Copyright
©The Author(s) 2020.
World J Hepatol. Dec 27, 2020; 12(12): 1358-1366
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1358
Published online Dec 27, 2020. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1358
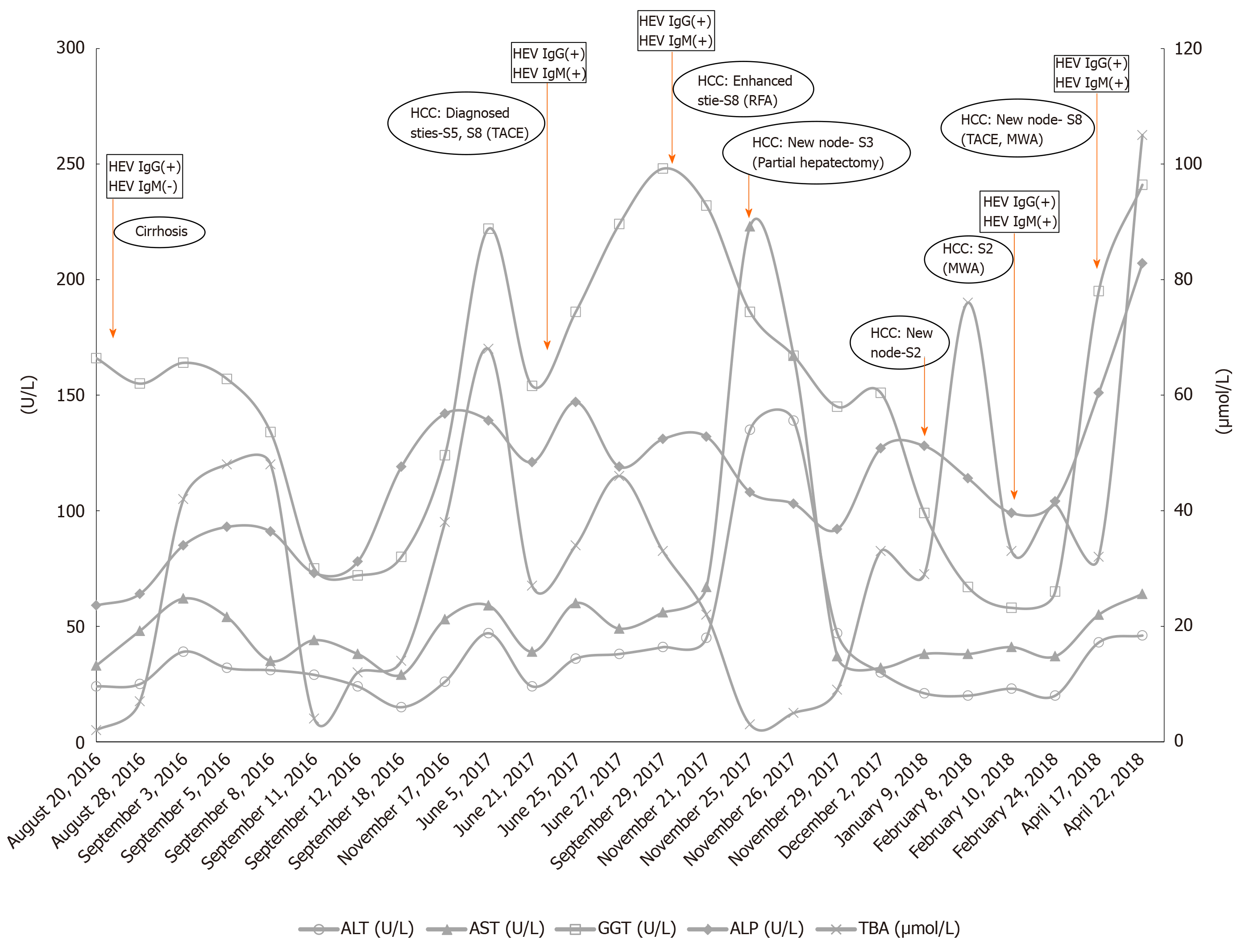
Figure 1 Biological measurements of liver function of the patient from August 2016 to April 2018.
