Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2022; 14(11): 1931-1939
Published online Nov 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i11.1931
Published online Nov 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i11.1931
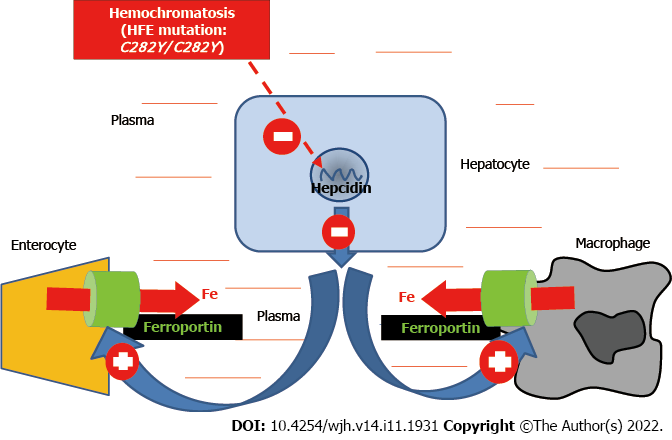
Figure 1 Mechanism of iron overload in HFE-related hemochromatosis.
The C282Y/C282Y mutations (homozygosity for C282Y) lead to decreased synthesis of the iron hormone hepcidin, which in turn causes an increased activity of the iron export protein ferroportin both at the digestive and splenic levels. The result is increased plasma iron leading to organ iron overload.
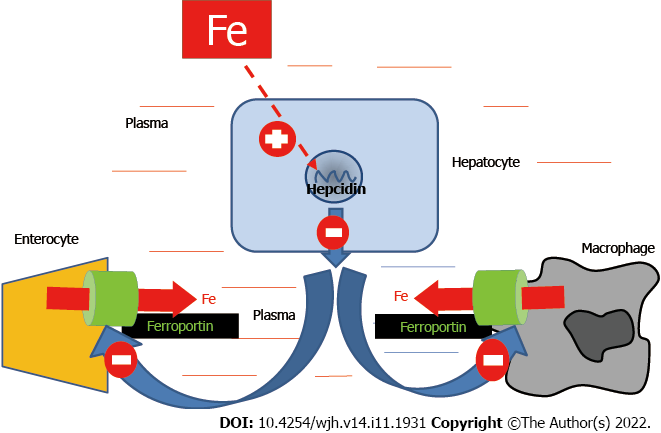
Figure 2 Schematic representation of systemic iron regulation.
Physiologically, increased plasma iron leads to an increased synthesis of the iron hormone hepcidin, causing in turn decreased activity of the iron export protein Ferroportin both at the digestive and splenic levels, which leads to compensatory decreased plasma iron. The reverse mechanism occurs in case of physiological iron deficiency. Please note that, in haemochromatosis, the body behaves as if it was chronically iron deficient.
- Citation: Alvarenga AM, Brissot P, Santos PCJL. Haemochromatosis revisited. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(11): 1931-1939
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i11/1931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i11.1931