Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Apr 27, 2022; 14(4): 812-826
Published online Apr 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.812
Published online Apr 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.812
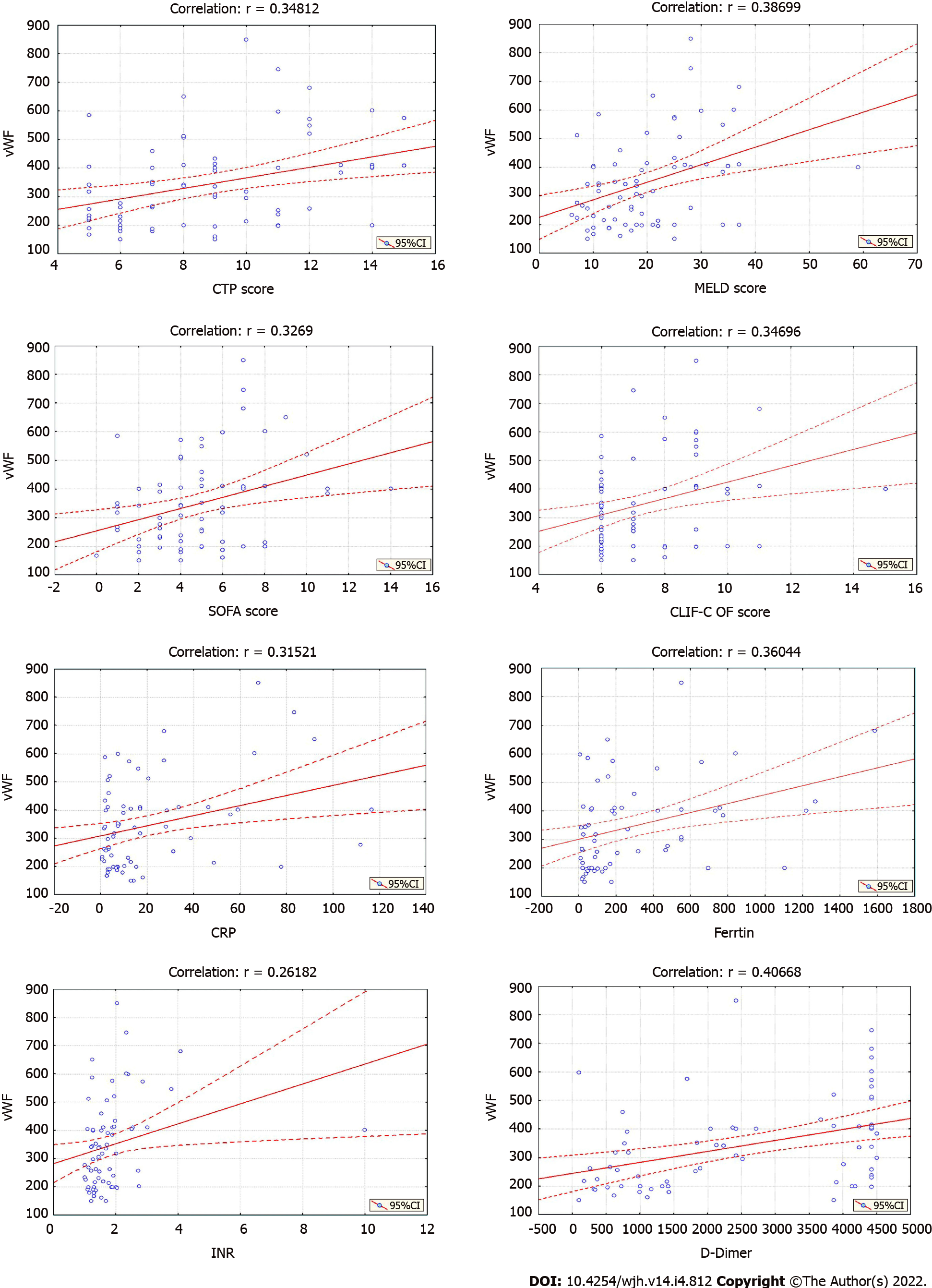
Figure 1 Significant positive linear correlation between von-Willebrand factor and C-reactive protein score, model for end-stage liver disease score, sequential organ failure assessment score, CLIF-consortium organ failure score, ferritin, C-reactive protein, international normalized ratio, and D-dimer level.
vWF: von-Willebrand factor; CTP: Child-Turcotte-Pugh; MELD: Model for End-stage Liver Disease; CRP: C-reactive protein; INR: International normalized ratio.