ALT: Alanine aminotransferase; AST: Aspartate aminotransferase; GGT: Gamma glutamyl transferase; ALP: Alkaline phosphatase; TBA: Total bile acid; HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; HEV: Hepatitis E virus.
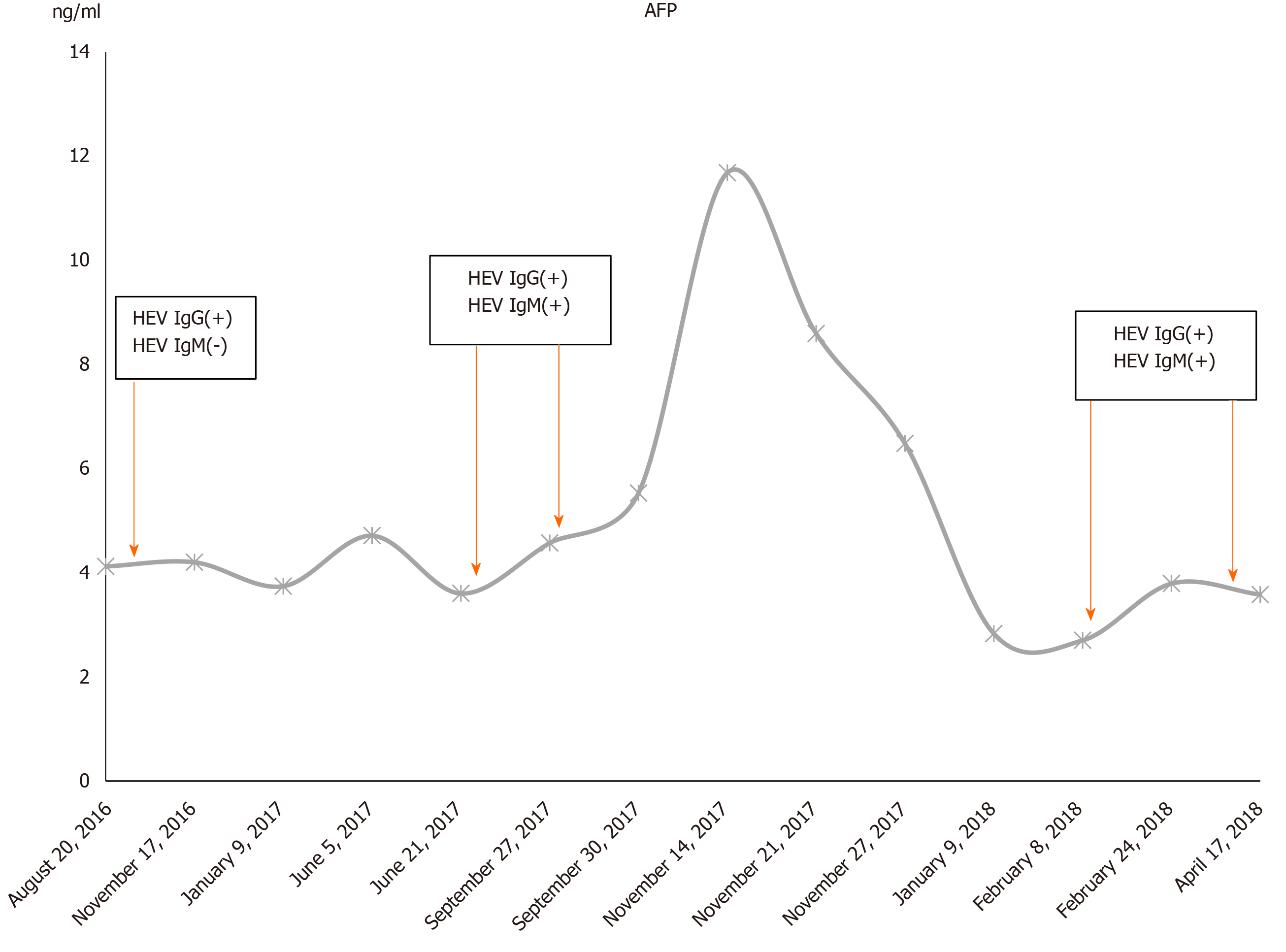
Figure 2 Alpha fetoprotein test results of the patient between August 2016 and April 2018.
