Copyright
©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Hepatol. Nov 27, 2021; 13(11): 1611-1628
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1611
Published online Nov 27, 2021. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1611
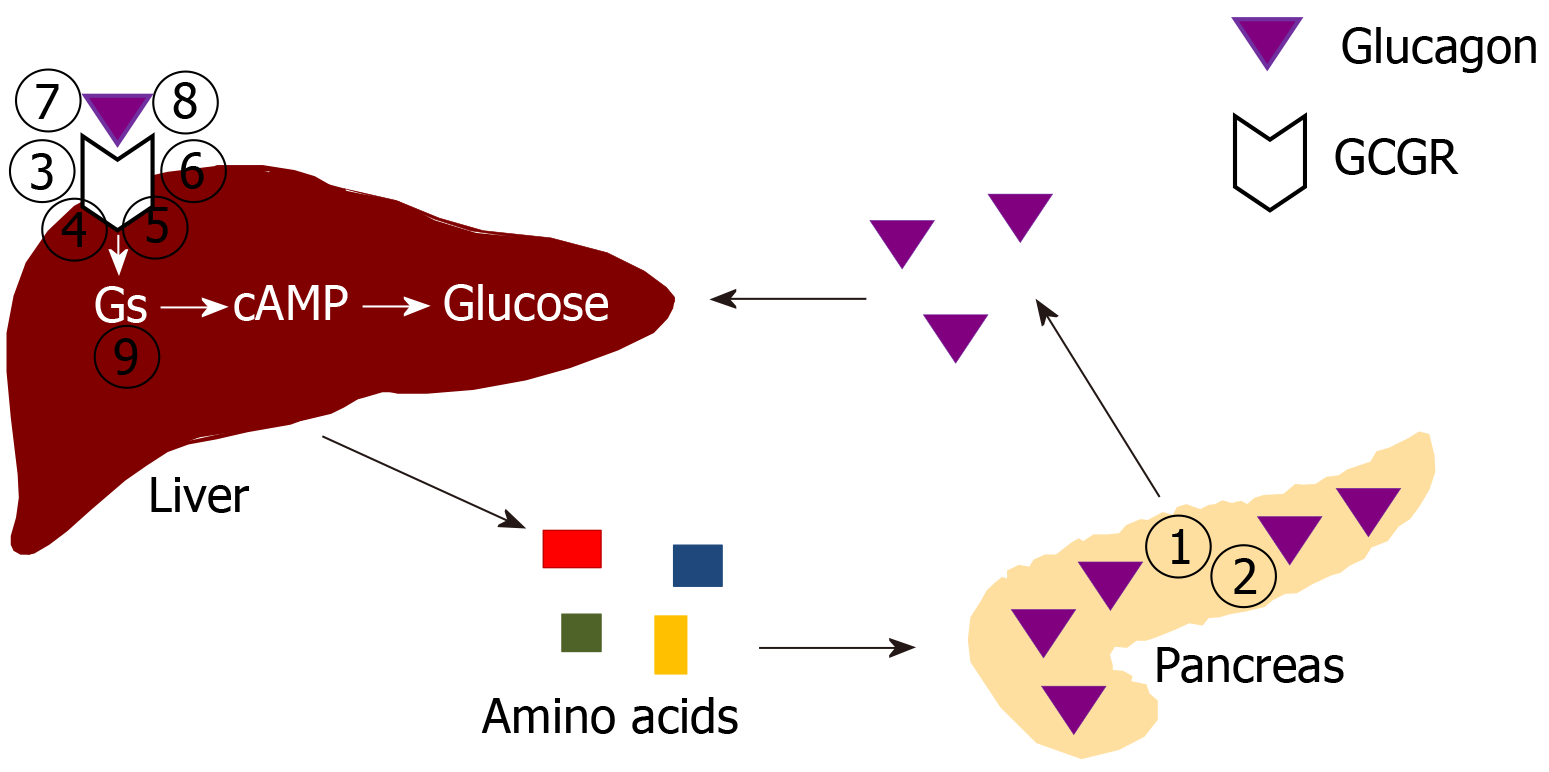
Figure 1 Schematic drawing of regulation of pancreatic α cell number and glucagon secretion by amino acid levels controlled by the liver.
The numbers indicate specific ways to disrupt glucagon signaling. (1) Glucagon deletion; (2) Prohormone convertase 2 deletion (with no mature glucagon secretion); (3) Glucagon receptor (GCGR) global deletion; (4) GCGR liver-specific deletion; (5) GCGR inactivating mutation; (6) GCGR antisense RNA; (7) GCGR antagonists; (8) GCGR antibodies; and (9) Gsα liver-specific deletion. See text for details. Citation: Yu R, Zheng Y, Lucas MB, Tong YG. Elusive liver factor that causes pancreatic α cell hyperplasia: A review of literature. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol 2015; 6(4): 131-139. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2015. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc[67]. GCGR: Glucagon receptor.