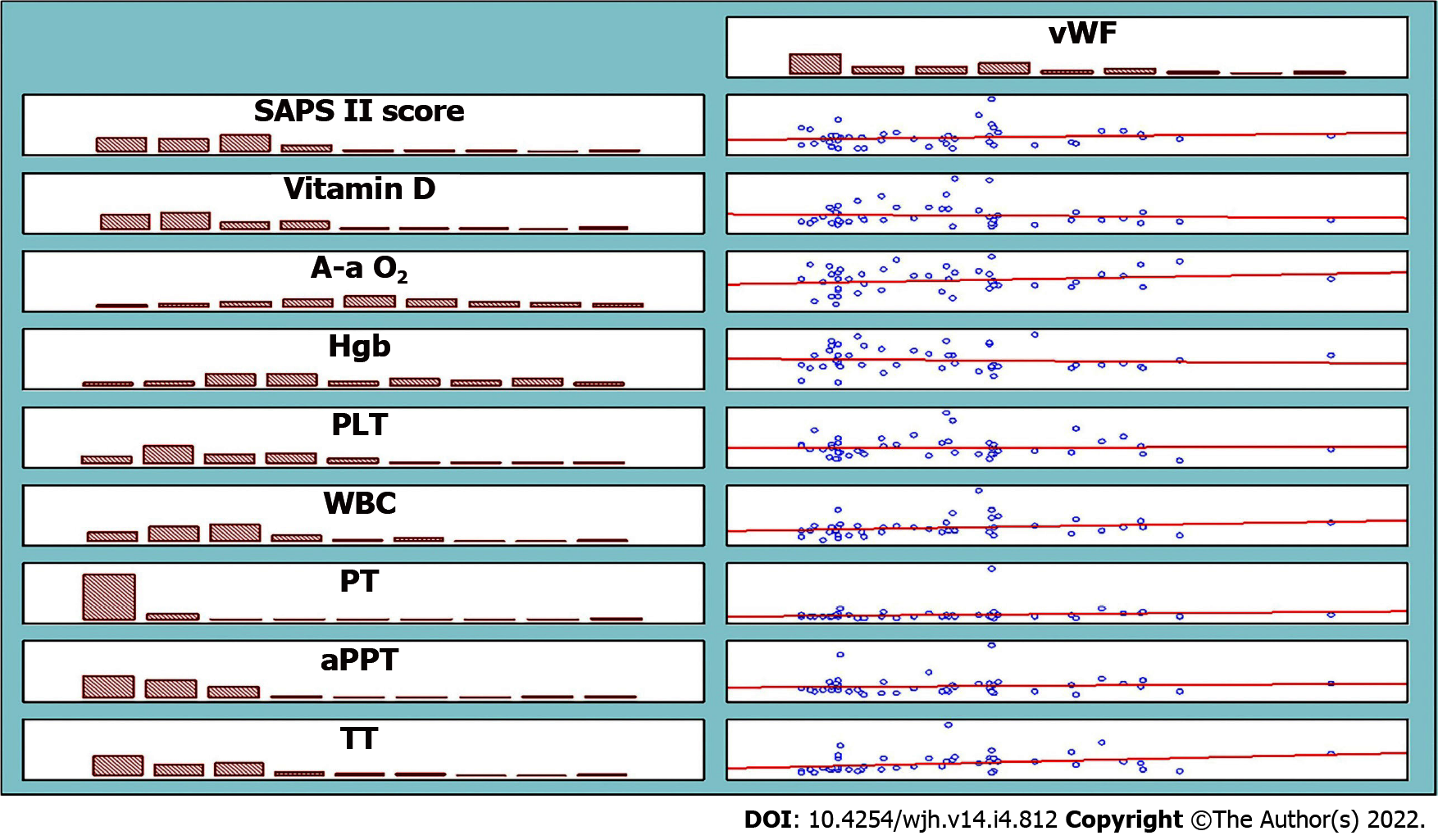
Figure 2 Weak or insignificant correlation between von-Willebrand factor and Simplified Acute Physiology Score II score, vitamin D, A-a O2, hemoglobin, platelets, white blood cell, prothrombin time, activated partial thromboplastinin time, and thrombin time.
vWF: von-Willebrand factor; SAPS: Simplified Acute Physiology Score; A-a O2:: Alveolar-arterial oxygen gradient; PLT: Platelets; WBC: White blood cell; PT: Prothrombin time; aPTT: Activated partial thromboplastinin time; TT: Thrombin time.
