Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. May 27, 2022; 14(5): 866-884
Published online May 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i5.866
Published online May 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i5.866
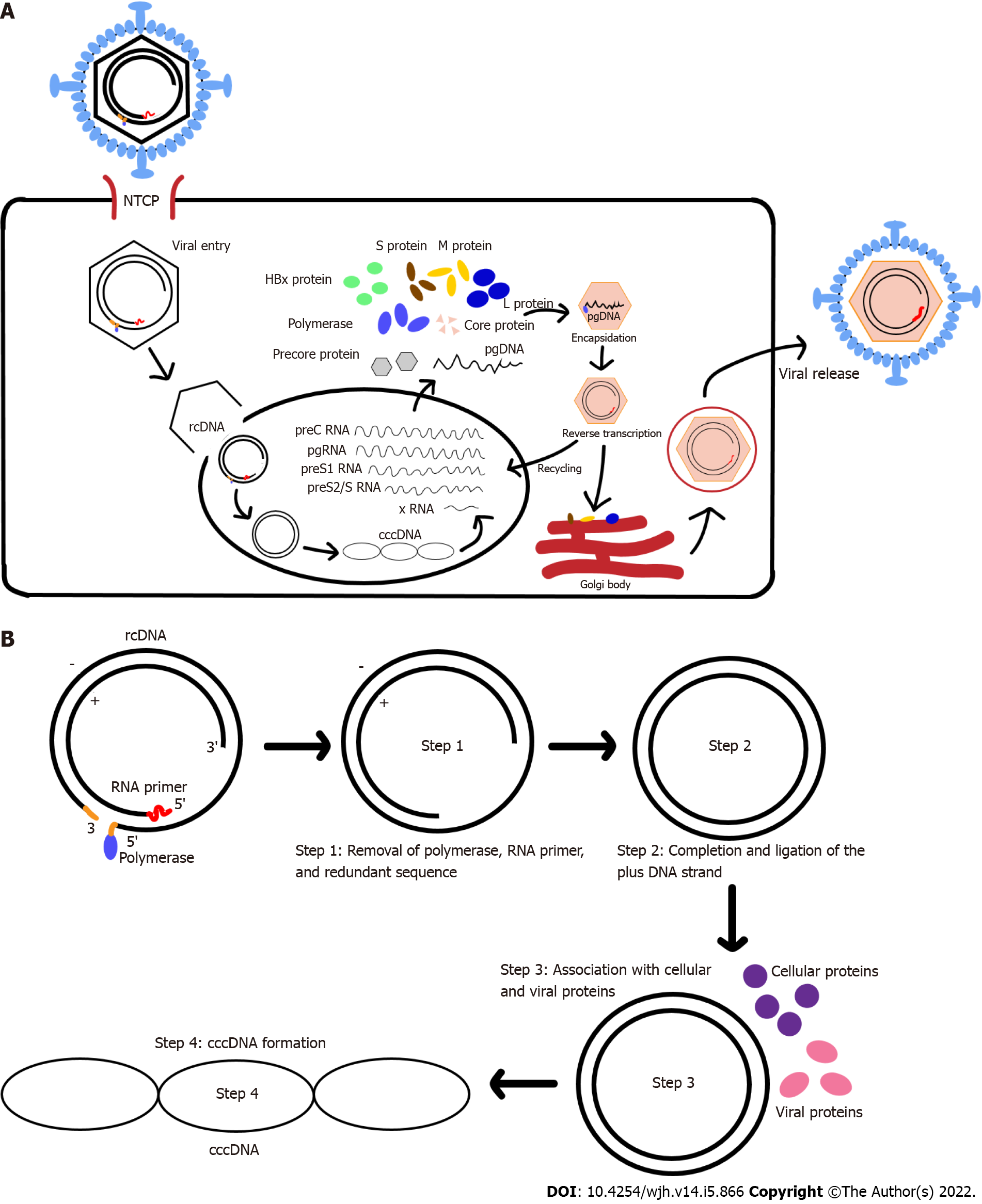
Figure 1 Hepatitis B virus life cycle and covalently clos circular DNA.
A: Hepatitis B virus entry and replication in host cell; B: Relaxed-circular DNA (rcDNA) conversion into covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA). HBV: Hepatitis B virus; cccDNA: Covalently clos circular DN; rcDNA: Relaxed-circular DNA.
