Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2022; 14(4): 827-845
Published online Apr 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.827
Published online Apr 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.827
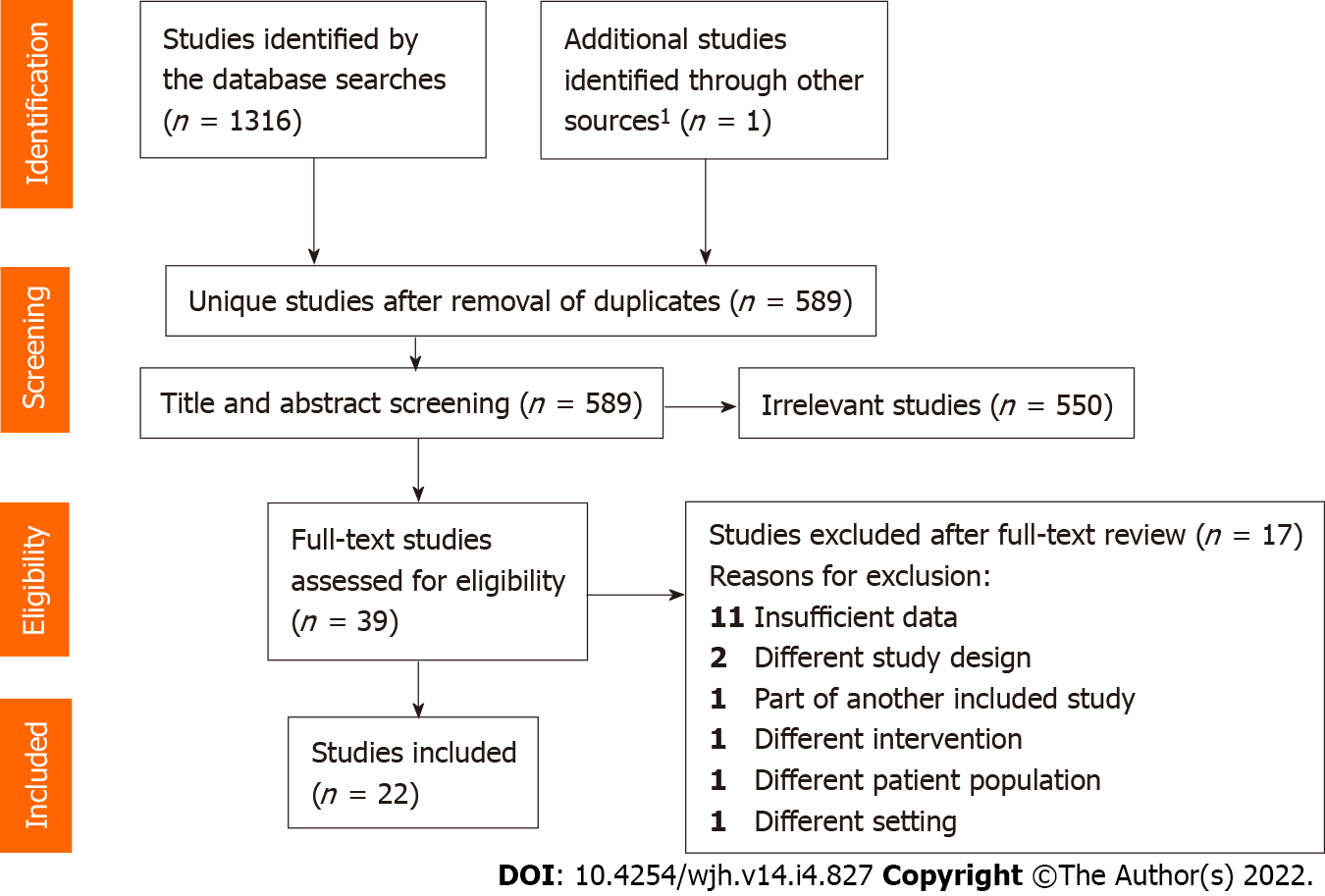
Figure 1 Flow diagram of study identification.
1Publication identified through screening of reference lists of all studies in the “Eligibility” assessment.
