Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Jul 27, 2020; 12(7): 378-388
Published online Jul 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.378
Published online Jul 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.378
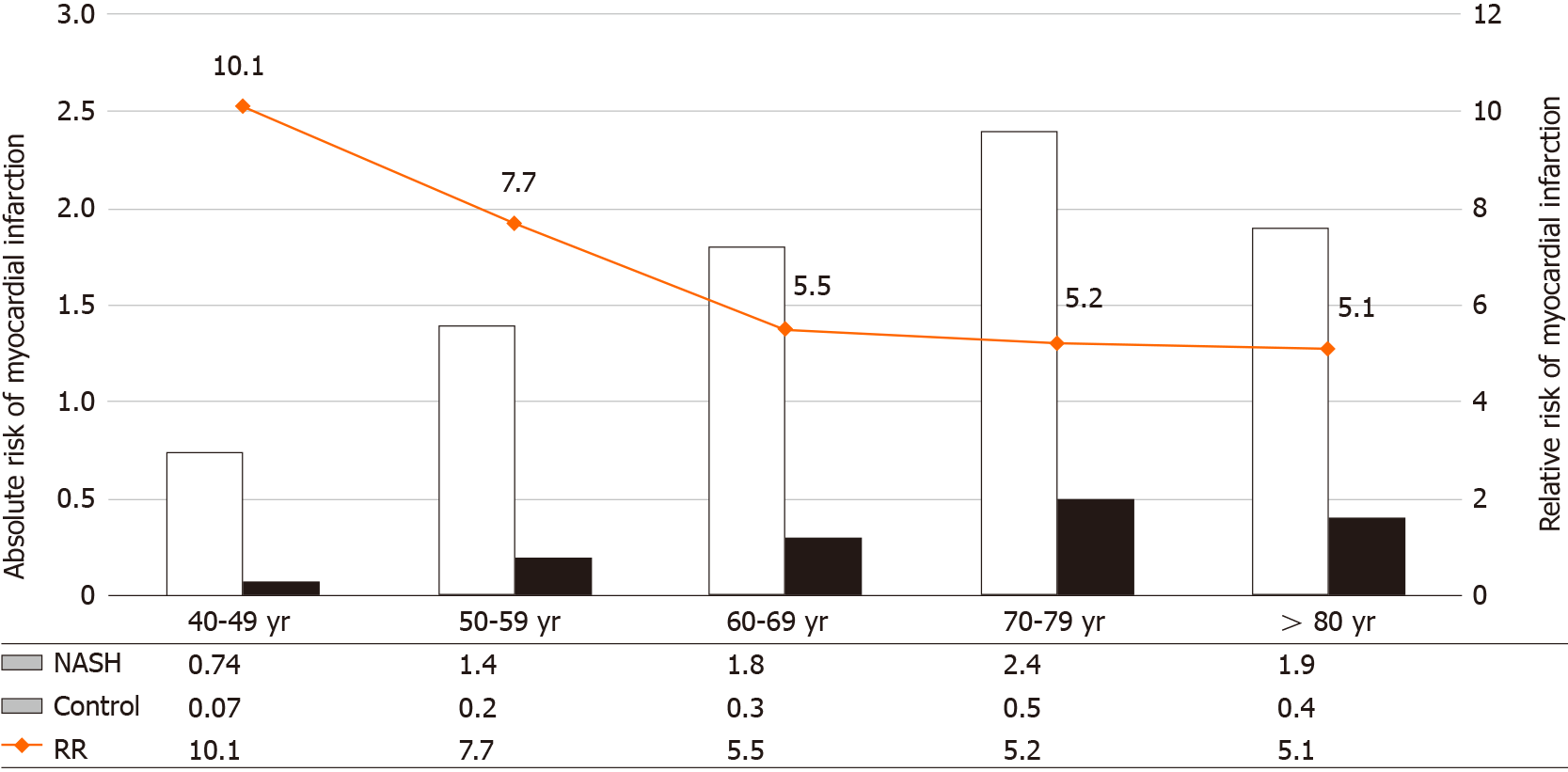
Figure 1 The relative and absolute risk of acute myocardial infarction in the study population.
