Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2022; 14(7): 1344-1356
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1344
Published online Jul 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1344
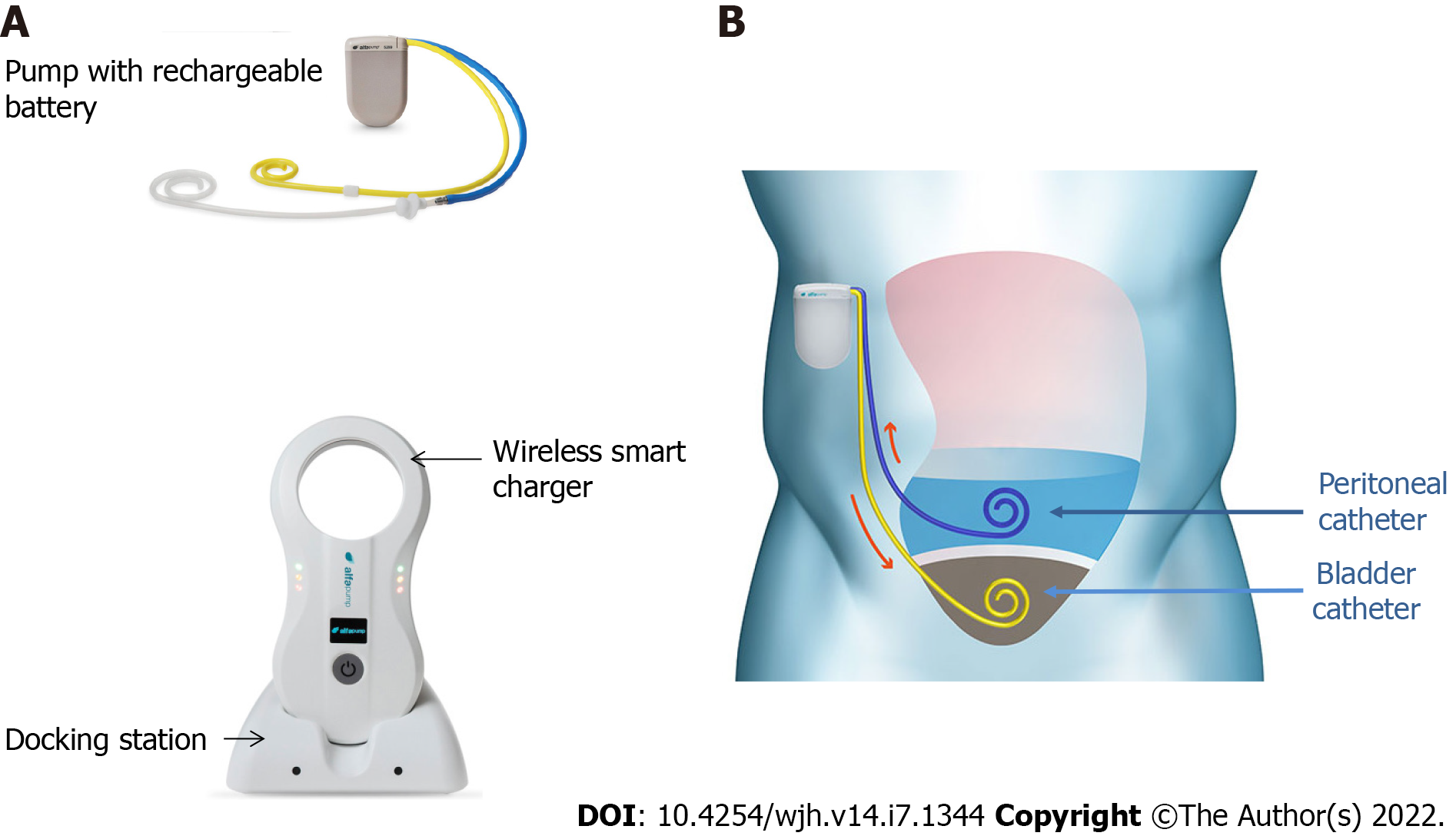
Figure 1 Alfapump® device and principles of its implantation.
A: The system consists of: (1) A pump, which contains a rechargeable battery and is connected to a peritoneal catheter and a bladder catheter; and (2) Charging accessories. The charger collects information and charges the pump through transduction; the docking station must be connected to the electrical network; B: The pump is positioned subcutaneously, under the costal margin (preferably on the right side), so that the patient is not hindered when sitting. The bladder must be full at the time of insertion of the bladder catheter; conversely, only a small amount of ascites is left in place for insertion of the peritoneal catheter, so that the pump can be tested before parietal closure. Images courtesy of Sequana Medical.
