Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Mar 27, 2022; 14(3): 634-646
Published online Mar 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.634
Published online Mar 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.634
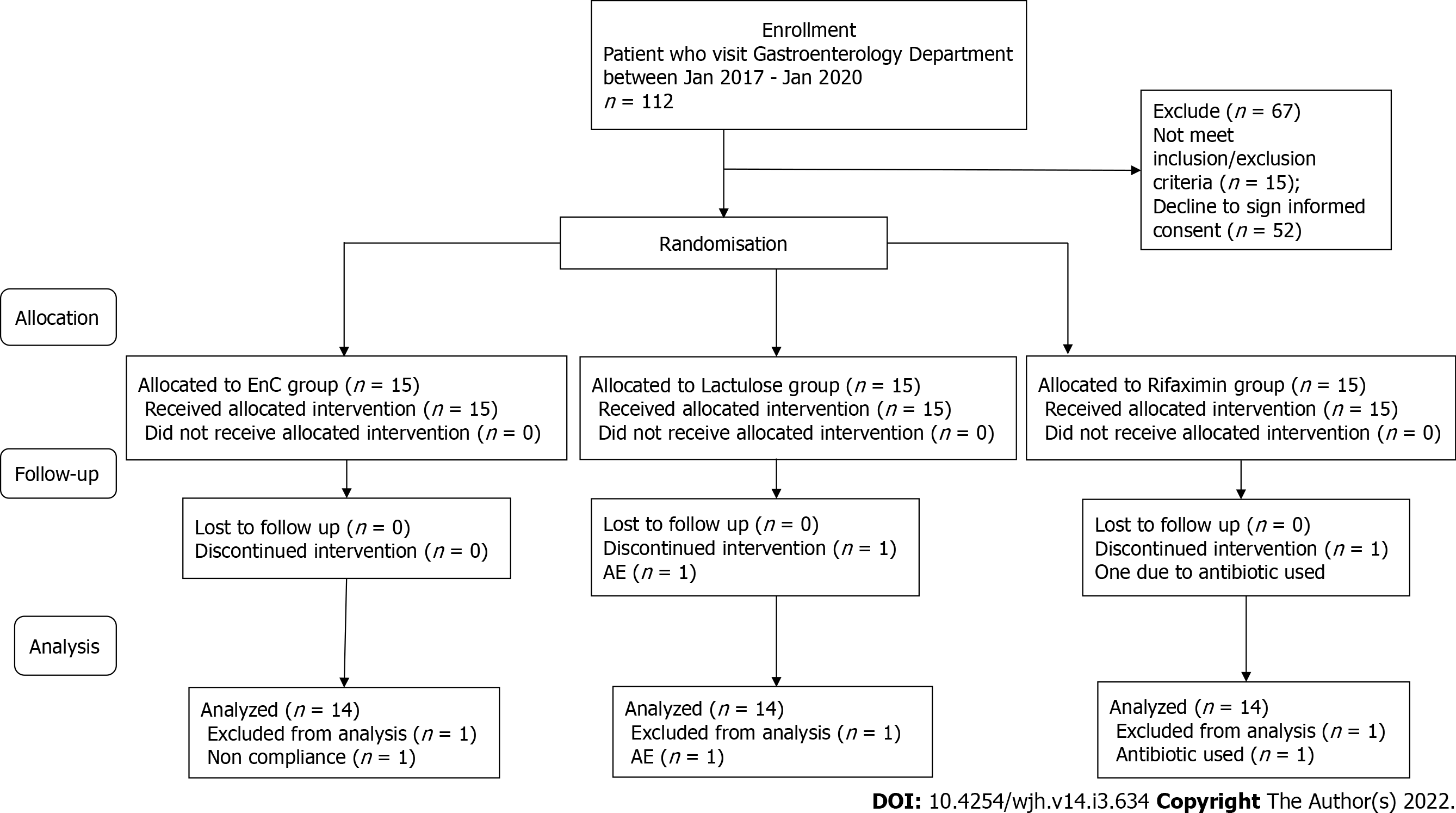
Figure 1 Consolidated standards of reporting trials flow chart - trial protocol.
AE: Adverse events.