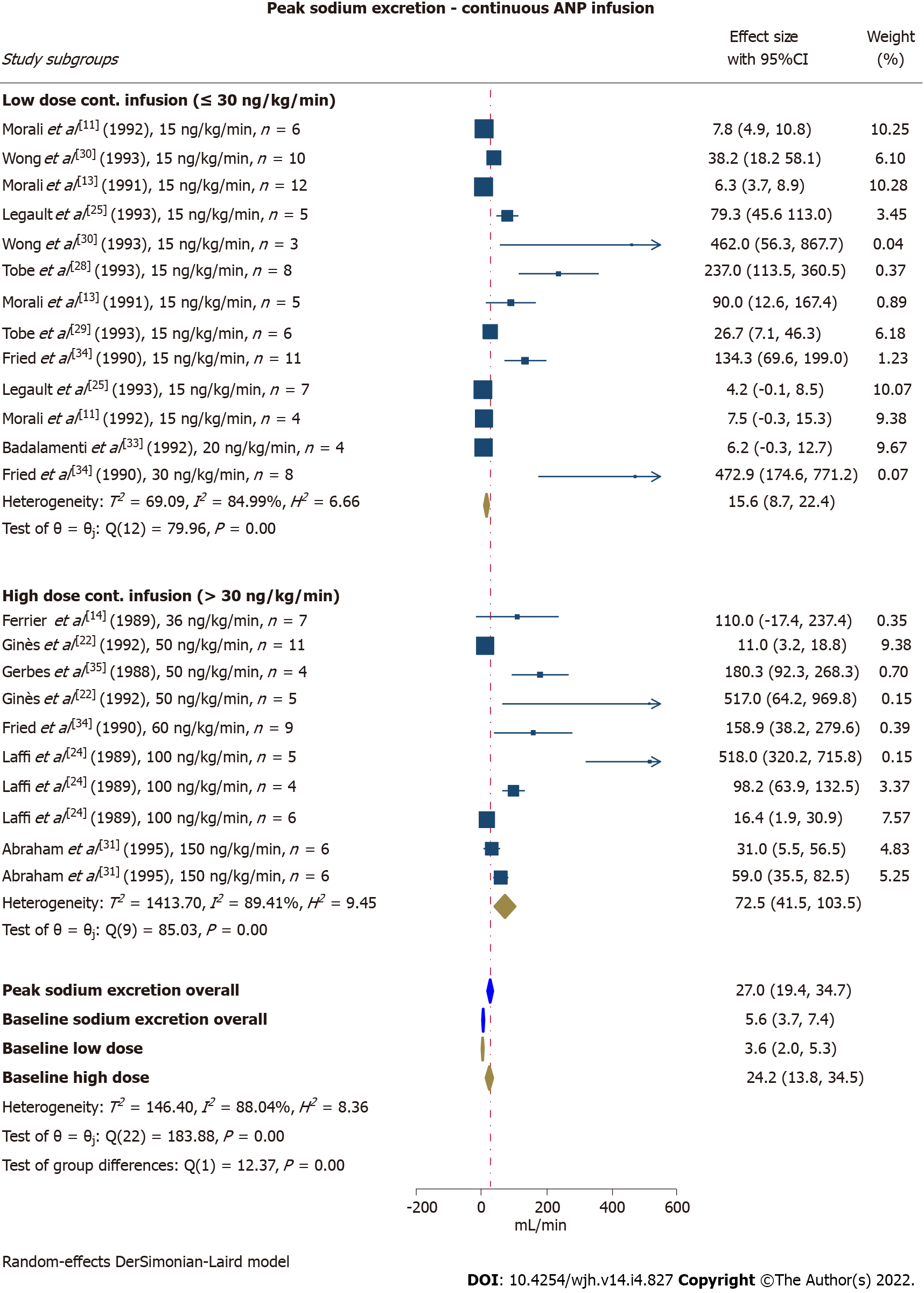
Figure 2 Effect of intravenous continuous atrial natriuretic peptide infusion on sodium excretion (μmol/min).
Analyses were performed on overall data and separately for studies applying low dose infusion (≤ 30 ng/kg/min) and high dose infusion (> 30 ng/kg/min). ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; CI: Confidence interval.
