Copyright
©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Hepatol. Oct 27, 2022; 14(10): 1844-1861
Published online Oct 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i10.1844
Published online Oct 27, 2022. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v14.i10.1844
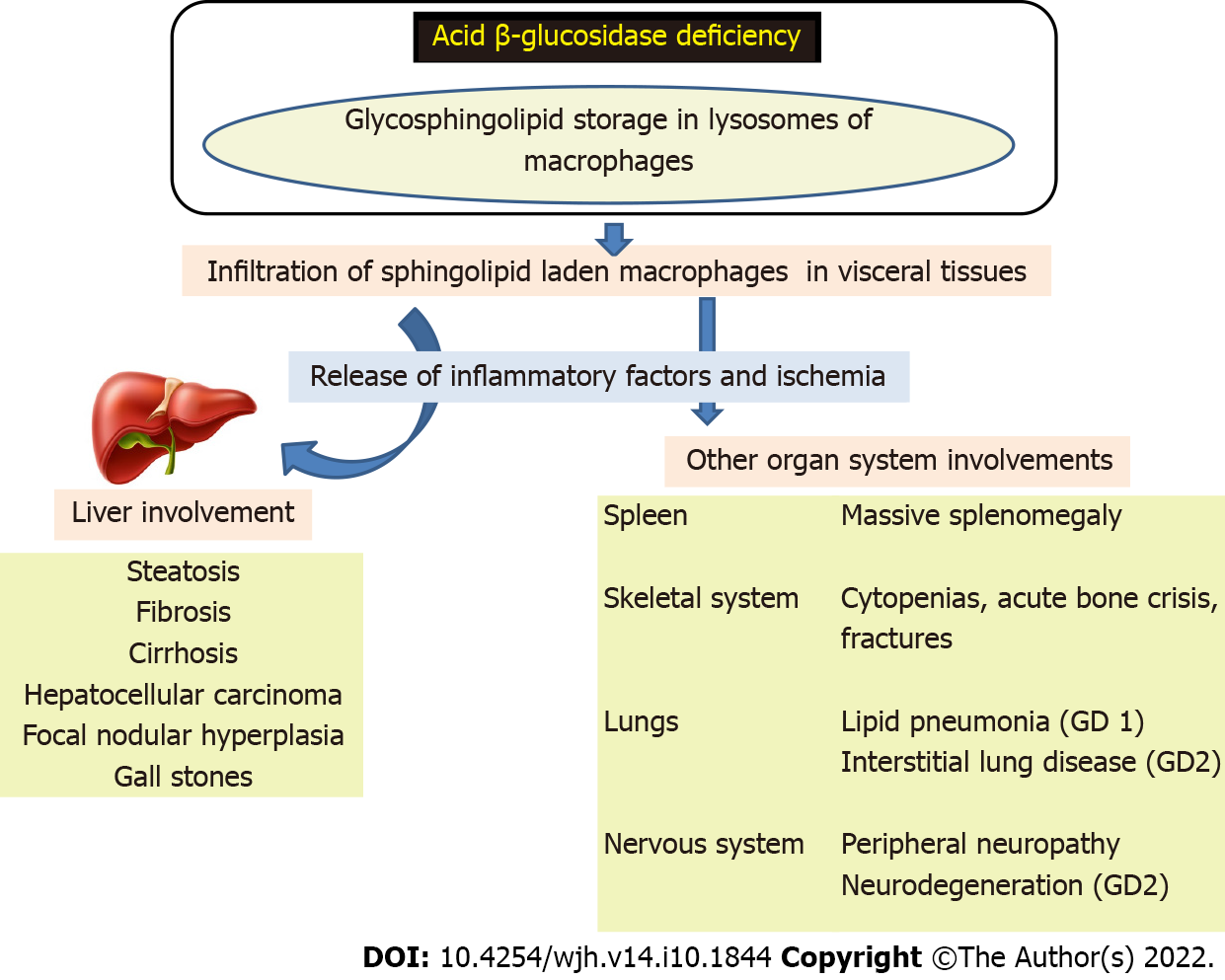
Figure 1 Pathogenesis of Gaucher disease.
GD: Gaucher disease.
