Copyright
©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2023; 15(12): 1315-1324
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1315
Published online Dec 27, 2023. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1315
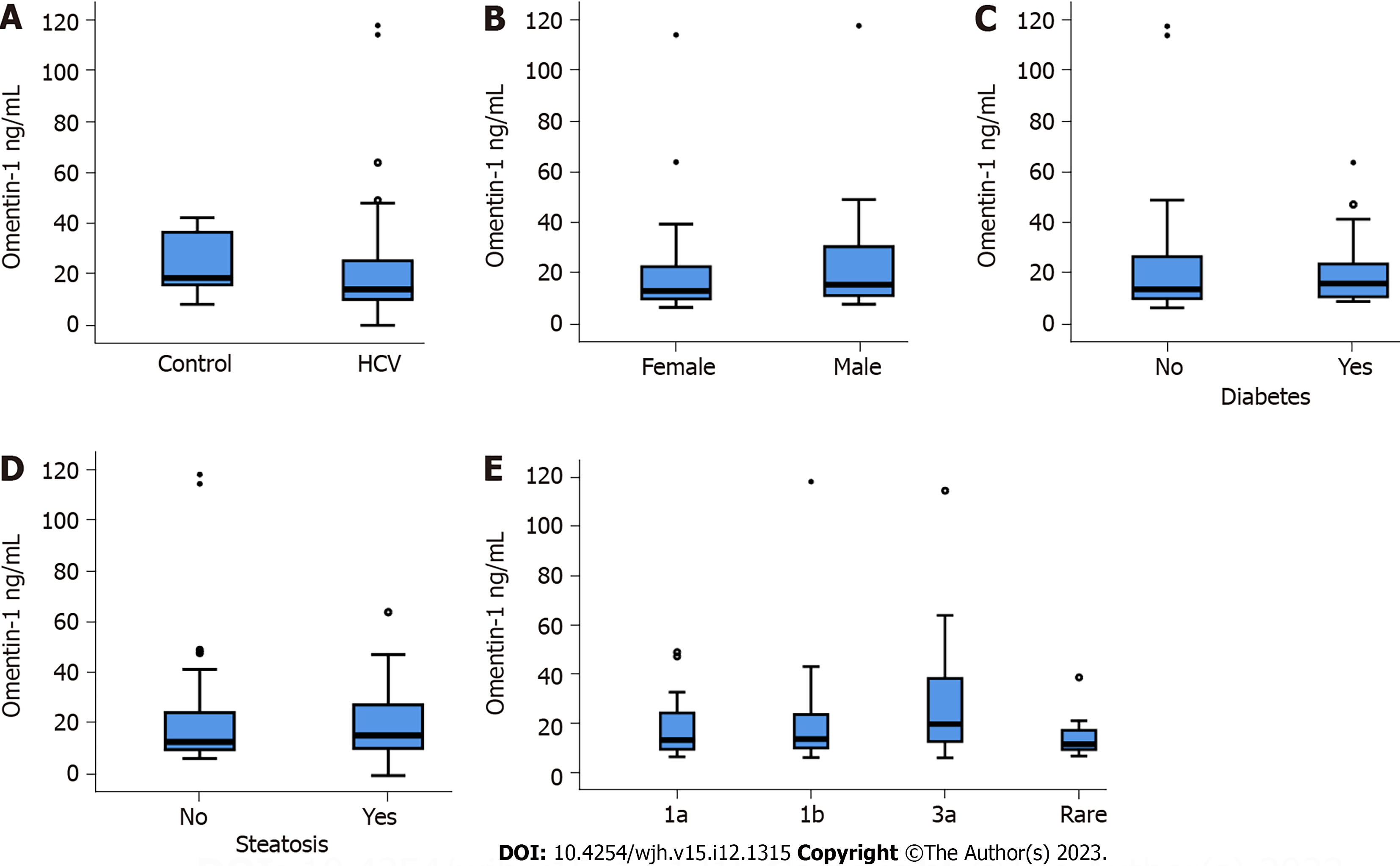
Figure 1 Serum omentin-1 levels of controls and patients with chronic hepatitis C virus.
A: Serum omentin-1 Levels of 14 controls and 84 patients with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV); B: Serum omentin-1 levels of 37 female and 47 male HCV patients; C: Serum omentin-1 levels of 15 patients with and 69 patients without diabetes; D: Serum omentin-1 levels of 38 patients with and 46 patients without steatosis; E: Serum omentin-1 levels of patients categorized for HCV genotype (Rare group signifies 8 patients with genotypes other than 1a, 1b, and 3a). The small circles or asterisks above the boxes mark outliers.