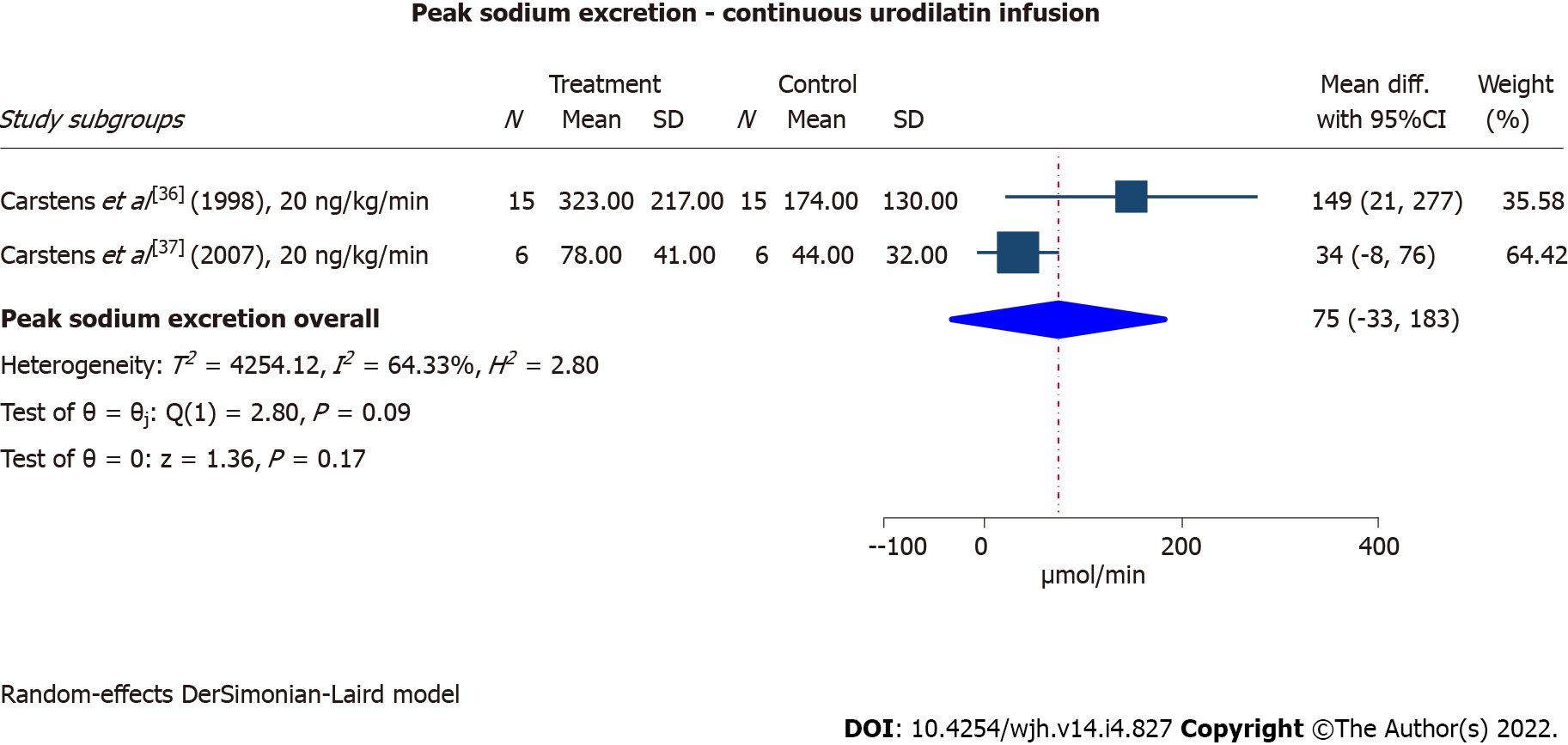
Figure 3 Effect of intravenous urodilatin and placebo infusion on sodium excretion (μmol/min).
As both studies were cross-over randomised controlled trials we used peak natriuretic response with urodilatin and placebo infusion to generate the forest plot. CI: Confidence interval.