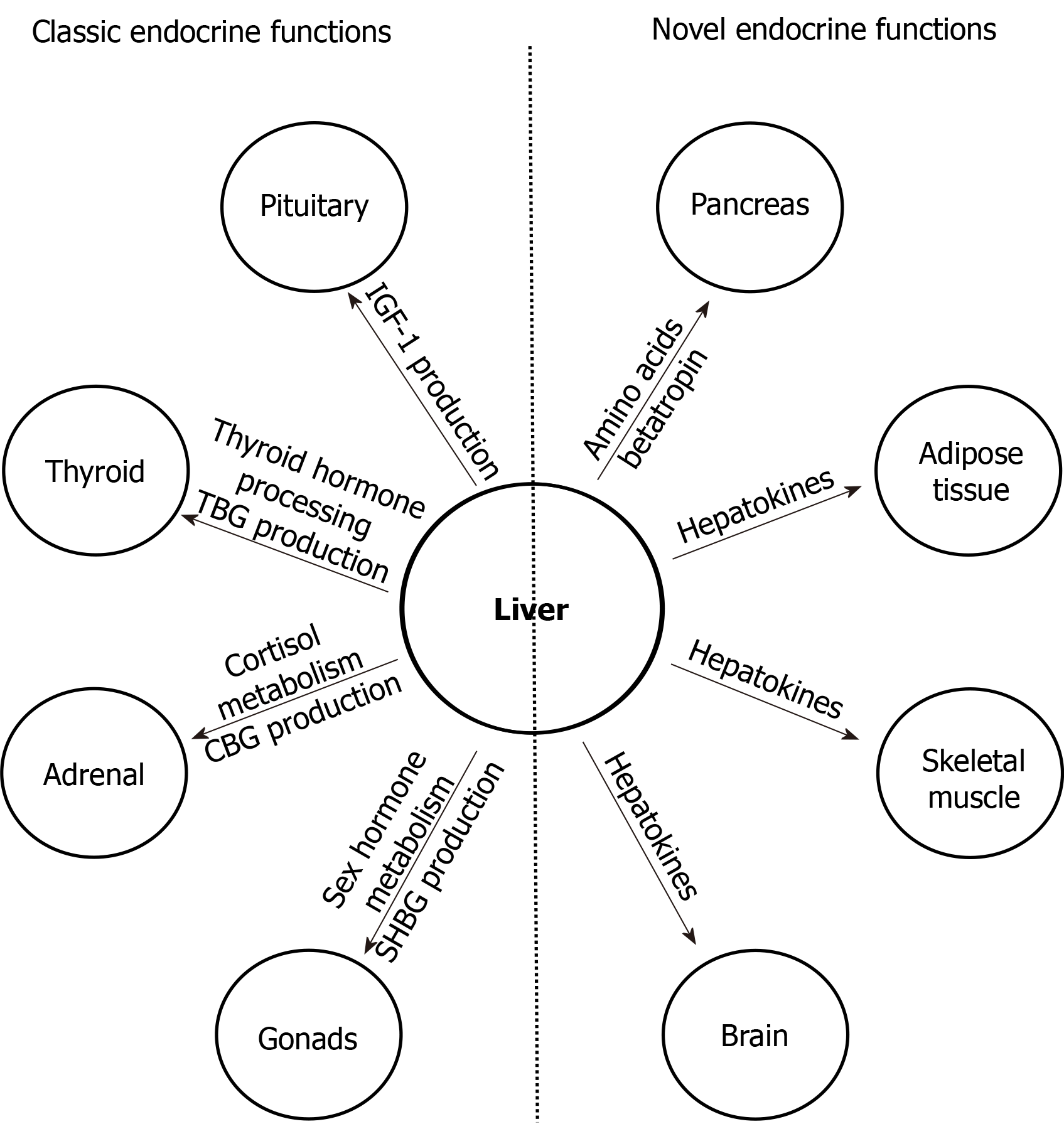
Figure 2 Major classic and novel endocrine functions of the liver.
Left, major classic endocrine functions of the liver; right, novel endocrine functions of the liver. See text for details. IGF-1: Insulin-like growth factor 1; TBG: Thyroxine binding globulin; CBG: Cortisol binding globulin; SHBG: Sex hormone binding globulin.
- Citation: Rhyu J, Yu R. Newly discovered endocrine functions of the liver. World J Hepatol 2021; 13(11): 1611-1628
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v13/i11/1611.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v13.i11.1611