AFP: Alpha fetoprotein; HEV: Hepatitis E virus.
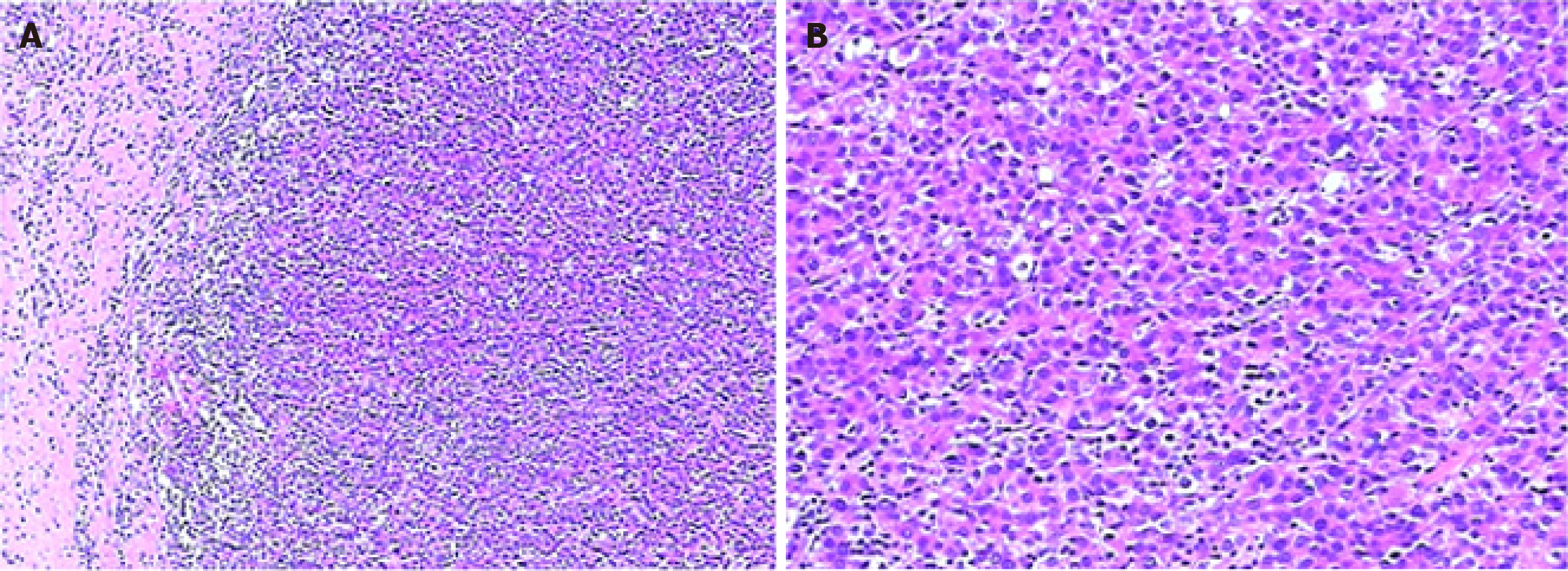
Figure 3 Histopathologic characterization of hepatocellular carcinoma.
A and B: Haematoxylin and eosin staining of the patient’s pathological tissue.
- Citation: Lin XN, Lin QX, Li SM, Xie KP, Hou J, Chen R. Hepatitis E virus re-infection accelerates hepatocellular carcinoma development and relapse in a patient with liver cirrhosis: A case report and review of literature. World J Hepatol 2020; 12(12): 1358-1366
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v12/i12/1358.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v12.i12.1358