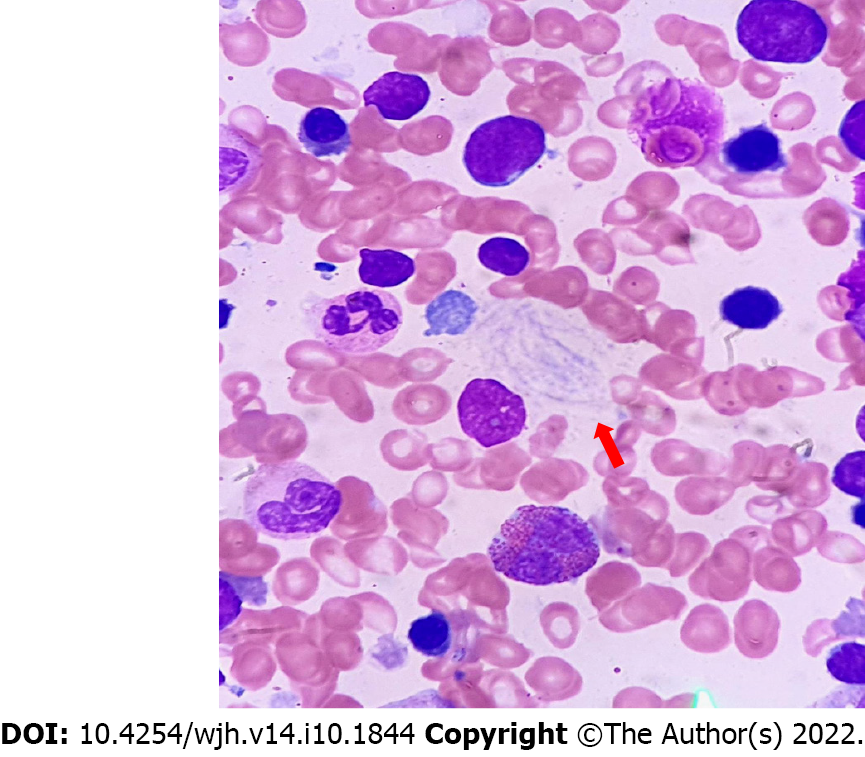
Figure 2 Histology of Gaucher disease.
Red arrow shows Gaucher cells.
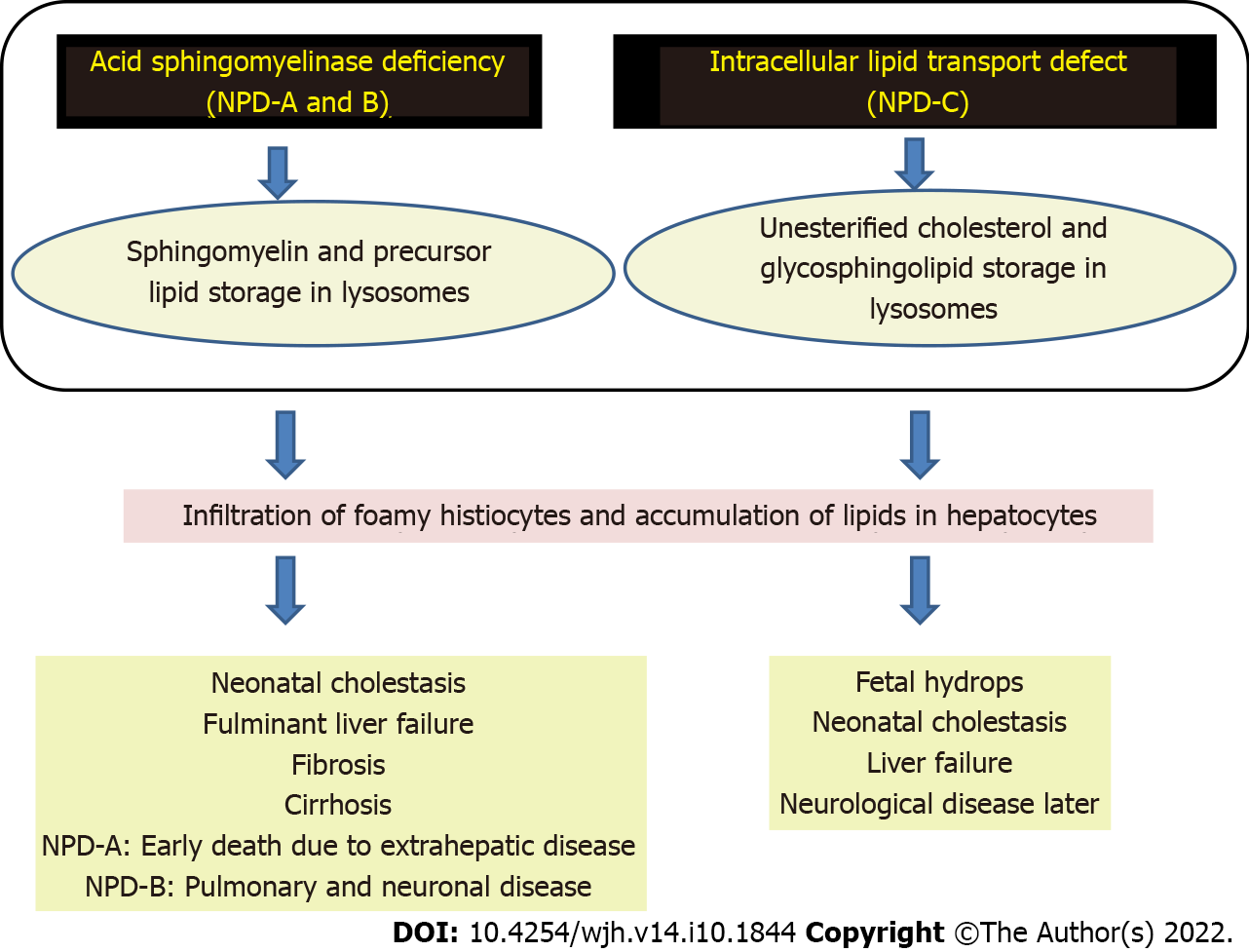
Figure 3 Pathogenesis of Niemann-Pick disease types A, B, and C.