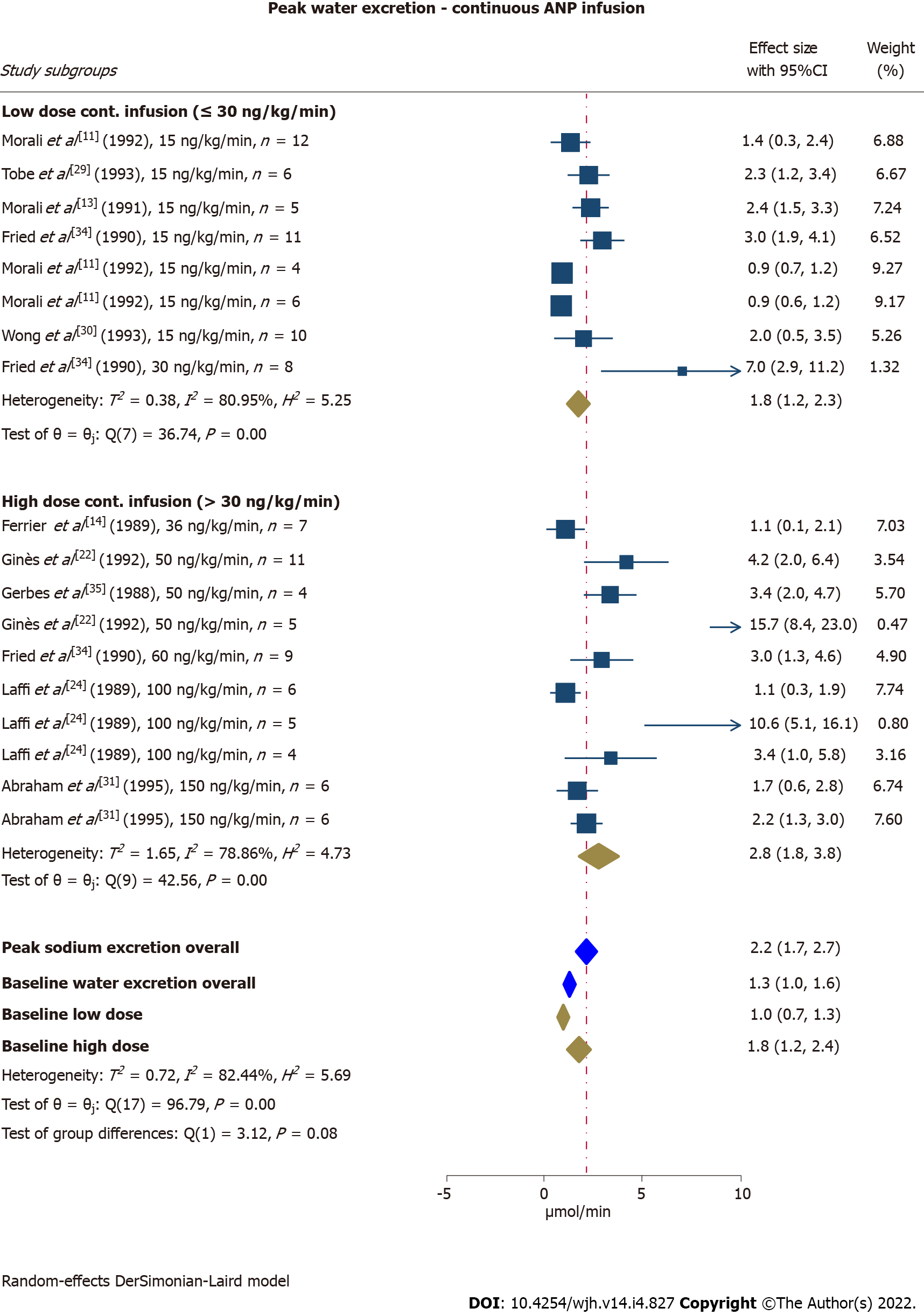
Figure 4 Effect of intravenous continuous atrial natriuretic peptide infusion on water excretion (mL/min).
Analyses were performed on overall data and separately for study subgroups receiving low dose infusion (≤ 30 ng/kg/min) and high dose infusion (> 30 ng/kg/min). ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; CI: Confidence interval.