The relative risk of myocardial infarction is higher in the younger patient group compared to the older population. The absolute risk of myocardial infarction however increases with aging. RR: Relative risk; NASH: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
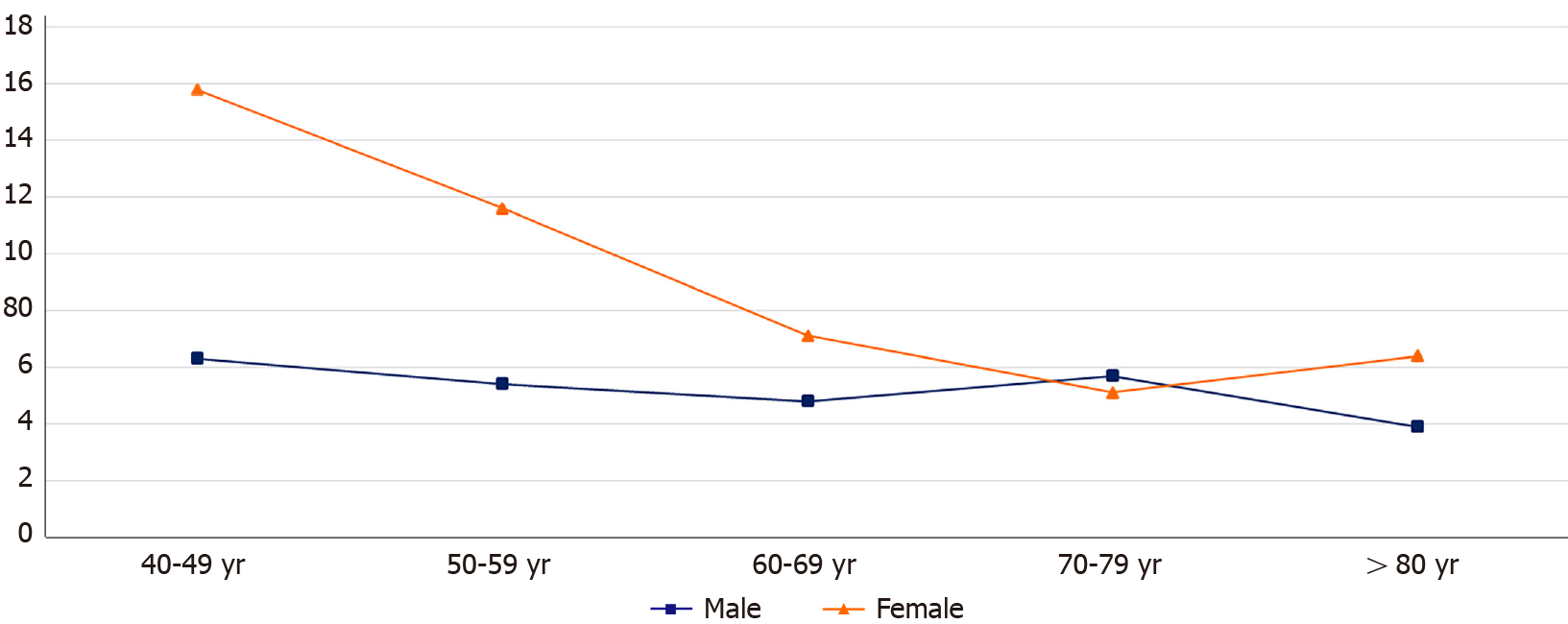
Figure 2 Gender based differences in relative risk of acute myocardial infarction in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Female patients had higher relative risk of myocardial infarction compared to their male counterparts in almost all age groups.