NPD: Niemann-Pick disease.
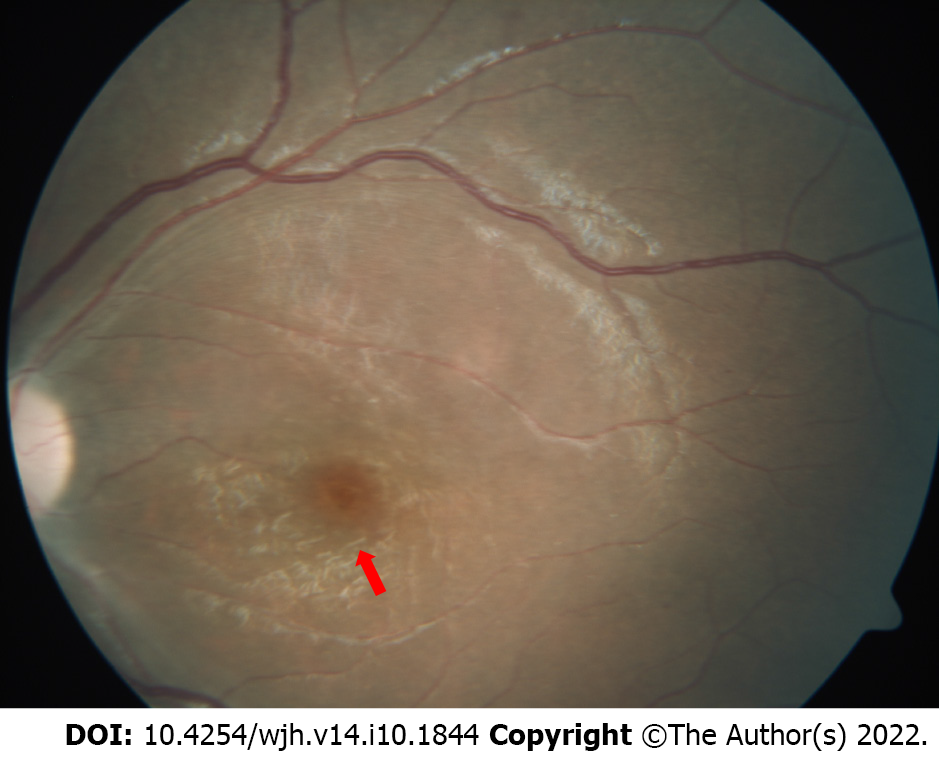
Figure 4 Fundus examination showing a cherry red spot (red arrow) with a background of white retina.
