Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2022; 14(6): 1226-1234
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1226
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1226
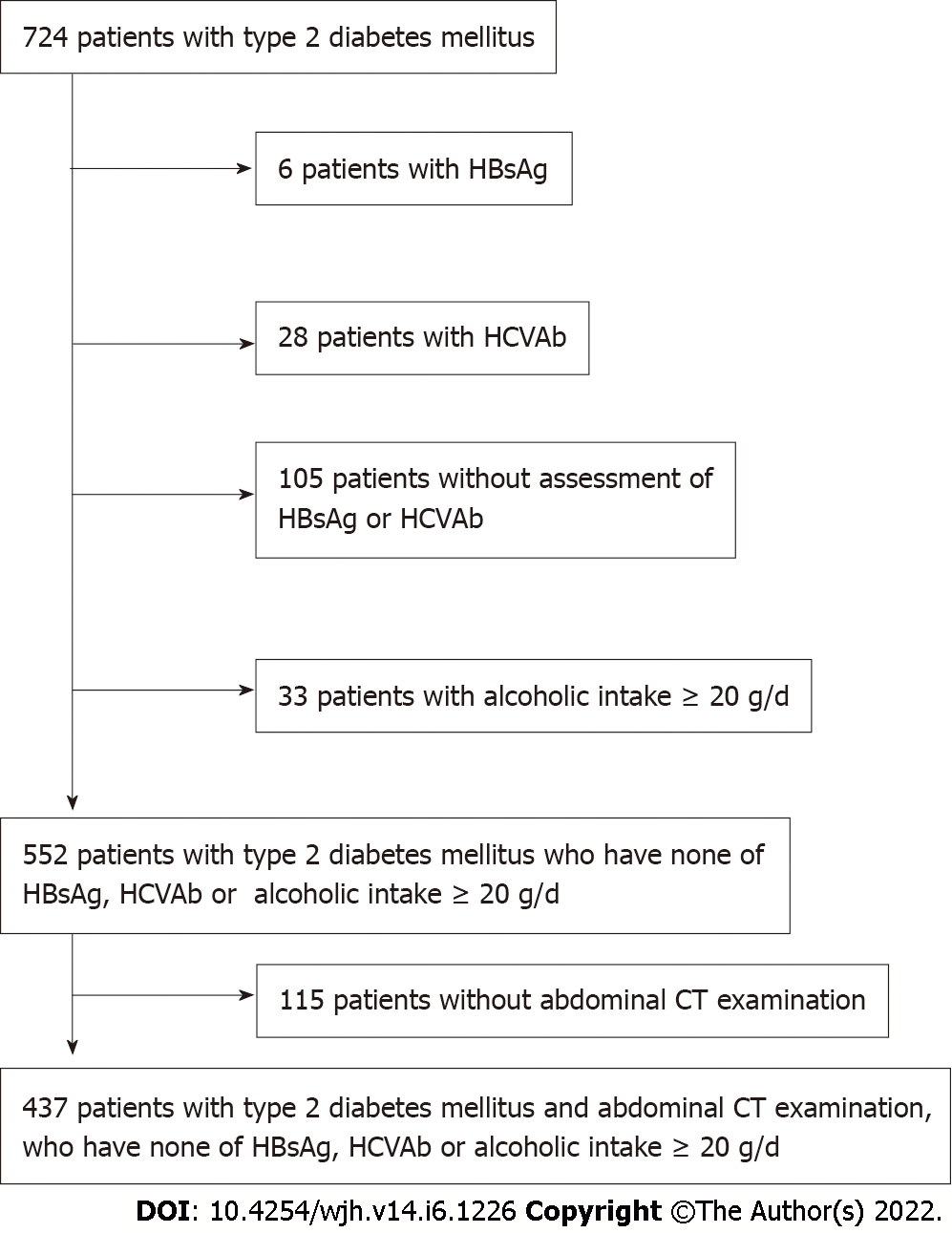
Figure 1 The participants in the present study consisted of 724 Japanese type 2 diabetic patients who consulted at Meijo Hospital from April 2019 to September 2020.
We excluded participants who had chronic hepatitis B (n = 6) and C (n = 28) infection, no assessment of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) and hepatitis C virus antibody (n = 105), and alcohol intake ≥ 20 g/d (n = 33). We also excluded 115 participants with no abdominal computed tomography examinations. The final analysis included 437 participants (269 men and 168 women). HCVAb: Hepatitis C virus antibody; HBsAg: Hepatitis B surface antigen; CT: Computed tomography.