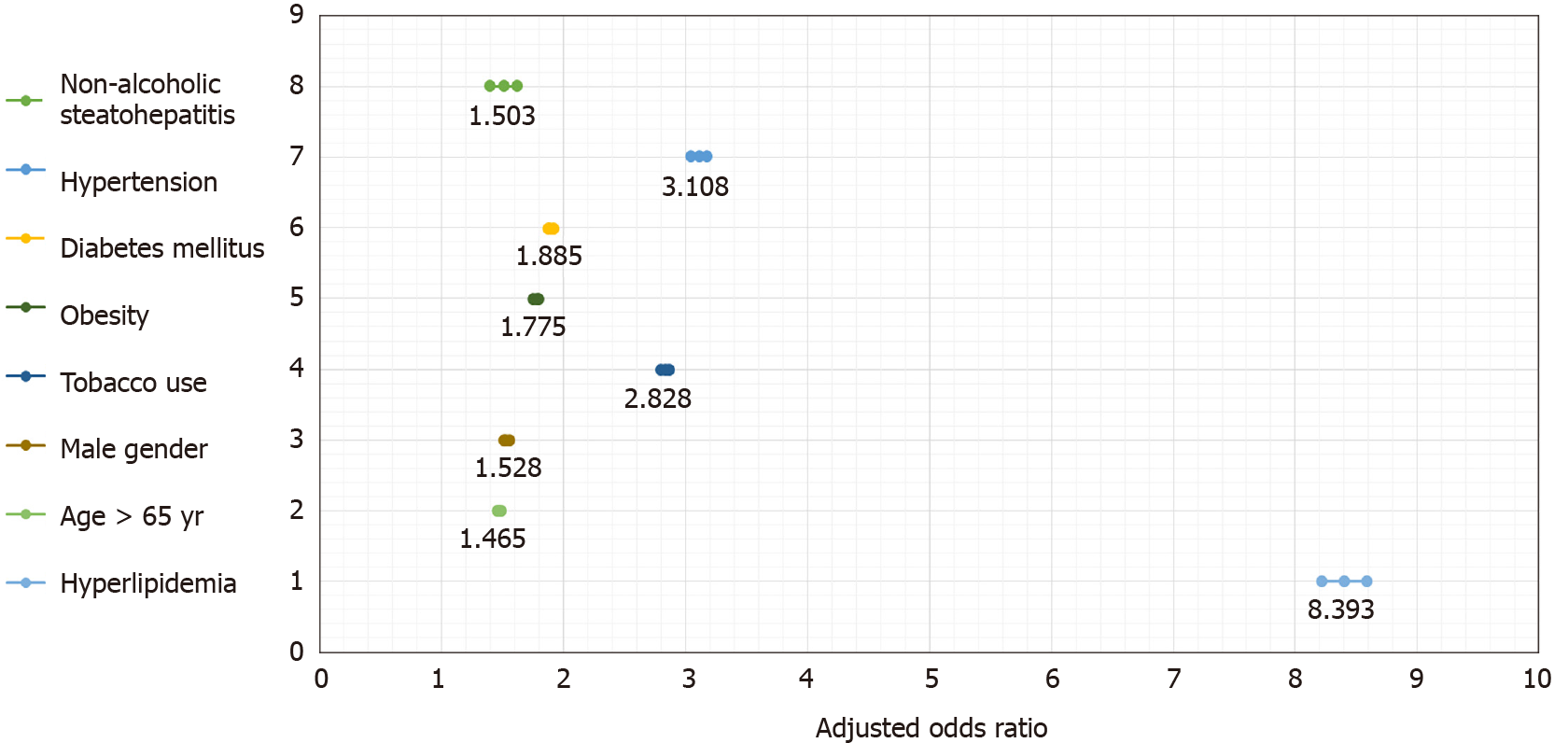
Figure 3 Forest plot showing adjusted odds ratio of having myocardial infarction.
The dots represent the odds ratio and the horizontal line represents the 95% confidence interval.
- Citation: Ghoneim S, Dhorepatil A, Shah AR, Ram G, Ahmad S, Kim C, Asaad I. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and the risk of myocardial infarction: A population-based national study. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(7): 378-388
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i7/378.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i7.378