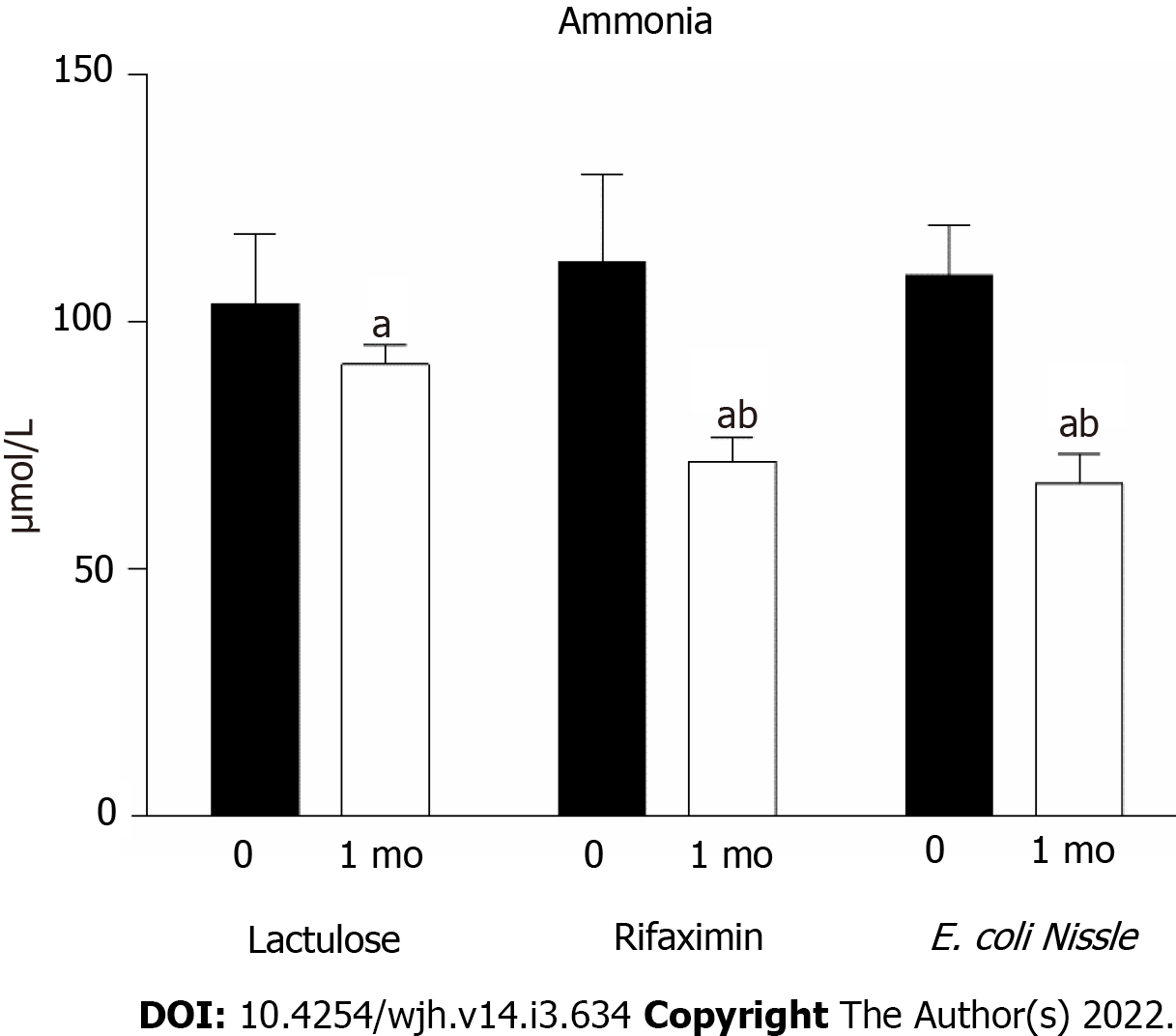
Figure 2 Serum ammonia concentration in patients with hepatic encephalopathy receiving treatment with lactulose, rifaximin and probiotics E.
coli Nissle 1917 (n = 14 in each group).aP < 0.05 as compared to pre-treatment levels; bP < 0.05 as compared to the lactulose treatment. E. coli: Escherichia coli.
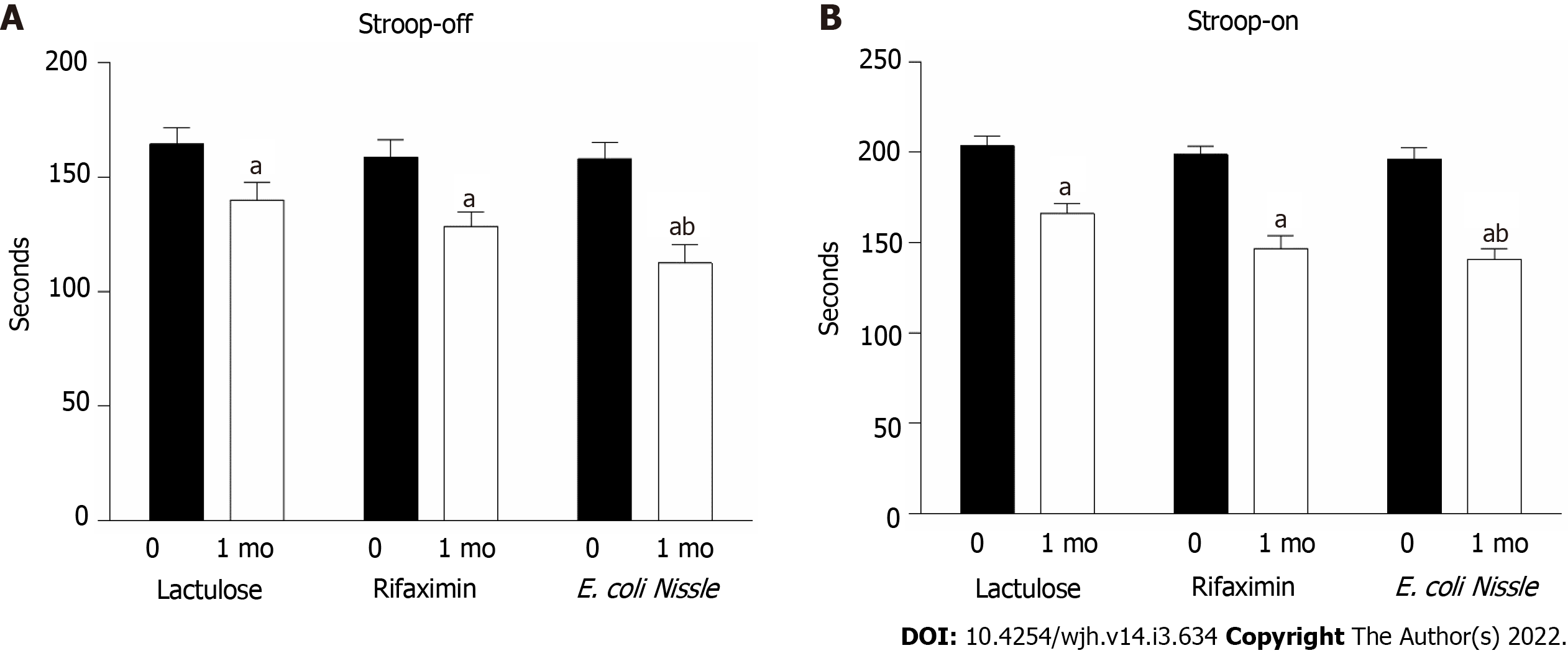
Figure 3 The total time of evaluation of stimuli in Stroop test in patients with hepatic encephalopathy receiving treatment with lactulose, rifaximin and probiotics E.
coli Nissle 1917 (n = 14 in each group). A: Stroop-off; B: Stroop-on. aP < 0.05 as compared to pre-treatment levels; bP < 0.05 as compared to the lactulose treatment. E. coli: Escherichia coli.