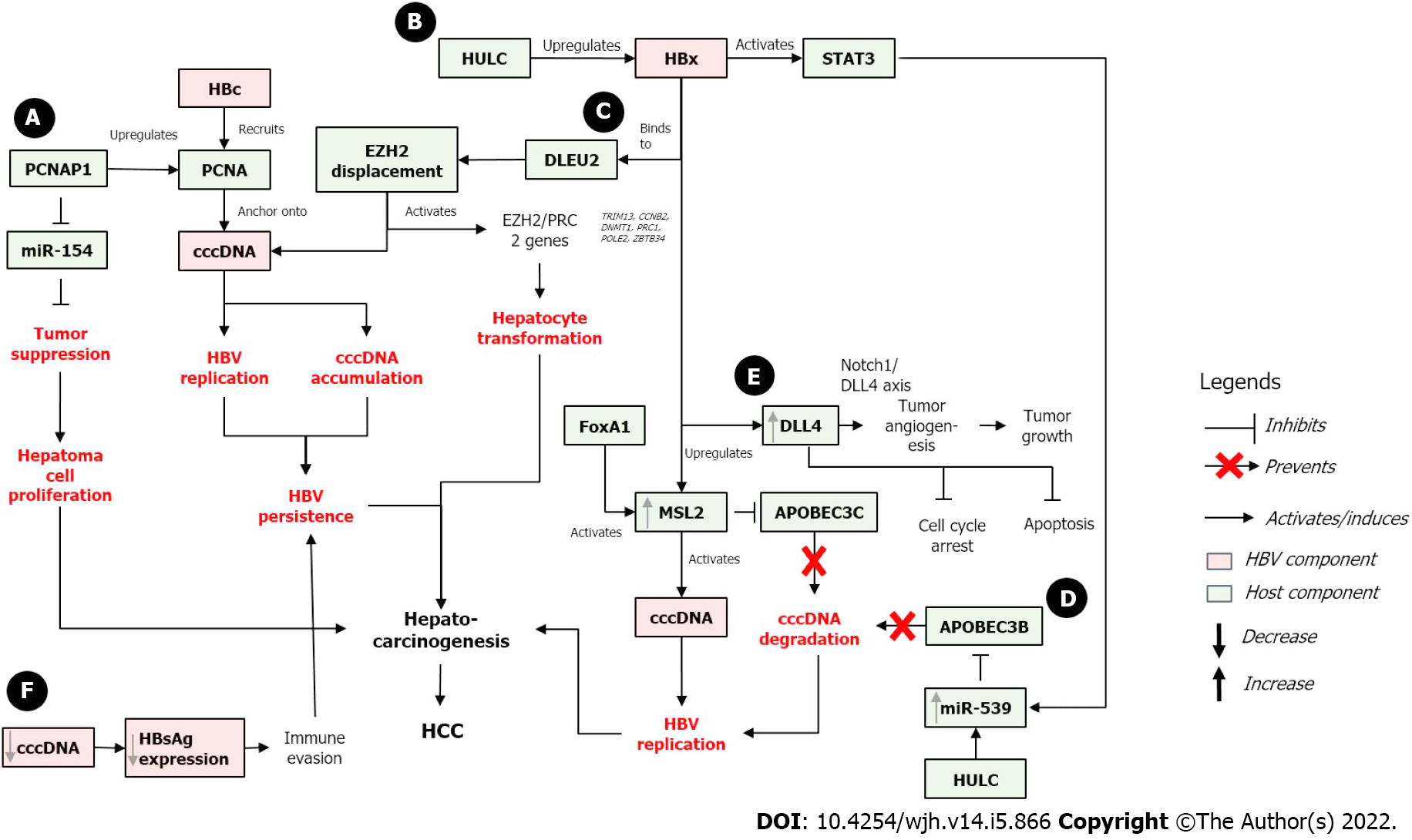
Figure 2 Proposed mechanisms for the role of covalently closed circular DNA in hepatocarcinogenesis.
A: Modulation of miR-154/PCNA/covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) signaling; B: Modulation of HBV X protein (HBx)/STAT3/miR-539/APOBEC3B; C: Positive feedback loop of HULC and HBx/MSL2/cccDNA; D: HBx/DLEU2 interaction to activate cccDNA; E: HBx/DLL4/Notch 1 signaling pathway; F: Reduction of cccDNA levels to avoid immune recognition.
- Citation: Bianca C, Sidhartha E, Tiribelli C, El-Khobar KE, Sukowati CHC. Role of hepatitis B virus in development of hepatocellular carcinoma: Focus on covalently closed circular DNA . World J Hepatol 2022; 14(5): 866-884
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i5/866.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i5.866