Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Hepatol. Feb 27, 2018; 10(2): 287-296
Published online Feb 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.287
Published online Feb 27, 2018. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.287
Figure 1 Influence of the multipotent stromal cells transplantation on mitotic activity of hepatocytes; Mitotic activity of hepatocytes in the residual livers at 3 (A, D), 7 (B, E) and 10 d (C, F) after the surgery; Mitotic index of hepatocytes is plotted against time after the surgery (G); HE staining.
Arrowheads indicate mitotic figures in hepatocytes (A, B, D); Mitotic index of hepatocytes: Horizontal axis represents time elapsed after the surgery, vertical axis represents mitotic index of hepatocytes, ‰; White columns represent hepatocyte proliferation in the comparison group, gray columns represent hepatocyte proliferation in the multipotent stromal cells transplantation group; The data is presented as mean values with confidence intervals. SR: Subtotal resection; MSC: Multipotent stromal cells.
Figure 2 Influence of the multipotent stromal cells transplantation on Ki67 index of hepatocytes.
Ki67 expression in the residual livers at 3 (A, D), 7 (B, E) and 10 d (C, F) after the surgery; cell nuclei are counterstained DAPI (blue); Index of Ki67+ hepatocytes is plotted against time after the surgery (G): Horizontal axis represents time elapsed after the surgery, vertical axis represents Ki67 proliferation index (InKi67) of hepatocytes; White columns represent hepatocyte proliferation in the comparison group, gray columns represent hepatocyte proliferation in the multipotent stromal cells transplantation group; The data is presented as mean values with confidence intervals. SR: Subtotal resection; MSC: Multipotent stromal cells.
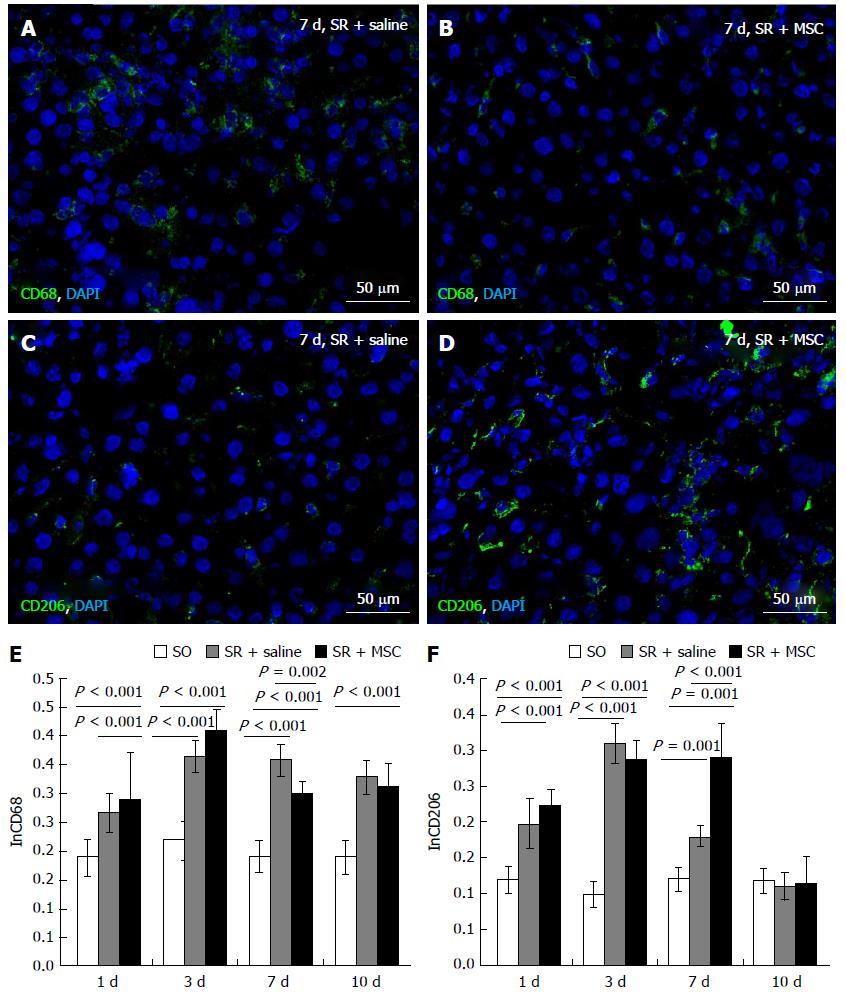
Figure 3 Influence of the transplantation on macrophage polarization profiles.
CD68+ cells (green) in the liver in the comparison group (A) and in the residual liver in the MSC transplantation group (B) on day 7 after the surgery. The diagram shows dynamic changes in the CD68+ cell content liver in the comparison group and in the multipotent stromal cells (MSC) transplantation group (E); Relative quantities of CD206+ cells (green) in the liver in the comparison group (C) and in the residual liver in the MSC transplantation group (D) on day 7 after the surgery; The diagram shows dynamic changes in the CD206+ cell content in the course of regeneration; cell nuclei are counterstained with 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue). In E and F, white columns represent the sham-operated animals, gray columns represent the comparison group, black columns represent the MSC transplantation group, horizontal axis represents time elapsed after the surgery. SR: Subtotal resection; SO: Sham-operated animals; MSC: Multipotent stromal cells.