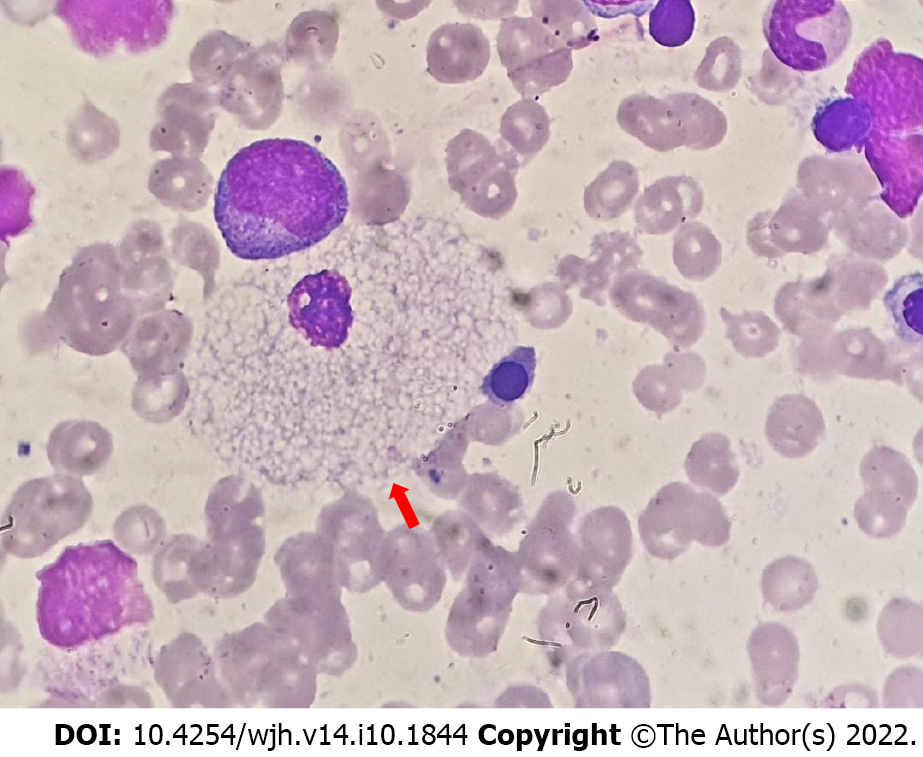
Figure 5 Histology in Niemann-Pick disease type B.
Red arrow shows a foamy vacuolated histiocyte.
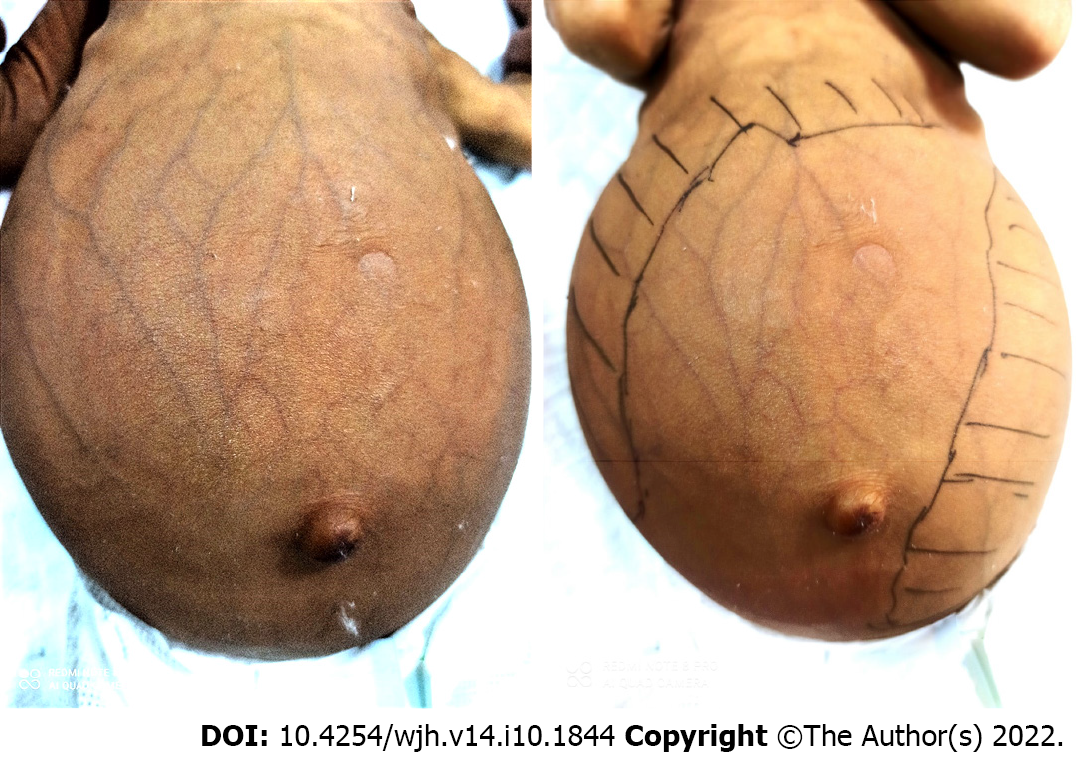
Figure 6 Infant with Niemann-Pick disease type C presenting as cholestasis, dilated abdominal veins, and massive hepatosplenomegaly.