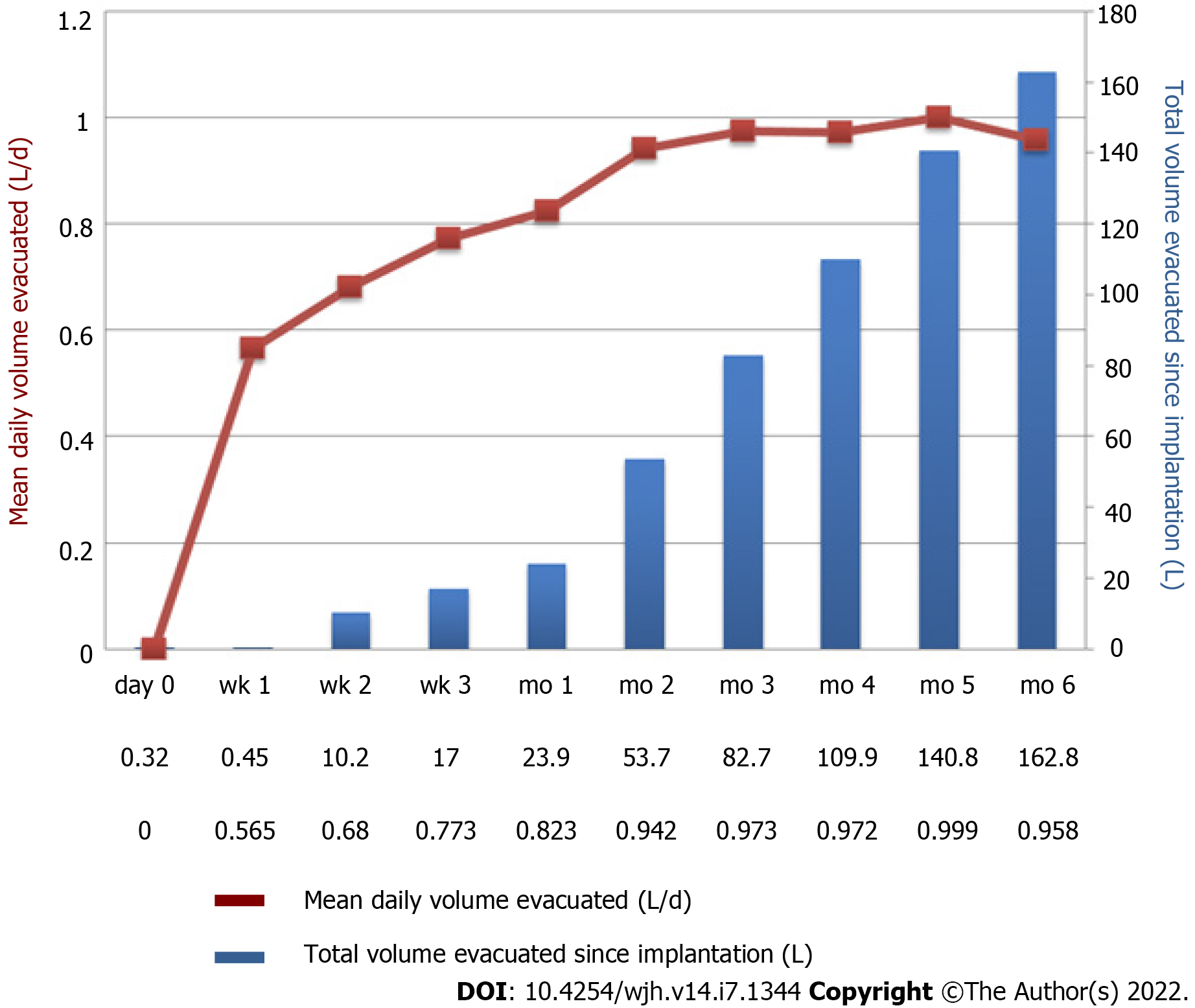
Figure 2 Example of pump activity during the first 6 mo after implantation of alfapump®.
A patient with refractory ascites was implanted with an alfapump®. The figure shows a progressive increase in the average daily volume of ascites evacuated (brown curve), resulting from adjustment of the pump by the clinician. The definitive rate is reached between the 1st and 2nd month. The bars (in blue) represent the total cumulative volume of ascites evacuated (Personal communication, Prof. Eric Nguyen-Khac, CHU Amiens, France).