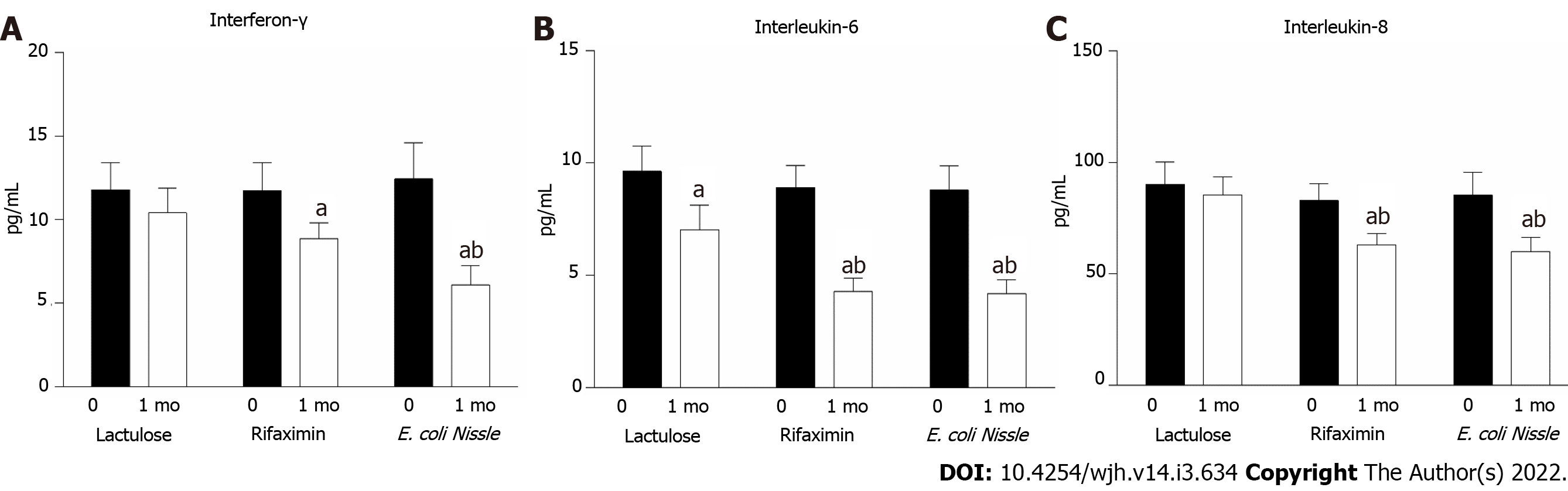
Figure 4 Serum cytokine levels in patients with HE receiving treatment with lactulose, rifaximin and probiotics E.
coli Nissle 1917 (n = 14 in each group). A: INF-γ; B: IL-6; C: IL-8. aP < 0.05 as compared to pre-treatment levels; bP < 0.05 as compared to the lactulose treatment. E. coli: Escherichia coli.
- Citation: Manzhalii E, Moyseyenko V, Kondratiuk V, Molochek N, Falalyeyeva T, Kobyliak N. Effect of a specific Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 strain on minimal/mild hepatic encephalopathy treatment. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(3): 634-646
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i3/634.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i3.634