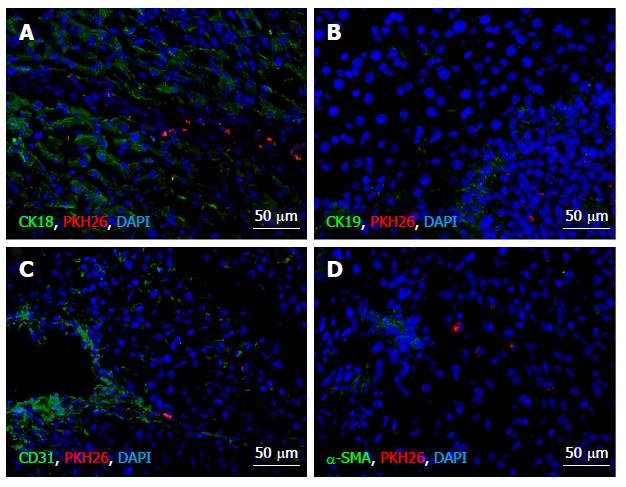
Figure 4 Immunochemical analysis of differentiation of the transplanted multipotent stromal cells on day 10 after the surgery.
Immunostaining of cell type-specific proteins, A: CK18 (hepatocytes); B: CK19 (cholangiocytes); C: CD31 (endotheliocytes); D: αSMA (smooth muscle cells). Fluorescent microscopy images display immunostaining (green), PKH26 label (red), and cell nuclei counterstained with 4′, 6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue).
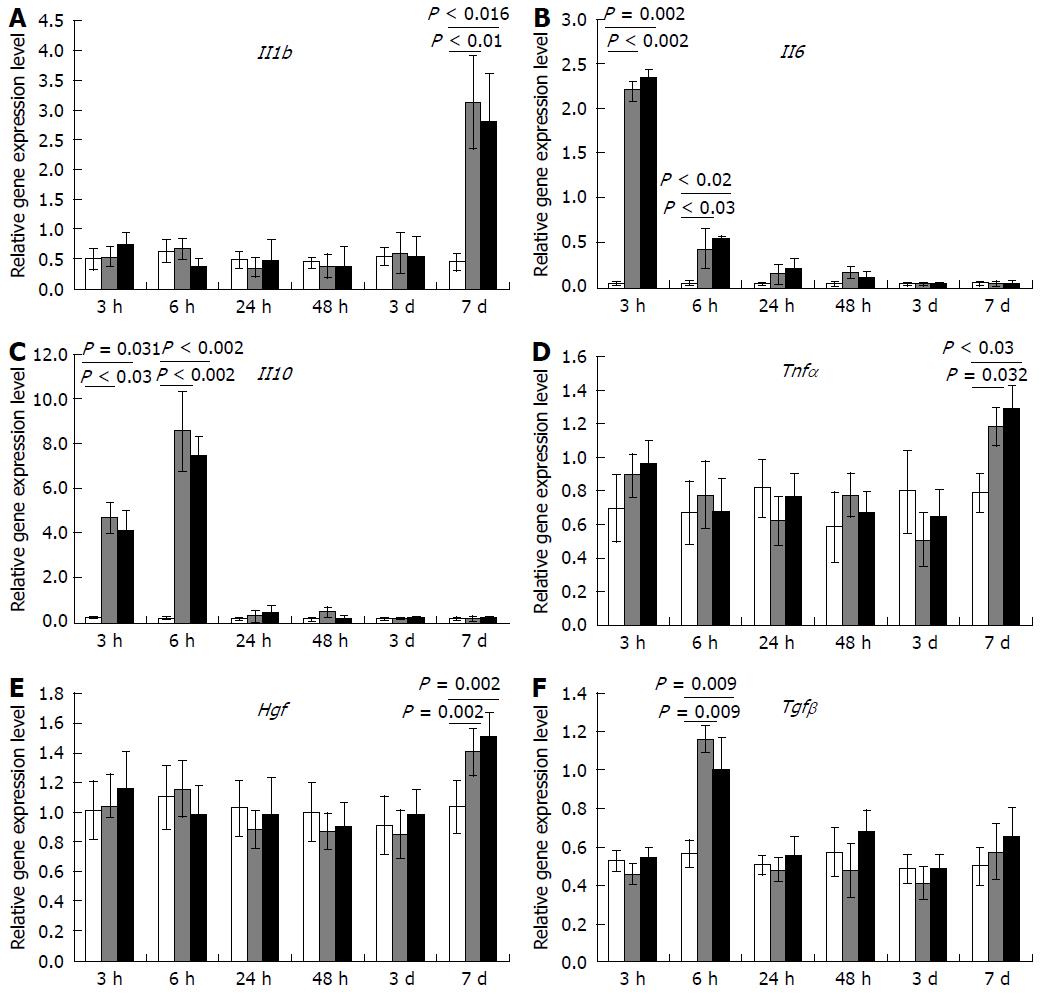
Figure 5 Influence of the transplantation on cytokine and growth factor gene expression within regenerating livers.
A: Il1b; B: Il6; C: Il10; D: Tnfα; E: Hgf; F: Tgfβ. White columns correspond to gene expression values (in relative units) for the sham-operated animals, gray columns represent the values for the comparison group, black columns represent the values for the Multipotent stromal cells transplantation group, horizontal axis represents time elapsed after the surgery; The data is presented as mean values with confidence intervals. SR: Subtotal resection; SO: Sham-operated animals; MSC: Multipotent stromal cells.
- Citation: Elchaninov A, Fatkhudinov T, Usman N, Arutyunyan I, Makarov A, Lokhonina A, Eremina I, Surovtsev V, Goldshtein D, Bolshakova G, Glinkina V, Sukhikh G. Multipotent stromal cells stimulate liver regeneration by influencing the macrophage polarization in rat. World J Hepatol 2018; 10(2): 287-296
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1948-5182/full/v10/i2/287.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v10.i2.287