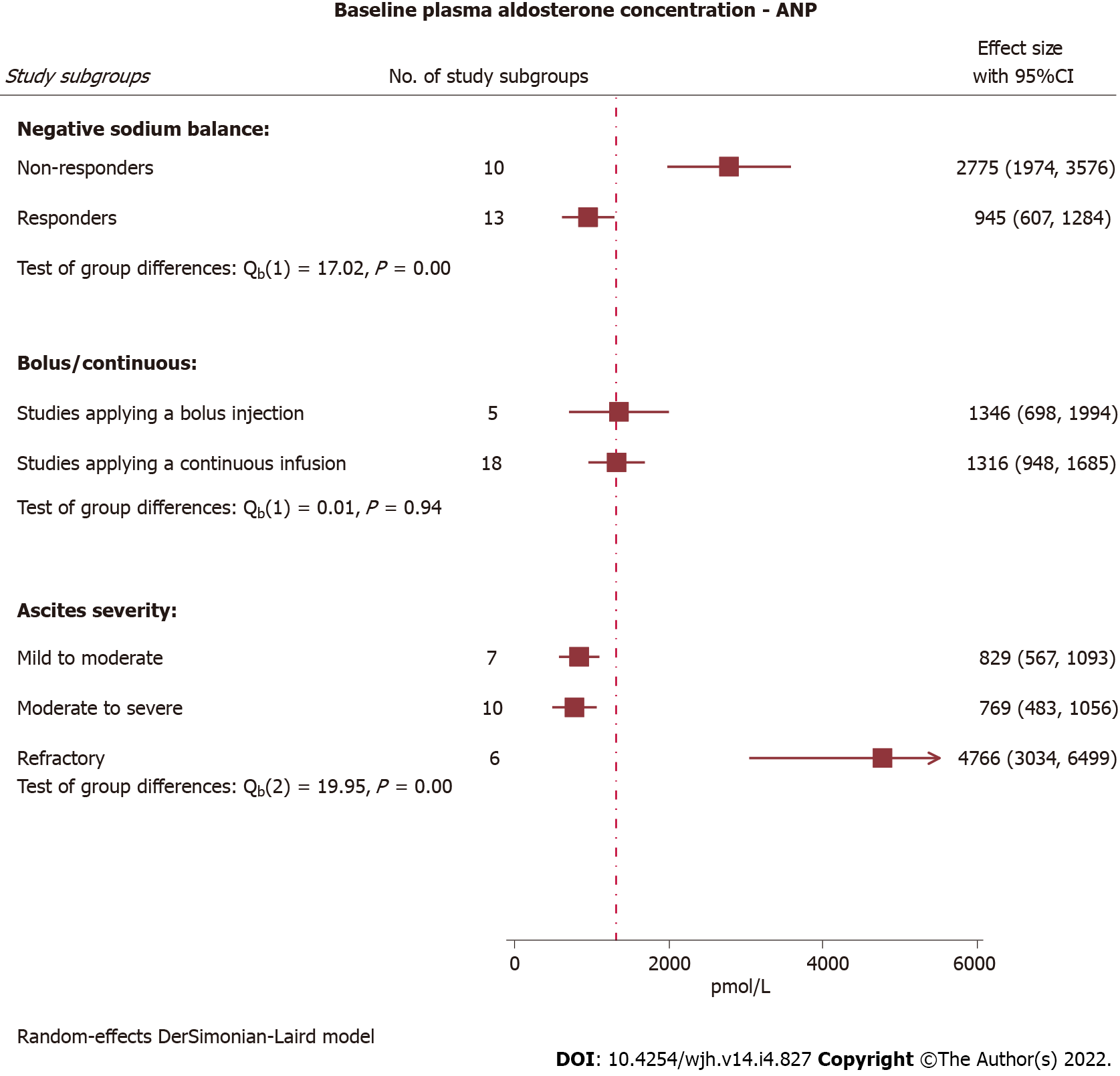
Figure 5 Baseline plasma aldosterone concentration in selected study subgroups.
Non-responders failed to obtain negative sodium balance following intervention with atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and were characterised by significantly higher baseline plasma aldosterone concentration compared with ANP responders (P < 0.01). Baseline aldosterone levels were similar for subgroups exposed to bolus injections and continuous infusions, and extremely elevated in subgroups with refractory ascites compared with non-refractory ascites. Dotted line represents overall baseline mean plasma aldosterone concentration. ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; CI: Confidence interval.