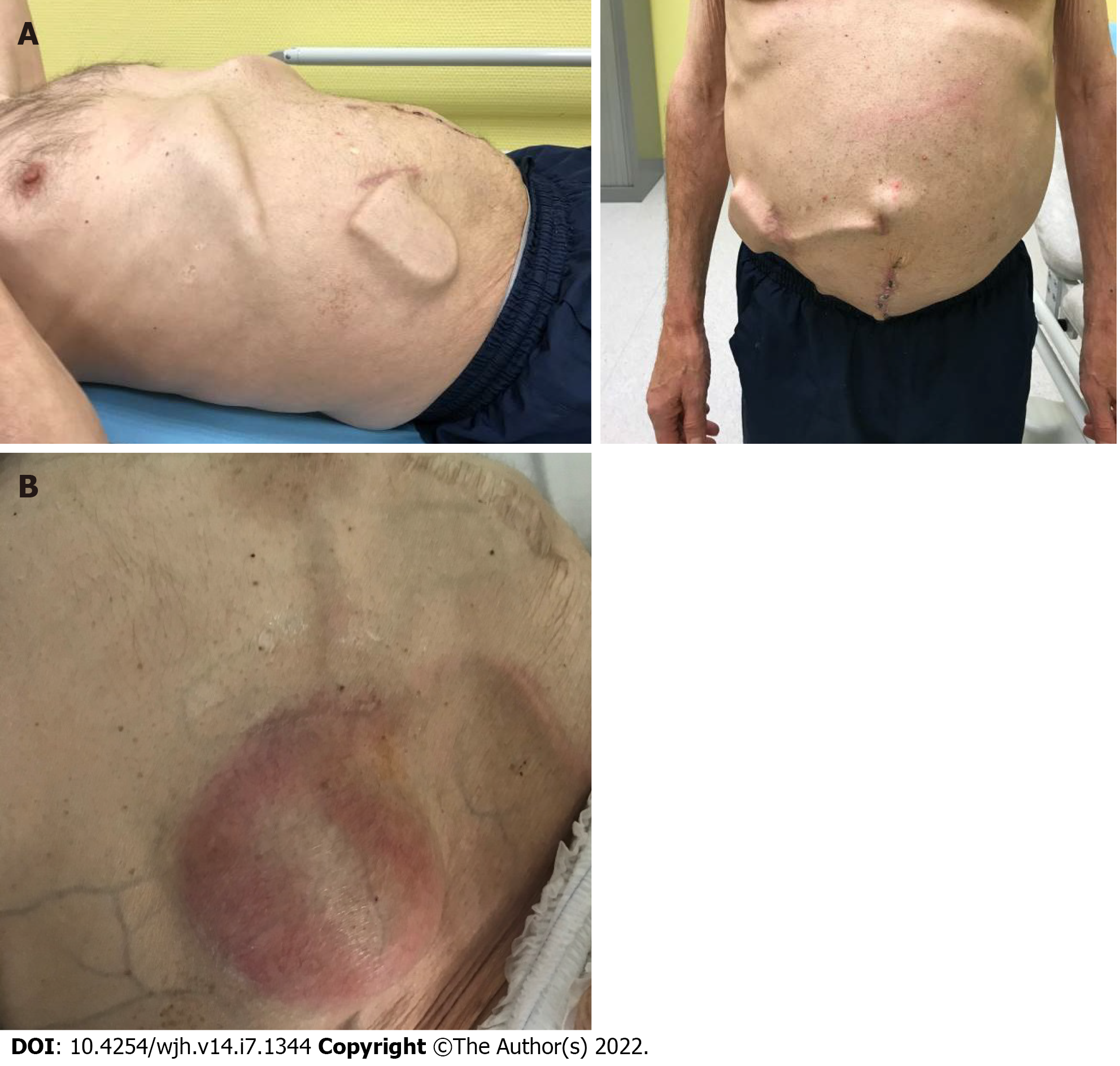
Figure 3 Example of an alfapump complication.
An alfapump® was implanted in July 2018, followed by omphalectomy in September 2018. A: October 2018: Increase in ascites after omphalectomy, leading to modification of the alfapump® settings and enabling subsequent deferral of paracentesis; B: February 2020: The patient was hospitalized for sepsis related to infection of the pump pocket, complicated with peritonitis and requiring pump explantation (Personal communication, Dr D. Weil-Verhoeven, CHU Besançon).