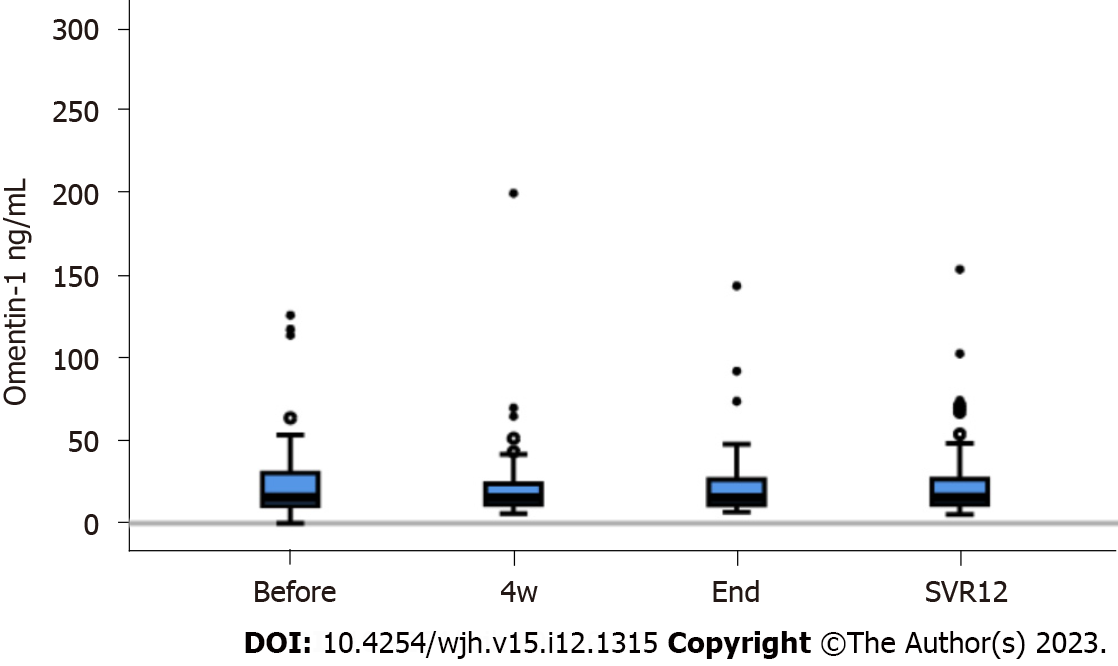
Figure 2 Serum omentin-1 levels during direct acting antiviral therapy.
Omentin-1 serum levels before therapy start (Before), at 4 wk after therapy start (4w), at therapy end (End) and at sustained virological response 12 (SVR12). Small circles or asterisks above the boxes mark outliers.
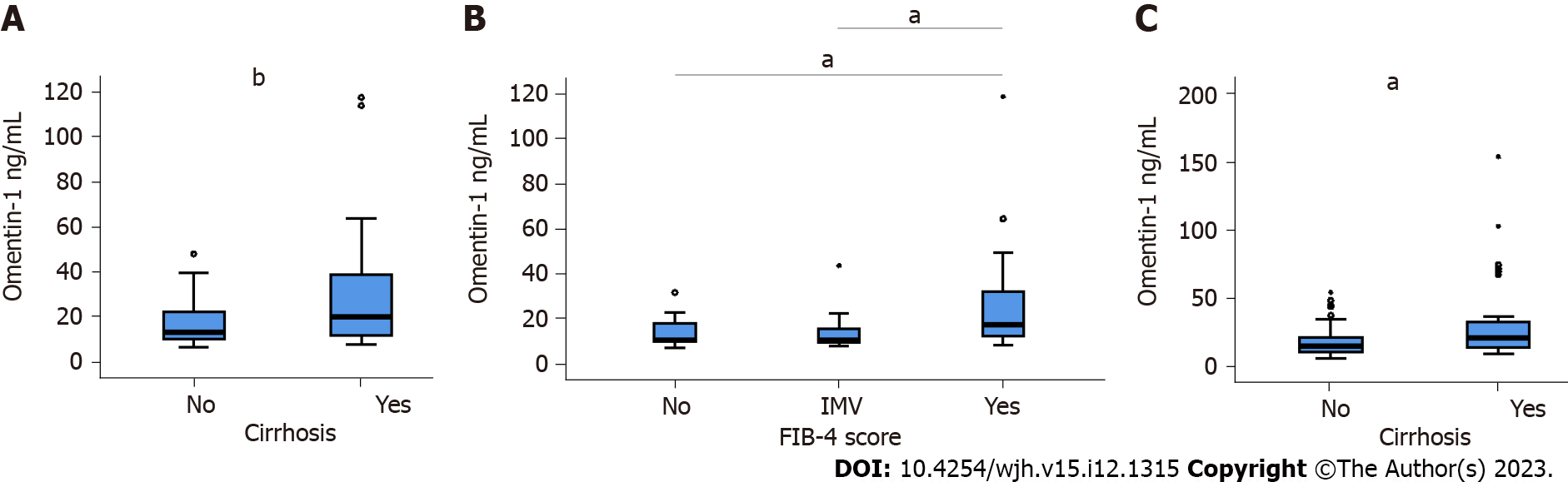
Figure 3 Serum omentin-1 in relation to liver fibrosis.
A: Serum omentin-1 levels of hepatitis C virus (HCV) patients with liver cirrhosis and non-cirrhotic patients, which was diagnosed by ultrasound before therapy; B: Serum omentin-1 levels of HCV patients categorized according to the fibrosis-4 score (26 patients no fibrosis = No; 18 patients had intermediate values = IMV, 40 patients had fibrosis = Yes) before therapy; C: Serum omentin-1 levels of HCV patients without and with liver cirrhosis, which was diagnosed by ultrasound, at sustained virological response 12 (SVR12). Small circles and stars above the boxes mark outliers. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.01.
- Citation: Peschel G, Weigand K, Grimm J, Müller M, Buechler C. Serum omentin-1 is correlated with the severity of liver disease in patients with chronic hepatitis C. World J Hepatol 2023; 15(12): 1315-1324
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v15/i12/1315.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v15.i12.1315