Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Sep 27, 2021; 13(9): 1069-1078
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.1069
Published online Sep 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.1069
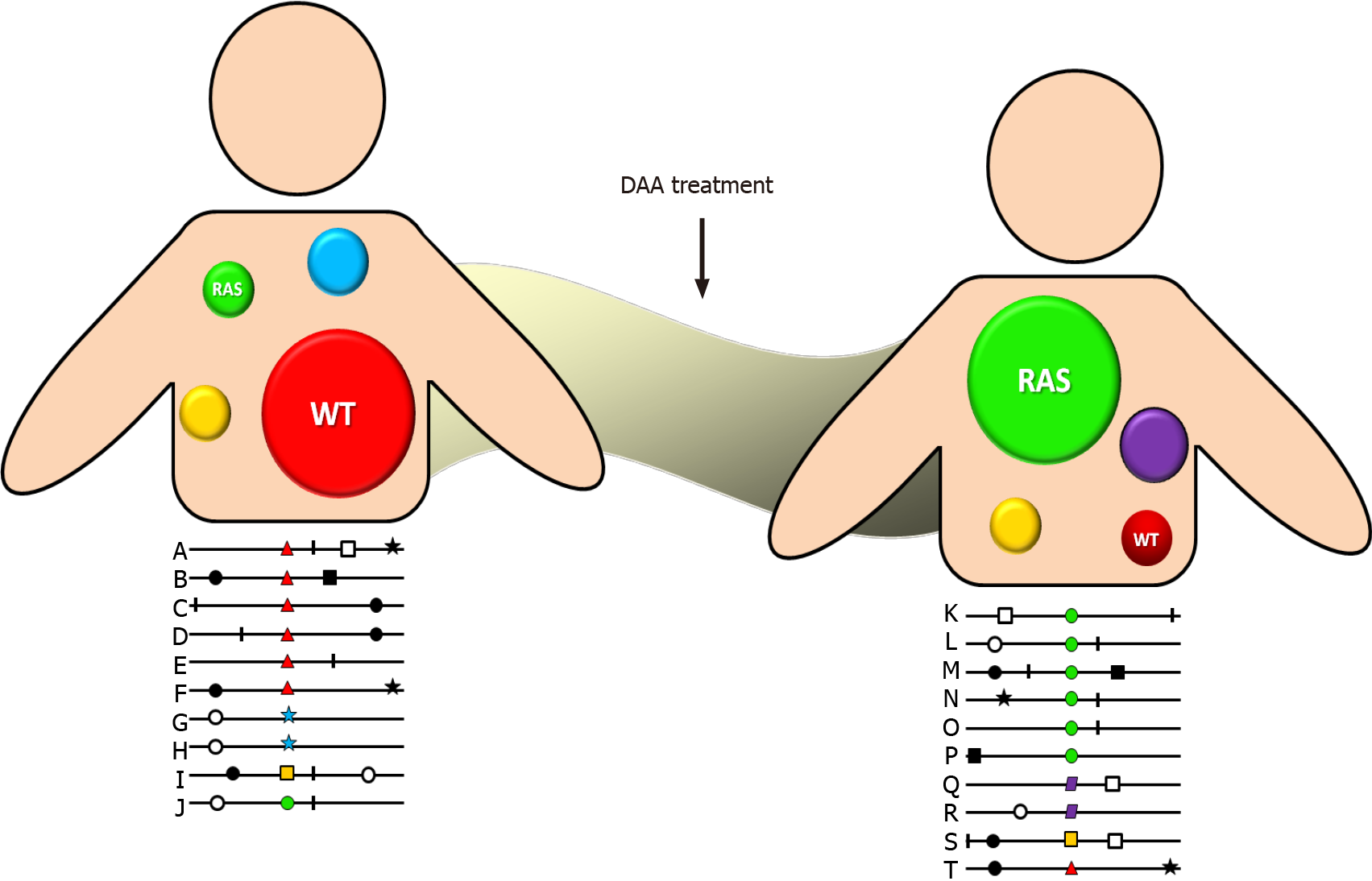
Figure 1 Quasispecies distribution.
Simplified representation of quasispecies infecting an individual. Each genome is identified with a letter. The mutation highlighted by a red triangle in the wild-type (WT) confers a selective advantage that results in dominance of that mutation after a given number of replication rounds in an untreated patient. After the pressure generated by direct-acting antiviral (DAA) treatment, a modification of the consensus sequence is observed, where a green circle confers resistance to treatment and becomes dominant. In the upper example, mutant classes are represented as circles of sizes proportional to the number of genomes in each class. Red circles represent the WT, green circles represent a variant with resistance-associated substitutions (RAS). Yellow, light blue, and purple circles are variants with changes of the WT that are not associated with treatment response.
- Citation: Ridruejo E, Pereson MJ, Flichman DM, Di Lello FA. Hepatitis C virus treatment failure: Clinical utility for testing resistance-associated substitutions. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(9): 1069-1078
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i9/1069.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i9.1069