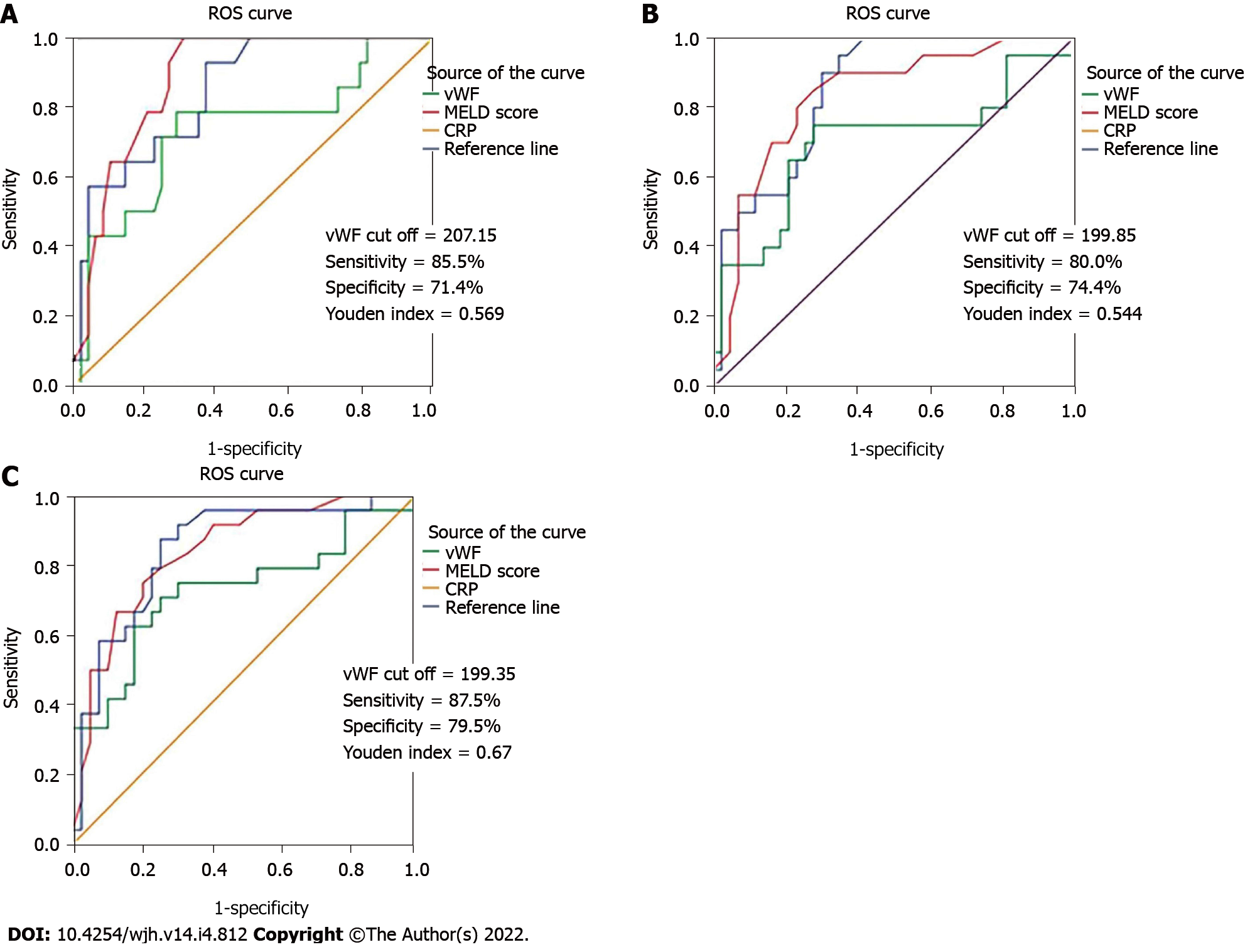
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of the diagnostic performance of von-Willebrand factor, model for end-stage liver disease score, and C-reactive protein for mortality.
A: 3-mo mortality; B: 6-mo mortality; C: 1-yr mortality. The difference between the area under the curve (AUC) values for von-Willebrand factor (vWF) and model for end-stage liver disease (MELD) score and between the AUC values for vWF and C-reactive protein (CRP) regarding all three follow-up periods was not statistically significant (Z = 1.459; P = 0.1444 and Z = 1.063; P = 0.2876 for 3-mo mortality, Z = 1.385; P = 0.1662 and Z = 1.601; P = 0.547 for 6-mo mortality, Z = 1.276; P = 0.20192 and Z = 1.366; P = 0.1718 for 1-yr mortality, respectively). ROC: Receiver operating characteristic.
- Citation: Curakova Ristovska E, Genadieva-Dimitrova M. Prognostic value of von-Willebrand factor in patients with liver cirrhosis and its relation to other prognostic indicators. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(4): 812-826
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i4/812.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i4.812