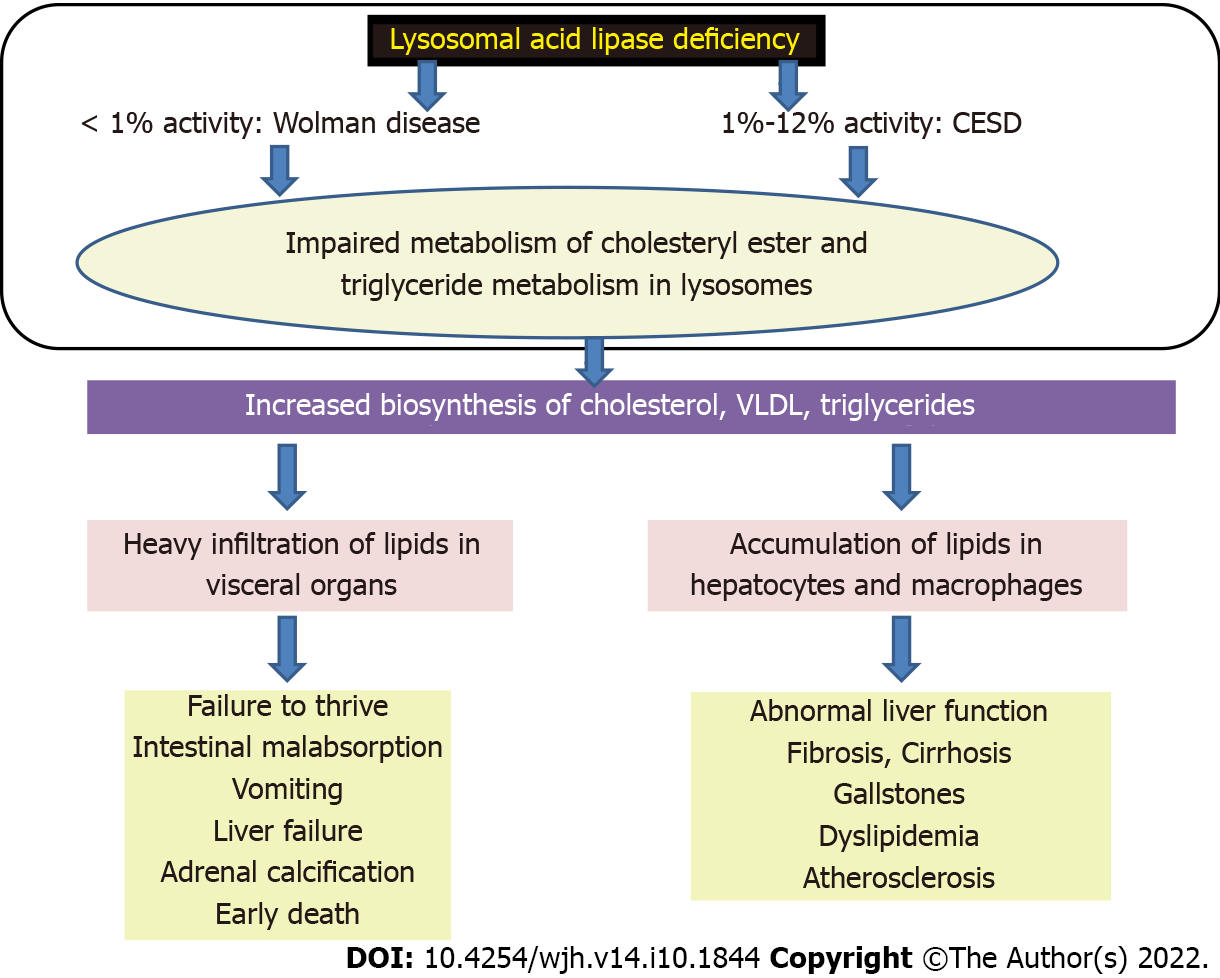
Figure 7 Pathogenesis of lysosomal acid lipase deficiency.
CESD: Cholesteryl ester storage disease; VLDL: Very low-density lipoproteins.
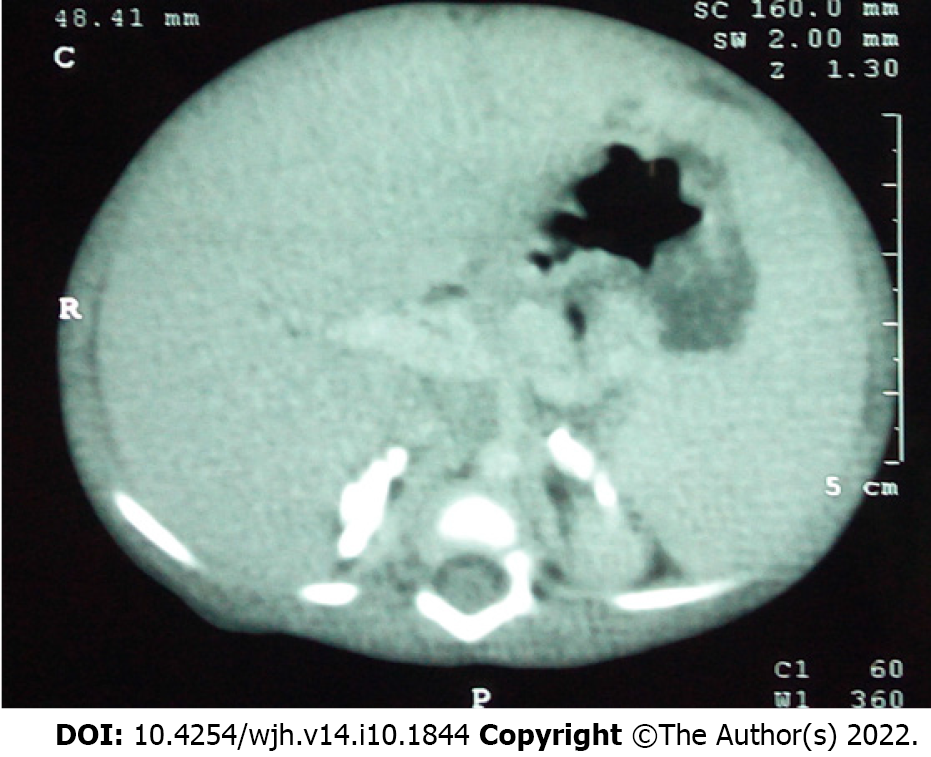
Figure 8 Computed tomography of the abdomen in an infant with Wolman disease showing bilateral adrenal calcifications.
- Citation: Sen Sarma M, Tripathi PR. Natural history and management of liver dysfunction in lysosomal storage disorders. World J Hepatol 2022; 14(10): 1844-1861
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v14/i10/1844.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v14.i10.1844