Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Jun 27, 2022; 14(6): 1131-1141
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1131
Published online Jun 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1131
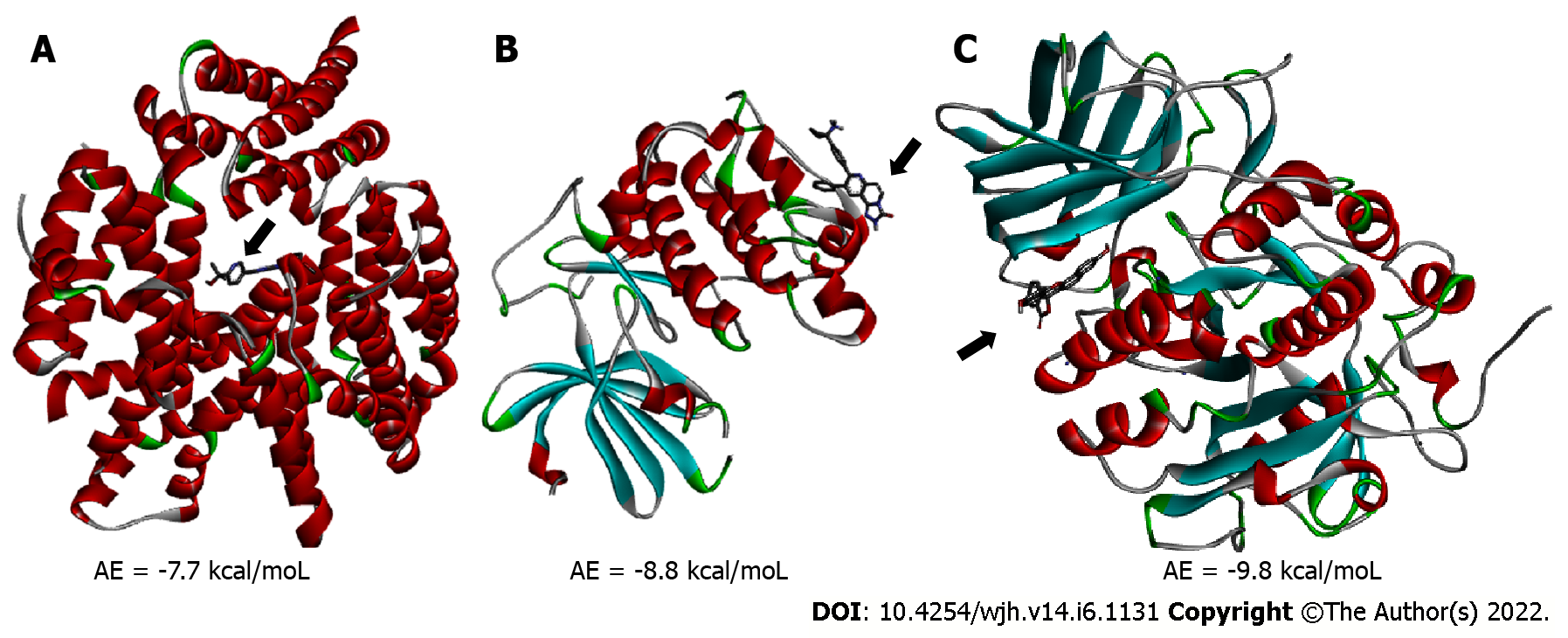
Figure 1 Panoramic view of the enzyme/inhibitor complexes.
A: mTORC1/CC-223 complex; B: Akt/MK-2206 complex; C: Furin/Naphthofluorescein complex. Arrow points to the inhibitor. Alpha helices are shown in red, Beta sheets are shown in blue, Random coils are shown in green and Turns are shown in grey. AE: Affinity energy.