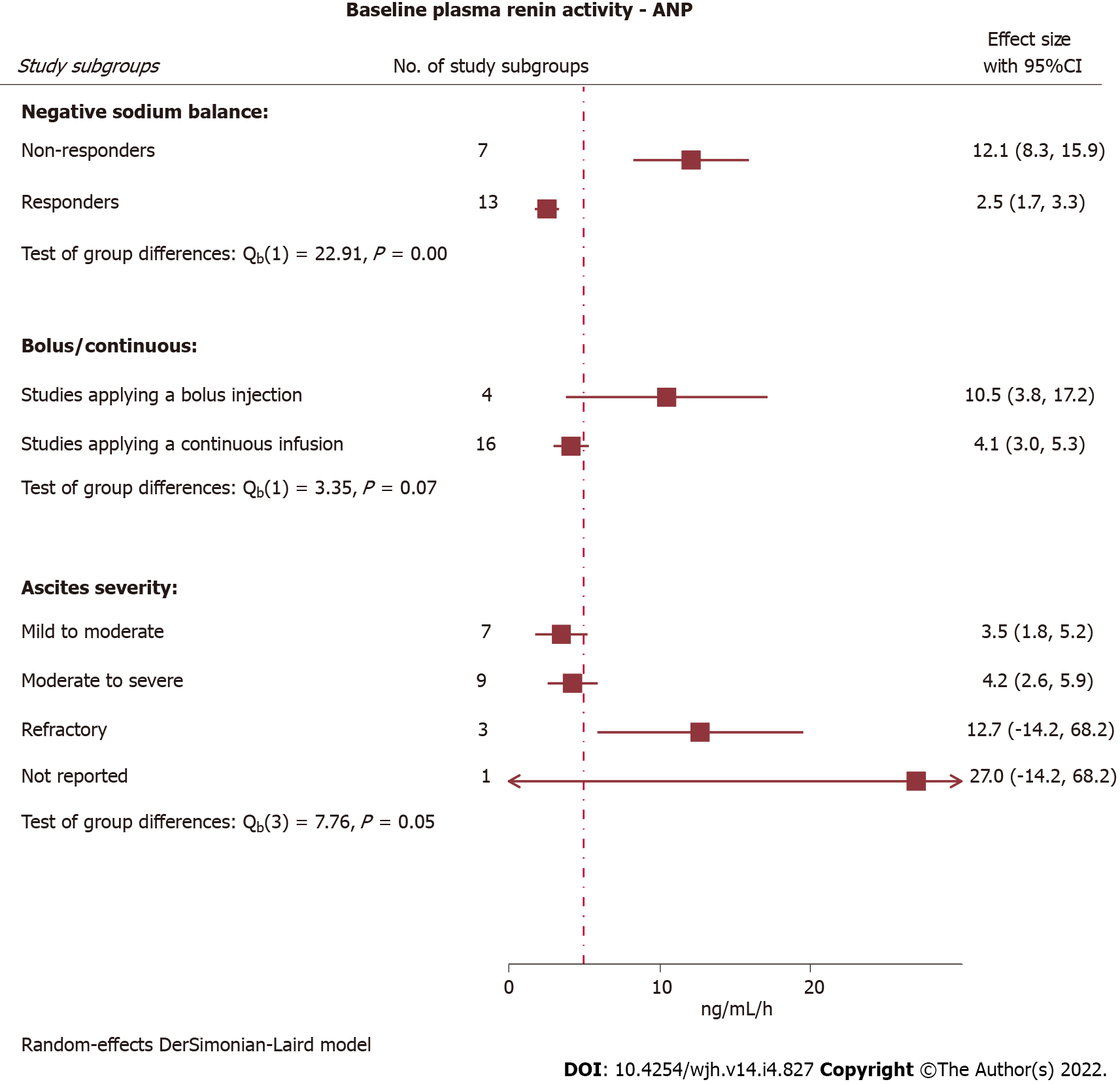
Figure 6 Baseline plasma renin activity in selected study subgroups.
Non-responders failed to obtain negative sodium balance following intervention with atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) and were characterised by significantly higher baseline plasma renin activity compared with ANP responders (P < 0.01). Baseline renin activity tended to be lower in subgroups exposed to continuous infusion than for subgroups exposed to bolus injection, while subgroups with refractory ascites had markedly elevated renin activity compared with non-refractory ascites. Dotted line represents overall baseline mean plasma renin activity. ANP: Atrial natriuretic peptide; CI: Confidence interval.
- Citation: Gantzel RH, Kjær MB, Jepsen P, Aagaard NK, Watson H, Gluud LL, Grønbæk H. Effects and safety of natriuretic peptides as treatment of cirrhotic ascites: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(4): 827-845
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i4/827.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.827