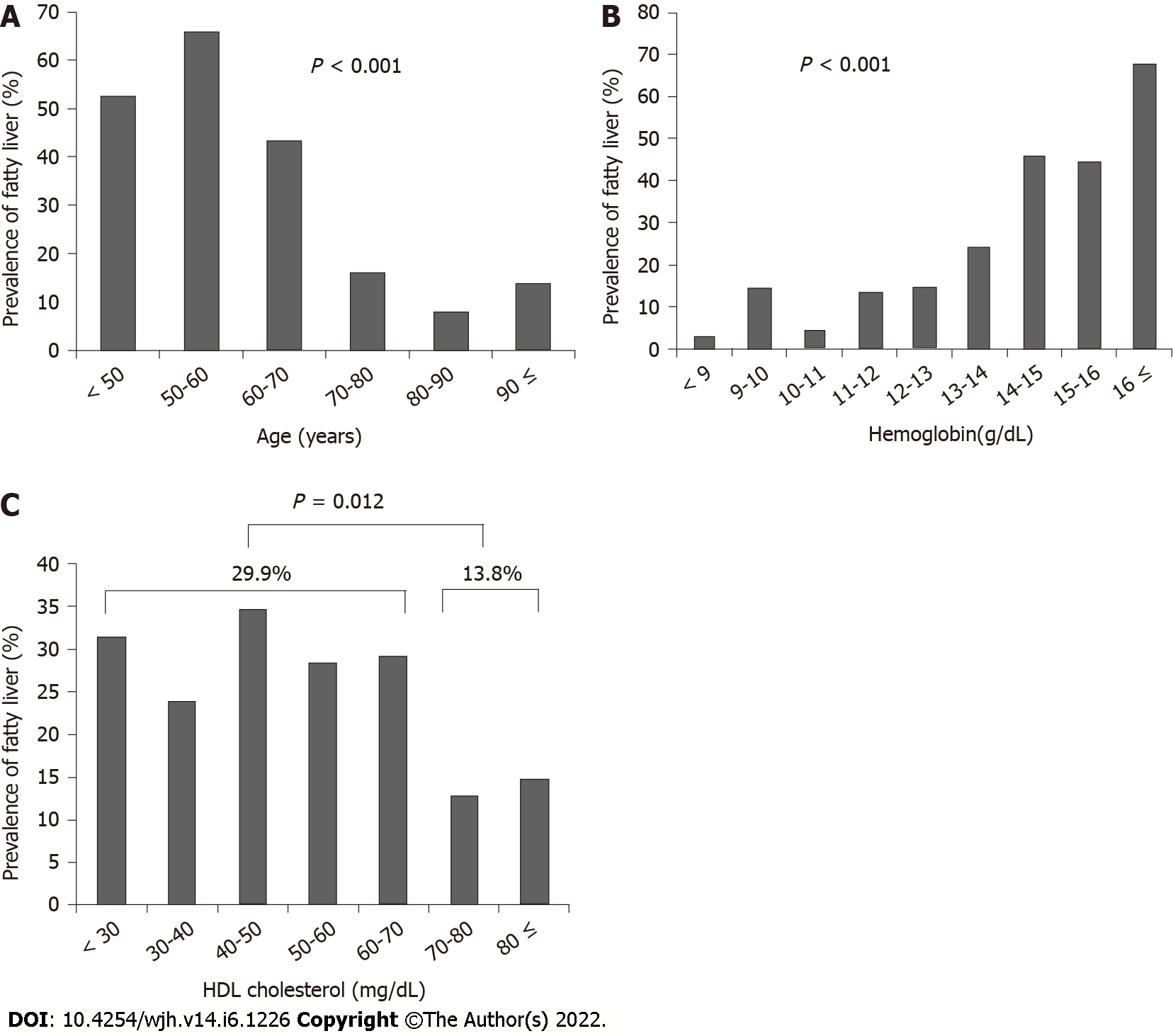
Figure 2 The patients were stratified according to age, hemoglobin level, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level, and the association with fatty liver was assessed.
A: The prevalence of fatty liver significantly decreased with age (P < 0.001); B: The prevalence of fatty liver significantly increased as hemoglobin increased (P < 0.001); C: The prevalence of fatty liver was significantly higher in patients with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol of < 70 mg/dL (29.9%) than those with HDL cholesterol ≥ 70 mg/dL (13.8%) (P = 0.012). HDL: High-density lipoprotein
- Citation: Yamane R, Yoshioka K, Hayashi K, Shimizu Y, Ito Y, Matsushita K, Yoshizaki M, Kajikawa G, Mizutani T, Watarai A, Tachi K, Goto H. Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its association with age in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(6): 1226-1234
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i6/1226.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1226