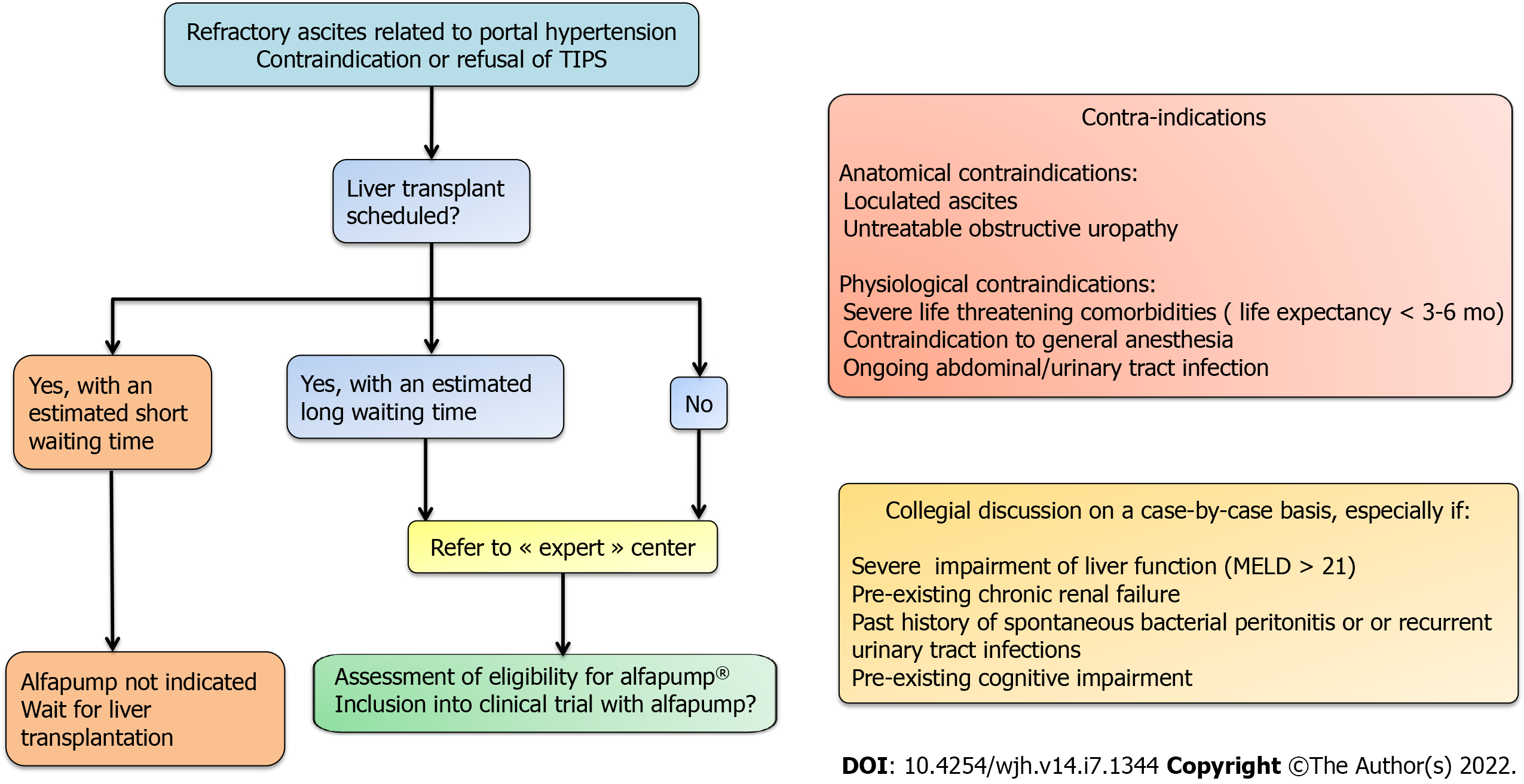
Figure 4 Decision-making algorithm and key evaluation criteria for eligibility for alfapump® implantation.
MELD: Model for end-stage liver disease; TIPS: Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
- Citation: Weil-Verhoeven D, Di Martino V, Stirnimann G, Cervoni JP, Nguyen-Khac E, Thévenot T. Alfapump® implantable device in management of refractory ascites: An update. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(7): 1344-1356
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i7/1344.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i7.1344