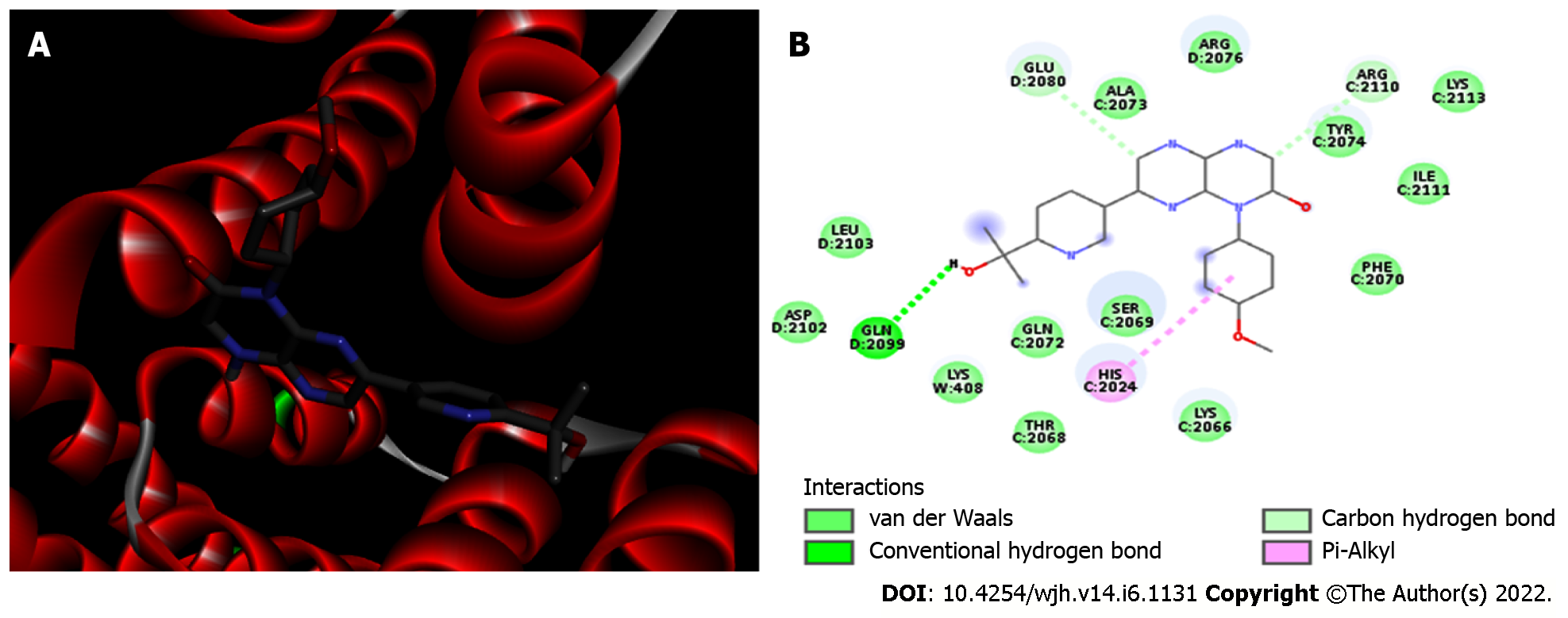
Figure 2 mTORC1/CC-223 complex.
A: 3D view of the CC-223 inhibitor (sticks) bound to the FKBP12–Rapamycin-Binding domain of mTORC1 (Protein Data Bank 5WBH). mTORC1 is shown in red alpha-helices; B: 2D diagram showing the mTORC1 residues that bind to CC-223. The internal legend indicates the bond type by color. Amino acid residues are shown in 3-letter code; the number indicates the position within the chain, and the capital letters (A, C and D) indicate which chain the residue belongs to.
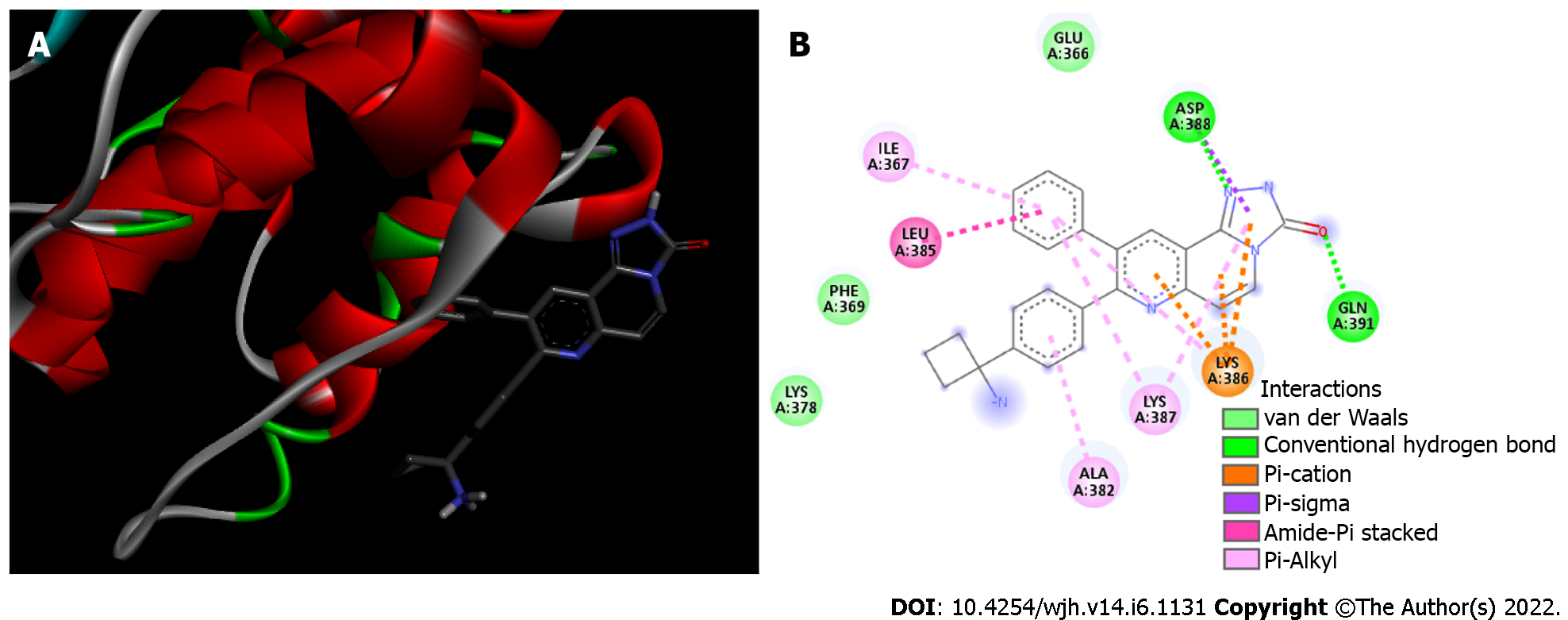
Figure 3 Akt/MK-2206 complex.
