 4 Vascular endothelial growth factor B participates in the “multiple-hit” of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.
Vascular endothelial growth factor B (VEGFB) regulates lipid metabolism, inflammation reaction, and glucose metabolism, which co-exist in the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease progression. VEGFB activates the AMPK phosphorylation to regulate free fatty acid oxidation and lipid synthesis. Long-term lipid metabolism disorders will cause inflammatory reactions and glucose metabolism disorders. VEGFB promotes the phosphorylation of protein kinase B (AKT) via combining with the VEGFR1 to affect macrophage migration and mitochondrial inflammation reaction. Meanwhile, VEGFB/VEGFR1 also plays an important role in inhibiting gluconeogenesis and promoting glycogen synthesis by activating the phosphorylation of AKT to regulate glucose metabolism. CaMKKβ: Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase β; VEGFR1: Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1; VEGFB: Vascular endothelial growth factor B; IR: Insulin receptor; IRS1: Insulin receptor substrate-1; PI3K: Phosphoinositide 3-kinase; AKT: Protein kinase B; AMPK: Adenosine 5‘-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase; ACC: A carboxylase; CPT1: Carnitine palmitate transferase-1; Lcad: long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase; SREBP: Sterol-regulatory element-binding protein; FAS: fatty acid synthase; NF-kB: Nuclear factor-kappa B; NF-AT: Nuclear factors of activated T; eNOS: endothelial nitric oxide synthase; FoxO1: Forkhead box protein-1; GSK-3: Serine/threonine kinase-3; PEPCK: Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase; G6Pase: Glucose 6 phosphatase;
- Citation: Li YQ, Xin L, Zhao YC, Li SQ, Li YN. Role of vascular endothelial growth factor B in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its potential value. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(6): 786-796
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i6/786.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i6.786