A: 3D view of MK-2206 inhibitor (sticks) bound to Akt kinase domain (Protein Data Bank 1GZN). Akt is shown in red alpha-helices, green random coils and grey turns; B: 2D diagram showing the Akt residues that bind to MK-2206. The internal legend indicates the bond type by color. Amino acid residues are shown in 3-letter code; the number indicates the position within the chain, and the capital letters (A) indicate which chain the residue belongs to.
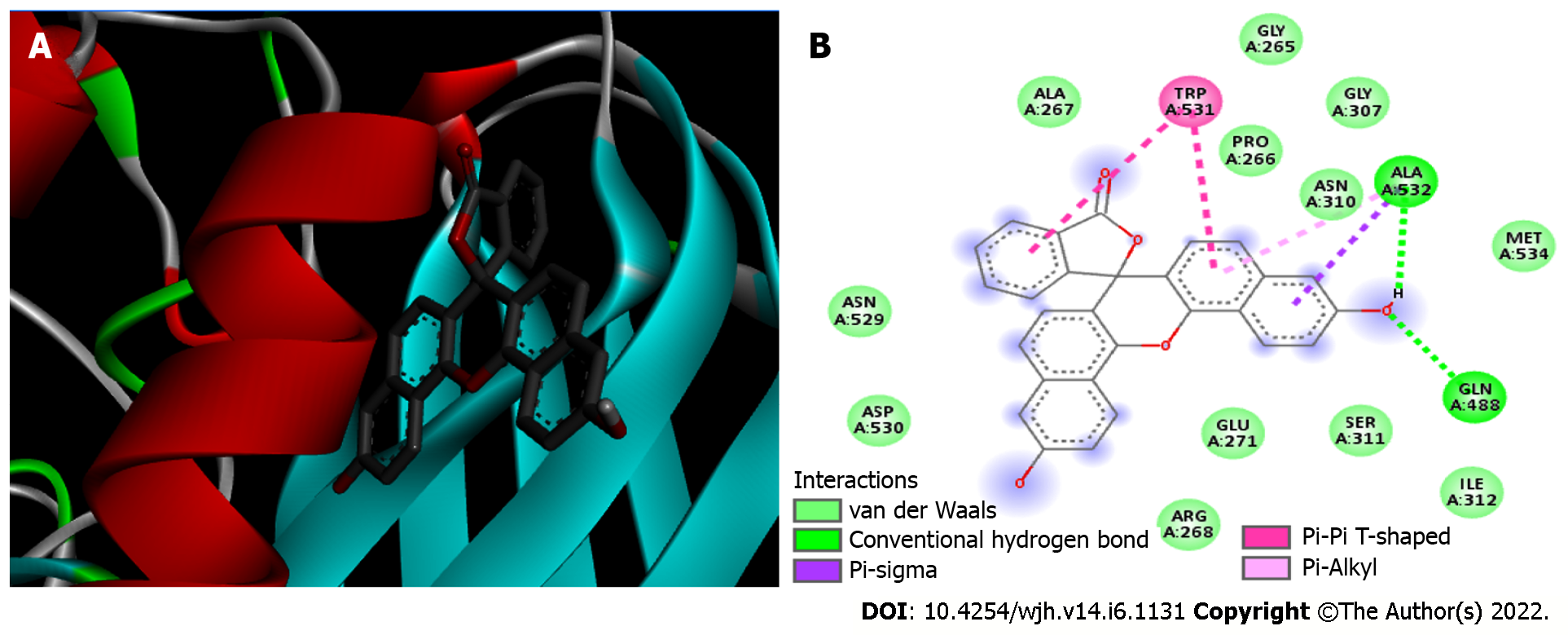
Figure 4 Furin/Naphthofluorescein complex.
A: 3D view of Naphthofluorescein inhibitor (sticks) bound to Furin (Protein Data Bank 5JXI). Furin is shown in blue beta sheets, red alpha-helices, grey random coils and green turns; B: 2D diagram showing the Furin residues that bind to Naphthofluorescein. The internal legend indicates the bond type by color. Amino acid residues are shown in 3-letter code; the number indicates the position within the chain, and the capital letters (A) indicate which chain the residue belongs to.
- Citation: Peiter GC, de Souza CBT, de Oliveira LM, Pagliarin LG, dos Anjos VNF, da Silva FAF, de Melo FF, Teixeira KN. COVID-19 liver and gastroenterology findings: An in silico analysis of SARS-CoV-2 interactions with liver molecules. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(6): 1131-1141
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i6/1131.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i6.1131